InChem foundation
1/276
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
277 Terms
What does the plum pudding model look like and consist of?
Positive mass with small, negative electrons embedded
What does the Rutherford atom look like and consist of?
Positive nucleus with negative electrons orbiting nucleus
What is the problem with the Rutherford atom?
All electrons are equal contradicting idea of atomic emission spectra
What is the atomic emission spectra?
When atoms are given a lot of energy & light is emitted
What is the Bohr atom?
Same as Rutherford atom but electrons are at different distances from the nucleus
How much energy do electrons closer to the nucleus have?
More stable & lower energy since they are more tightly bound
What are transitions?
When electrons absorb energy and it moves from a lower energy level (ground state) to a higher energy level (excited state)1
What do emission lines represent?
Energy levels in atom
What is the formula of showing energy in a quantum level?
En = k / n2
n = Quantum number e.g n=1 etc
k = Plancks constant
What is the problem with the atomic emission spectra?
-Works for hydrogen, but not for heavy atoms
Doesn't explain periodic properties
-Bohr model doesn't explain everything
What is the deviation for De Broglie's equation?
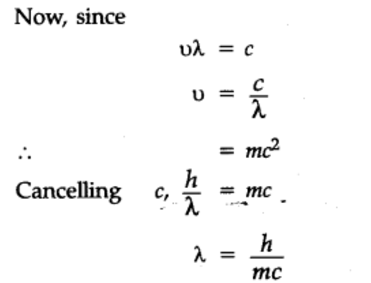
What is the wave particle duality?
Subatomic particles can act as both particles & waves (electrons can diffract)
What is Heisenberg's uncertainty principle?
Uncertainty associated with momentum
Why is uncertainty associated with momentum
To see electron, light waves reflect from spherical electron & meets eye
Light wave adds energy & changes momentum of electron
What is the problem with Bohr's atom?
Shows orbit which gives electron well defined orbit, however electrons do not exist in orbits
What is used instead of orbits?
Orbitals = Area of space around the nucleus where electrons are seen (probability distributions)
Why must wavelengths be in integral number when electron moves in circular manner?
Destructive interference may occur (λ n = 2 pi r)
What is schrodingers equation?
Describes how wave function evolves overtime?
What does the wave function describe?
Amplitude of x, y or z (only applies to ELECTRONS)
What does wave function^2 represent?
Probability density
What are the components of wave function?
Wave function = Rn1 (r) x Y 1 m1
n1 & m1 = Quantum numbers
Y = Angular wave function (Direction)
What is the n (principal) quantum number?
Includes positive integer values (0 not included)
e.g = n=1 ,2,3,4 etc
What does n (principal) quantum number determine?
Size of orbital therefore energy
What is L (Azimuthal) quantum number?
-Known as angular momentum
Includes positive integer values (0 included) up to a max of n -1
e.g = n=4 L can be 0,1,2 or 3
What does L (Azimuthal) quantum number determine?
Affects shape so no changes in energy
What is the mL quantum number?
-Known as magnetic quantum number
-Includes positive integer values (0 included) between -L & +L values
e.g = At L=2 can be -2,-1, 0 ,1,2
What does mL quantum number determine?
Orientation of orbital
How do you name orbitals?
L = 0 -> S
L = 1 -> p
L = 2 -> d
L= 3 -> f
L = 4 -> g
-Letter code preceded by principal quantum number e.g n=3 & L=1 so 3p orbital
What is the radial wavefunction?
R = Function of distance from nucleus (r)
-R never goes to 0 as r -> infinity
What is the Bohr radius?
Probable distance of electron from nucleus for H atom in ground state
What is irrelevant for negative values of R?
-Electron probability as square of negative values give out positive
-Not relevant to electrostatic charges
What is negative values of R important for?
Bonding
What are radial distribution functions (RDF)?
Total probability electron will be found at given distances from nucleus regardless of electron
What are the limitations of using wavefunction^2?
Only gives probability of finding electron at a single point
How do you find RDF?
Probability of electron being at r x number of locations at r
What happens if n (orbital size & energy) increases?
Area of max probability (density) increases
What is boundary surface?
Where there is 90% probability of finding an electron.
When is boundary surface used?
When there is a small probability of finding an electron far away from nucleus
What are radial nodes?
Distances with 0 probability
How do you find number of radial nodes?
n - L -1
What is angular wavefunction dependent on?
L & ml only (no n)
What shape do ns orbitals give off?
Spherical shape
What is L=0 (ml 0) name?
ns (s orbitals)
What is L=1 (ml can be -1,0,+1) name?
np orbitals (p orbitals)
What shape do np orbitals give off?
Dumbell shape
What is l=3 (ml -3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3) name?
nf (f orbitals)
What shape is nf orbitals?
A lot more angular nodes
What are angular nodes?
Planes with 0 electron probability
What are orbital shapes independent of?
n (orbital size)
What is l=2 (ml is -2,-1,0,1,2) name?
nd (d orbital)
What shape is nd orbitals?
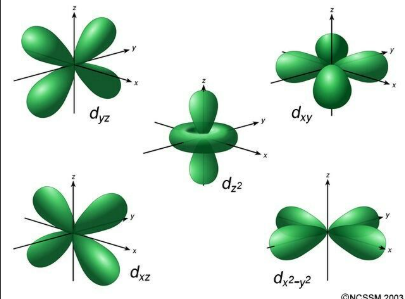
What does V (potential energy) in Schrodingers equation include?
Sum of electron attraction & repulsion
Why can Schrodingers equation only be applied to the H atom and carbocations with 1 electron?
No electron repulsion in H atom (1 electron only)
Why can't Schrodingers equation be applied to atoms with more than one atom?
Location of electrons must be seen for atoms with more than one electron
How do you make it so Schrodingers equation can be used for atoms with more than one electron?
-Use H atom (or carbocations with one electron) as all orbitals have similar shapes
-Orbital energies vary depending on effective nuclear charge
What quantum number(s) do orbital energies depend on now for atoms with more than one electron?
n & l (energy, size & shape)
Why do electrons in orbitals with larger n quantum number have higher energy?
They have probability distribution further from the nucleus & experience less nuclear charge so are less tightly bound
Why do electrons in orbitals with smaller n quantum number have lower energy?
Lower probability distribution from nucleus & experience greater nuclear charge so are more tightly bound
What is the shielding effect?
When outer electrons feel lower effective nuclear charge so have higher energy
Why is s<p<d<f in terms of energies?
-In RDF graph, 2s has a residual maximum (2 peaks)
-So 2s penetrates closer to nucleus than 2p electrons so experiences greater nuclear charge
Why do orbital energies decrease with increasing Z (atomic number)?
Electrostatic attraction of electron increases
Why does 4s become more penetrating for K & Ca?
As Z increases, 4s becomes more penetrating
-> Stronger nuclear charge = Energy decreases
What is electron penetration?
How close an electron can get to the nucleus
Why does 3d have lower energy than 4s from Sc onwards?
Sufficient electrons
What is the Afbau principle?
"Add 1 proton, 1 electron & some neutrons to orbital of LOWEST ENERGY available"
What is ms quantum number?
Spin quantum number
-> Have values of +1/2 or -1/2
What is Pauli exclusion principle?
No 2 electrons in any system can have identical values for all FOUR quantum numbers
-> Values of ms must be different (Must have opposite spins)
What is Hund's rule?
Most stable state is one with identical or parallel spins
->Otherwise repulsion between electrons may occur
What are valence electrons?
Incomplete orbitals with higher energy & are affected by chemical reactions
What are core electrons?
All orbitals with specific quantum number are full
-> e.g = 1s2 for He to F
Why are full & half filled shells more stable in neutral atoms?
Electron repulsion is minmised
What is periodicity?
Similar chemical properties
Why does periodicity occur?
Valence orbitals
How does electron fill for transition metals?
4s always empties before 3d
Who first drafted the periodic table?
Mendeleev
What did Mendeleev do?
Ordered periodic table by increasing atomic weights (relative atomic masses)
What did Mosely discover?
Periodic table instead ordered by increasing atomic numbers -> Defines periodic table
What is the structure of the periodic table?
ns2 np6 = Noble gases -> fully filled shells
ns1 = Group 1
ns2 = Group 2
ns2 np5 = Group 17 metals
ns2 np4 = Group 16 metals
ns2 np3 = Group 5 metals
What are the main group elements?
s- block -> groups 1&2
-p- block -> groups 13-18
What are transition elements?
Incomplete d-orbitals is either metal, compound or complex
What are NOT transition metals?
Zn, Cd & Hs
What are actinides or actinoids?
Partially filled 5f orbitals
What are lathanides or lathanoids?
Partially filled 4f orbitals
What are some multi-electron system rules?
-Same quantum numbers as hydrogen
-Same angular functions as hydrogen
-Radial functions similar to hydrogen, but contracted of increased nuclear charge
Why are electrons placed far apart as possible?
Minimizes colombic (electrostatic) repulsion
Are parallel spins in an electron more unstable or stable?
Stable
What is the formula for electron energies in multi-electron systems?
E = -Rn hc Z^2 / n^2
What is the effective nuclear charge?
Electron experiences less nuclear charge than full nuclear charge because of shielding
What does shielding from other electrons depend on?
n (principal quantum number)
What does penetration refer to?
Electron density. Electrons in orbitals have different wavefunctions and RDF
Why does 2s get filled before 2p?
-2p has no radial node
-2s is less shielded of radial node so experiences greater nuclear charge & lower energy
So 1s shields 2p more than 2s
Why is 4s filled before 3d?
-4s has 3 radial nodes (n-L-1)
-3d max closer to nucleus than 4s
What does effective nuclear charge depend on?
Which shell electron is in -> Valence electrons in 3s experiences smaller nuclear charge than 1s of shielding
What is Slater's rules?
Effective nuclear charge (Zeff) = Z - S
-Z = Actual nuclear charge
-S = Shielding constant
Why doesn't perfect shielding exist?
-Electrons with same n contribute to 0.35 to s (shielding constant) ->Not much
-Electrons with 1 below n contribute to 0.85 to s -> Better shielding
-Electrons with low n contribute 1 to s -> Perfect shielding
What is ionisation energy?
Sufficient energy required to detach one or more electrons from a gaseous atom, molecule or ion to form one gaseous ion
Are ionisation energies always positive?
Yes
What happens to energy required for second,third,fourth etc ionisation energies?
Increases each time
What are the general trends for first ionisation energy?
-General increases across period
-General decreases down the group
Why does first ionisation energy decrease down a group?
Increasing principal quantum number, energy required to remove electron decreases. However, no dramatic decrease of shielding