AP BIO UNIT 3
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
What are reactants?
molecules on the left side of the arrow which substances present at the start of the reaction.
What are products
molecules on the right side of Arrow which the new substances forms from the reaction.
what is activation energy?
the initial mom of energy needed to be absorbed by the reactions in order for a chemical reaction to occur
for activation energy what is typically the form of the activation energy in?
the form of heat.
the reactions that have high activation Energies __.
occur slowly.
the reactions that have small activation Energies__
occur quickly.
enzymes are blank that act as _ in cells and organism enzymes are __ that act as blank in cells and organisms
Proteins and catalysts.
enzymes _metabolic reactions by _the activation energy
speed up & lowering
why is the shape of an enzyme important?
it allows it to bind to the reactants needed for chemical reaction and insist in the breaking and forming of new bonds.
the region on the enzyme were substance bind to is called the_?
active site.
The Binding of a substrate to the active cite creates an induced fit what does this mean?
The enzyme changes shape to embrace the substrates to ensure it does not detach until the reaction is complete.
can enzymes be used again in a chemical reaction?
yes.
What is a catalyst?
a chemical that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction meaning these never go away and never change shape.
Why do enzymes have a specific shape inactive site.
they only bind to a specific substrate this means that the enzymes control very specific reactions.
What type of substrates binds to the active site on enzymes+EX?
weak interactions. ionic bonds hydrogen bonding and polar / no polar interactions.
why don't substrates bind to active sites of covalent bonds?
they are too strong.
do substrates actually touch the active site?
no they kind of levitate above them it's like a magnet.
the name of the enzymes always ends with what?
-ase
how can the rate of enzyme activity be sped up?
by increasing the subject concentration in a solution.
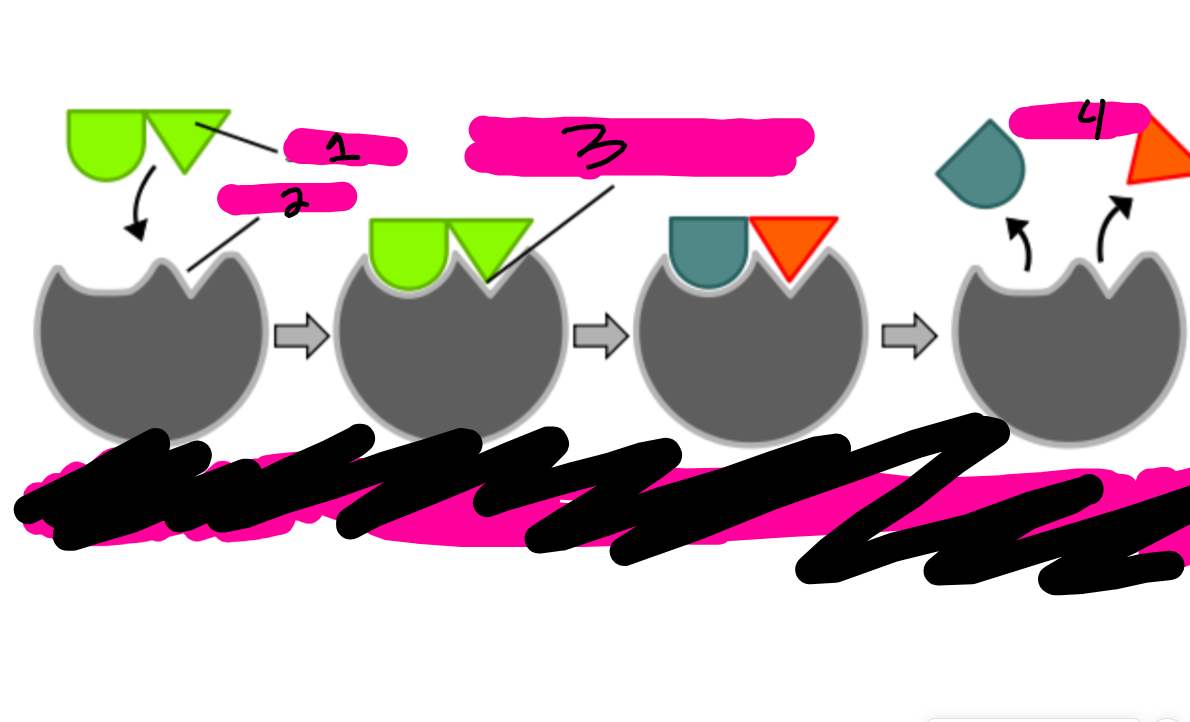
label the image.
1:subrate. 2:active site. 3:complex. 4:products
Whenever all of the enzyme molecules in a solution are being bonded with a substrate what are the enzymes?
they are saturated.
at enzymes saturation the enzymes are all working at Max Speed and rate of the reaction how can these factors be increased?
by adding more enzymes. each enzyme can only work with each substrate.
what are the three factors that cause enzymes to denature?
salinity. temperature. Ph.
how does salinity affect our enzymes?
it's a temporary change and a positive or negative charge.
how does temperature change our enzymes
if the temperature is hot it is permanently damaged the enzyme. if it's cold it's just a temporary.
What are the optimal pH values for enzymes+effects? what are the exceptions?
6 to 8.These changes are temporary. some exceptions like pepsin a digestive enzymes that's in the stomach works best of a pH of 2.trypsin a digestive enzyme in the intestine works best at a pH of 8.
How do the mutations of the amino acid sequence of a protein affect our enzyme?
if an amino acid is found in the active site of an enzyme and it is changed it can lead to an enzyme no longer being able to bind to the substrate if it's outside of the active site it can also affect the folding of the enzyme in the shape of its active site.
many enzymes require non-protein helpers called __to help them catalyze reactions?
COFACTORS
what is an inorganic and organic cofactor?
inorganic cofactors include things such as metal ions. organic cofactors called coenzymes include things such as vitamins organic molecules with carbon.
How to Inhibitors affect our enzymes?
they selectively attached to an enzyme and stop it from binding to its subject causing a reduction in its reaction rate.
what is it a competitive inhibitor?
reduce the productivity of an enzyme by attaching to the enzymes active site and blocking substrates from attaching.
what is a non-competitive inhibitor?
bind to the enzyme at location that is not the active site causing the enzyme and its active site to change shape and preventing the enzymes active site from attaching to the substrate.
what is a reversible inhibitor?
they temporary associate with the binding site of the enzyme without forming any permanent bonds eventually they fell off.
what is an irreversible inhibitor?
form covalent bonds with enzyme at The Binding site and do not attach permanently inhibiting the enzyme. these are diseases.
how can the reversible competitive Inhibitors overcome?
they increase the concentration of substrate
how can non-competitive Inhibitors overcome?
they can't. they cannot become overcome by increasing the substrate concentration because it's a permanent solution .
Why do enzymes have allosteric resolution?
this means that they can be turned on and off.
what is an allosteric activation?
stimulates an increase of enzyme activity. occurs when The Binding of a regulatory molecule called an activator stabilizes with the accurate conformation of the enzyme. It's like there's this switch that can push the enzyme into overdrive—zooming super fast .
What is an allosteric inhibition?
a form of allosteric relation that decreases enzyme activity. this is the same thing as non-competitive and imitation. this occurs when The Binding of the regulatory molecule called an inhibitor stabilizes the inactive form of the enzyme in which the substances cannot bind to the active site of the enzyme.
What is a metabolic pathway?
a series of chemical reactions that are needed to take a certain substrate and turn it into a desired final product.
what is feedback inhibition?
regulates the metabolic pathways. this process involves the end product shutting down the middle of both pathway by binding to it and inhibiting an enzyme that is used earlier in the pathway.
what does feedback inhibition prevent?
prevents a cell from forming synthesizing more product that is needed in wasting chemical resources.
Why is it okay for cells to complementalize where reactions take place within the cell?
this increases the efficiency of the cell because it prevents conflicting types of reactions from competing with one another. sales accomplish this by making sure that certain enzymes are located eyes to many certain areas within the cell. Example: the enzyme ATP synthesizes is embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondria organelle where ATP synthesis occurs.
What is metabolism?
The totality of an organism's chemical reaction.
what are the two types of metabolic pathways describe them?
there is catabolic and anabolic. the combination of these two make up the organisms metabolism.Catabolism (catabolism) break down complex molecules into simpler compounds these Pathways release energy. anabolic pathways ( anabolism) build complex molecules from simple or ones anabolic Pathways consume / require energy.
There are two types of energy kinetic and potential what are the descriptions of these?
kinetic energy is the energy associated with motion or movement of matter. this includes thermal energy which involves random movement of atoms or molecules examples of kinetic energy are heat and light. because light travels in waves which is movement. potential energy is the energy that matter possesses because of its location or structure. this includes chemical energy which is stored in a molecular structure such as chemical bonds. this energy can be released in a chemical reaction such as glucose.
what is thermodynamics?
energy that can be converted from one form to another such as potential energy to kinetic or kinetic energy to potential energy. it's the study of energy transformations.
what are the two laws of thermodynamics?
the first law of thermodynamics states that energy can be transferred and transformed but it cannot be created or destroyed. the second law of thermodynamics states that every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe. during this energy transfer or transformation some energy is lost into the environment as heat.
what does entropy mean?
the measure of disorder or randomness
True or false? organisms create organized structures from less organized starting materials which decreases and trophy.
true. anabolic Pathways put amino acids together to build proteins.
True or false? organisms also take an organized forms of modern energy from their surroundings and replace them with less ordered forms which increases entropy.
true because catabolic Pathways break down complex organize molecules from food into smaller less organized molecules.
since living systems increase their entropy of their surroundings much more than they increase their internal energy what law of thermodynamics does this follow?
the second law of thermodynamics.
in human bodies do we have more entropy or less infantry?
less that's meaning our body is organized
in the universe,what is the amount of entroy compared to human bodies is there less entory or more entropy?
more because they're less organized
what is free energy?
Free energy is a way to measure how much energy is available to do useful work in a system, especially during chemical reactions.
It helps predict whether a reaction will happen on its own or needs a push.
what is the formula for the change in free energy?
ΔG=Gfinal-Gintial
What happens if the change in free energy is negative?
the process is releasing free energy and it occurs spontaneously.
what is a spontaneous process?
where there is no input of energy required this can happen quickly or very slowly
if the free energy is positive what will happen?
an input of energy is required for The process to occur and it will not occur spontaneously.
during spontaneous change the free energy ___and the stability of the system increases.
decreases
What are exogonic reactions+ detla G?
reactions that release free energy to their surroundings and they occur spontaneously these products have less free energy than reactants and the Delta G is negative which means we have enough.
true or false? the greater decrease in free energy the more work the reaction can perform.
true.
What is the cellular respiration formula
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + ATP
If I have a negative Delta G what does this mean for my reaction?
that it's spontaneous = exergonic=free energy is being released.
Endergonic reactions do what?
absorb free energy from the surroundings and do not occur spontaneously these products have more free energy than the reactants and the Delta G is positive.
What is Delta G?
the quantity of energy required to drive the reaction
So if I now have a positive Delta G what's follows this?
not spontaneous and organic and free energy is required.
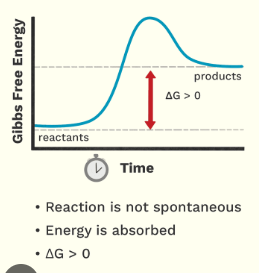
Is this an Endergonic or exergonic graph?
Endergonic
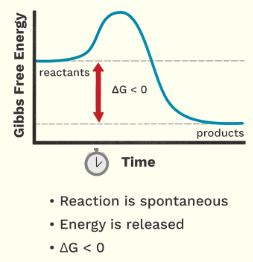
Is this endergonic or exergonic graph?
exergonic
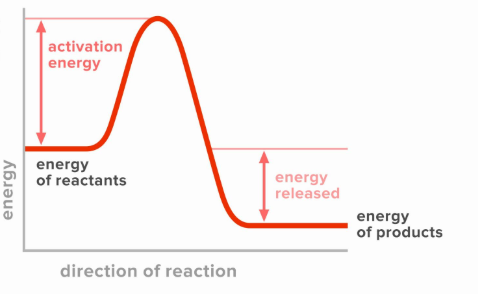
What is activation energy?
the initial amount of energy the reactants need to absorb to become a products. this energy is typically supplied in the form of heat from the surrounding.
can reactants occur if the activation energy is not achieved?
no.
reactions with large activation energies occur _while reactions with small activation energies occur _?
slowly
True or false. energy input must exceed energy loss to maintain ordered and to power cellular processes.
true.
Sell your processes that release energy may be coupled up with what cellular processes?
processes that require energy
how many phosphate groups does ATP have?
three.
what is a phosphate group?
negatively charged and repel to each other
In the cell can the energy from the exogonic reaction of ATP hydrolysis cannot be used to drive endergonic reactions?
yes.
Which two things does ATP coupling produce spontaneous?non-spontaneous? endogonic ? exergonic?
exergonic and spontaneous
What is endothermic?
a reaction and absorbs heat from its surroundings to proceed taking in heat.
what is Exothermic?
releases heat into its surrounding as it goes all about giving its heat out.
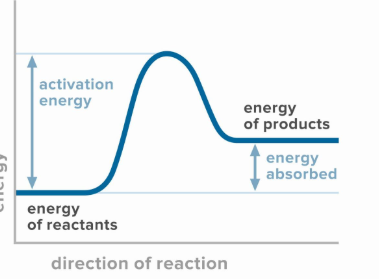
Is this exothermic or endothermic?
Endothermic
Is this exothermic or endothermic?
exothermic
What are autotrophs?
self feeders these are organisms not sustain themselves without eating anything made from other organisms. they are producers in the ecosystem and they're the base of the food chain plants.
they are two types of autotrophs chemoautotrophs and photoautotrophs what do these mean?
photoautotrophs are organisms that use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds through photosynthesis.
Chemoautotrophs are organisms that obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic substances (like hydrogen sulfide or ammonia) to synthesize organic compounds from carbon dioxide
what are heterotrophs?
they are unable to make their own food and most rely on compounds made by other organisms they are consumers in the ecosystem and eat producers.
what is the difference between herbivores omnivores carnivores and decomposers?
herbivores eat plants omnivores eat both carnivores only eat meat and decomposers break things down.
what is photosynthesis also include the formula?
convert solar energy into chemical energy or food for plants. 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂.
Cells carry specific __that are specialized to carry out photosynthesis?
chloroplast
Is photosynthesis a redox(reduction) reaction?
Yes, photosynthesis is a redox reaction because it involves the transfer of electrons, with water being oxidized and carbon dioxide being reduced.
what is the major site of photosynthesis?
the leaves.
why do plants have a green pigment?
the green colors from Chlorophyll
What are the microscopic pores on the leaf?
they're called the stoma this is where CO2 enters the leaf and O2 exits
what is a mesophyll cell?
this is where chloroplasts are found in the interior tissue of the leaf and a typical mesophyll cell has 30 to 40 Chloroplast
The chlorophyll is in the membranes of __which are connected sacs in the chloroplast __may be stuck in columns called __.
thylakoids. Thylakoids. Grana.
What is stroma?
chloroplast contain this it's a dense fluid found outside the thylakoid
Photosynthesis consists of two phases which are.
the light reactions and the Calvin cycle
Explain the light reaction process of photosynthesis?
this happens in the thylakoids.it splits water which releases 02 produces ATP and then forms NADPH
Explain the Calvin cycle part of photosynthesis?
this is found in the stroma it forms sugar from CO2 using ATP and NADPH.
Light is a form of ___energy which is also called ___radiation. light consists of discrete wave particles called ___. light energy travels in waves and the wavelength determines the ____.
Electromagnetic. electromagnetic. photons. the type of electromagnetic radiation.
Are pigments substances that absorb certain wavelengths of visible light?
yes.