ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is an aldehyde?
the C=O is at the end of the chain
name will end in -al
What is a carbonyl?
contains a C=O bond
What is a ketone?
the C=O is in the middle of the chain
name will end in -one
What’re the intermolecular forces found in carbonyls?
pure carbonyls cannot hydrogen bond to themselves but are attracted by permanent dipole forces
How soluble are carbonyls?
smaller carbonyls are soluble in water as they can form hydrogen bonds with water
How can carbonyls react?
the C=O bond is polarised as O is more electronegative than the carbon, so the positive carbon atom will attract nucleophiles
What can primary alcohols be oxidised into?
aldehydes and ketones
What can secondary alcohols be oxidised into?
ketones
What can tertiary alcohols be oxidised into?
do not oxidise
What is the reagent used to oxidise alcohols?
potassium dichromate
What occurs in the oxidation of aldehydes?
forms a carboxylic acid
reagent - potassium dichromate and dilute sulfuric acid
conditions - heat under reflux
How can you test for aldehydes using tollens reagent?
heat gently with tollens
with aldehydes a silver mirror coats the test tube
with ketones there is no visible change
How can you test for aldehydes using fehlings solution?
heat gently
with aldehydes the blue ions turn red
with ketones there is no visible change
What reducing agents are used to reduce carbonyls into alcohols?
NaBH4
LiAlH
What conditions is required to reduce carbonyls?
NaBH4 in aqueous ethanol
room temperature and pressure
What’re aldehydes reduced into?
primary alcohols
What’re ketones reduced into?
secondary alcohols
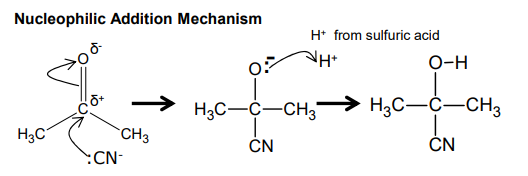
Outline the nucleophilic addition mechanism for propanone

What is catalytic hydrogenation?
carbonyls are reduced using catalytic hydrogenation
reagent - hydrogen and nickel catalyst
conditions - high pressure
What happens when hydrogen cyanide is added to carbonyles?
forms hydroxynitrile
reagent - potassium cyanide and dilute sulfuric acid
conditions - room temperature and pressure
What is the nucleophilic addition mechanism between propanone and :CN-?
Why does nucleophilic addition of HCN to aldehydes and ketones form a racemate?
the planar carbonyl group is approached equally from both sides of the HCN attacking species