Lecture 5 - Panic Disorder
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are the physical symptoms of panic disorder?
Palpitations, pounding heart, or
accelerated heart rate
2. Sweating
3. Trembling or shaking
4. Sensations of shortness of breath or
smothering
5. Feelings of choking
6. Chest pain or discomfort
7. Nausea or abdominal distress
8. Feeling dizzy, unsteady, light-headed,
or faint.
9. Chills or heat sensations
10. Paresthesias (numbness or tingling
sensations
11. Derealization or depersonalization
What emotional symptoms of panic disorder are there
Fear of dying (e.g. choking or having a heart
attack)
Fear of losing control or “going crazy”
Constant worrying about having another attack
Adapting behavior (avoiding busy places)
Fear that others might notice a panic attack
Anticipating with anxiety certain events
Focusing on bodily symptoms
Appraising bodily symptoms as dangerous
Always anticipating panic attacks
Always carry certain attributes to prevent PA
What is the prevalence of panic disorder?
United states and Europe: 2-3% of 12-month
prevalence
Estimated lifetime prevalence 1.7% with 2.7%
projected lifetime risk in mental health surveys
Women more likely to have it (2:1)
What is the comorbidity like for people with panic disorder?
Generally, 80% of individuals with panic
disorder have a lifetime comorbid mental
diagnosis:
Any other anxiety or related disorder
Major depressive disorder
Mild alcohol use disorder
They also have comorbidity with physical disorders (Cardiac arrhythmias, hyperthyroidism,
asthma, COPD and irritable bowl syndrome)
What are risk factors for panic disorder?
Behavioural: Neuroticism, anxiety sensitivity, behavioural inhibition and harm avoidance
Environmental: Stressors in the months leading up to the panic attacks, drug use
Genetic/physiological: Hereditary, increased risk if your immediate family members have anxiety, depressive, or bipolar disorders
What different aspects of panic appraisal are there?
1. Catastrophic consequences of panic
2. Likelihood of panic in agoraphobic situation
3. Perceived self-efficacy in coping with panic
What is anxiety sensitivity?
The predisposition to believe that symptoms of anxiety are harmful (leading to increased vigilance towards physical symptoms of arousal)
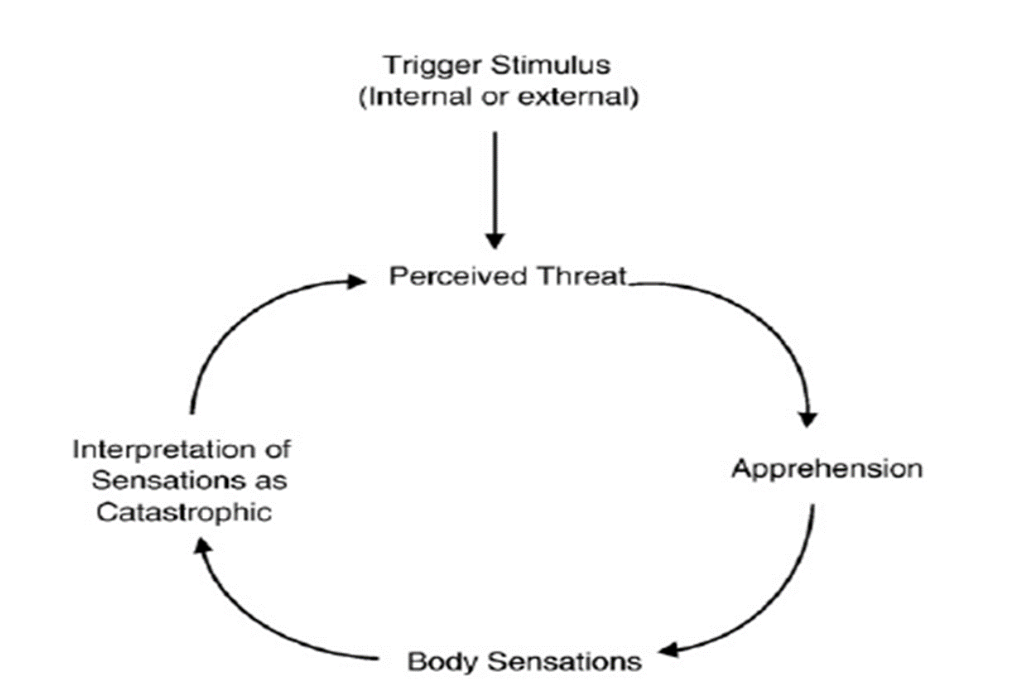
Explain Clark’s cognitive model of panic?
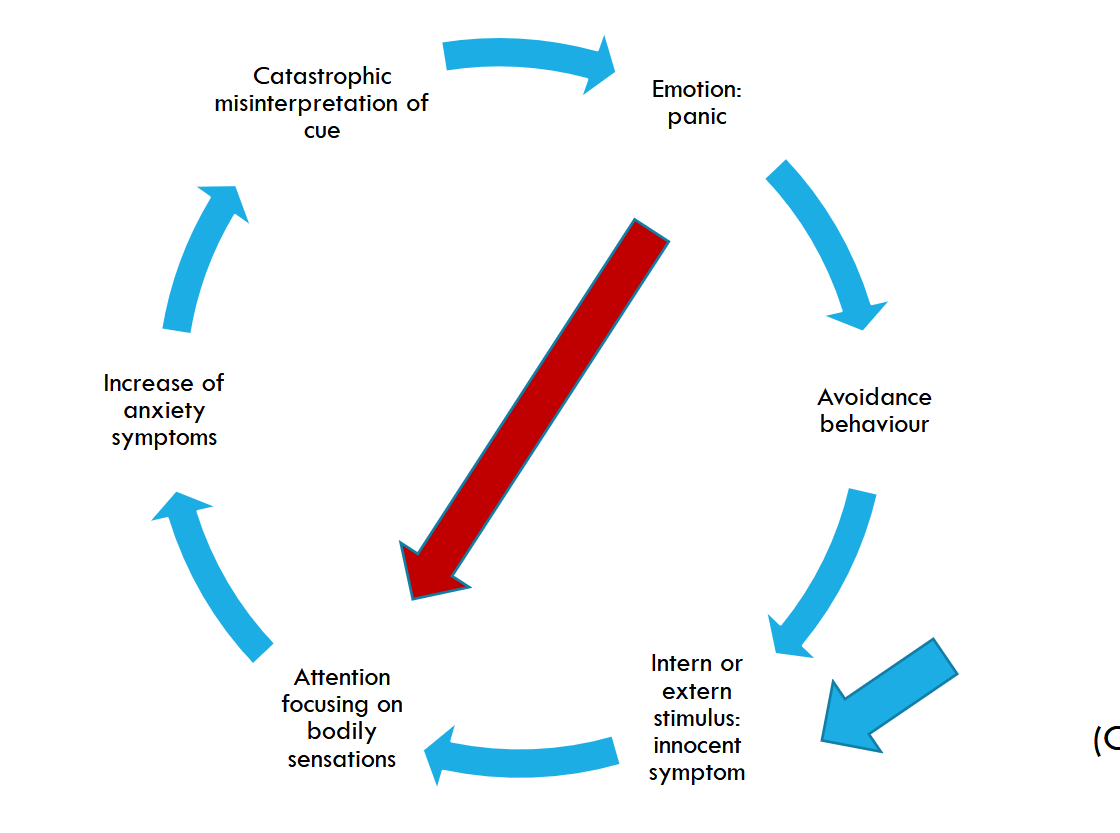
Explain Craske’s model of panic disorder
What does exposure therapy for panic disorder aim to do?
Reduce avoidance behaviours
How do you test the idea that you will have a heart attack if your heart starts racing?
Exercise or get patient’s heart racing in another way
How can you test the idea that one is “going crazy”?
e.g. make them watch an optical illusion
What is interoceptive exposure therapy?
Exposure therapy where the thing the patient is being exposed to is their own bodily sensations
How can you test a fear of suffocation?
By making the patient hyperventilate
Why does interoceptive exposure therapy work?
Learning that CS (= feared cue) does not lead to US (= catastrophe)
What can be a problem with therapists when it comes to exposure therapy?
The therapist can be overly anxious about doing the exposure measures, which can lead to the patient not being properly “exposed”. Some therapists think, that, for example, it is unethical for a therapist to deliberately induce tension in clients. or that most clients struggle to tolerate the stress of exposure therapy.
Why is it important that therapists commit to properly doing exposure therapy?
More therapist behaviors that encourage approach—and less use of accommodation, unrelated talk, and externalizing language—predicted greater subsequent habituation during individual exposure
tasks (exposure-level), and also predicted improved patient clinical outcomes via higher “total dose”
of habituation across treatment (patient-level indirect effect)
What are some positive aspects of virtual reality therapy?
Situations that can’t be easily simulated in vivo can be simulated there
Efficacy is similar to that of in vivo
CBT (including exposure therapy) is an effective treatment, but it has a relatively high percentage (10-40% of non-respondence). What treatment could potentially be used instead?
Recent studies have indicated that EMDR as a second step intervention has
potentially an additional value in panic disorder (and) agoraphobia.
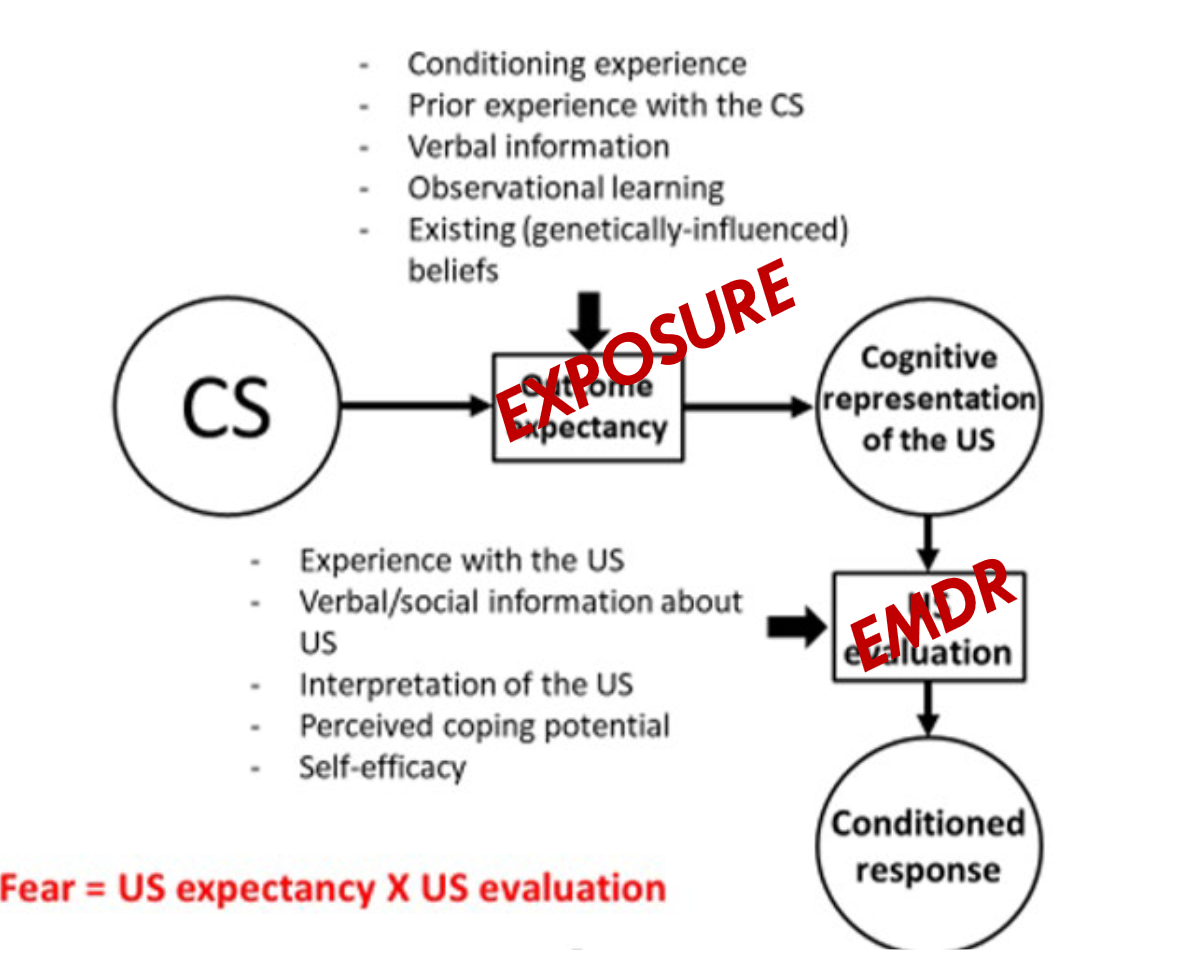
Explain based on this why EMDR could be useful in treating panic disorder
There are different pathways for anxiety aquisition. CBT for example targets the expectancies that people have. However, EMDR can also help, for example by reducing the fear towards the US