atoms, ions, and molecules
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
isotopes
atoms of the same element with the same number of protons and electrons but differ in number of neutrons
octet rule
atoms obtain an outer shell with eight electrons and gain chemical stability through the loss, gain, or sharing of electrons.
covalent bond
formed between two atoms sharing the same electrons
ion
atom with an electric charge (positive or negative)
cations
ion with a positive charge
anions
ion with a negative charge
ionic bond
cations and anions binding together
molecule
composed of two or more different elements to form a different entity
molecular formula
numbers and types of atoms composing a molecule
isomer
molecules composed of the same number and types of elements but arranged differently
glucose + galactose molecular formula
C6H12O6
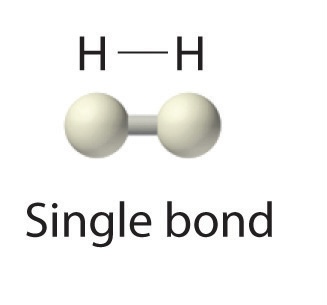
single covalent bond
sharing one pair of electrons between atoms
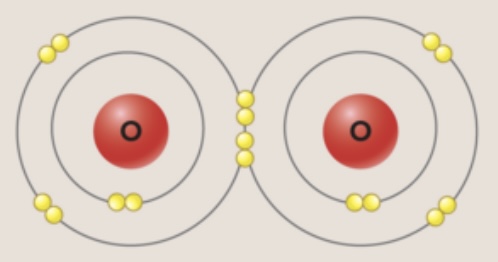
double covalent bond
sharing two pairs of electrons between two atoms
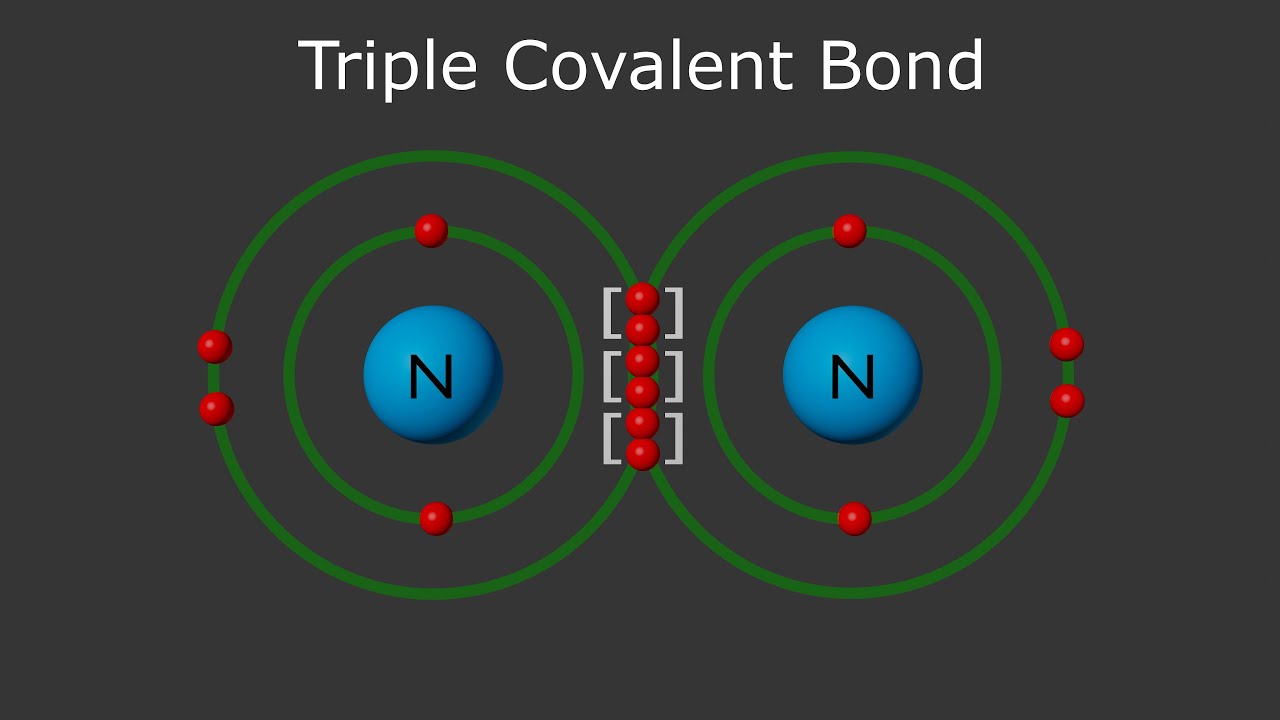
triple covalent bond
three pairs of electrons shared between atoms in some molecules
nonpolar covalent bond
two atoms that equally share electrons
polar covalent bond
sharing of electrons between two atoms of different types
amphipathic
molecules with both nonpolar and polar components
intermolecular attractions
molecules with weak attractions to other molecules
hydrophobic interaction
when nonpolar molecules are placed in water (or another polar substance)
intramolecular attraction
intermolecular attraction that occurs between different portions of a large molecule
organic molecules
molecules containing carbon (glucose, protein, triglycerides)
inorganic molecules
molecules without carbon (sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide)
water (H2O)
polar molecule composed of one oxygen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms
phases of water
solid, (ice) gas, (vapor water) liquid (water)
cohesion
attraction of water molecules
adhesion
attraction of water molecules and another substance other than water
surface tension
inward pulling of cohesive forces at the surface of water
solvent
liquid that dissolves one or more solutes
universal solvent
water
hydrophilic
water-loving (dissolves in water)
hydrophobic
water-fearing (doesn’t not dissolve in water)
acid
substance that dissociates in water to produce both H+ and an anion
base
substance that accepts a hydrogen ion
pH
value indicating the relative hydrogen ion concentration of a solution; any number between 0 and 14