Food Analysis Exam 1
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Specificity / selectivity
ability to detect the component of interest specifically in the presence of other components
affected by presence of interfering substances
broad spectrum s very specific
crude fat analysis: compounds soluble in an organic solvent, including triglycerides, phospholipids , cholesterol, fat soluble vitamins ( A, D , E and K )
GC-TEA (gas chromatograph thermal energy analyzer) : analysis of N -nitrosamines : selectively analyze the compounds with no structure
accuracy
describes nearness of an experimental value to the true value
methodology : calibration , standard reference material , % rrecovery , omparison to a well characterized method
precision
describes the reproducibility of replicate measurements. Precision refers to the agreement between values in a set of data.
accuracy vs precision
all replicate measreuments agreeing welel doesn’t mean they are close to true valueall replicate measreuments agreeing welel doesn’t mean they are close to true value
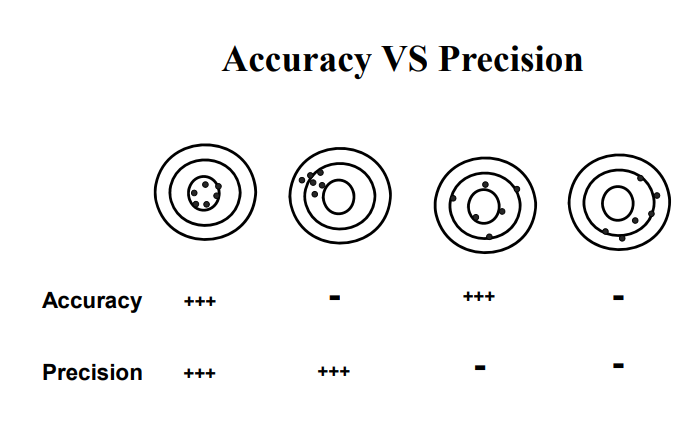
evaluating precision
1) mean
2) SD
3) Coefficient of variation ( SD / mean ) x 100%
a CV below 5% = acceptable
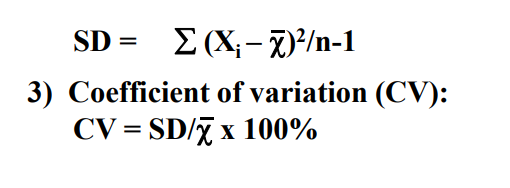
sensitivity
ratio between the magnitude of the intrumental response and the amount of the compound analyzed
detection limit
the lowest concentration of an analyte that can be detected with a statistical significance
in instrumental analysis , the limit of detection can be researched when the signal to nose ratio is 2:1
signal to nose ratio
the response to the analyte divided by the electronic noise of the detection system
Linear range
interval between upper and lower levels of analyte in a linear doese-response
directly proportional to analyte concentration within a given range
standard curves
used to determine unknown concentrations
concentration of substance must be prortional to measurement
linear regression most often used to construct curve
systematic errors
errors that can be determined and eliminated are called systematic errors or determinate errors
sources :
methods, equipment / materials , personal judgements, mistakes
random errors
random errors that cant be determined and controlled , also called indeterminate errors
effects can be effect of many small uncontrollable variables and personal judgements that lead to uncertainty in a measured value
Daily Value terms ( RDI and DRV )
RDI (Reference daily intake) : used for essential vitamins and minerals
Daily Reference value (DRV) : used for food components : total fat , saturated fat , cholersterol, total carbohydrate, dietary fat , sodium, potassium , protein
based on 2000 or 2500 calorie intake
adding significant figures
he sum or difference of two measurements
can be no more accurate than the least accurate
of any individual measurement
moisture vs total solids
moisture = measure of the water content of a material
total solids: dry matter after moisture removal
water + solids = 100%
structure of water
dipolar nature . “ H slgightly positive and O slightly negative . one molecular can bind 4 molecular throuhgh hydrogen bonds
types of water
free water, bound water, water of crystallization
free water
immobolized water : blocked by cell membrane or subcellular structures, not flow freely
capillary water : hold by capillary force or intercellular water
fluid water: freely move ex: blood
free water retains physcial properties and acts as solvent and is easy to form ice which causes damage of tissue strucutre