Path sci 2 term 2
1/452
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
453 Terms
Approximately what percentage of neoplasms are classed as malignant?
a. 25%
b. 45%
c. 60%
d. 10%
e. 5%
25%
Histology is a complex process, but which one of the below is not a step in the histology process?
a. Microtomy of tissues (sectioning)
b. Processing of the tissues
c. Spreading of tissue onto agar plates
d. Embedding of tissue
e. Grossing of specimens into cassette sized pieces
Spreading of tissue onto agar plates
Immunohistochemistry commonly employs panels of antibodies to identify cell and tissue characteristics to differentiate tumour types. If you were trying to differentiate between an adenocarcinoma & squamous cell carcinoma of the Lung using the following antibodies - P63, TTF1, CK5/6, Napsin A – what would the results for an adenocarcinoma show?
a. P63 negative – TTF1 positive – CK5/6 negative – Napsin A positive
b. P63 negative TTF1 negative -CD5/6 negative – Napsin A positive
c. P63 negative – TTF1 negative – CK5/6 positive – Napsin A negative
d. P63 positive – TTF1 negative – CK5/6 positive – Napsin A negative
e. P63 positive – TTF1 positive – CK5/6 negative – Napsin A negative
P63 negative – TTF1 positive – CK5/6 negative – Napsin A positive
Special Staining is a supportive diagnostic tool. Which of the following pathologies can be detected using this tool?
a. All of the above
b. Differentiation of tissue structures
c. Vascular Invasion
d. Detection of pathogens
e. Identification of minerals
All of the above
The transformation of one cell type into another cell type is a known as…
a. Dysplasia
b. Neoplasia
c. Apoptosis
d. Hyperplasia
e. Metaplasia
Metaplasia
To understand the severity of a tumour, staging must be considered. A commonly utilised approach is the TNM staging system. What does TNM stand for?
a. Tissue, Nodular, Migrating
b. Tissue, Nodes, Metastasis
c. Tumour, Necrosis, Metastasis
d. Tumour, Nodes, Margins
e. Tumour, Nodes, Metastasis
Tumour, Nodes, Metastasis
Which of the following features will a pathologist investigate when assessing for benign vs malignant differences?
a. Size
b. All of the above
c. Margins
d. Colour
e. Necrosis
All of the above
Which of the following processes does not produce Neoplasia?
a. Normal cell division/Decreased Apoptosis
b. All of the above
c. Normal cell division/Normal Apoptosis
d. Increased cell division/Normal Apoptosis
e. Increased cell division/Reduced Apoptosis
Normal cell division/Normal Apoptosis
Which one of the below is a malignant epithelial tumour?
a. Leiomyoma
b. Basal Cell Papilloma
c. Transitional Cell Papilloma
d. Chondroma
e. Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Which one of the below is a typical feature of a benign neoplasm?
a. Endophytic (grow inwards)
b. Fast growing
c. Poorly circumscribed
d. Remain localised (do not normally invade)
e. Necrotic hallmarks
Remain localised (do not normally invade)
Which surface appearance is associated with more aggressive tumour behaviour?
a. Annular
b. Polypoidal
c. Ulcerative
d. Sessile
e. Papillary
Ulcerative
Which type of differentiation is regarded as the most severe?
a. Well Differentiated
b. Moderately differentiated
c. Poorly Differentiated
d. Undifferentiated
e. Semi Differentiated
Undifferentiated
Adenosis is…
a. Scarring of tissue
b. An increase in the number of glands
c. A fluid filled gland
d. A change of one cell type to another cell type
e. Fewer but larger glands
An increase in the number of glands
ER, PR, and HER2 are prognostic markers commonly assessed together by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in breast cancer diagnosis. If a patient’s tumour is positive for the ER marker, this indicates…
a. The tumour cells have high progesterone levels
b. The tumour cells have low oestrogen receptor expression
c. The tumour cells have low progesterone levels
d. The tumour cells are positive for the HER2 gene
e. The tumour cells have high oestrogen receptor expression
The tumour cells have high oestrogen receptor expression
Fibroadenoma is a benign tumour. What histological hallmarks can be seen microscopically when using H&E stain?
a. Mitosis
b. All of the above
c. Percanalicular/Intracanalicular
d. Large nuclei
e. Poorly circumscribed stroma
Percanalicular/Intracanalicular
Fibrocystic disease is a benign non-cancerous condition which can be characterised by which morphological features?
a. Cysts
b. Apocrine Metaplasia
c. Adenosis
d. All of the above
e. Fibrosis
All of the above
Fine Needle Aspirate (FNA) is a diagnostic tool used to withdraw fluid containing cells from a lump of interest to identify malignant cells. What stain is commonly used on an FNA sample?
a. H&E
b. IHC
c. EVG
d. Alcian Blue
e. Giemsa
Giemsa
On H&E examination, what is the key microscopic hallmark of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ?
a. Tumour cells confined to the ducts
b. Tumour cells invading the stroma
c. Tumour cells confined to the lobules
d. Tumour cells present in both ducts and lobules
e. Tumour cells invading the nipple
Tumour cells confined to the ducts
HER2 is an important prognostic marker used within breast cancer – where patients are scored to assess their viability for treatment with Herceptin. But which HER2 score requires further analysis via in-situ hybridisation staining to identify gene amplification ensuring correct patients are treated with Herceptin.
a. 3+ score
b. 2+ score
c. 0 score
d. Any HER2 positive score required further analysis
e. 1+ score
2+ score
OSNA is a fast supportive diagnostic technique which provides information relating to metastatic disease by staging
a. Parasternal Lymph Node using CK5/6
b. Parasternal Lymph Node using CK19
c. Sentinal Lymph Node using CK5/6
d. Axillary Lymph Node using CK20
e. Sentinal Lymph Node using CK19
Sentinal Lymph Node using CK19
The histological feature “comedo” in ductal carcinoma in situ means…
a. Dysplasia Changes
b. Central Necrosis
c. Nuclear Pleomorphism
d. Ducts completely filled with malignant cells
e. Cell proliferation
Central Necrosis
Which of the following is a malignant invasive breast cancer?
a. Ductal Carcinoma In situ
b. Fibrocystic Disease
c. Ectasia
d. Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma
e. Adenoma
Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma
Which of the following structures are features of breast anatomy?
a. All of the above
b. Lobule
c. Acinus
d. Segmental Lactiferous Ductus/Lactiferous Sinus
e. Collecting Duct
All of the above
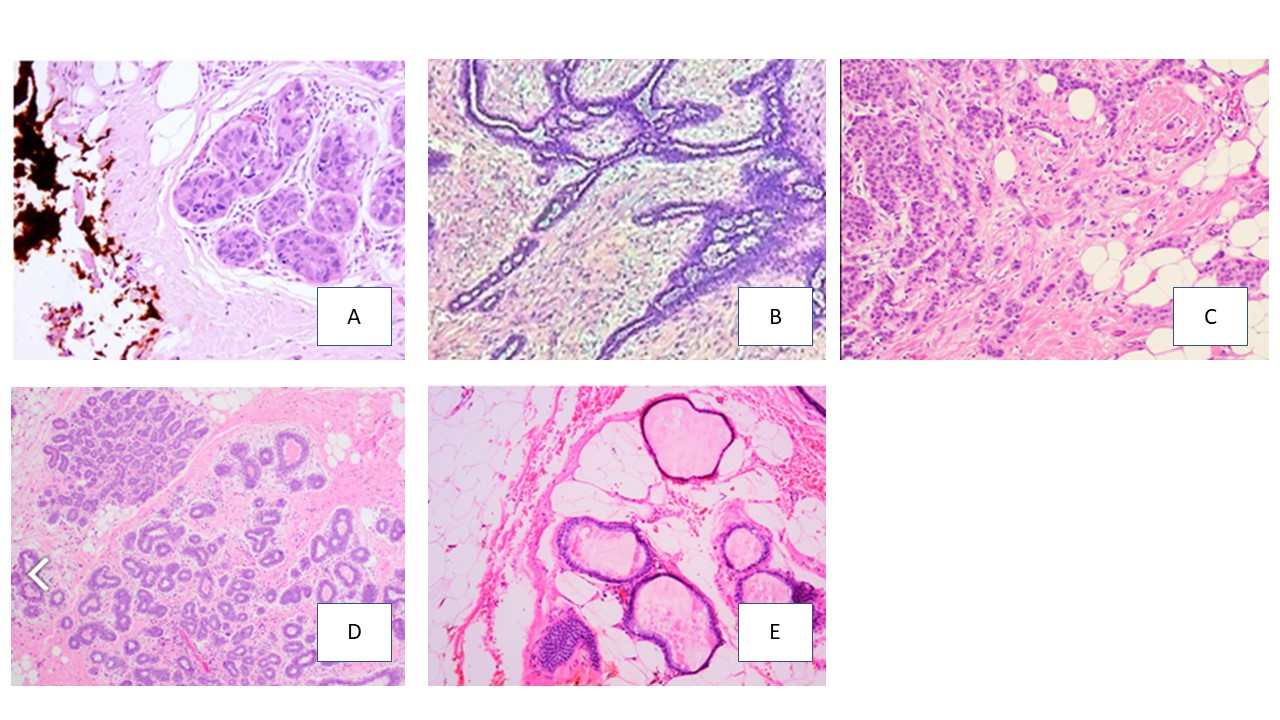
Which of the following H&E images shows and invasive infiltrating carcinoma?
a. Image A
b. Image B
c. Image C
d. Image D
e. Image E
Image C
The presence of abnormal cells is a known as…
a. Dysplasia
b. Neoplasia
c. Apoptosis
d. Hyperplasia
e. Metaplasia
Dysplasia
Increased cell production on normal tissue or organ is a known as…
a. Dysplasia
b. Neoplasia
c. Apoptosis
d. Hyperplasia
e. Metaplasia
Hyperplasia
Abnormal, uncoordinated and excessive cell growth is a known as…
a. Dysplasia
b. Neoplasia
c. Apoptosis
d. Hyperplasia
e. Metaplasia
Neoplasia
What is meant by differentation?
The degree to which the tumor looks like the cell of origin
Do all Neoplasias have a swelling?
No could be something like leukemia or myeloma
Programmed cell death is a known as…
a. Dysplasia
b. Neoplasia
c. Apoptosis
d. Hyperplasia
e. Metaplasia
Apoptosis
Is neoplasia always malignant?
No can be either benign or malignant
Neoplasia is the continuation of growth in the absence of physiological stimuli. True or false
True, even if there is a stimuli it will continue growing even when removed.
What are some of the stimuli that cause neoplasia?
Genetic
Metabolic
Environmental ( chemical, radiation, parasite, virus)
What are the hallmarks of benign neoplasms?
Localised
slow growing
Grows away from surface (Exophytic)
Well circumscribed
Closely resembles parent cell
Still can cause significant problems
Also though confined to the site of origin what clinical problems can benign neoplasms cause?
Pressure on tissues
Obstruction to flow
Hormone production
Transform to malignant
What do fibroblasts do for malignant neoplasms?
They provide nutritional elements and support.
What are the hallmarks of malignant neoplasms?
Invasive
Fast growing
Grows into surface (Endophytic)
Poorly defined
Doesn’t normally resemble parent cell
Mitotic figures
What are the morphology features of a malignant neoplasm?
Large nucleus size
Irregular cell size and shape
Prominent nucleoli
Scarce cytoplasm
Intensely coloured cells (nuclei)
Mitotic figures
Invasion
Differentiation
What are the 4 categories of differentiation?
Undifferentiated
Poorly differentiated
Moderately differentiated
Well differentiated
Which type of differentiation is regarded as the least severe?
a. Well Differentiated
b. Moderately differentiated
c. Poorly Differentiated
d. Undifferentiated
e. Semi Differentiated
Well Differentiated
What is the differentiation used for?
Very important for grading
Correlates strongly with prognosis/survival
Indicates appropriate treatment plan
What is special staining used for?
To identify
pathogens,
tissue structures,
minerals/products
vascular invasion
What does IHC stand for?
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry commonly employs panels of antibodies to identify cell and tissue characteristics to differentiate tumour types. If you were trying to differentiate between an adenocarcinoma & squamous cell carcinoma of the Lung using the following antibodies - P63, TTF1, CK5/6, Napsin A – what would the results for an Squamous cell carcinoma show?
a. P63 negative – TTF1 positive – CK5/6 negative – Napsin A positive
b. P63 negative TTF1 negative -CD5/6 negative – Napsin A positive
c. P63 negative – TTF1 negative – CK5/6 positive – Napsin A negative
d. P63 positive – TTF1 negative – CK5/6 positive – Napsin A negative
e. P63 positive – TTF1 positive – CK5/6 negative – Napsin A negative
P63 positive – TTF1 negative – CK5/6 positive – Napsin A negative
What do mammary glands consist of?
Ducts and lobules
What are the three groups of lymphatics in the breast?
Axillary nodes
Parasternal nodes
Posterior intercostal nodes
What is the function of oestrogen in breast pathology?
It stretches ducts to produce channels
What is the function of prolactin in breast pathology?
Promotes production of progesterone preparing glands for milk
What is the function of progesterone in breast pathology?
Increases the number and size of lobules in preparation for breast feeding
What is the function of oxytocinin breast pathology?
helps release milk
What are types of fibrocystic disease?
Cysts
Fibrosis
Aprocrine metaplasia
Adenosis
What is stroma fibrosis?
When a cyst breaks the fluid escapes into stroma
cuases inflammation and recruitment of new fibroblasts
overtime leads to scarring known as fibrosis
Non cancerous
What is Aprocrine metaplasia?
When epithelial cells which line ducts in the breast change from columnar to apocrine
Non cancerous change
Apocrine cells look larger and pinker than normal cells
Normally seen in areola
What is Adenosis in breast pathology?
An increase in the number of glands
Non cancerous
Glands could be larger too
Often seen with columnar cell change and hyperplasia
What is mastitis?
Tissue surrounding ducts becomes inflamed and swollen
Can lead to bacterial infection
Ducts become narrowed
What is the classification of fibrocystic disease?
Benign proliferative disease
What is the classification of Fibroadenoma?
Benign tumor
What is the classification of Ductal Carcinoma Insitu?
Malignant Non Invasive breast carcinoma
What is the classification of Infiltrating Ductal?
Malignant invasive breast carcinoma
What percentage of malignant invasive breast carcinomas are infiltrating ductal?
20%
45%
60%
75%
80%
75%
ER, PR, and HER2 are prognostic markers commonly assessed together by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in breast cancer diagnosis. If a patient’s tumour is positive for the PR marker, this indicates…
a. The tumour cells have high progesterone levels
b. The tumour cells have low oestrogen receptor expression
c. The tumour cells have low progesterone levels
d. The tumour cells are positive for the HER2 gene
e. The tumour cells have high oestrogen receptor expression
The tumour cells have high progesterone levels
HER2 is an important prognostic marker used within breast cancer – where patients are scored to assess their viability for treatment with Herceptin. But which HER2 score means patients are instantly eligible to be treated with Herceptin.
a. 3+ score
b. 2+ score
c. 0 score
d. Any HER2 positive score required further analysis
e. 1+ score
3+ score
HER2 is an important prognostic marker used within breast cancer – where patients are scored to assess their viability for treatment with Herceptin. But which HER2 scorees means patients are neagtive?
a. 3+ score
b. 2+ score
c. 0 score
d. Any HER2 positive score required further analysis
e. 1+ score
0 and 1 scores
A pus-filled bump of the skin is …
a. Lichenfication
b. A rash
c. A papule
d. A macule
e. A pustule
A pustule
Dermatosis is a common condition affecting the skin, this is caused by…
a. All of above
b. Fungal
c. Bacteria
d. Virus
e. Autoimmunity
Al of the above
The epidermis consists of which cell type?
a. Melanocytes
b. Basal epithelial cells
c. All of the above
d. Langerhan cells
e. Squamous epithelial cells
All of the above
When observed macroscopically, which of the following skin diseases is characterised by a butterfly pattern on the face due to symmetry seen in this feature?
a. Tinea
b. Impetigo
c. Vitiligo
d. Lupus
e. Actinic Keratosis
Lupus
When observed macroscopically, which of the following skin diseases is characterised by white patches?
a. Vitiligo
b. Lupus
c. Acne
d. Tinea
e. Impetigo
Vitiligo
Which of the below is a morphological feature of the dermis?
a. Lacks nerves
b. Lymphatics
c. Shows stratification
d. Sitting on basement membrane
e. Avascular
Lymphatics
Which of the following can overcome the barrier functions of the skin to cause disease?
a. Parasitic
b. All of the above
c. Mechanical
d. Thermal
e. Chemical
All of the above
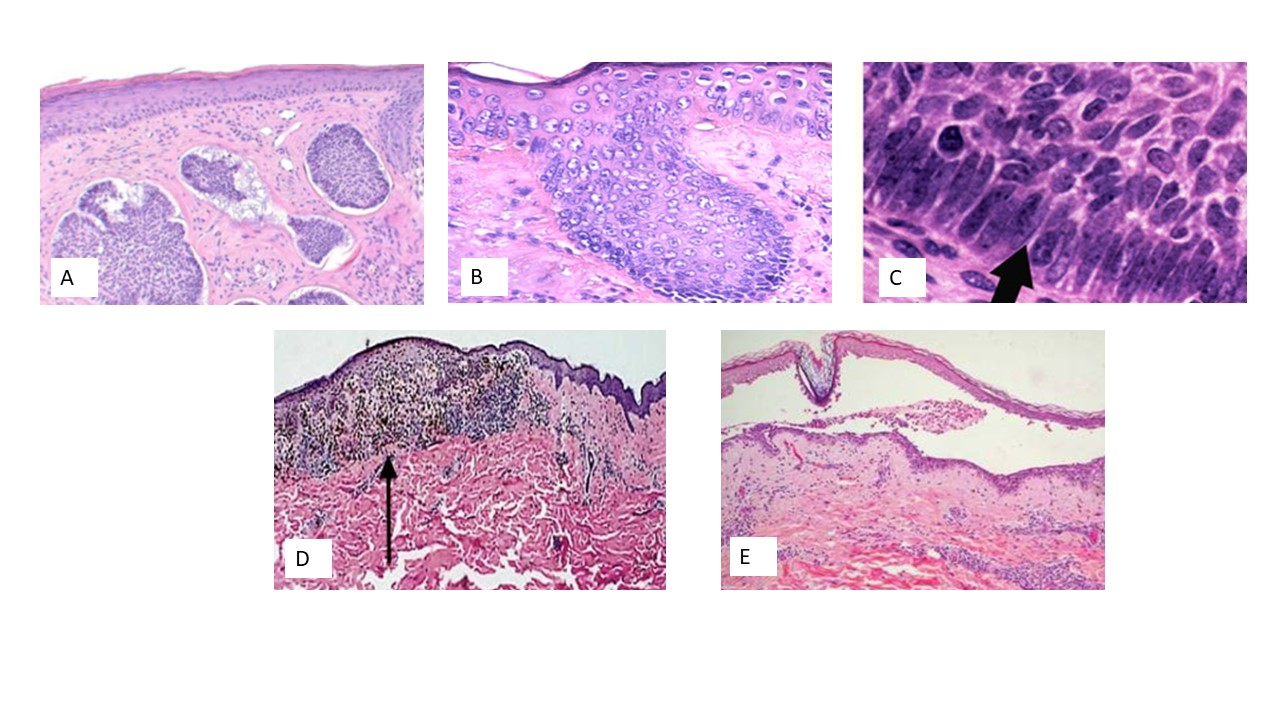
Which of the following H&E images shows Malignant Melanoma?
Image A
Image B
Image C
Image D
Image E
Image D
Which of the following is a key hallmark of a benign tumour?
a. Uneven shapes
b. Well defined borders
c. Ulcerative
d. Metastatic
e. Uneven colour
Well define borders
Which of the following terms is used to describe a thick discolouration of the skin?
a. Lichenfication
b. Vesicle
c. Plaque
d. Macule
e. Bullae
Lichenfication
Which of the statements below best describes the histological hallmarks seen within a H&E of Basal cell carcinoma?
a. Palisading cells – Atypical melanocytes – invasive locally
b. High nuclei to cytoplasm ratio – Atypical melanocytes - Great capacity to spread
c. Palisading cells – small basophilic cells – great capacity to spread
d. High nuclei to cytoplasm ratio – small basophilic cells – Great capacity to spread
e. Palisading cells – Small basophilic cells – invasive locally
Palisading cells – Small basophilic cells – invasive locally
What does palisading mean?
a rim or layer of cells who nuclei line up
Which panel of antibodies is important when differentiating basal cell carcinoma from malignant melanoma & squamous cell carcinoma?
a. Melan A – S100 – P63
b. BCL2 – EMA – P16
c. EMA – P16 – P63
d. BEREP4 – CD10 – BCL2
e. P63 – EMA – BCL2
BEREP4 – CD10 – BCL2
Which panel of antibodies is important when differentiating squamous cell carcinoma from malignant melanoma & basal cell carcinoma?
a. Melan A – S100 – P63
b. BCL2 – EMA – P16
c. EMA – P16 – P63
d. BEREP4 – CD10 – BCL2
e. P63 – EMA – BCL2
EMA – P16 – P63
What are some example of dermatosis?
Impetigo
Lupus
vitiligo
Acne
Tinea
Moles
Actinic keratinosis
What are the main points of pemphigus?
Intraepidermal (within epidermis)
effects middle age to elderly
high mortality
IgG attack intercellular junctions (desmosomes)
seperation above basement membrane
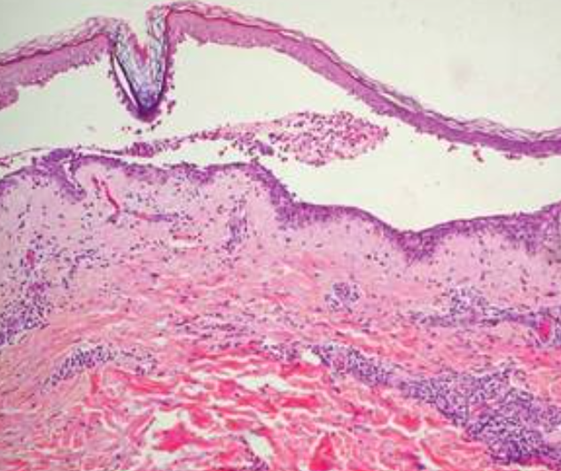
Is this Pemphigus or Pemphigoid?
Pemphigus
What are the main points of Pemphigoid?
Subepithelial (Below epidermis)
Effects elderly
Self-limiting
IgG attack basement membrane (hemidesmosomes)
separation at basement membrane
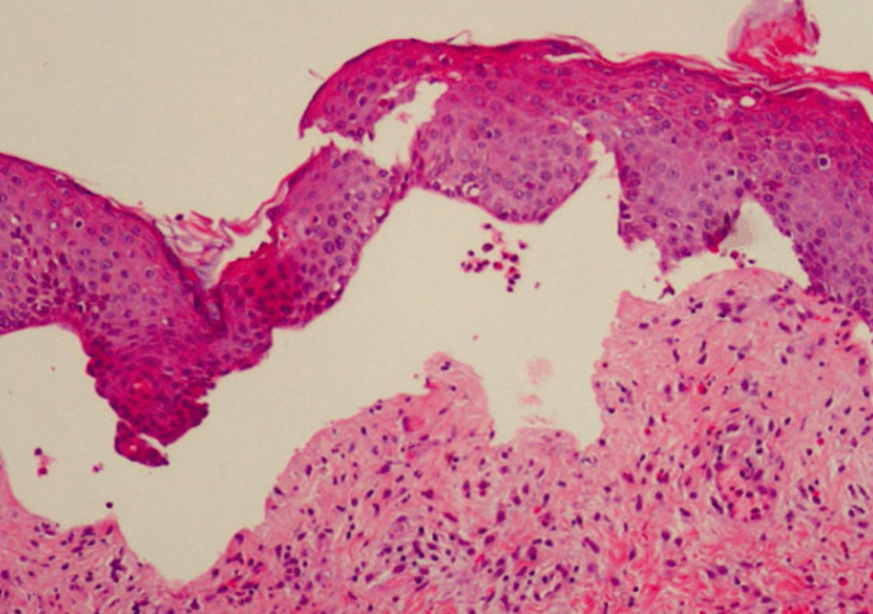
Is this Pemphigus or Pemphigoid?
Pemphigoid
Is basal cell papilloma malignant or benign?
Benign
Is basal cell carcinoma malignant or benign?
Malignant
is melanoma malignant or benign?
Malignant
What are the key hallmarks of benign skin tumors?
Do not metastasise
Well define borders
Slow growth
Non cancerous
What are the key hallmarks of malignant skin tumors?
Can metastasise
Irregular borders
uneven shapes
uneven colour
ulcerative
fast growth
What is basal cell papilloma also known as?
seborrhoeic wart
how common is basal cell papilloma?
common 90% of people over 60 get them
How common is basal cell carcinoma?
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
80%
Most common form of skin cancer
What are the microscopic features of basal cell carcinoma?
Palisading cells
mitosis
small basophilic cells
ulceration
islands of basophilic tumor cells arising from basal layer of epidermis
What is Mohs surgery?
technique to remove skin cancer
usually for bsc scc
used intraoperatively
keep going until all neoplastic cells are free from margins
What is the prognosis on malignant melanoma dependent on?
Breslow score
The thickness of the lesion
What does the ABCDEF checklist stand for in malignant melanoma?
Asymmetry
Border irregularity
Colour
Diameter
Evolution
Funny looking
Fluid-filled cysts found within the mouth are called (a) …
a. Lipoma
b. Torus
c. Mucoceles
d. Schwannoma
e. Papilloma
Mucoceles
If you were using immunohistochemistry to differentiate salivary gland/duct carcinoma from other types of head and neck tumour, which of the following antibody panels would be most suitable?
a. S100 – CK8 – CK5/6
b. P16 – HMB45 – MelanA
c. Androgen Receptor – GCDFP15 – CK7 – GATA3
d. S100 – HMB45 – Melan A
e. P53 – CK8 – CK5/6 – P16
Androgen Receptor – GCDFP15 – CK7 – GATA3
If you were using immunohistochemistry to differentiate squamous cell carcinoma from other types of head and neck tumour, which of the following antibody panels would be most suitable?
a. S100 – CK8 – CK5/6
b. P16 – HMB45 – MelanA
c. Androgen Receptor – GCDFP15 – CK7 – GATA3
d. S100 – HMB45 – Melan A
e. P53 – CK8 – CK5/6 – P16
P53 – CK8 – CK5/6 – P16
If you were using immunohistochemistry to differentiate melanoma of the oral cavity from other types of head and neck tumour, which of the following antibody panels would be most suitable?
a. S100 – CK8 – CK5/6
b. P16 – HMB45 – MelanA
c. Androgen Receptor – GCDFP15 – CK7 – GATA3
d. S100 – HMB45 – Melan A
e. P53 – CK8 – CK5/6 – P16
S100 – HMB45 – Melan A
Tuberculosis (TB) develops gradually and is characterised histologically by formation of granulomas. What is the causative agent of TB?
a. HPV
b. Fungi
c. Cancer
d. HIV
e. Mycobacterium
Mycobacterium
What is the name given to the white patches seen within the mouth and tongue that are linked with oral cancer?
a. Difficulty swallowing
b. Leukoplakia
c. Sore
d. Erythroplakia
e. Ulcer
Leukoplakia