Understanding DNA Structure and the Central Dogma
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Central Dogma
Process: DNA codes for RNA, which codes for proteins.
DNA
Molecule carrying genetic information in organisms.
Nucleotide
Building block of DNA, consisting of phosphate, sugar, base.
Double Helix
Structure of DNA resembling a twisted ladder.
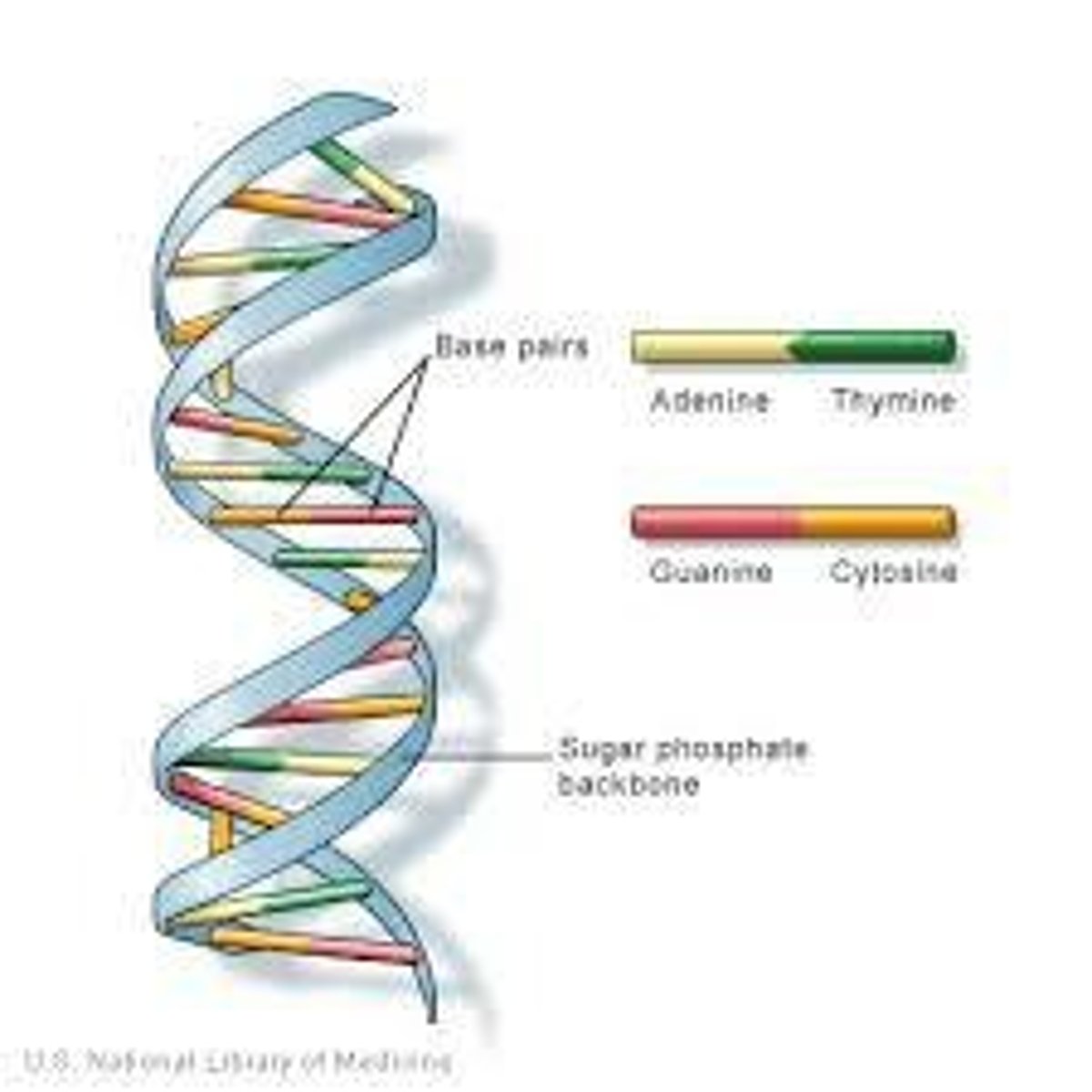
Nitrogenous Bases
A, T, G, C; form the steps of DNA.
Chargaff's Rule
A pairs with T, G pairs with C.
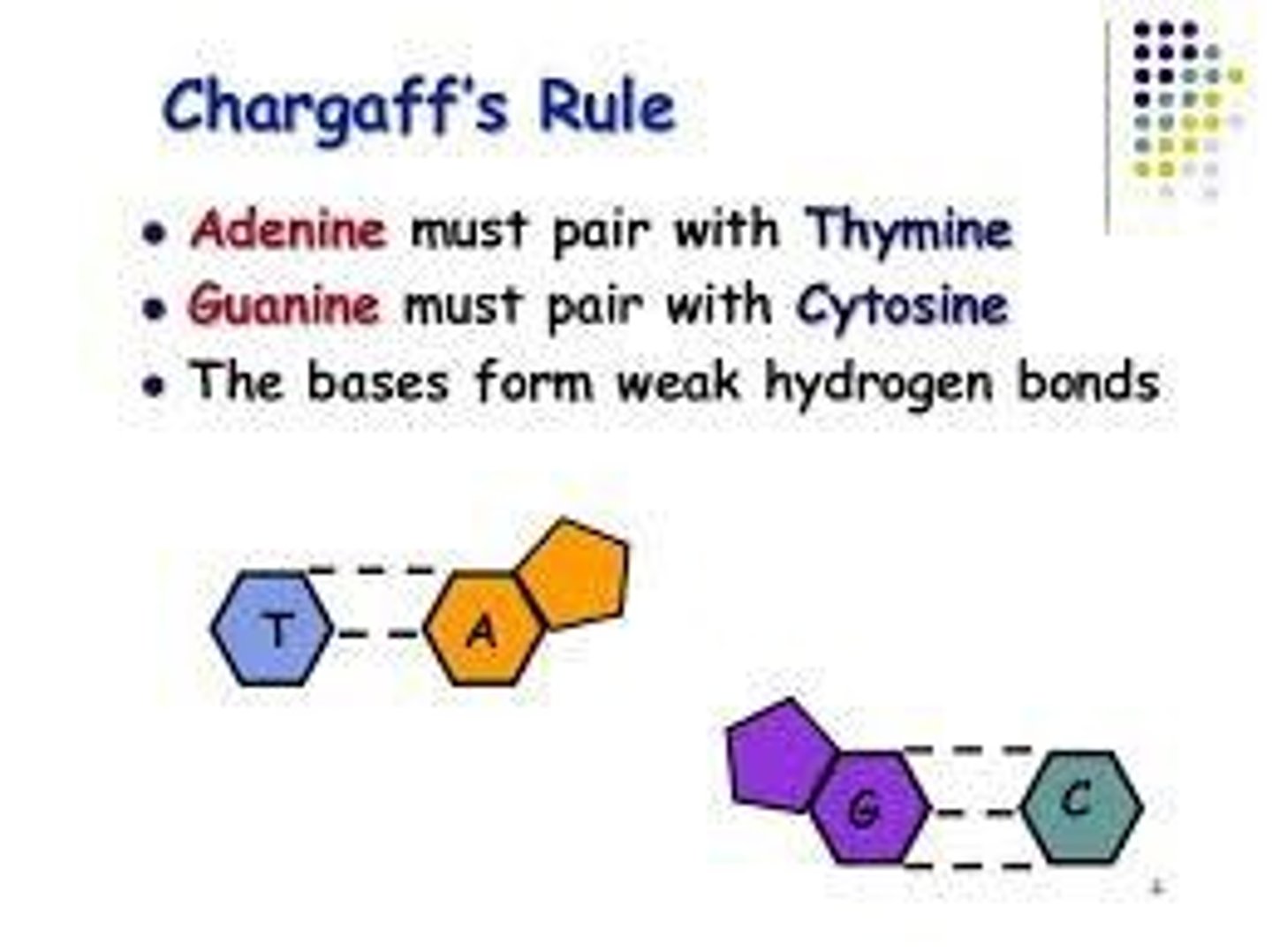
Hydrogen Bonds
Hold nitrogenous bases together in DNA.
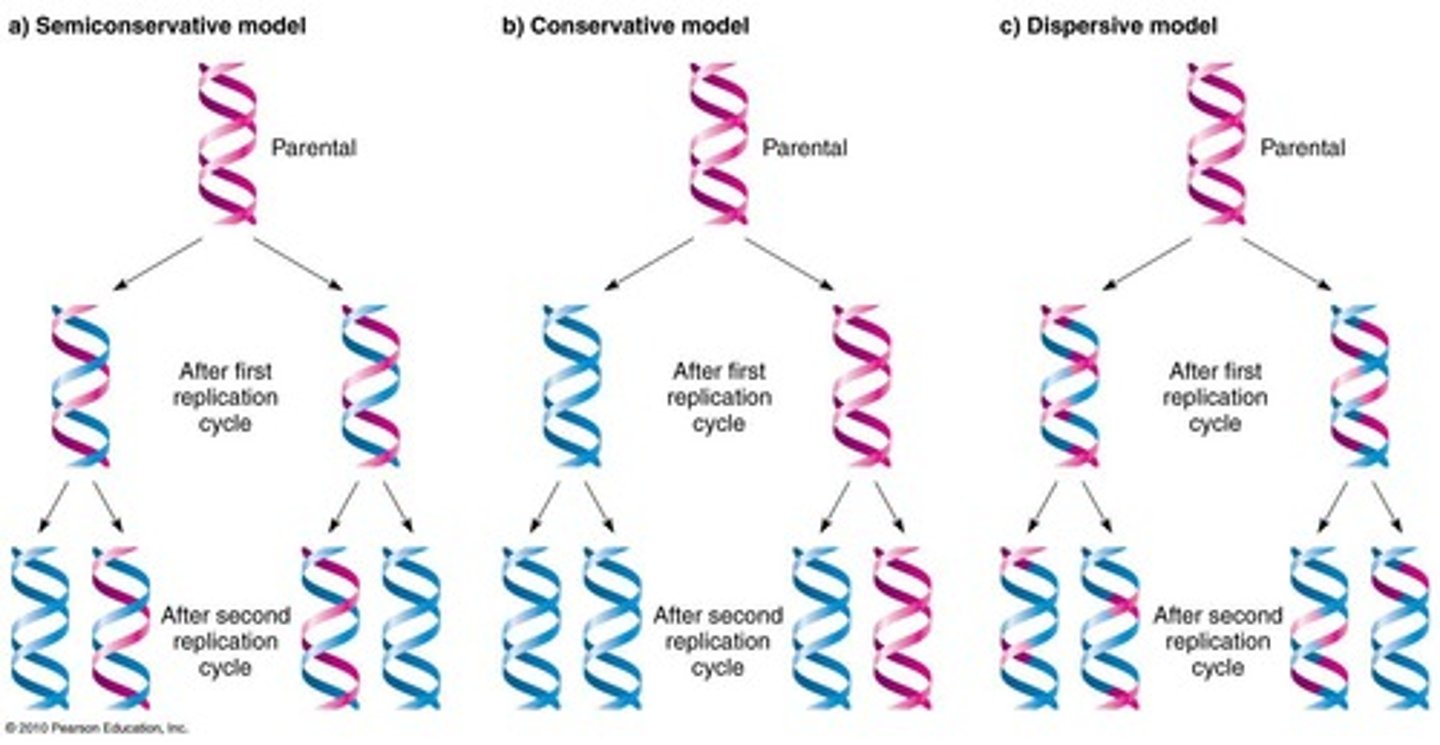
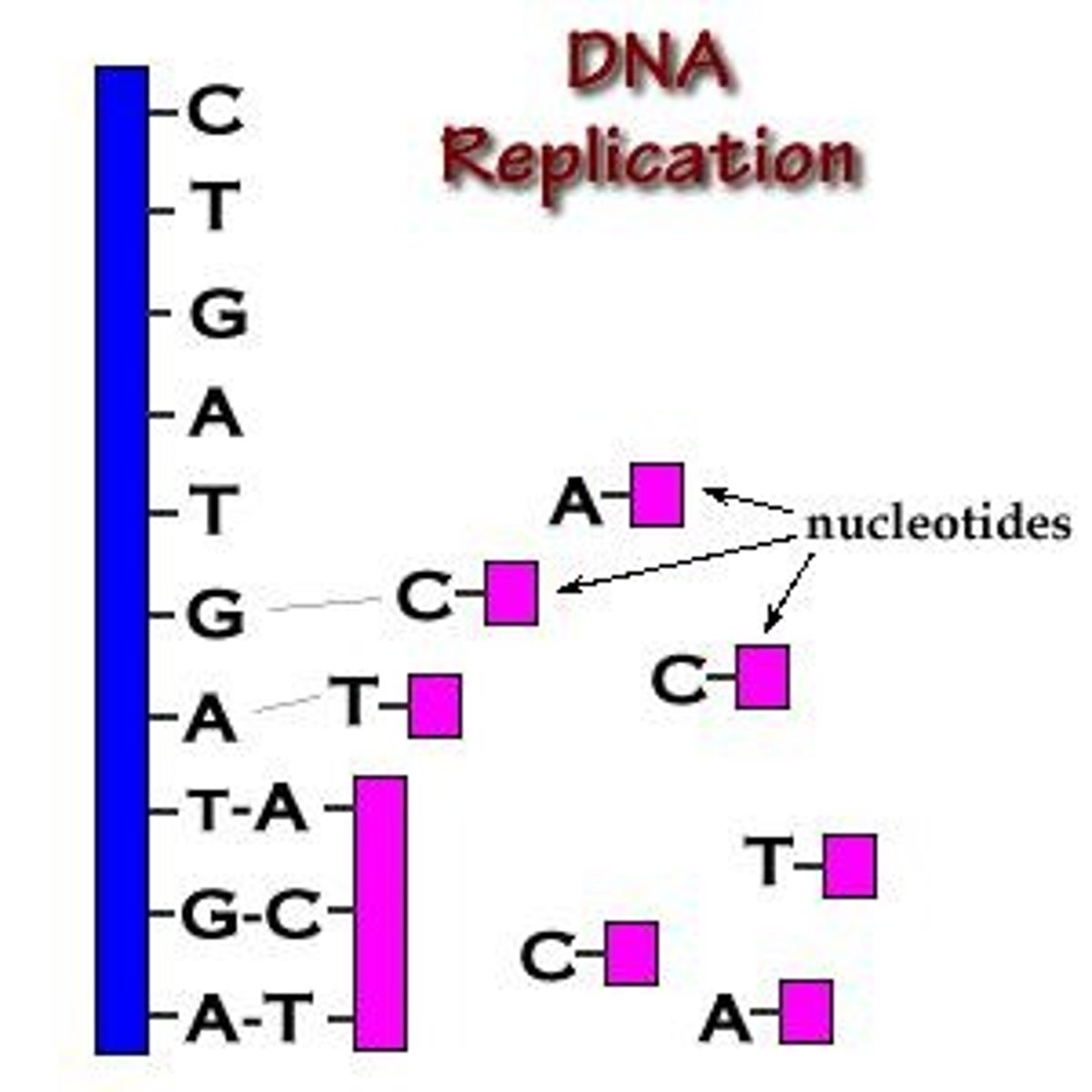
Semiconservative Replication
Each new DNA molecule retains one original strand.
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme synthesizing new DNA strands during replication.
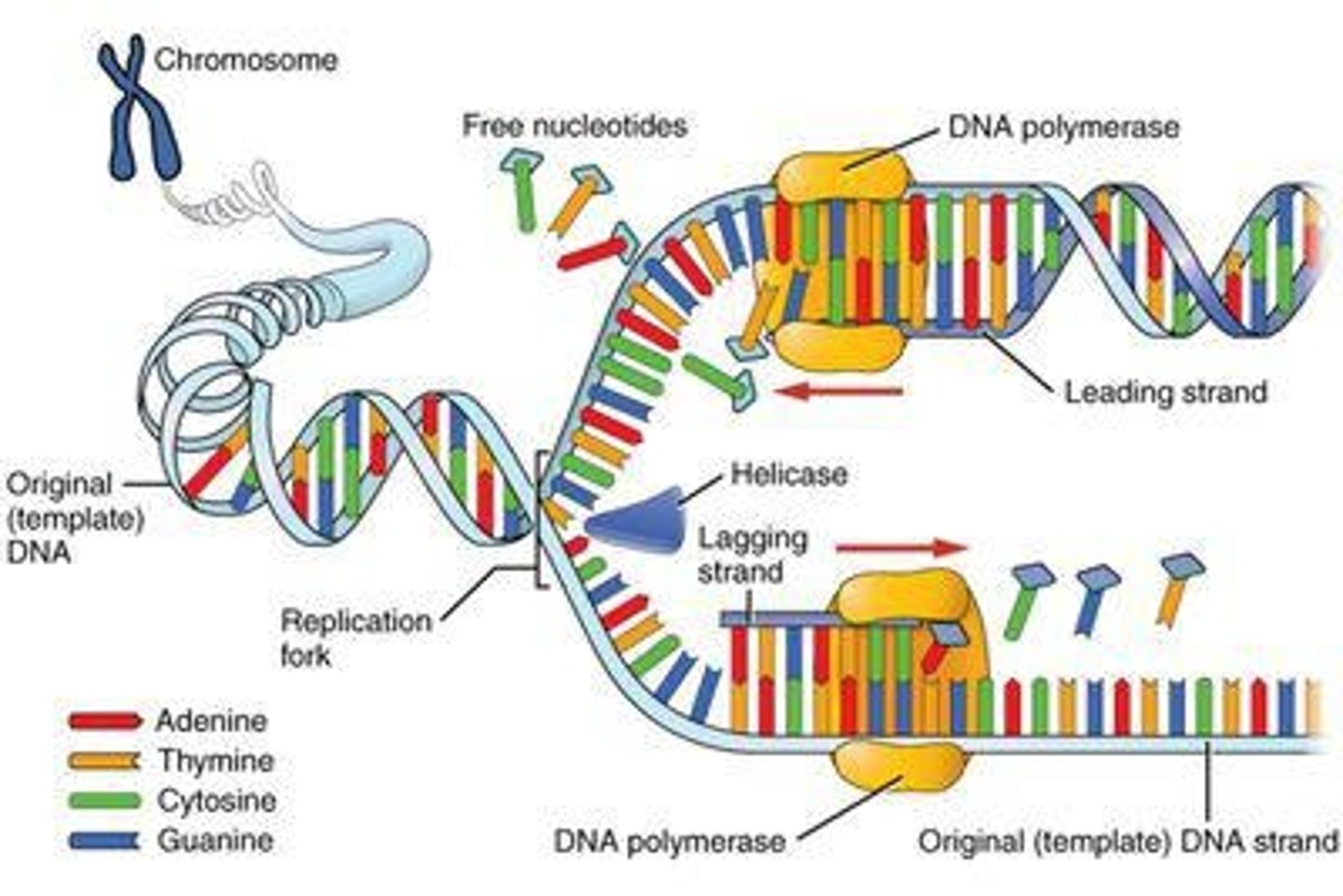
Transcription
Process of synthesizing RNA from DNA template.
Translation
Process of synthesizing proteins from mRNA.
mRNA
Messenger RNA; carries genetic information from DNA.
Gene
Segment of DNA coding for a specific protein.
Genome
Complete set of genetic material in an organism.
Protein Synthesis
Assembly of proteins from amino acids using mRNA.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid; involved in protein synthesis.
Amino Acid
Building blocks of proteins, coded by mRNA.
Codon
Three-nucleotide sequence on mRNA coding for an amino acid.
Traits
Physical characteristics determined by protein expression.
Erwin Chargaff
Scientist known for Chargaff's Rule on base pairing.
Rosalind Franklin
Produced X-ray images crucial for DNA structure discovery.
Francis Crick
Co-discoverer of DNA's double-helix structure.
James Watson
Co-discoverer of DNA's double-helix structure with Crick.
Maurice Wilkins
Contributed to understanding DNA structure through X-ray diffraction.
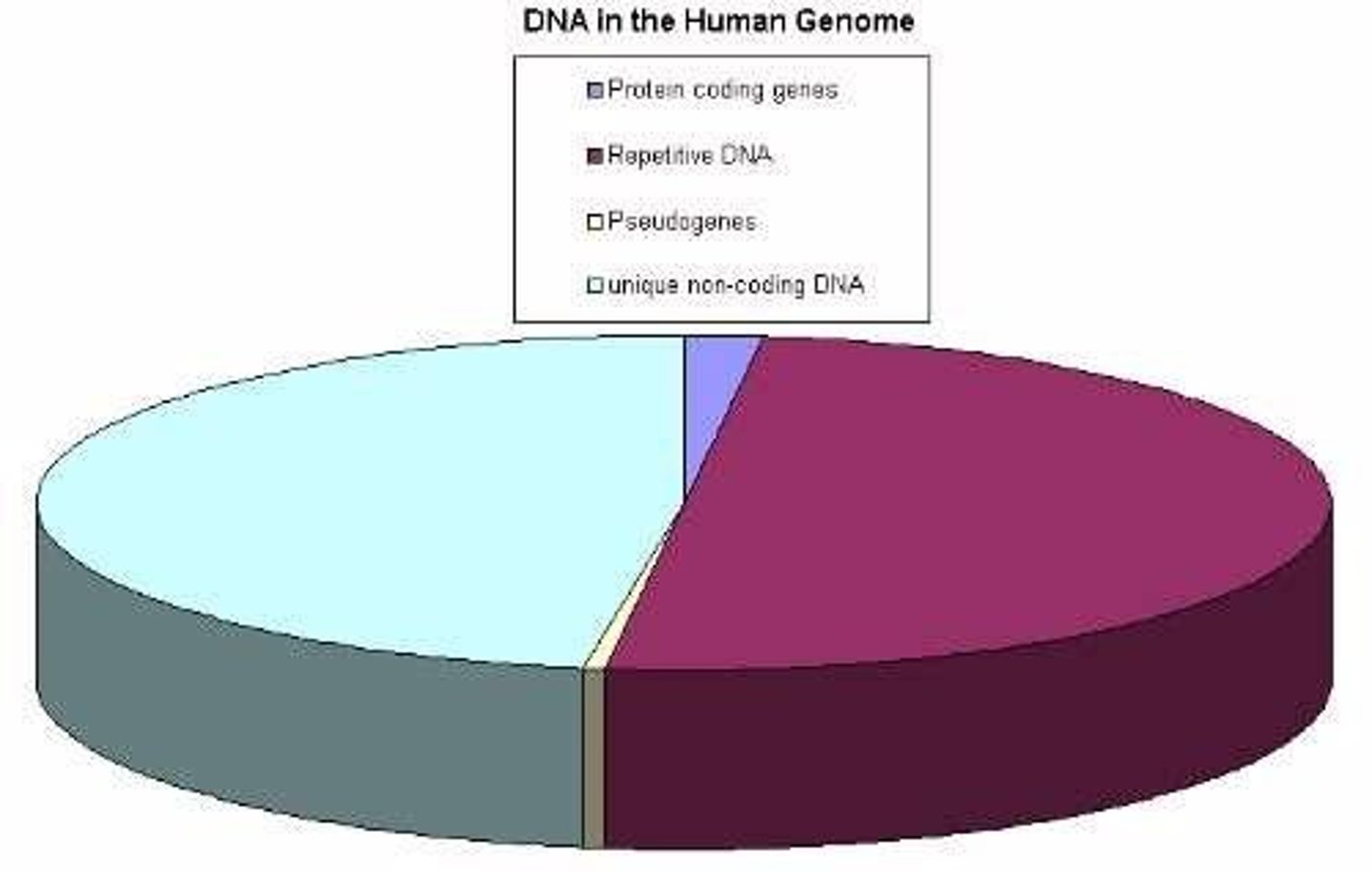
Non-coding DNA
98.5% of human genome; function still under investigation.
RNA Polymerase
Enzyme that synthesizes RNA during transcription.
Phenotype
Observable traits resulting from gene expression.