Teaching Strategies in Medical Laboratory Science
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Syllabus
A guideline for the instruction of a subject based on subject standards.
Course Outline
A blueprint for the implementation of a subject/course that covers the overview of a subject, specific contents, pedagogies, and assessment methods.
Course Outline/Syllabus
A contract between teachers and learners that includes the name of the course, a one-paragraph course description, a list of course objectives, a topical outline, teaching methods, methods of evaluation, textbooks and other readings, and the name of the instructor.
Value of Objectives
Guide the selection and handling of course materials and help determine whether students have learned what the teacher intended to teach.
Educational Objectives
Used to identify the intended outcomes of the education process that guide the design of curriculum units.
Instructional Objectives
Describe the teaching activities, specific content areas, and resources used to facilitate effective instruction.
Behavioral Objectives
Also referred to as learning objectives, these are action-oriented, learner-centered, and focused on short-term outcomes.
Characteristics of Objectives
Good objectives must be SMART.
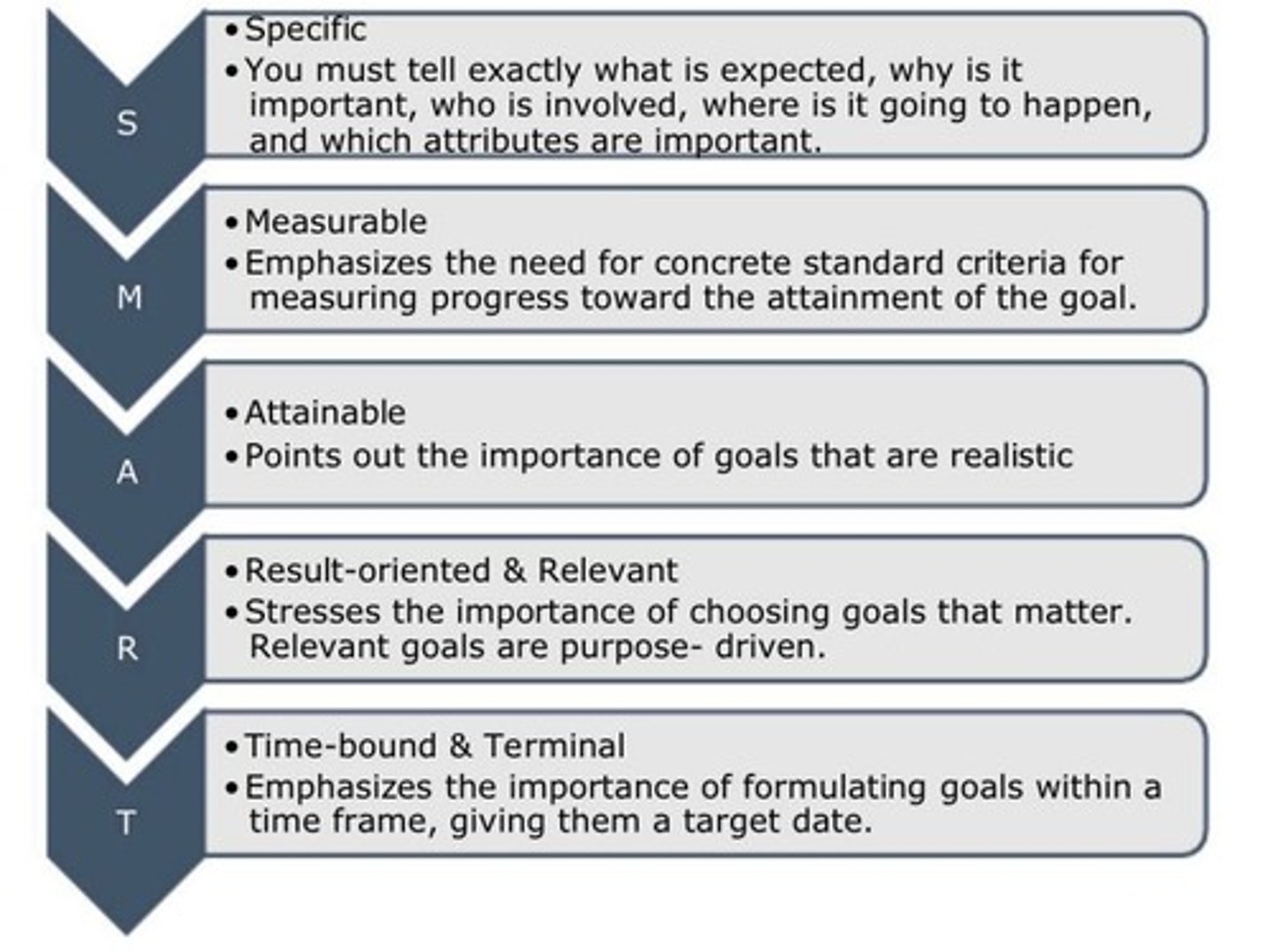
SMART Objectives
Objectives that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Factors Affecting Choice of Method
Selection of method depends on the objectives and type of learning, course content, and compatibility between teachers and teaching methods.
Types of Objectives
Includes educational objectives, instructional objectives, and behavioral objectives.
Assessment Methods
Various methods for assessing student performance in relation to course objectives.
Course Description
A one-paragraph summary of what the course covers.
Topical Outline
A structured list of topics covered in the course.
Teaching Methods
The strategies employed by instructors to facilitate learning.
Methods of Evaluation
The techniques used to assess students' understanding and performance.
Textbooks and Readings
The materials required for the course.
Instructor's Name
The name of the person teaching the course.
Cognitive Objectives
Objectives that focus on knowledge and mental skills.
Affective Objectives
Objectives that focus on attitudes and values.
Psychomotor Objectives
Objectives that focus on physical skills and actions.
Course Materials
Resources selected based on the course objectives.
Learning Outcomes
The specific skills or knowledge that students are expected to acquire by the end of the course.
STRATEGY
is a specific plan of action, a tactic or a scheme which the teacher devises to achieve goals and learning objectives.
INSTRUCTIONAL OR TEACHING STRATEGY
is the overall plan for a learning experience which makes use of one or more methods of teaching and includes content and process to achieve the desired outcomes.
INSTRUCTIONAL METHODS
are techniques and approaches used by the teacher to make the learner understand the content to be learned.
Examples of Instructional Methods
1. Lecture, group discussion, one-to-one instruction 2. Demonstration and return demo 3. Gaming and simulation 4. Role-playing and role modeling 5. Self-instruction modules 6. Computer-assisted instruction 7. Distance-learning techniques.
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS
means by which information is shared with the learner.
Examples of Instructional Materials
Books, Videos, Posters.
Device
is a teaching aid or tool, a visual aid or instructional aid.
Examples of Devices
1. PPT presentation 2. Video - cds 3. Flashcards 4. Pictures, objects 5. Chalk/whiteboard 6. OHP 7. Slides 8. Films, tapes.
TIME ALLOTMENT
Determining time allotment is one of the seven steps in curriculum design.
Allocated time
is the amount of time specified for an activity or events.
Factors that Determine Time Allotment
1. Importance of the Subject 2. Child's Ability 3. Grade Level 4. Average Number of Days.
Importance of the Subject
Address the learners needs and interest; Determine the time amount to be spent on each subject.
Child's Ability
Learner is willing to engage actively in learning; Time allotment must agree with the child's readiness for the learning material/experience.
Grade Level
Increasing attention-span of the learners upon their maturity, age, and development.
Average Number of Days
Determine the total available time; Consider the public holidays, and special school occasions.
ASSESSMENT
Measurement and the evaluation of your students.
Test
a specific form of measurement.
Measurement
involves systematic quantification of data; systematic in that it is collected in an organized manner according to 'rules'.
Evaluation
places a judgment on the collection of data.
Assessment
the integration of both quantitative and qualitative data collected to provide information on the nature of the learner, what is learned, and how it is learned.
Assessment Formula
Assessment = Measurement + Evaluation.
Formative Assessment
Pinpoints whether students have achieved the objective of the lesson taught.
Summative Assessment
Considered as terminal assessment of learning, the main purpose of this is to give rating or grades to students based on their performance or achievement.
Performance Assessment
Undertaken to determine whether students can demonstrate their learning through performance in real or simulated situations.
Test Blueprint
Development involves listing content to be taught/tested, estimating amount of instructional time, determining the level of understanding expected, and developing an ideal answer as items are written.
Normative Grading
Not being used in universities; Used in board exam.
Normal Curve Grading
A fixed percentage will get certain grades; not recommended.
Distribution Gap Method
Rank order composite scores, where gaps occur, make grade cuts; not recommended.
Competency-Based Grading
Uses some absolute standard set a priori; used in universities.
Fixed Percentage Grading
A fixed percentage set a priori for grading.
Content-based Method
Gives grade to each component, multiplies each component by weight, then produces final grade.
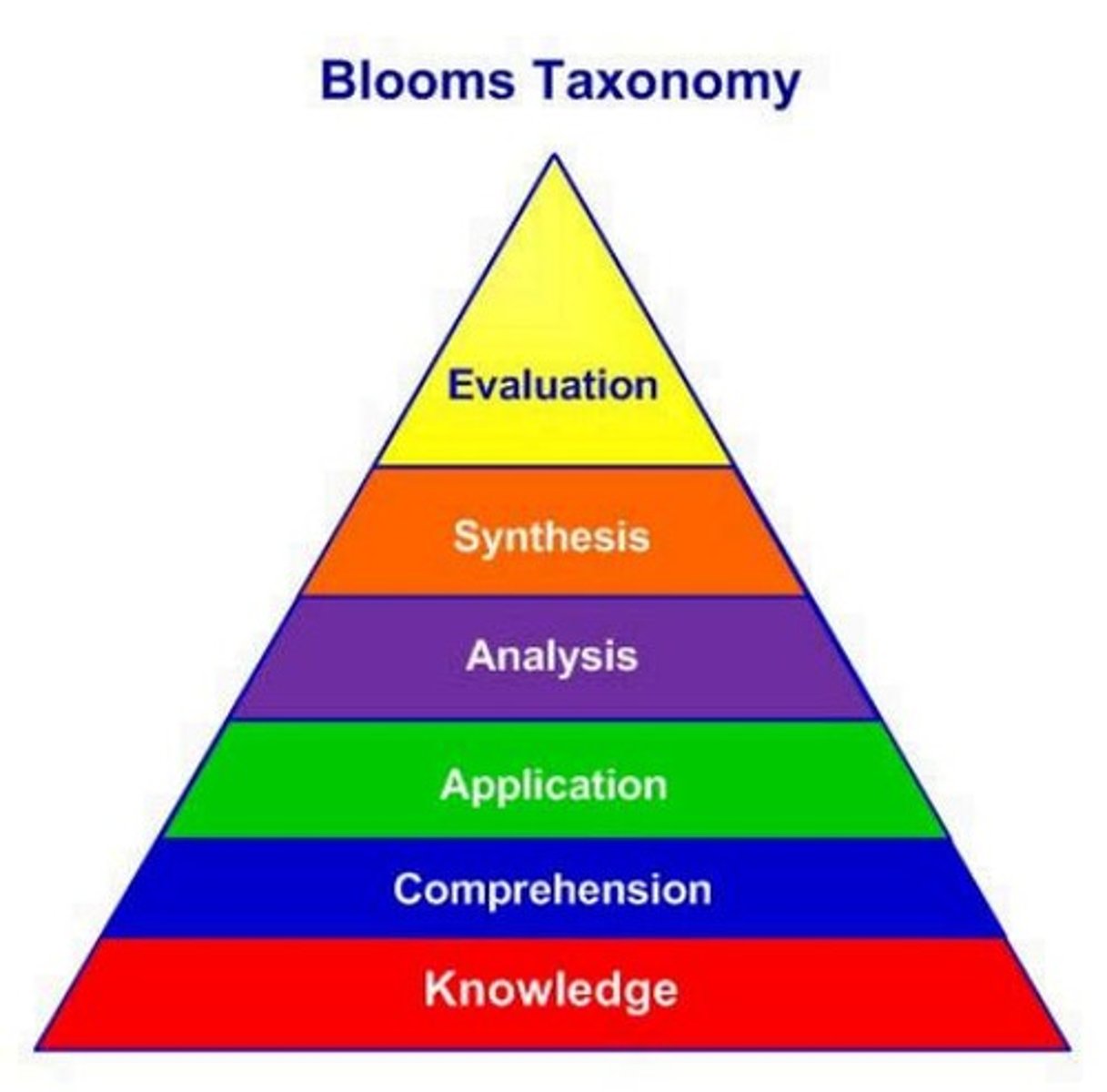
Bloom's Taxonomy
Developed by Benjamin Bloom, it recommends specific verbs to use when writing learning objectives so that the objectives can be measured.
Cognitive Domain
Involves knowing and thinking.
Psychomotor Domain
Involves doing.
Affective Domain
Involves feeling and valuing.
Knowledge in Bloom's Taxonomy
More on recall, remembering basic knowledge.
Objectives of Assessment
To diagnose student strength and weaknesses, monitor student progress, assign grades, determine instructional effectiveness, influence public perceptions of educational effectiveness, evaluate teachers, and clarify instructional intentions.
Examples of Formative Assessment
Quiz, homework exercises, assignments.
Examples of Summative Assessment
Prelims, Midterm, Finals.
Examples of Performance Assessment
Group projects, written assessments, demonstrations, portfolios.
Levels of Cognitive Domain
Describes the levels of the cognitive domain in Bloom's Taxonomy.
Learning Objectives
Create specific learning objectives that align with each level of Bloom's Taxonomy.
Knowledge of terminology and conventions
Understanding of terms, trends, sequences, classifications, categories, criteria, methodologies, principles, theories, and structures.
Comprehension
Understanding; explain the idea/concepts, relates to translation, interpretation, and extrapolation.
Application
Used the information in a particular situation; use of abstractions in particular situations.
Bloom's Taxonomy
A classification of learning objectives within education, focusing on cognitive skills.
Analysis
Analysing; distinguish different aspects; comparing, relates to breaking a whole into parts.
Synthesis
Creating your own new ideas/point of view; putting parts together in a new form such as a unique communication, a plan of operation, and a set of abstract relations.
Evaluation
Justify your own point/decision; judging in terms of internal evidence or logical consistency with facts developed elsewhere.
Cognitive Domain
Known as the 'thinking' domain; involves acquiring information and developing the learner's intellectual abilities, mental capacities, understanding, and thinking processes.
Knowledge Level
Ability of the learner to memorize, recall, define, recognize, or identify specific information, such as facts, rules, principles, conditions, and terms, presented during instruction.
Comprehension Level
Ability of the learner to demonstrate an understanding of what is being communicated by recognizing it in a translated form, such as grasping an idea by defining it or summarizing it in his or her own words.
Application Level
Ability of the learner to use ideas, principles, abstractions, or theories in specific situations, such as figuring, writing, reading, or handling equipment.
Analysis Level
Ability of the learner to recognize and structure information by breaking it down into its separate parts and specifying the relationship between the parts.
Synthesis Level
Ability of the learner to put together parts into a unified whole by creating a unique product that is written, oral, or in picture form.
Evaluation Level
Ability of the learner to judge the value of something by applying appropriate criteria.
Psychomotor/Skills Domain
Known as the 'skills' domain; involves acquiring fine and gross motor abilities such as walking, handwriting, manipulating equipment, or performing a procedure.
Perception Level
The initial level of the psychomotor domain, focusing on the awareness of stimuli.
Set Level
The readiness to act, involving mental, physical, and emotional sets.
Guided Response Level
The early stages of learning a complex skill, where learners are guided in their responses.
Mechanism Level
The intermediate stage in learning a skill where the learner can perform the skill with some degree of proficiency.
Complex Overt Response Level
The ability to perform a skill with a high degree of proficiency and efficiency.
Adaptation Level
The ability to modify and adapt learned skills to fit new situations.
Perception Level
Ability of the learner to show sensory awareness of objects or cues associated with some task to be performed.
Set Level
Ability of the learner to exhibit readiness to take a certain kind of action as evidenced by expressions of willingness, sensory attending, or body language favorable to performing a motor act.
Guided Response Level
Ability of the learner to exert effort via overt actions under the guidance of an instructor to imitate an observed behavior with conscious awareness of effort.
Mechanism Level
Ability of the learner to repeatedly perform steps of a desired skill with a certain degree of confidence, indicating mastery to the extent that some or all aspects of the process become habitual.
Complex Overt Response Level
Ability of the learner to automatically perform a complex motor act with independence and a high degree of skill, without hesitation and with minimum expenditure of time and energy.
Adaptation Level
Ability of the learner to modify or adapt a motor process to suit the individual or various situations, indicating mastery of highly developed movements that can be suited to a variety of conditions.
Origination Level
Ability of the learner to create new motor acts, such as novel ways of manipulating objects or materials, as a result of an understanding of a skill and a developed ability to perform skills.
Affective Domain
The affective domain is known as the 'feeling' domain. Learning in this domain involves an increasing internalization or commitment to feelings expressed as emotions, interests, beliefs, attitudes, values, and appreciations.
Receiving Level
Ability of the learner to show awareness of an idea, fact, or consciousness of a situation or event in the environment.
Responding Level
Ability of the learner to respond to an experience, at first obediently and later willingly and with satisfaction.
Valuing Level
Ability of the learner to regard or accept the worth of a theory, idea, or event, demonstrating sufficient commitment or preference to an experience that is perceived as having value.
Organizational Level
The ability of the learner to organize, classify, and prioritize values by integrating a new value into a general set of values.
Characterization Level
Ability of the learner to display adherence to a total philosophy or worldview, showing a firm commitment to the values by generalizing certain experiences into a value system.