Neuro 102 week 1 lab
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Dorsal/ Superior
Top of the Brain
Ventral/inferior
The bottom of the brain
Lateral
Towards the side
Medial
Towards the middle
meninges
protective coverings,
which enclose the brain
and spinal cord
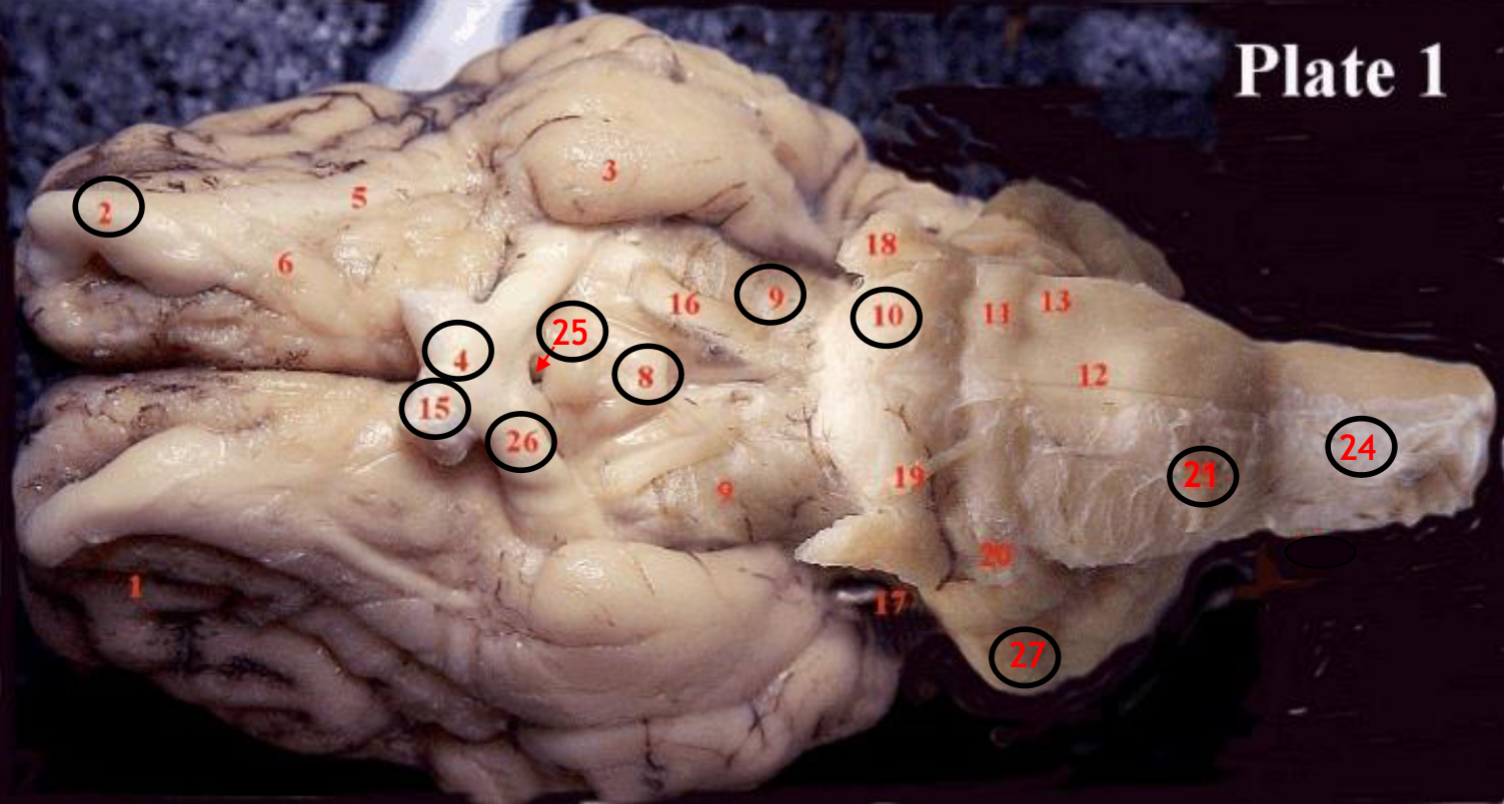
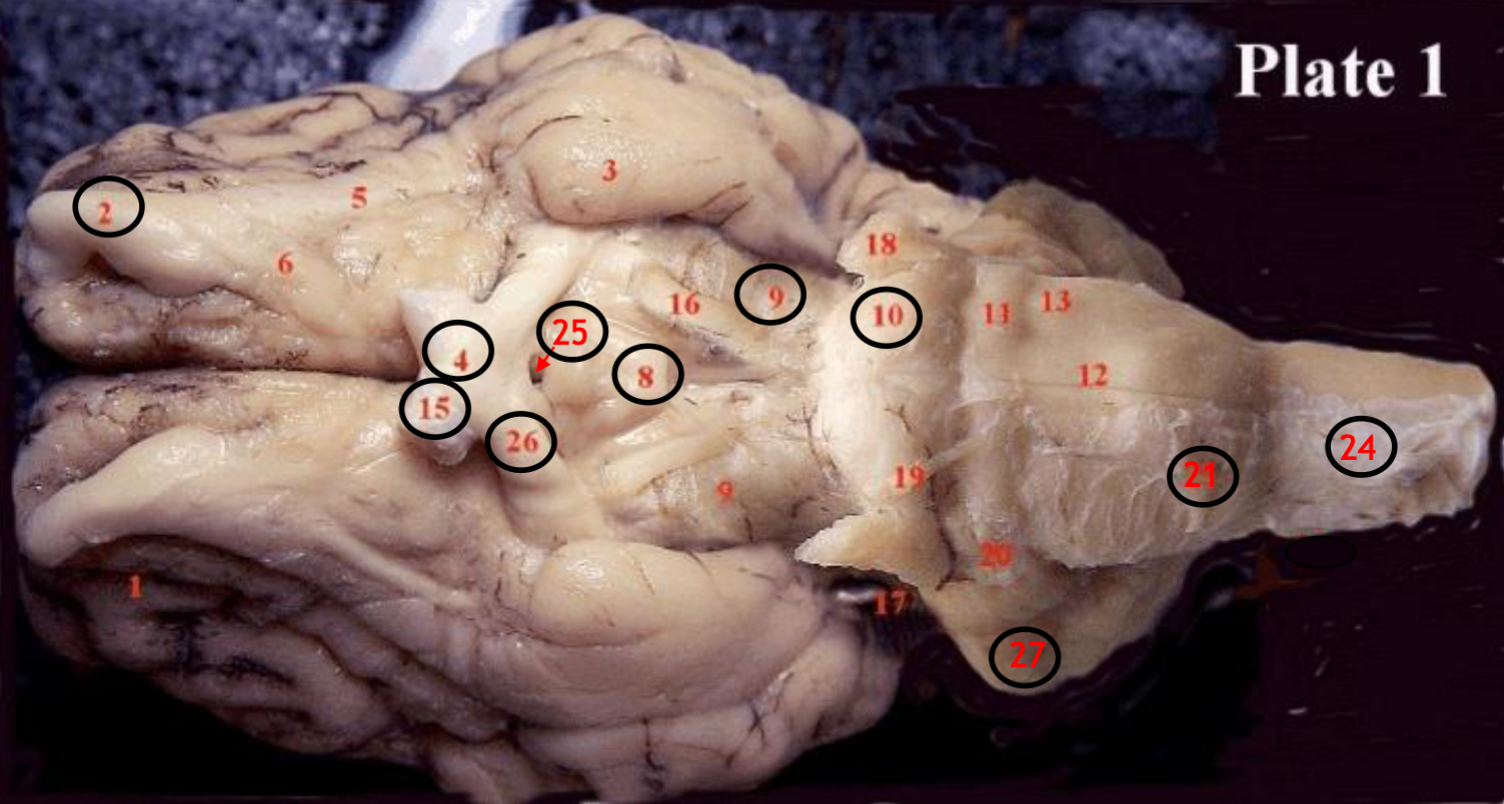
#2
olfactory bulb
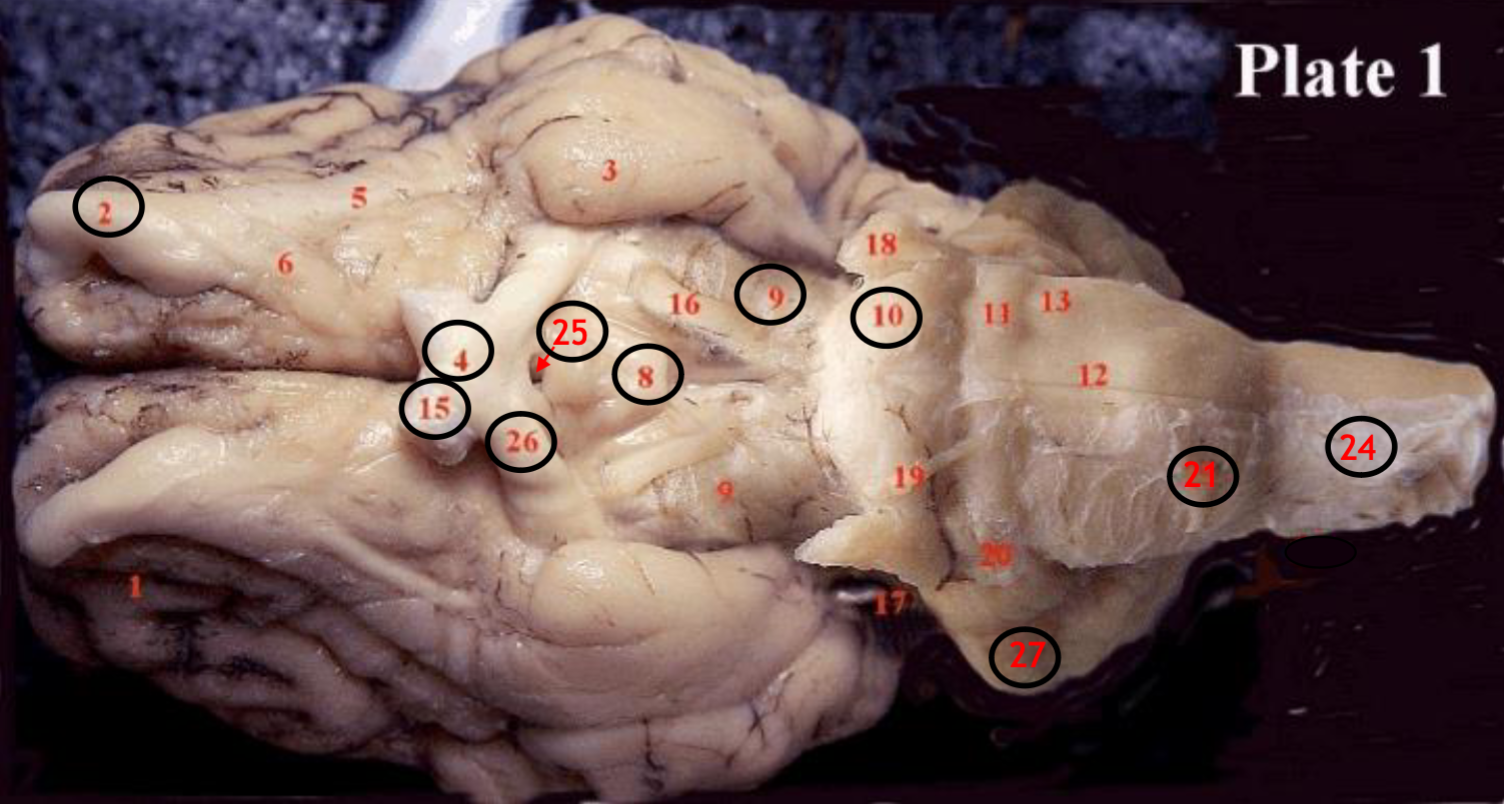
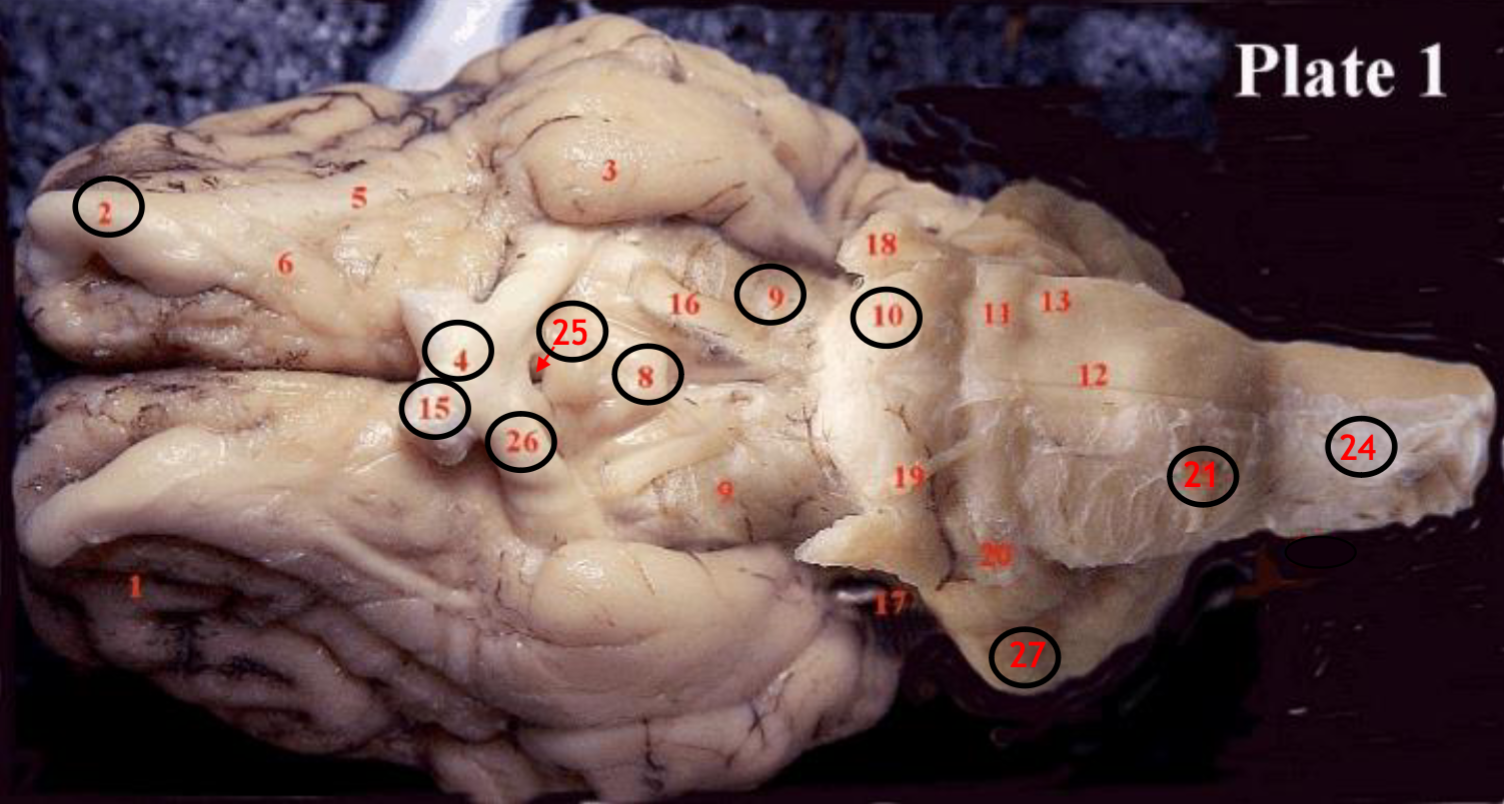
#4
optic chiasm
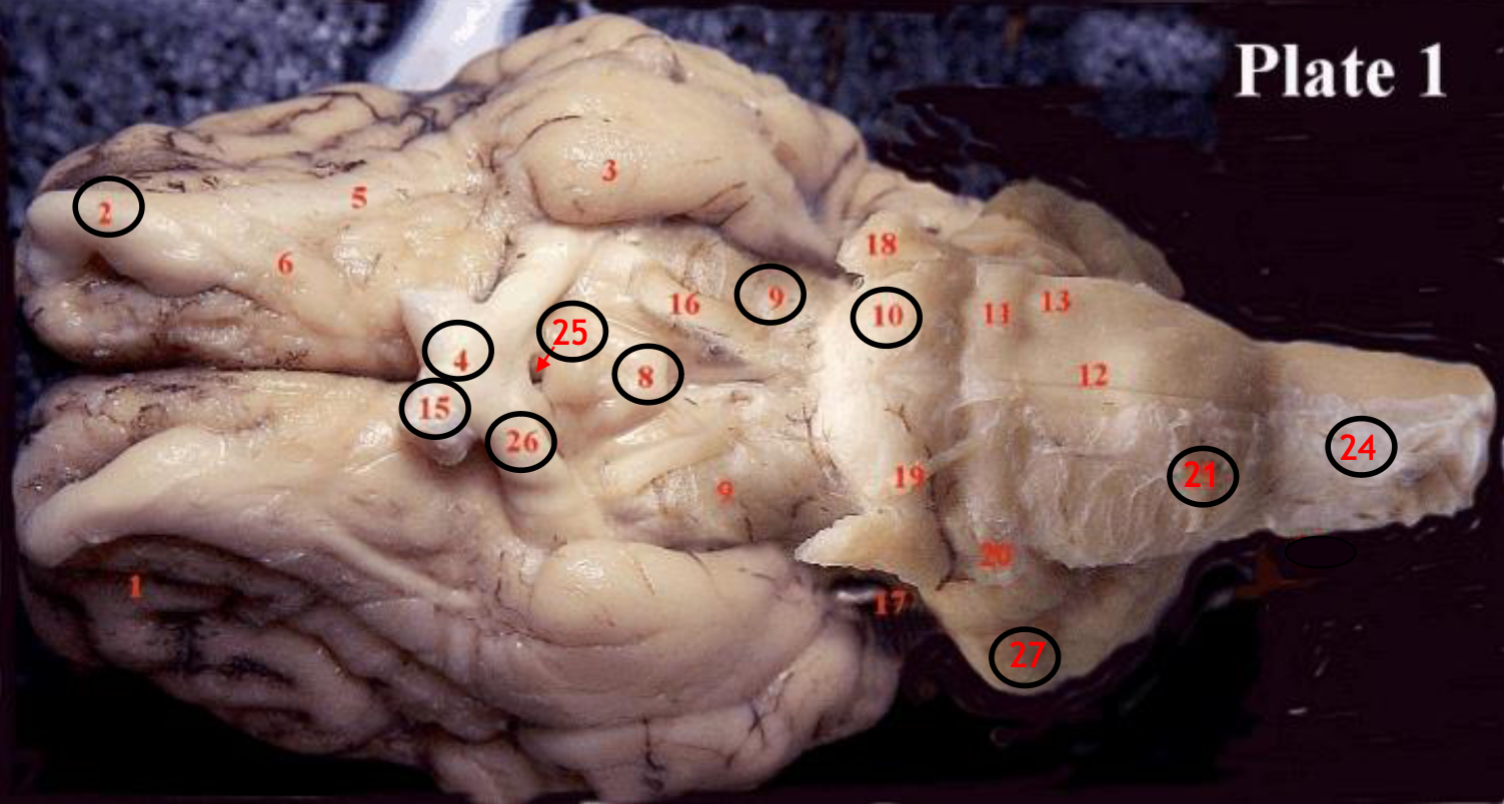
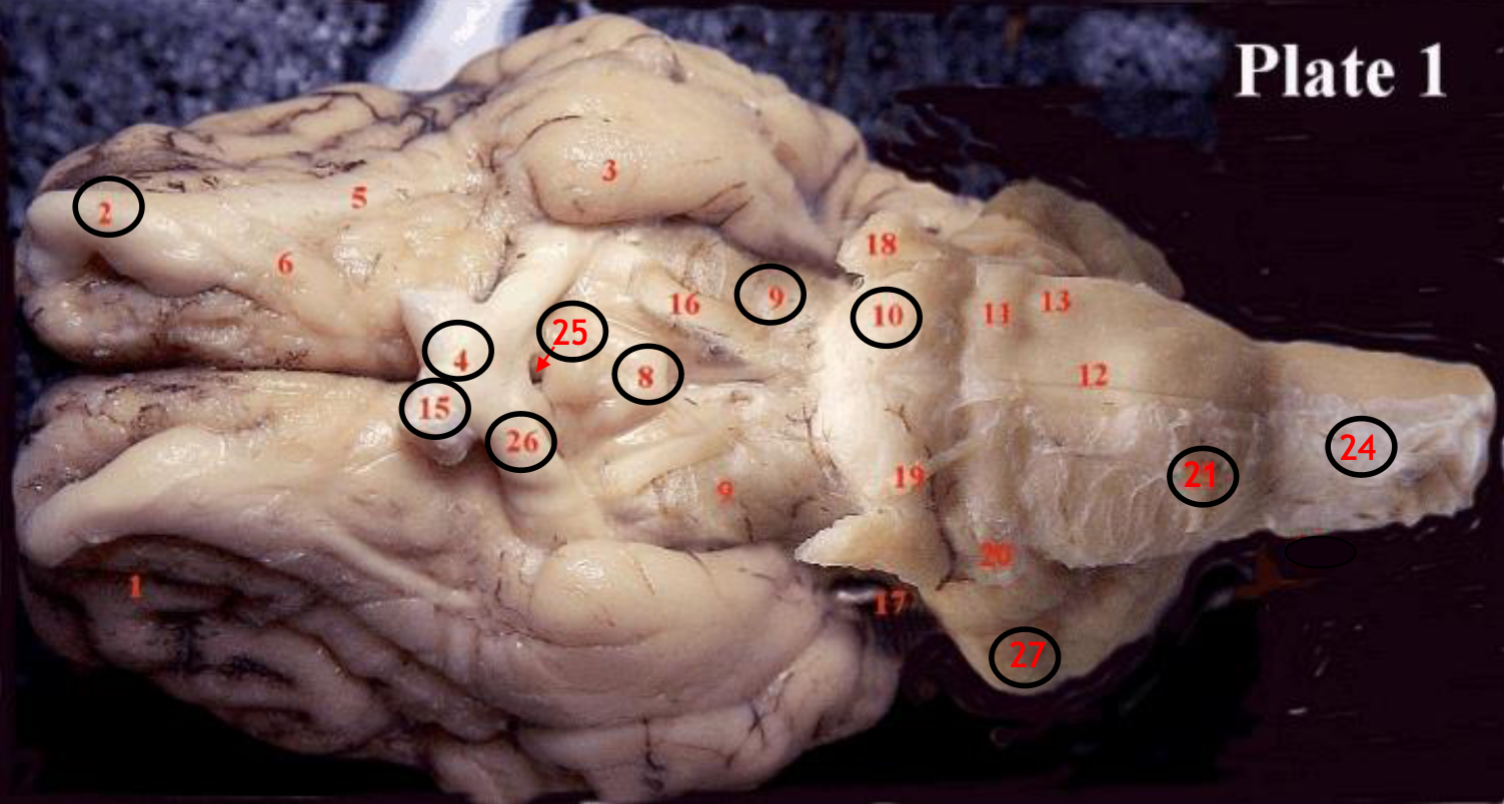
#8
mammillary body
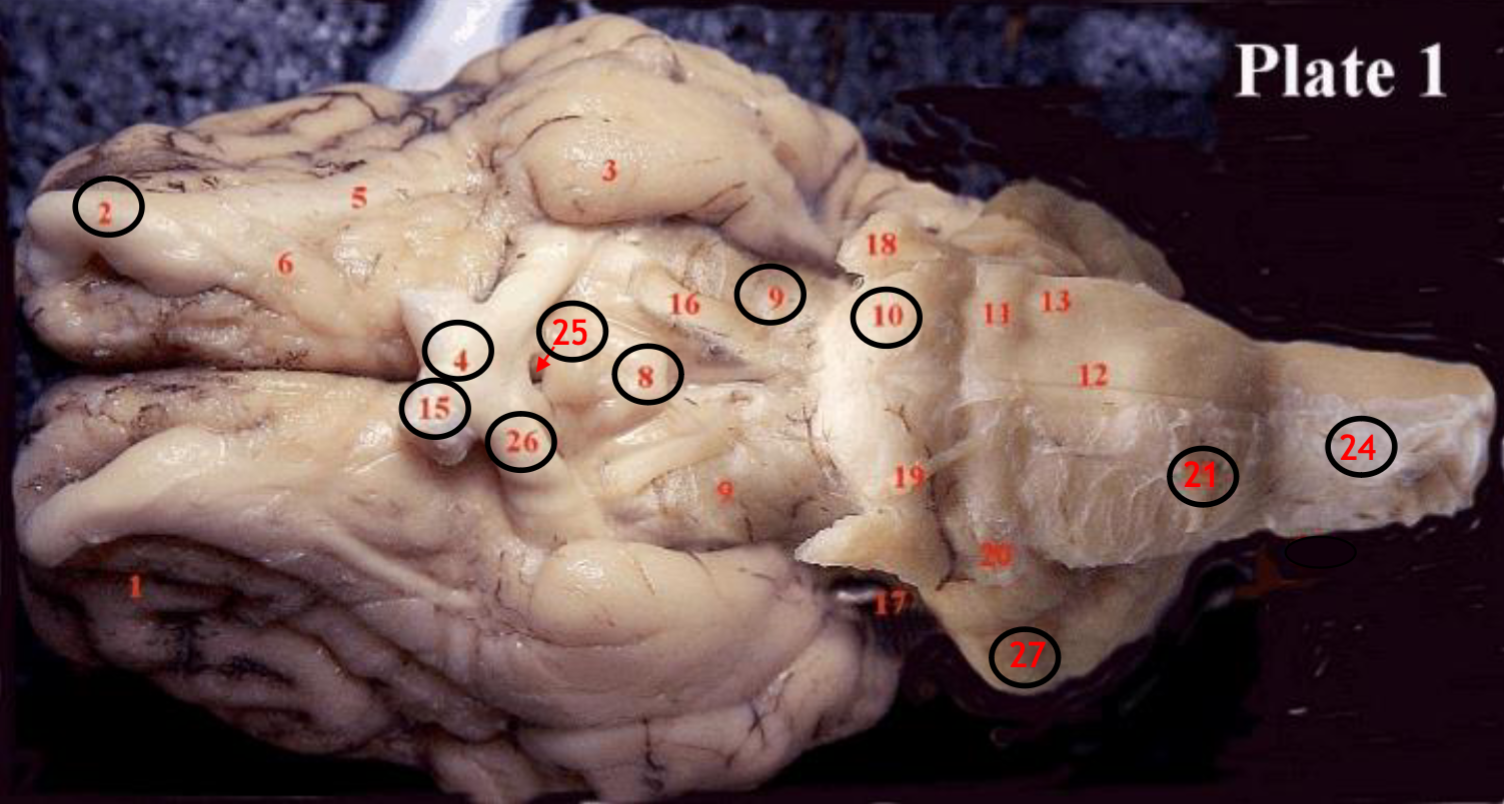
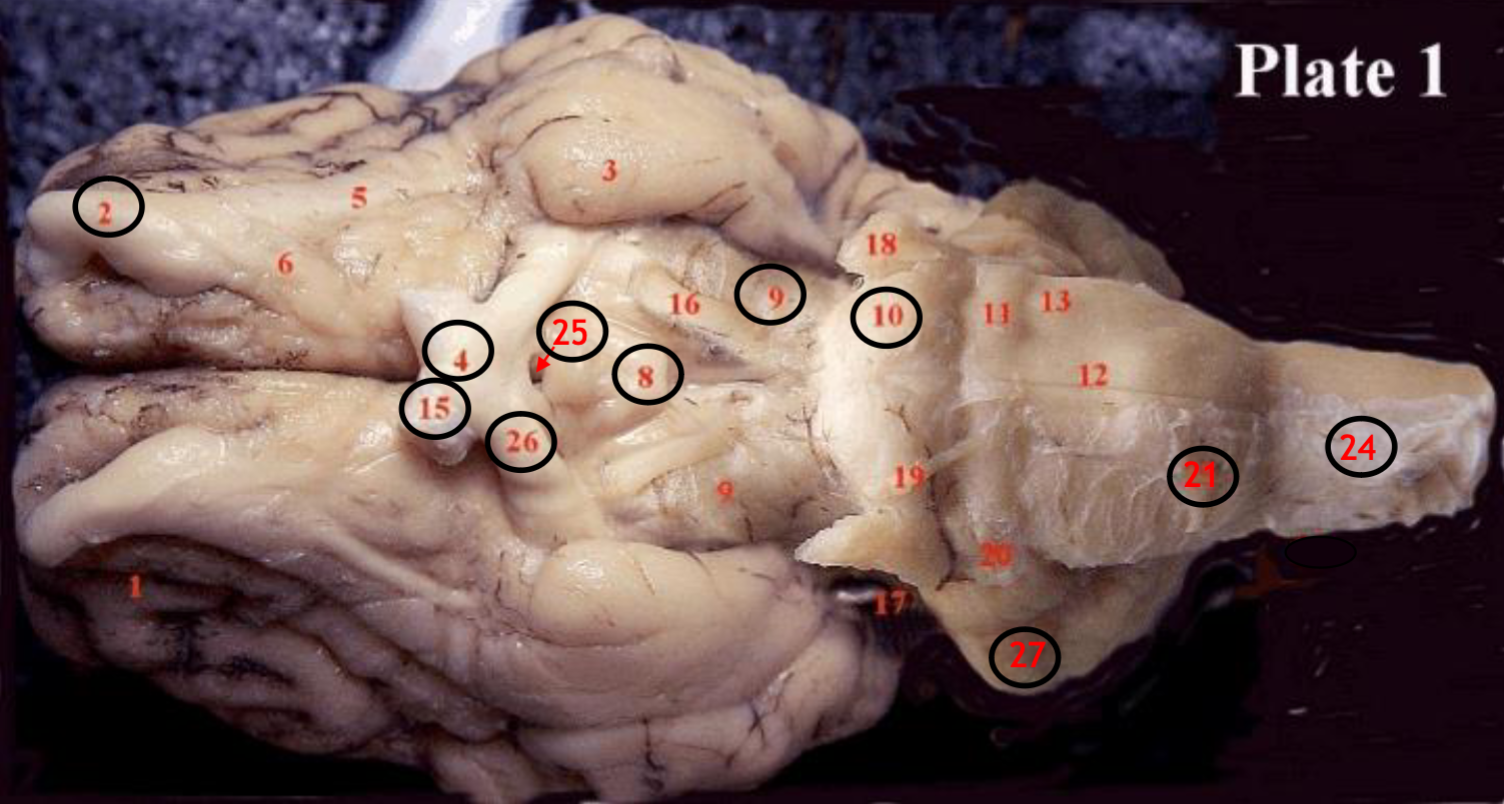
#9
Midbrain

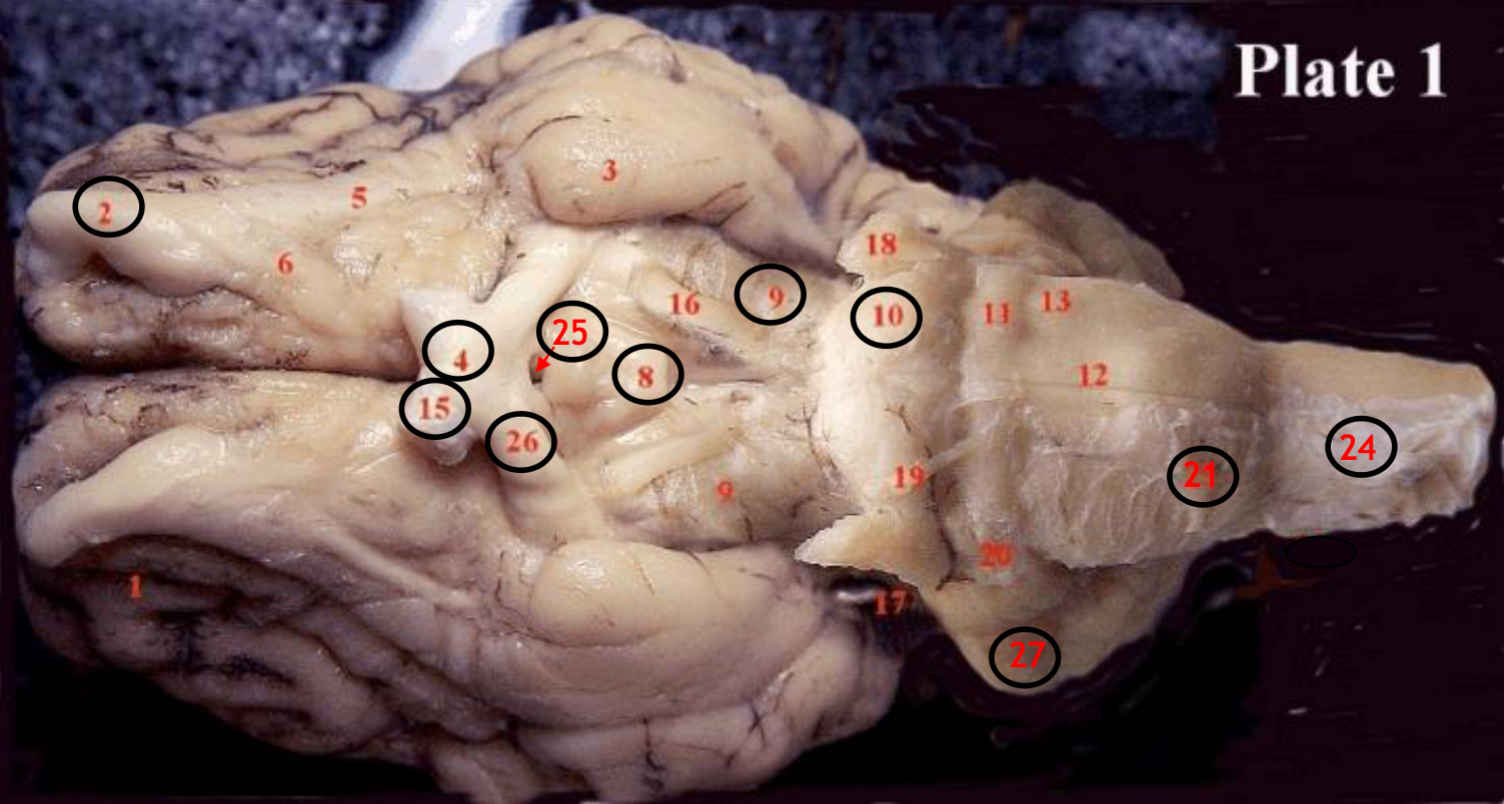
#10
Pons
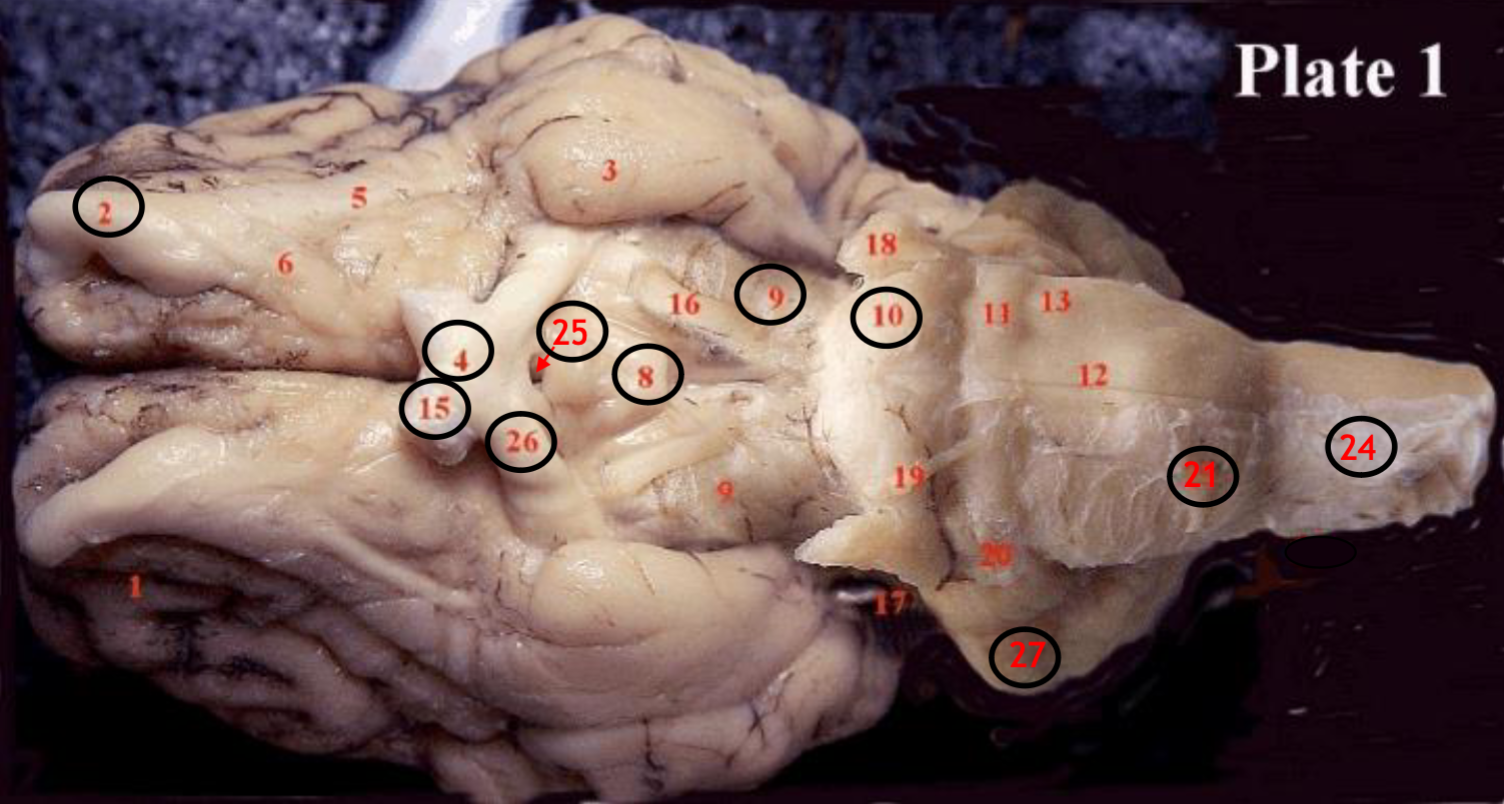
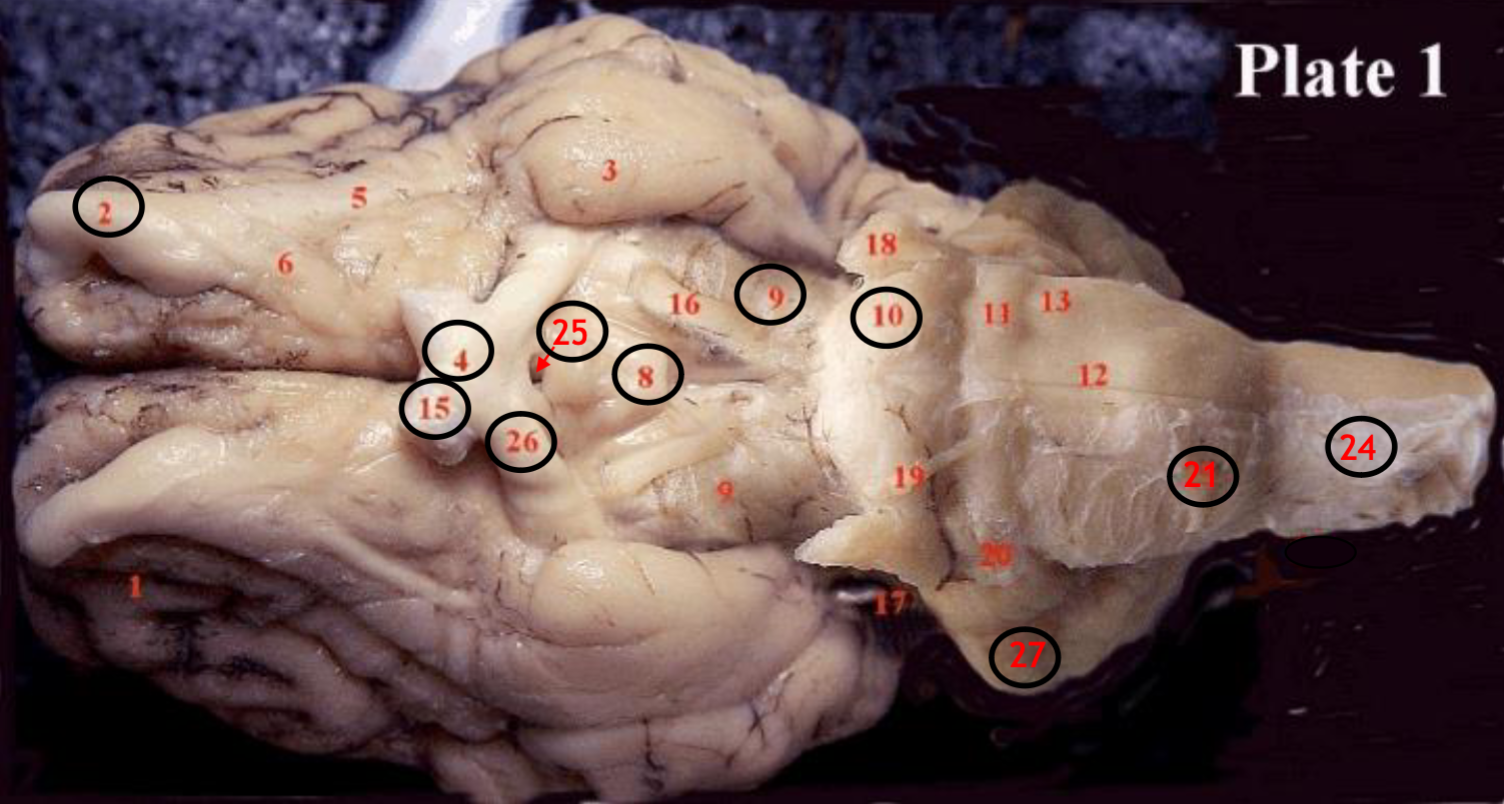
#15
optic nerve
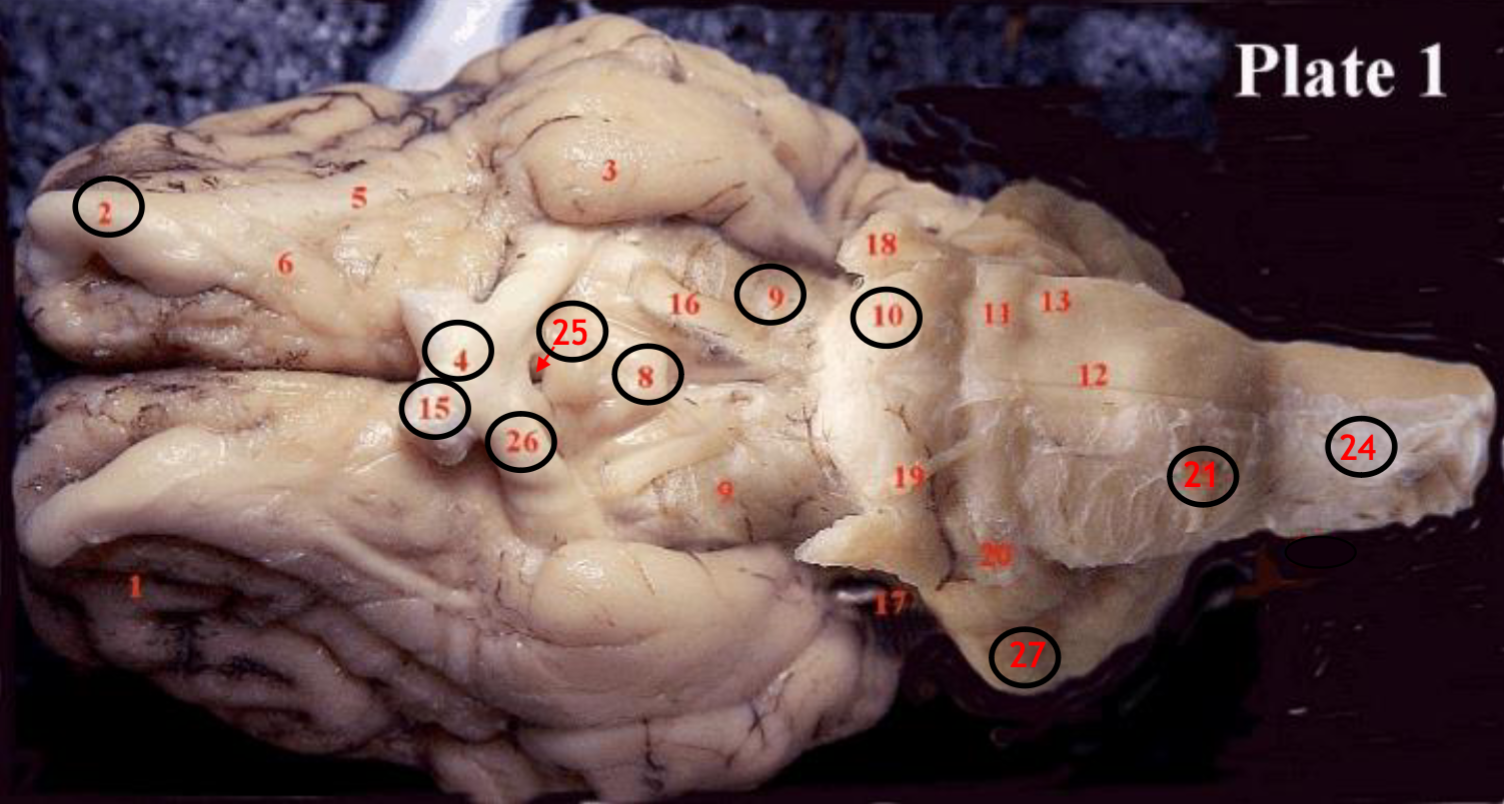
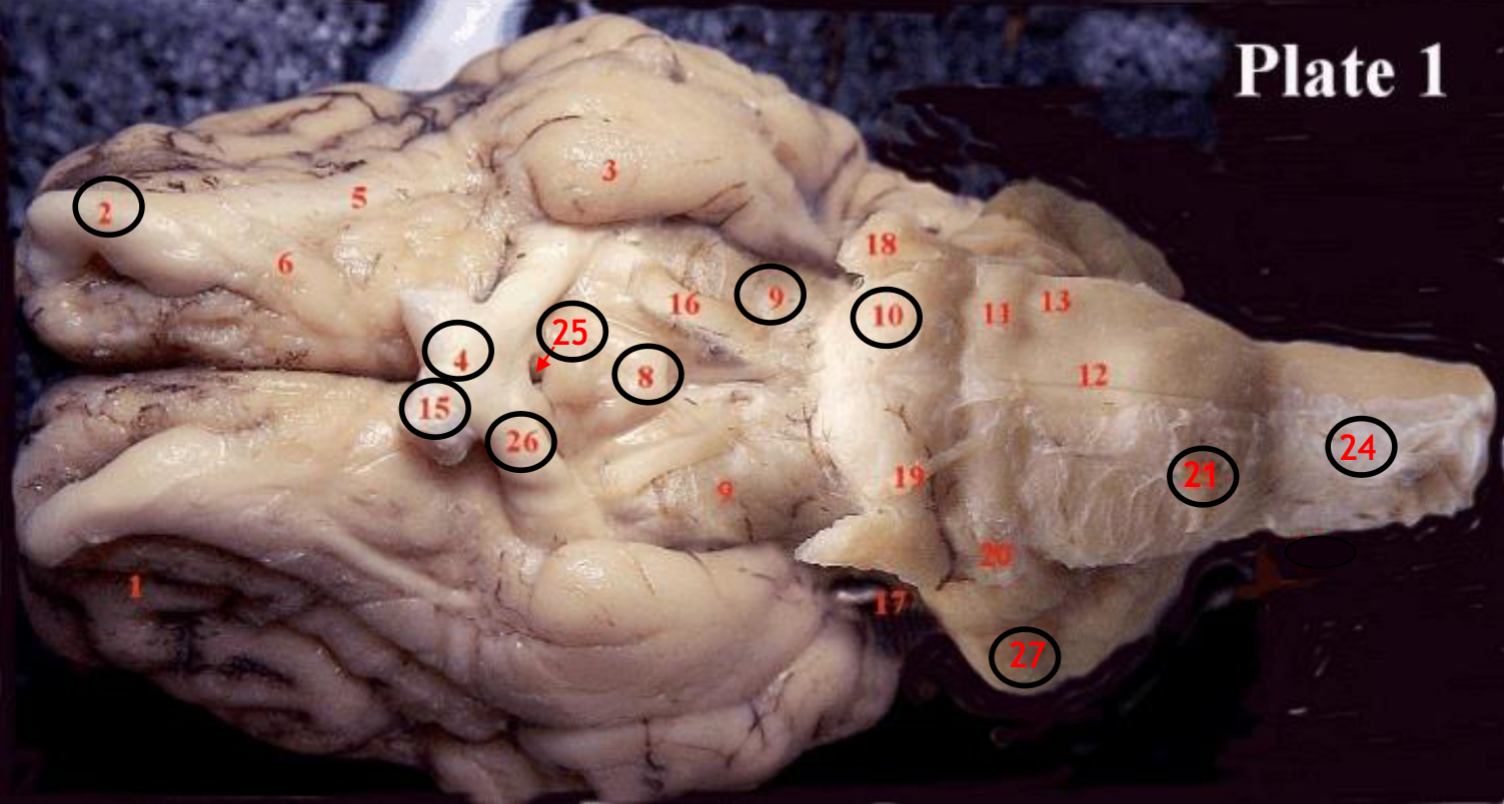
#25
Infundibulum
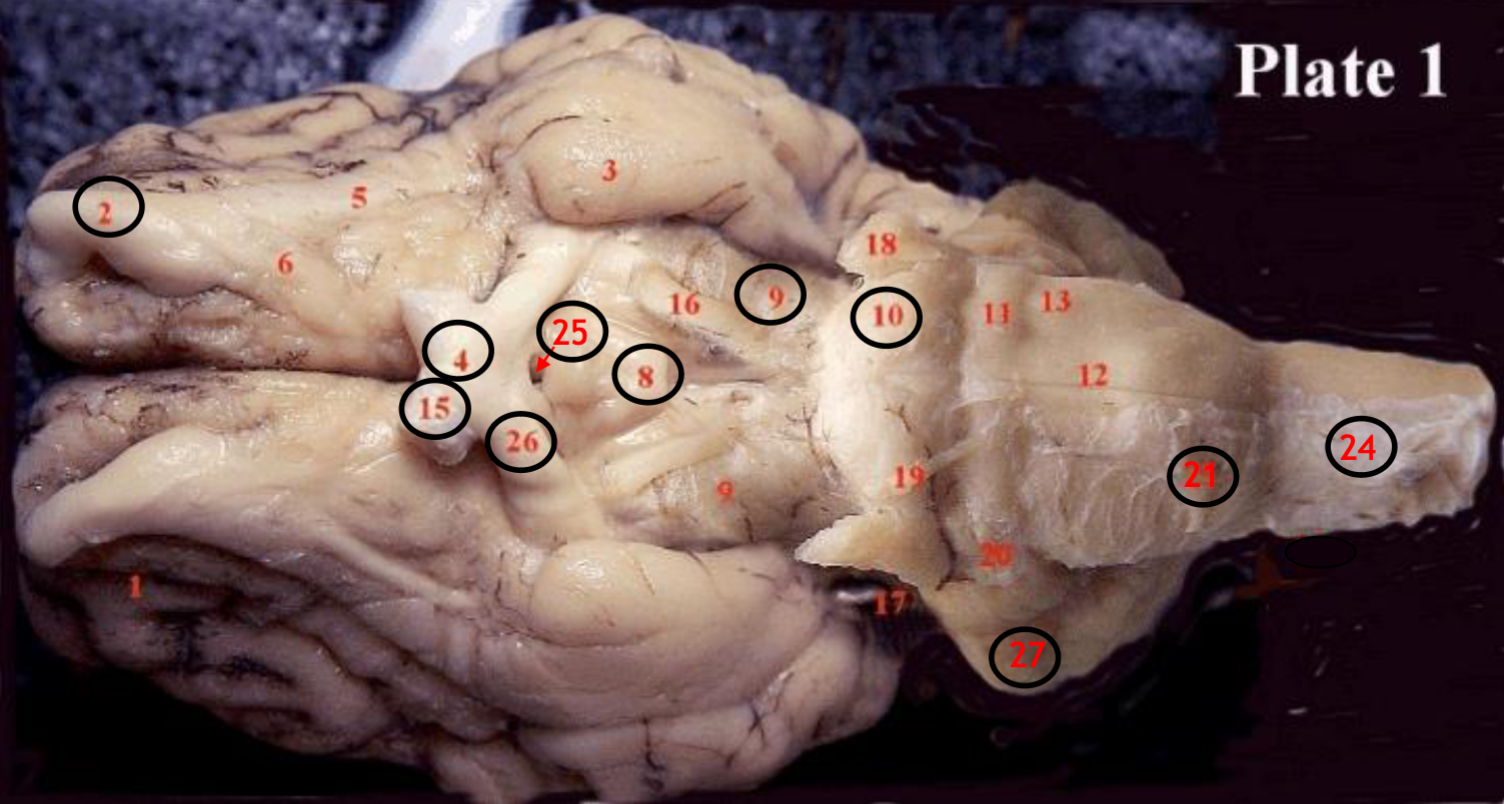
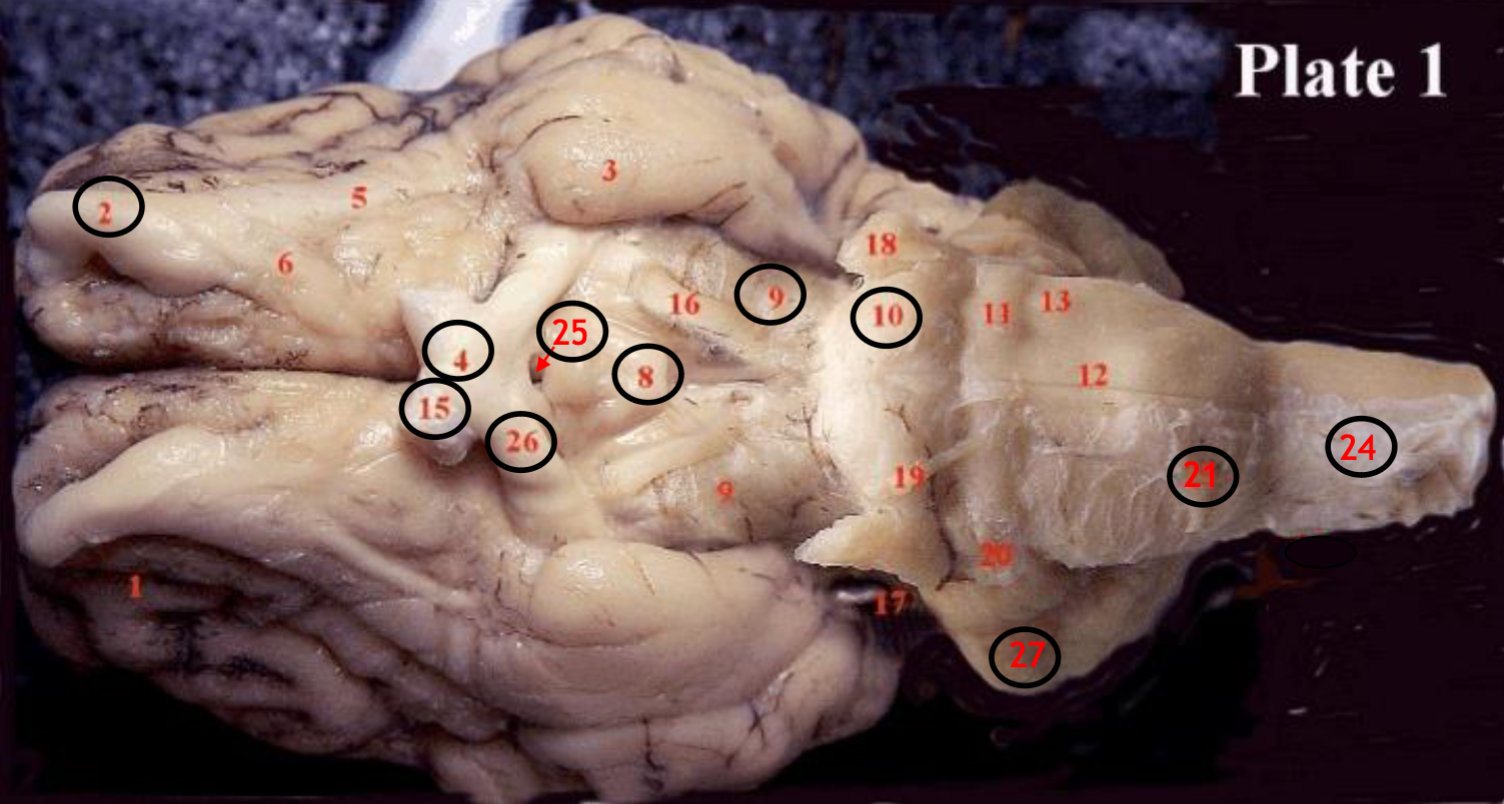
#21
medulla
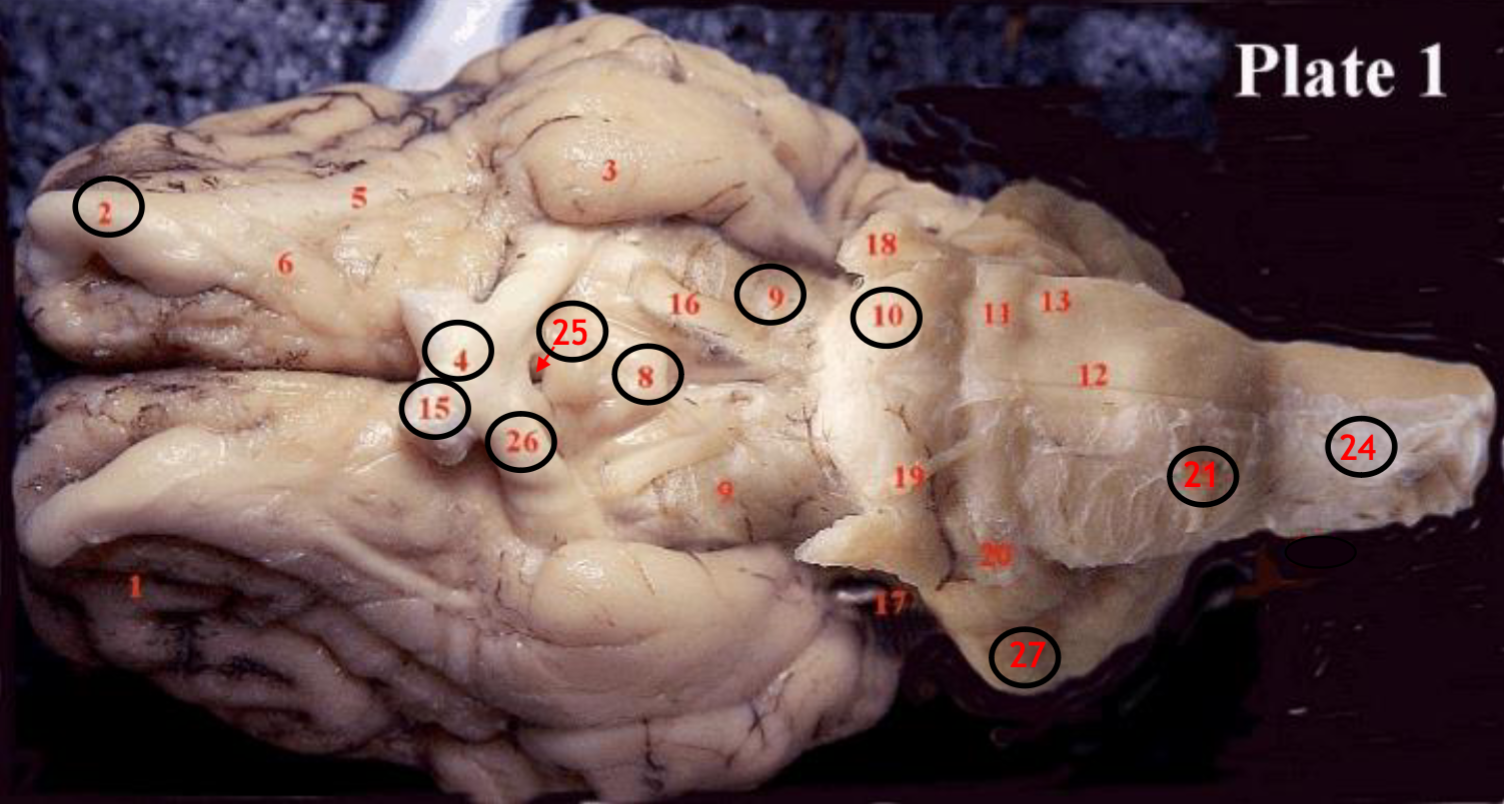
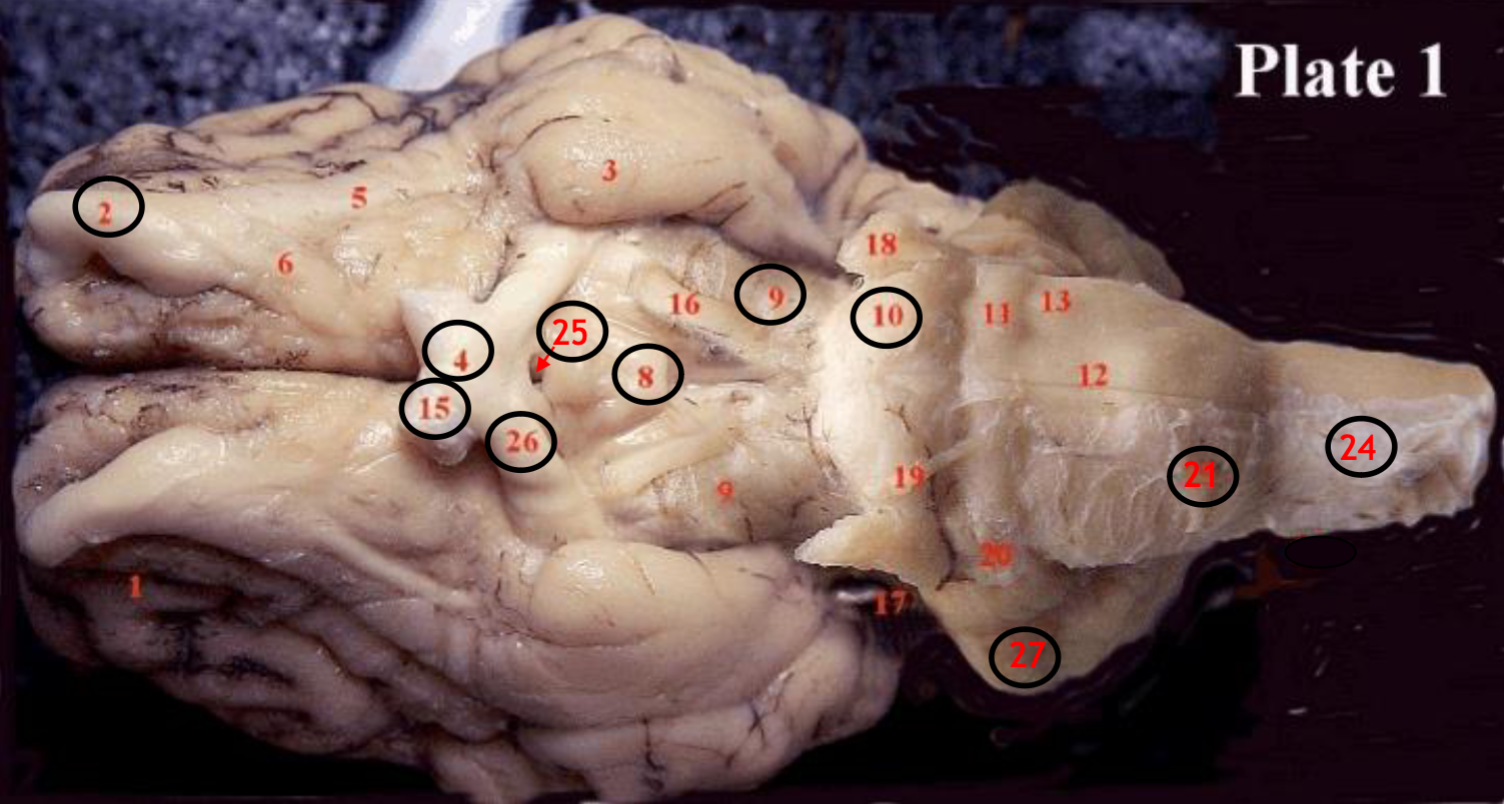
#24
spinal cord
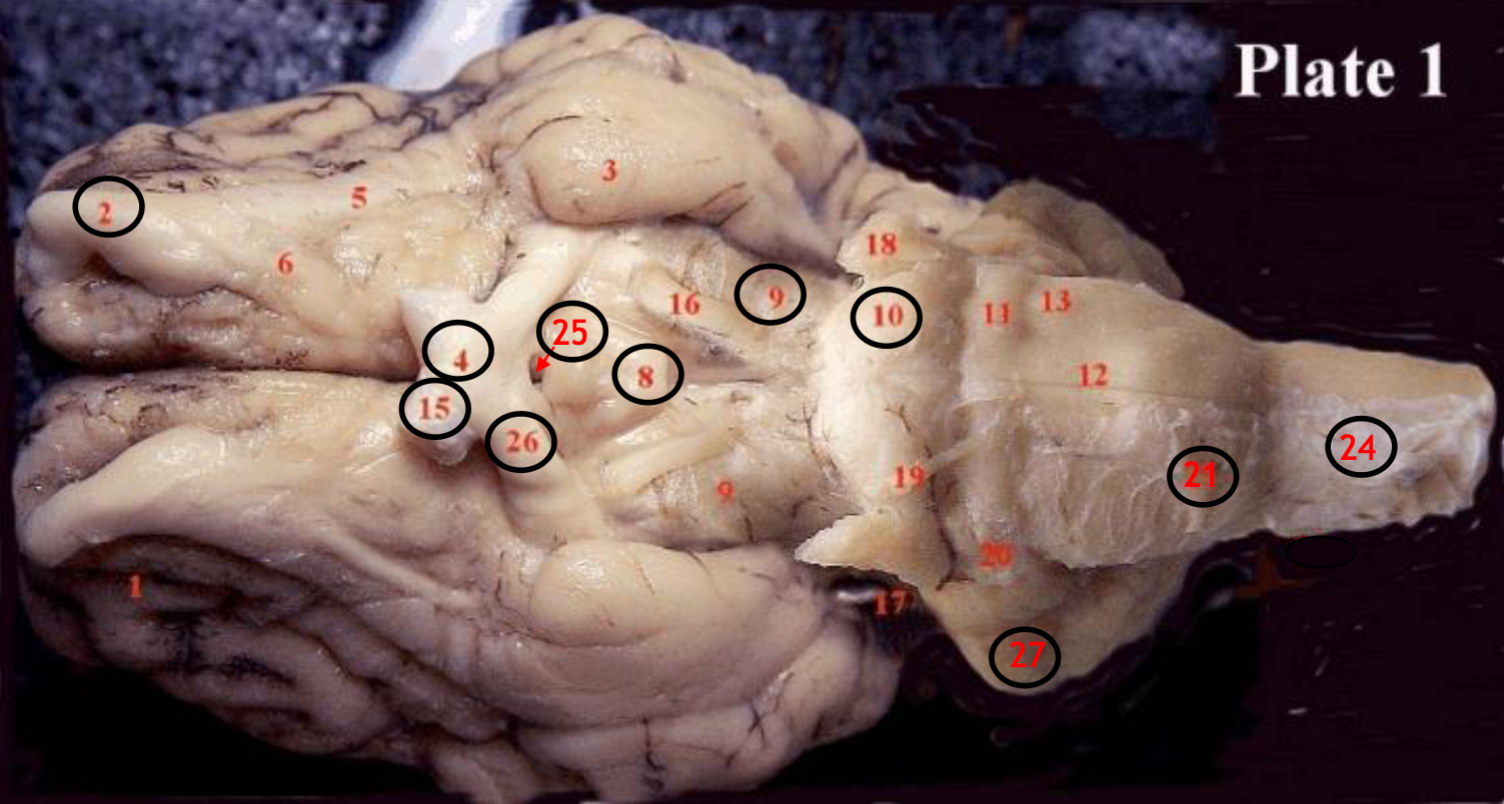
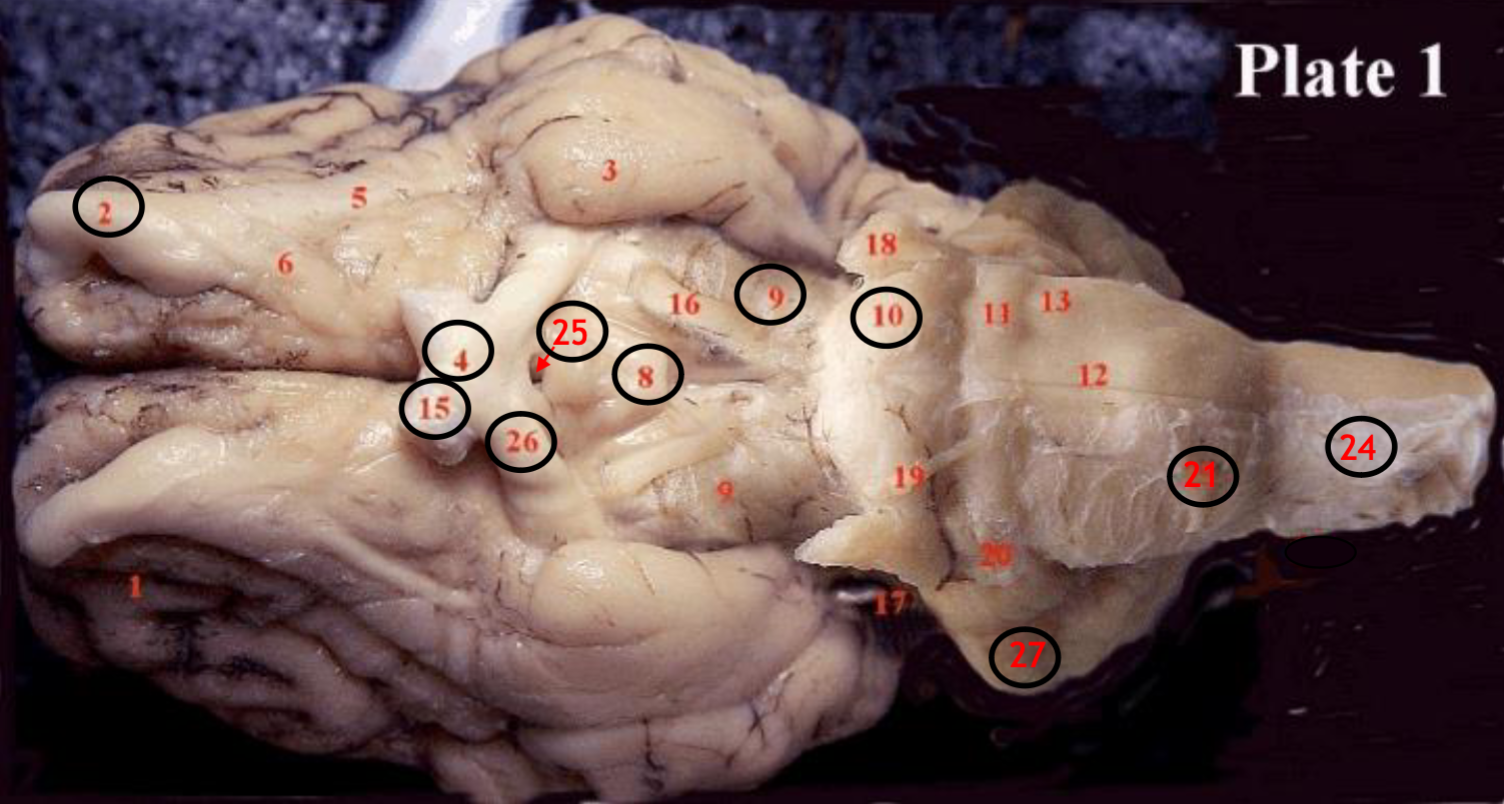
#26
optic tract
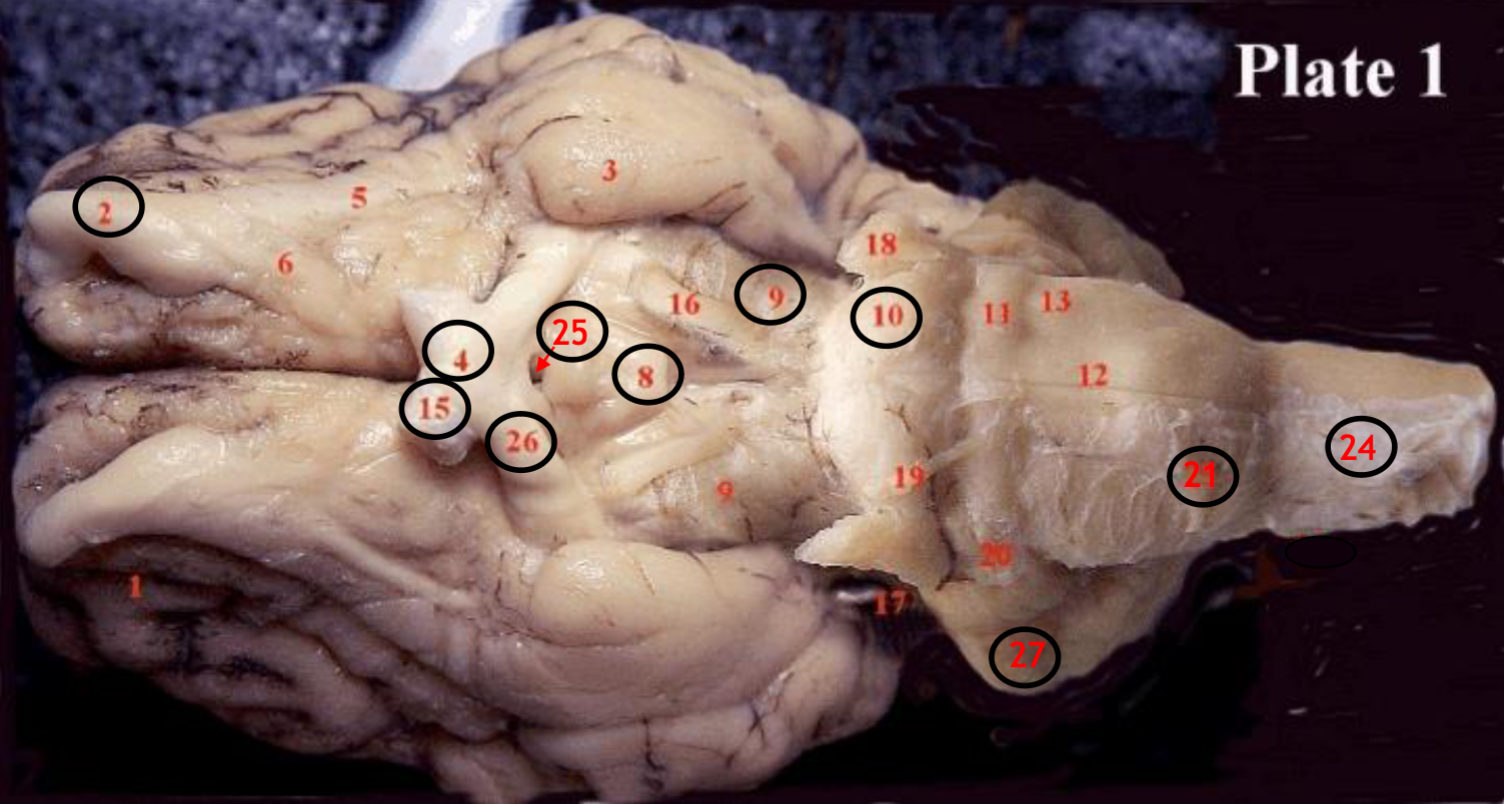
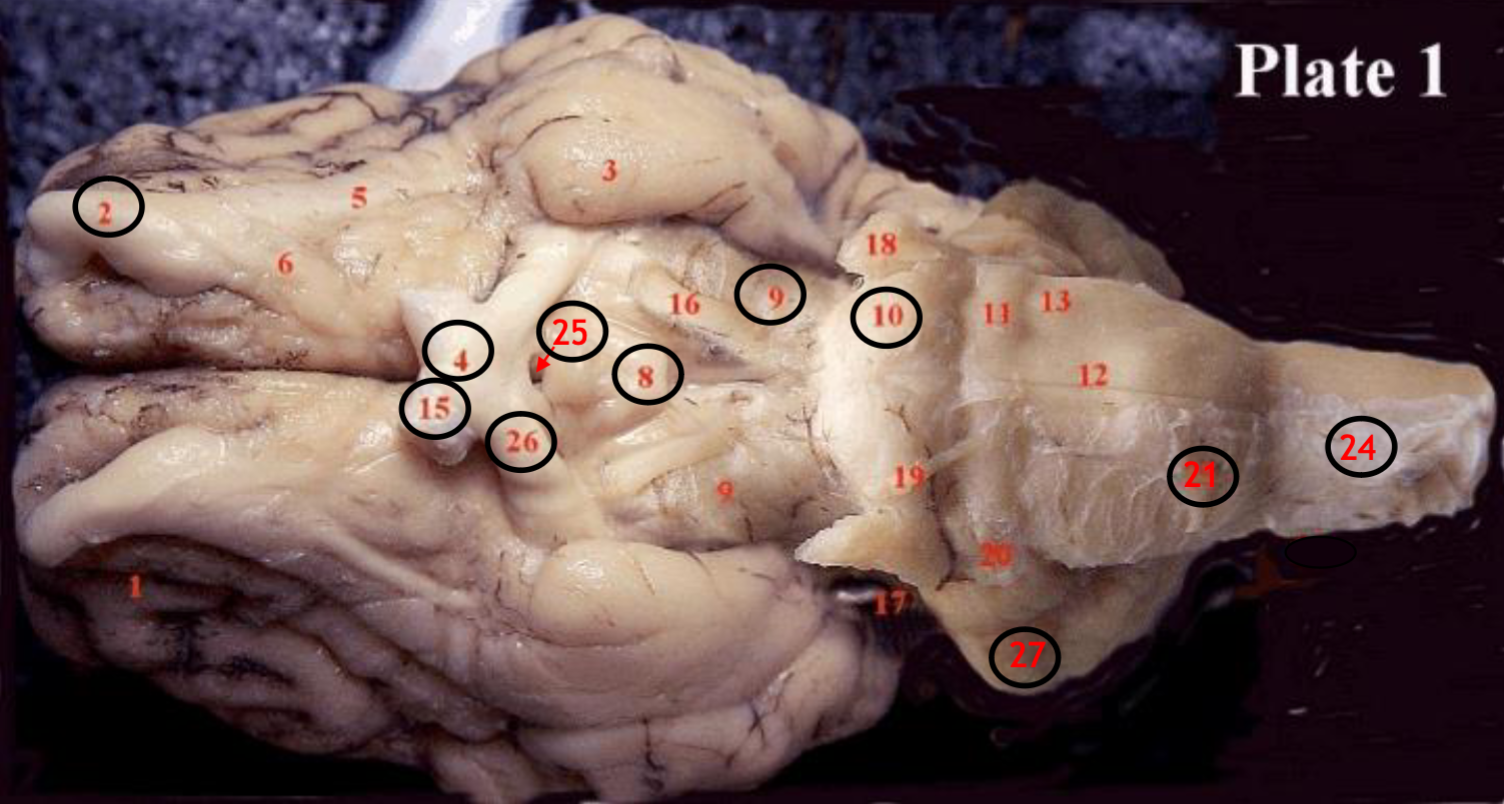
#27
cerebellum
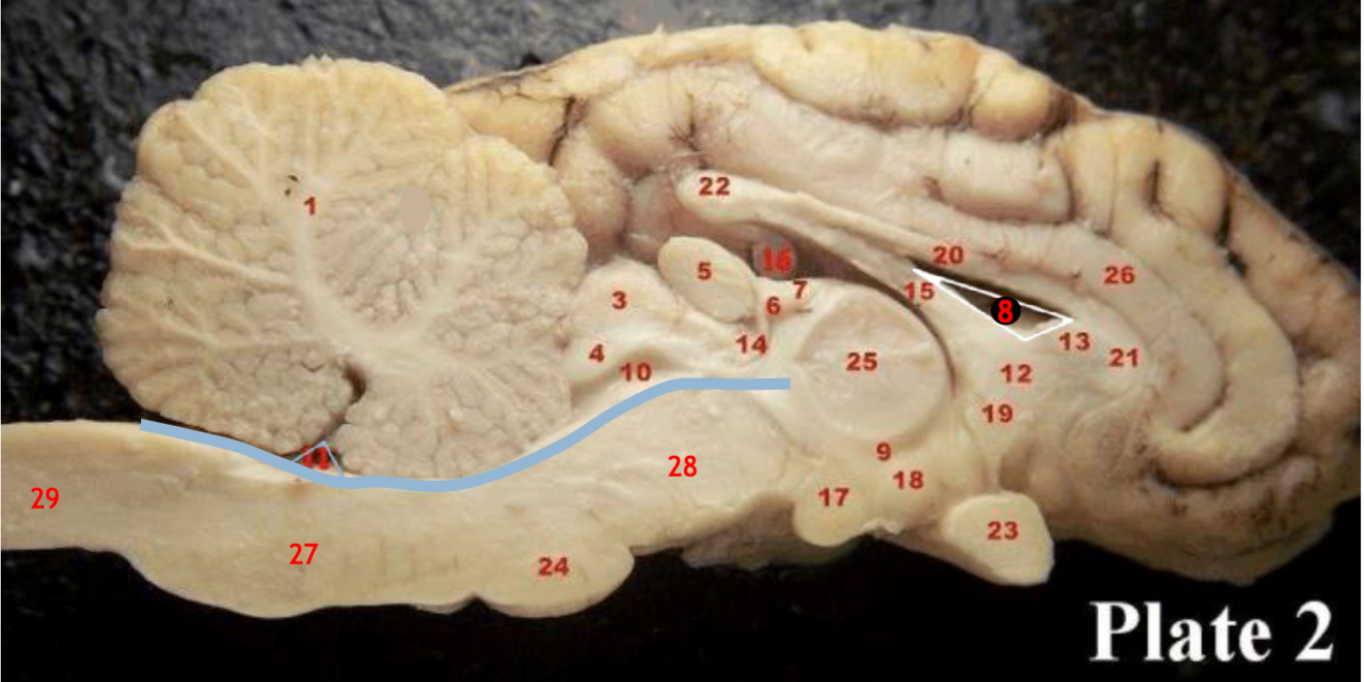
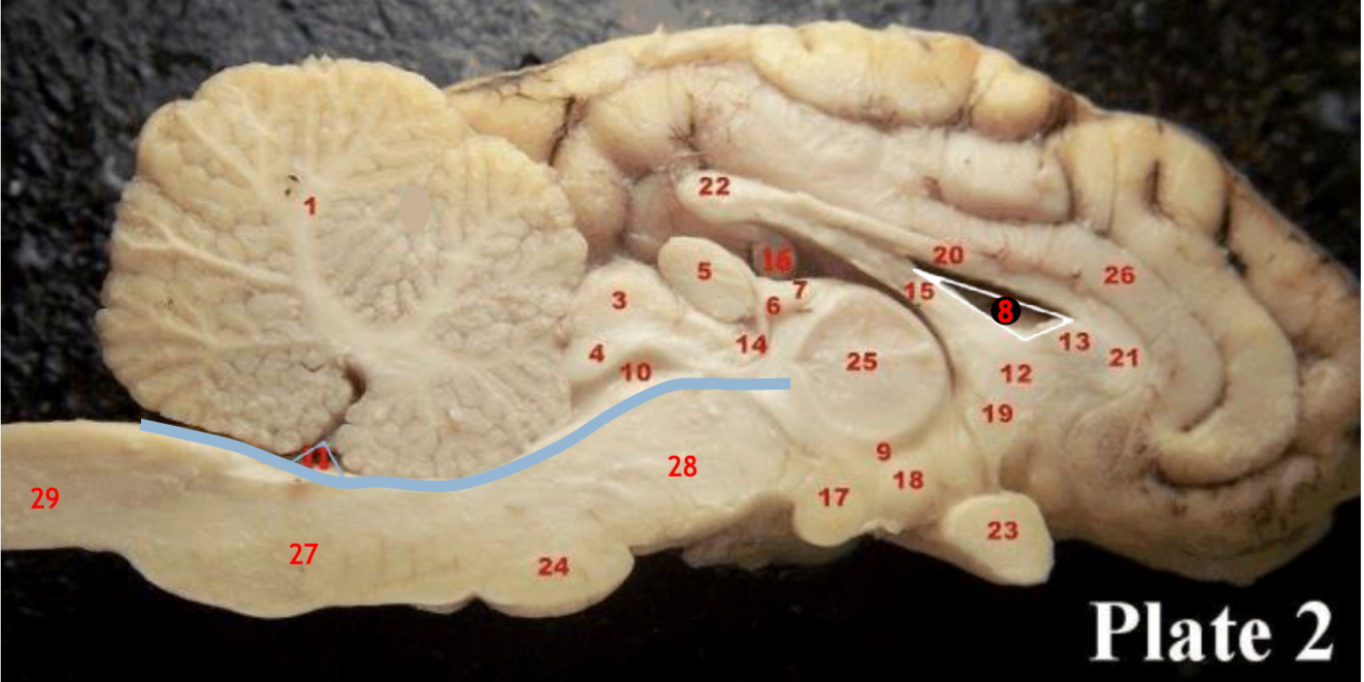
(20,21,22)
Corpus callosum
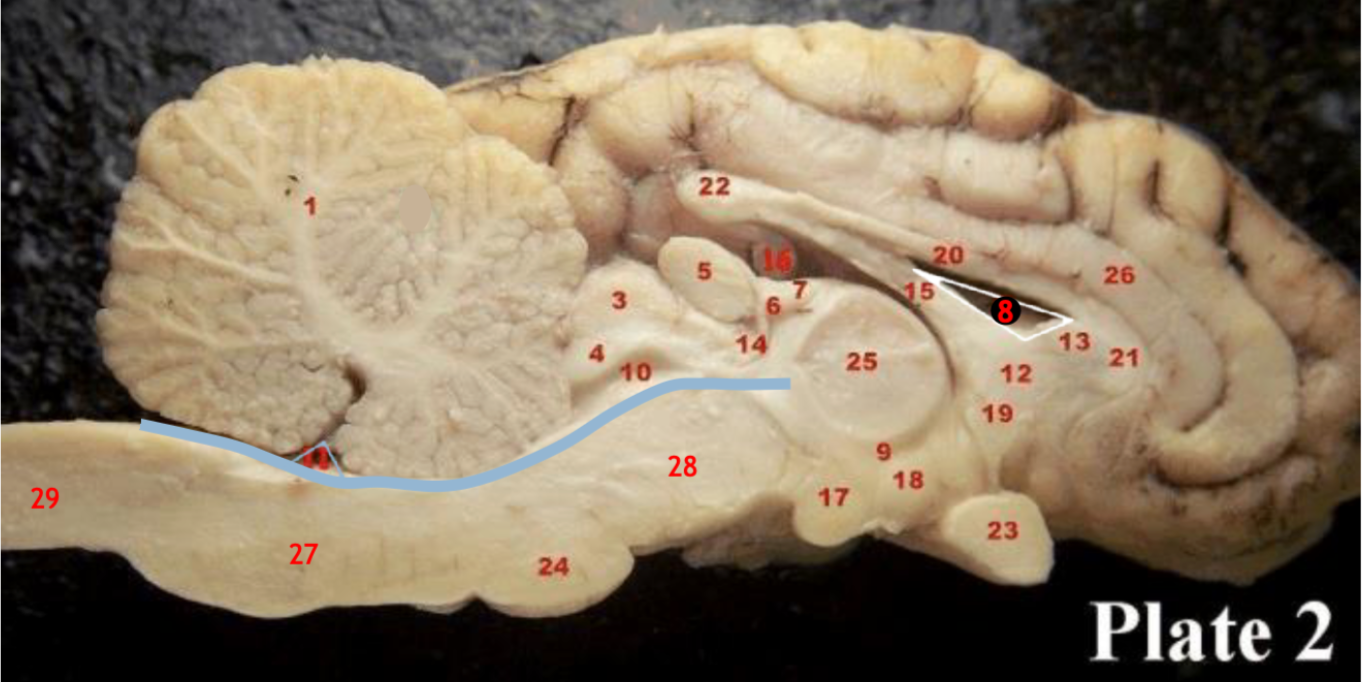
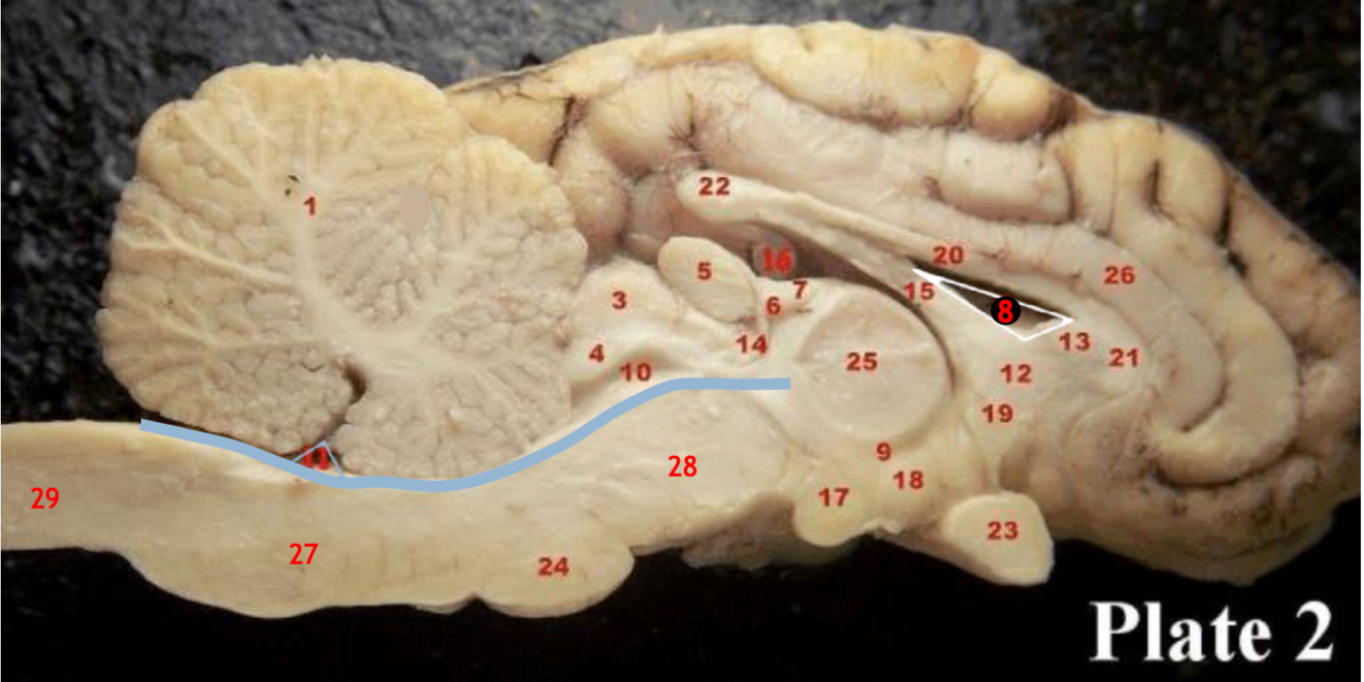
(5)
Pineal gland
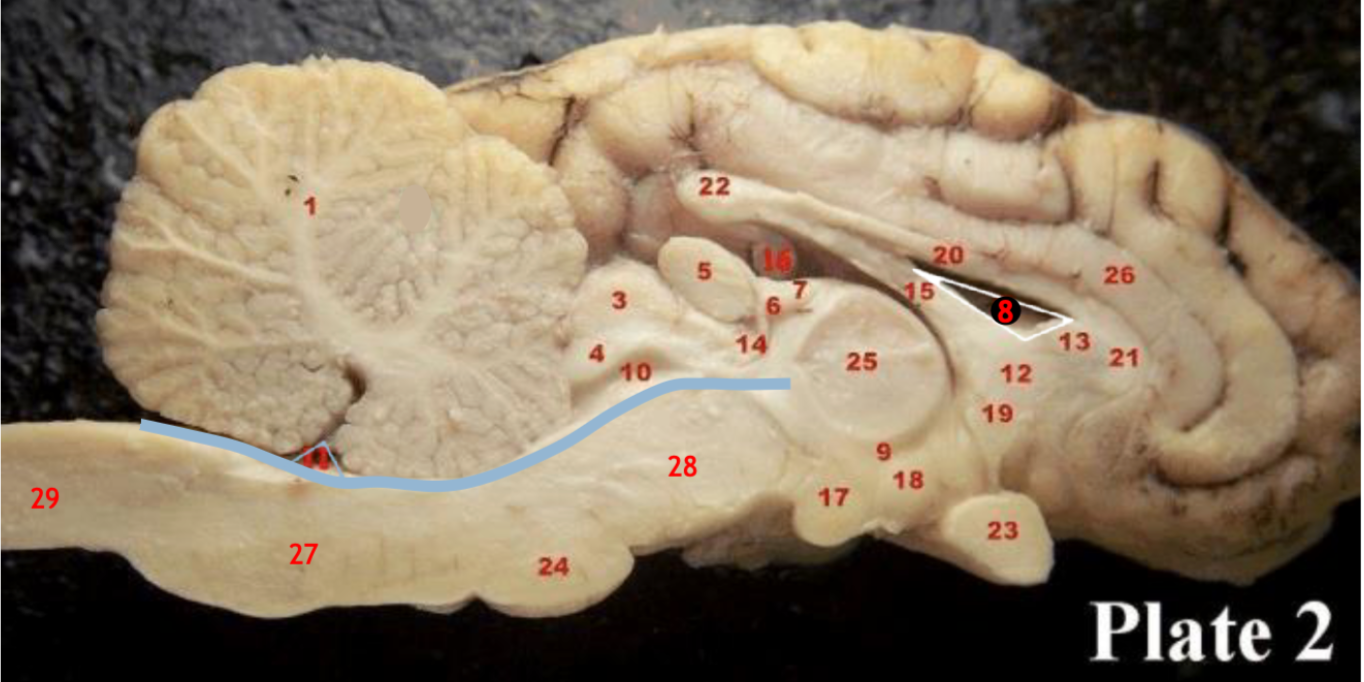
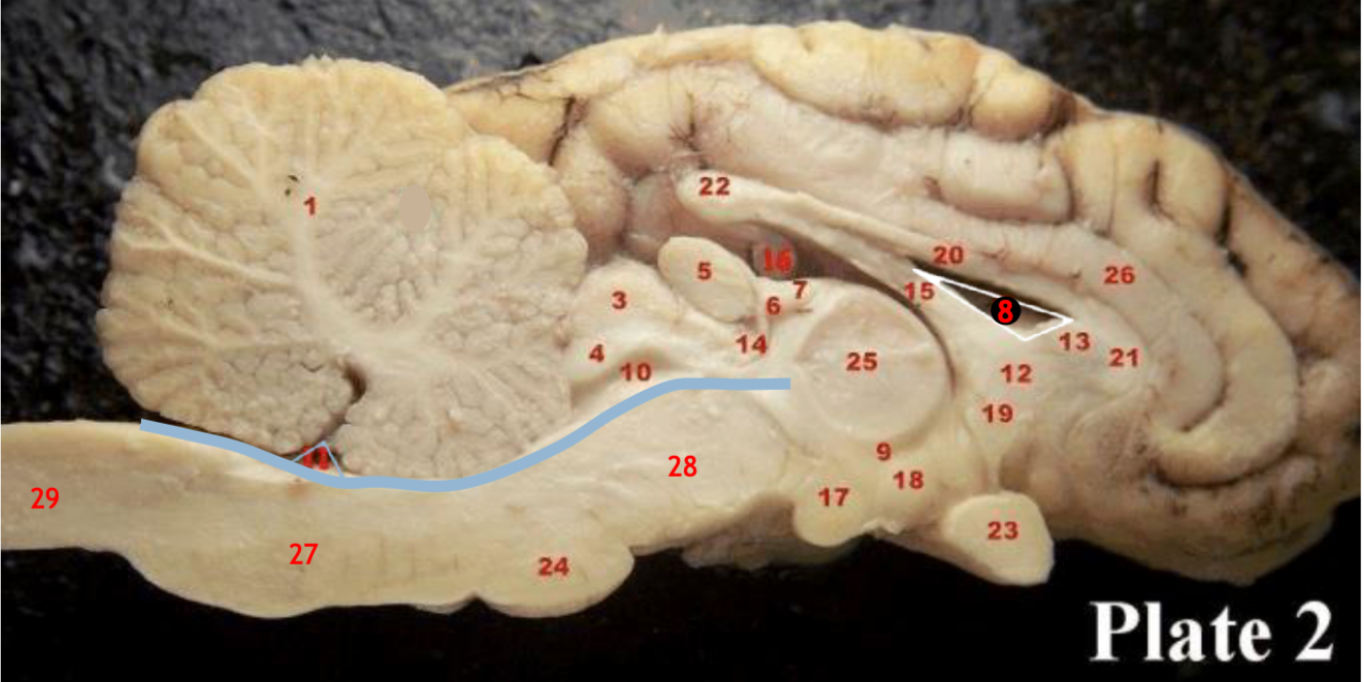
(3)
Superior colliculi
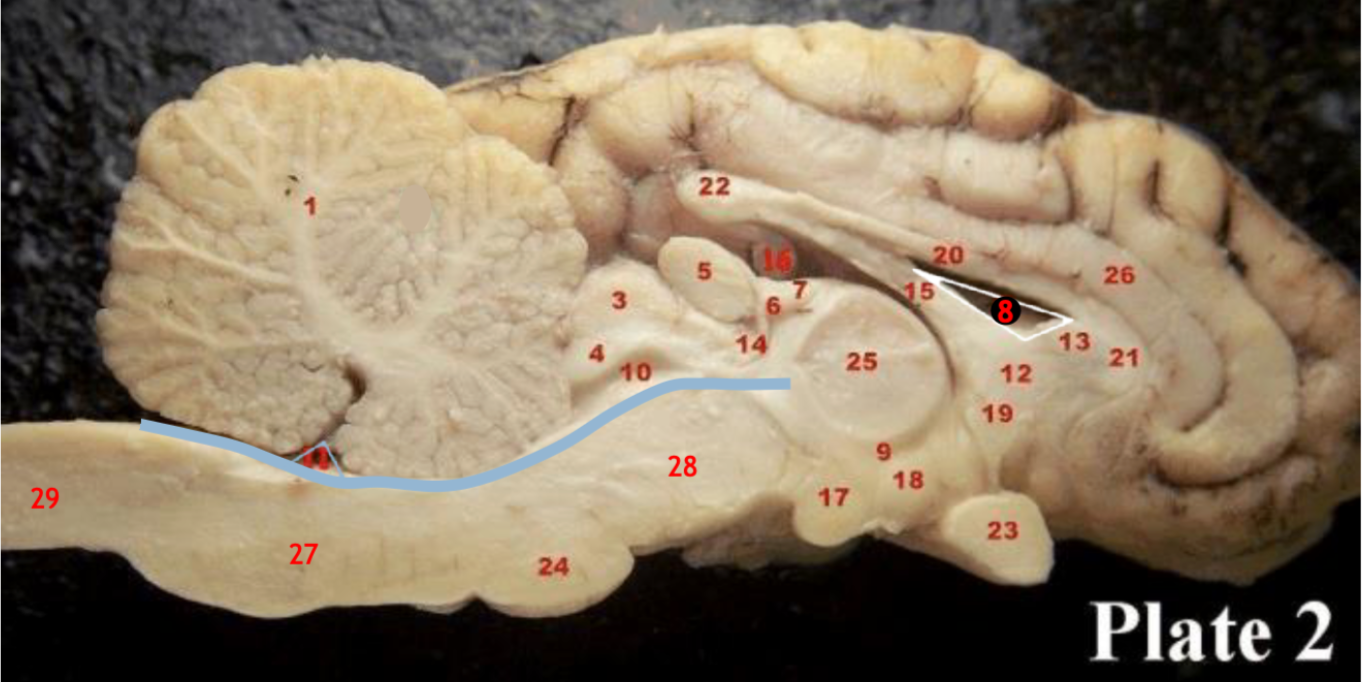
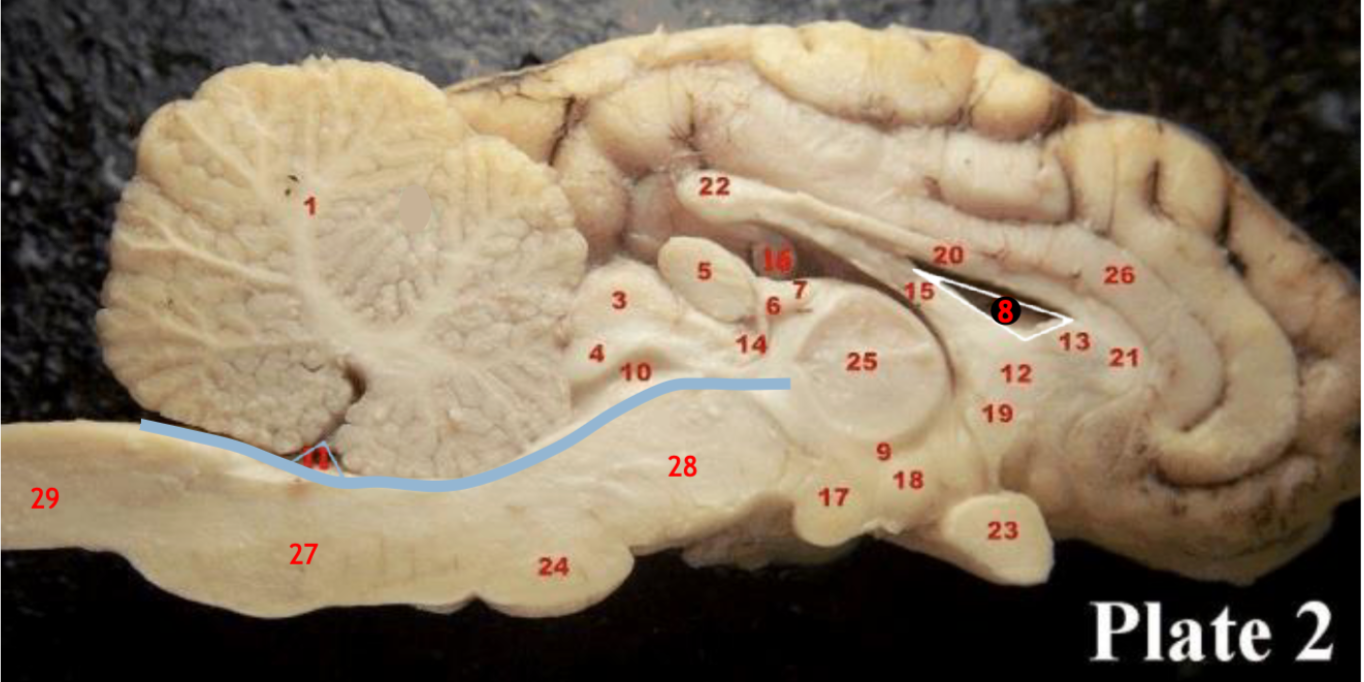
(4)
inferior colliculi
(23)
Optic chiasm
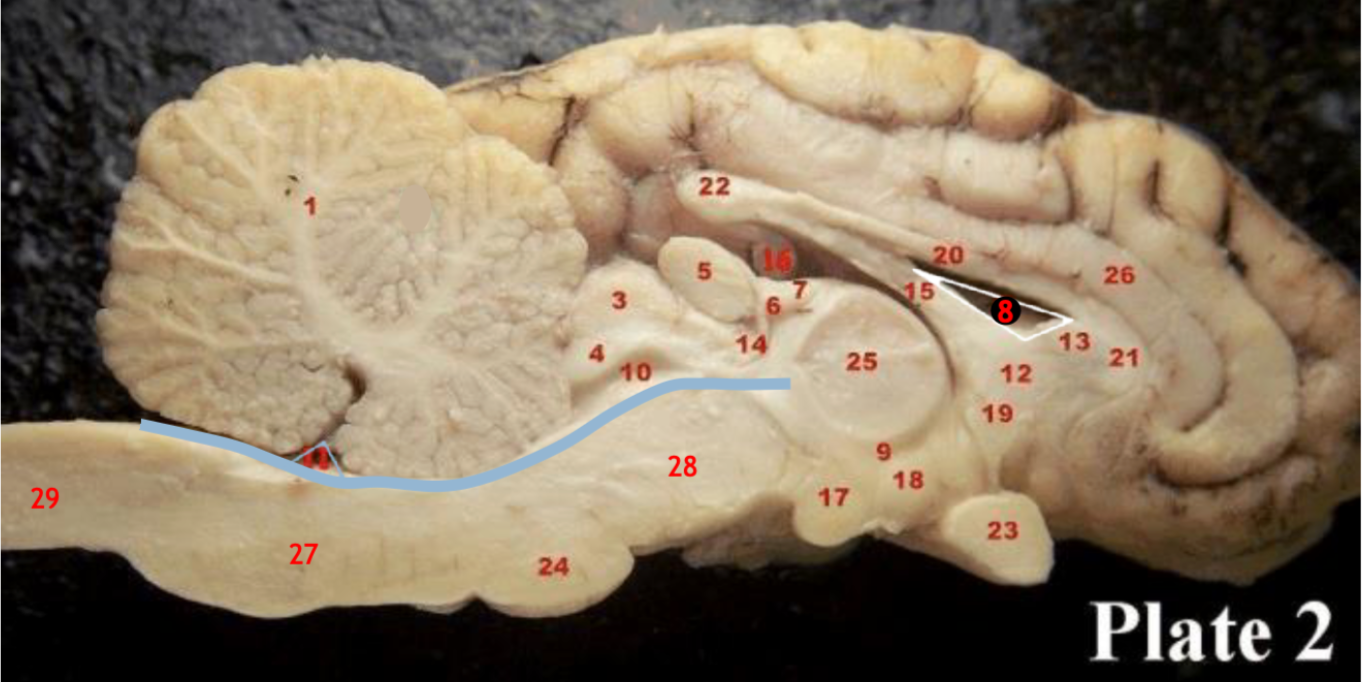
(17)
Mammillary body
(24)
Pons
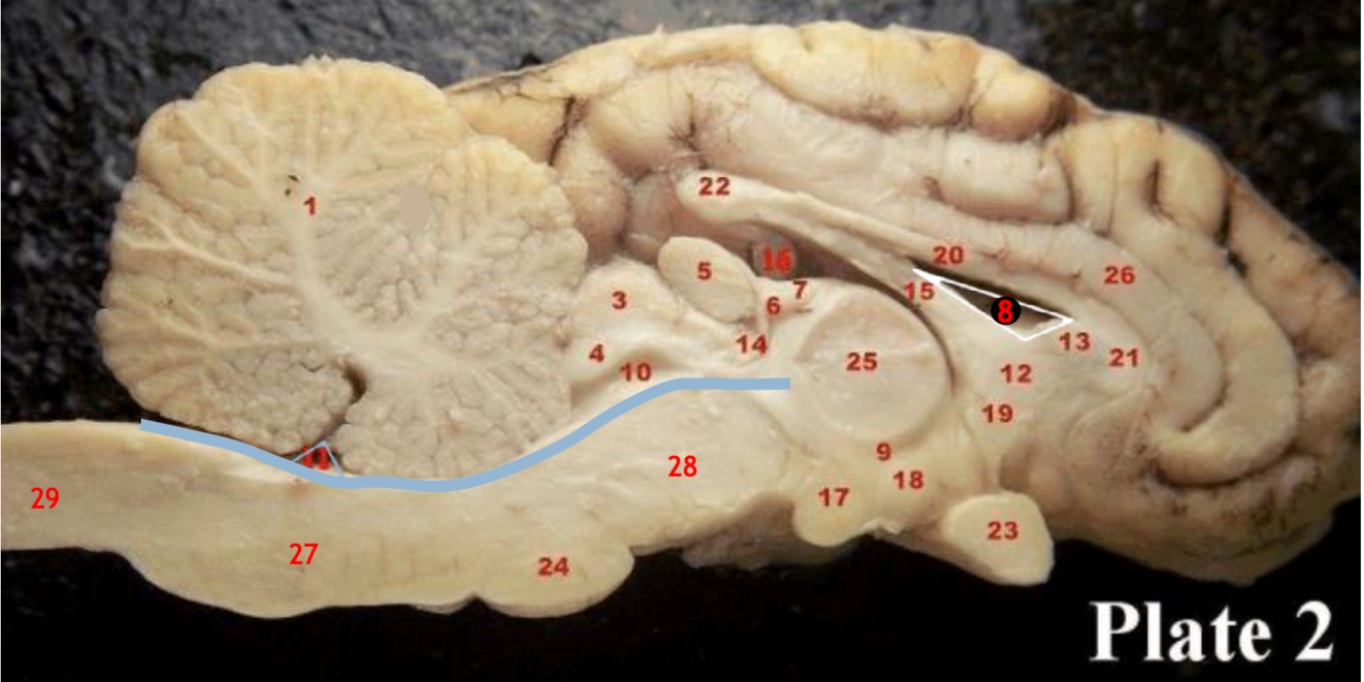
(1)
Cerebellum
(28)
Midbrain
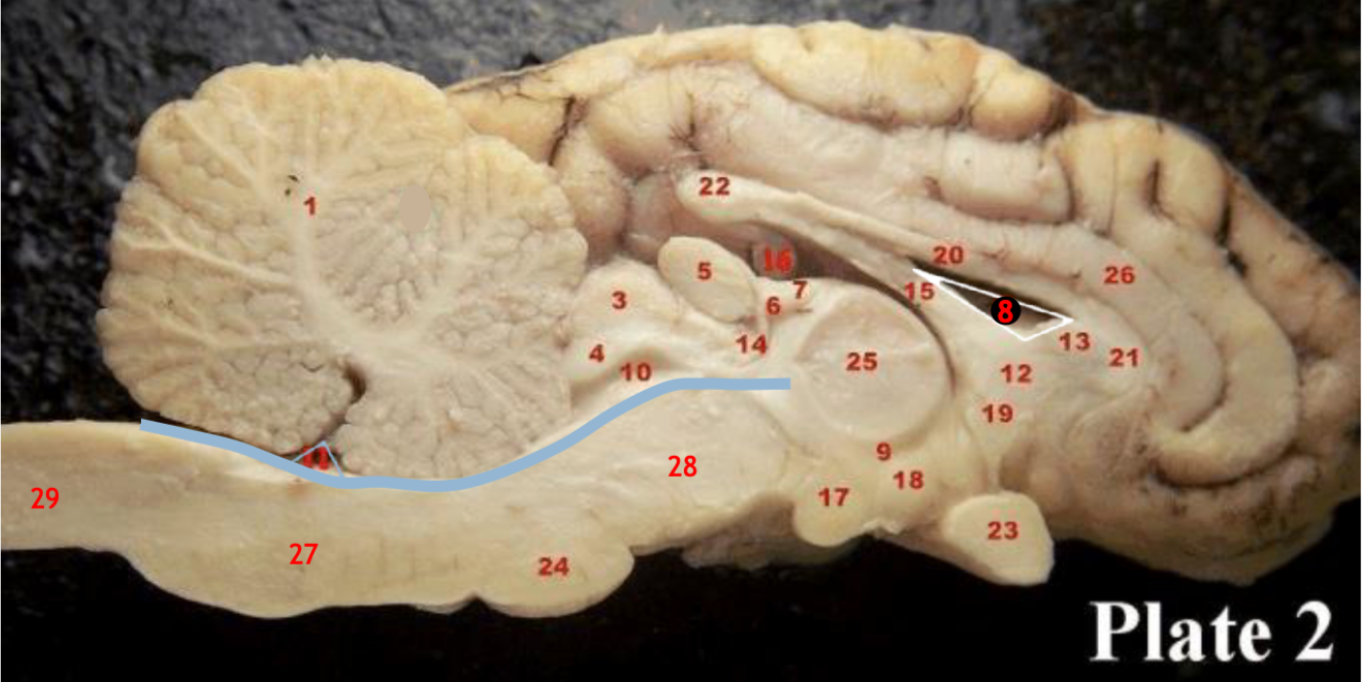
(27)
Medulla
(29)
Spinal cord
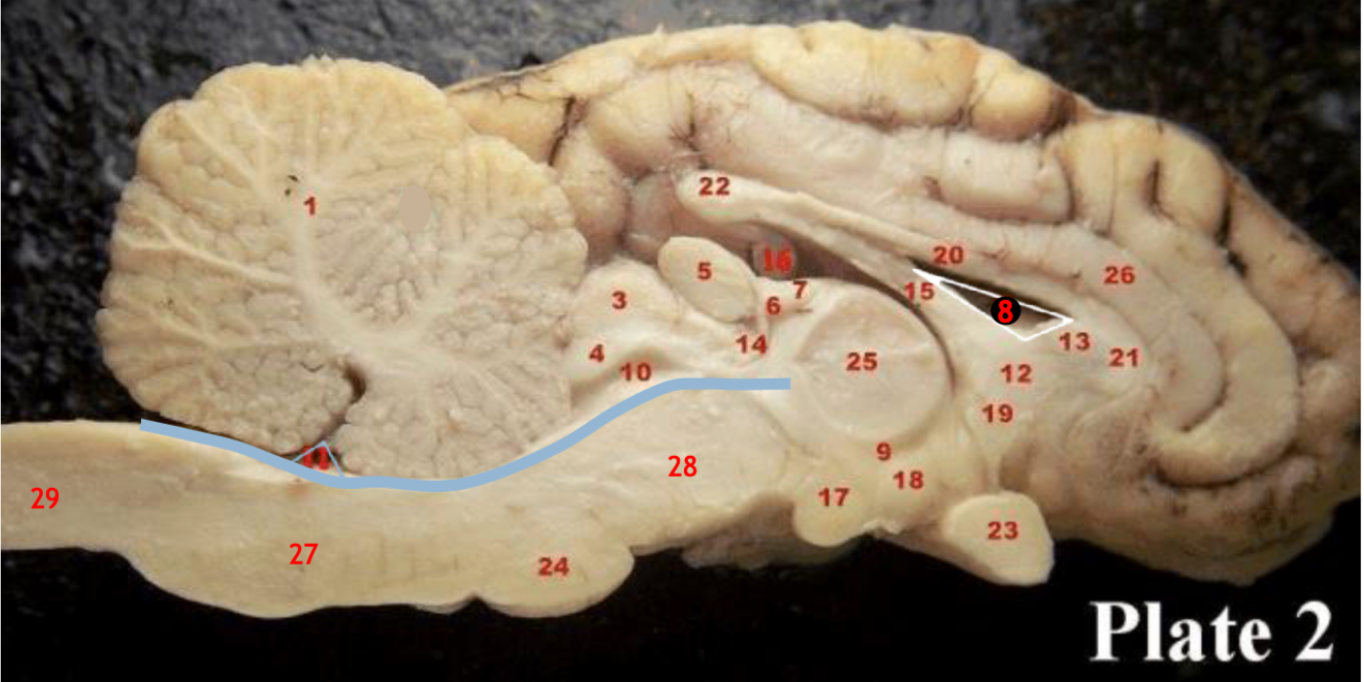
(8)
Lateral ventricle
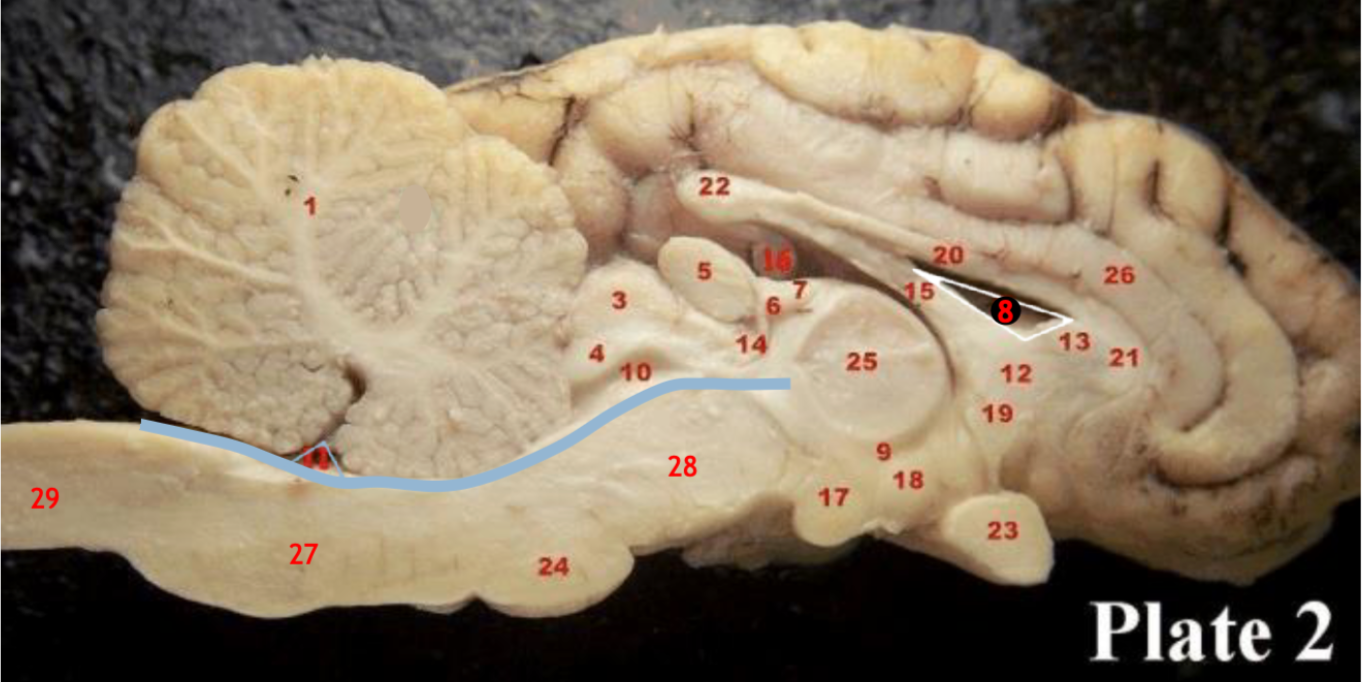
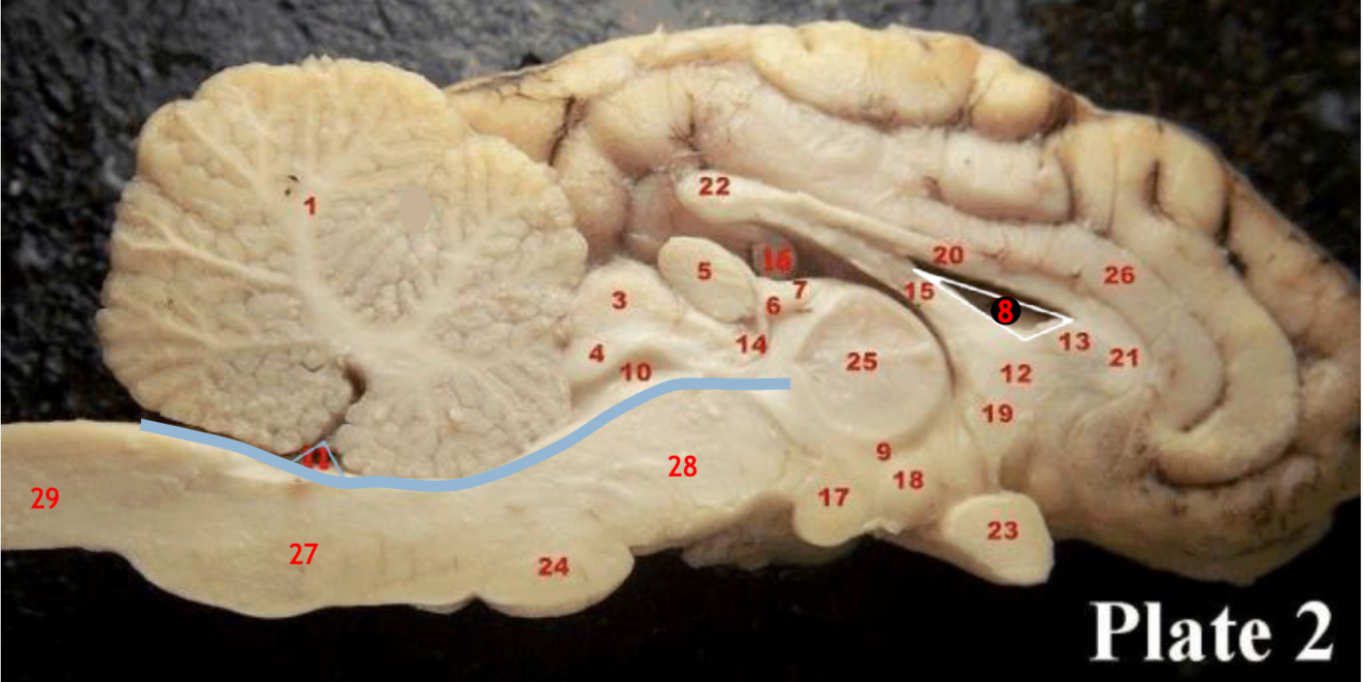
(10)
Cerebral aqueduct
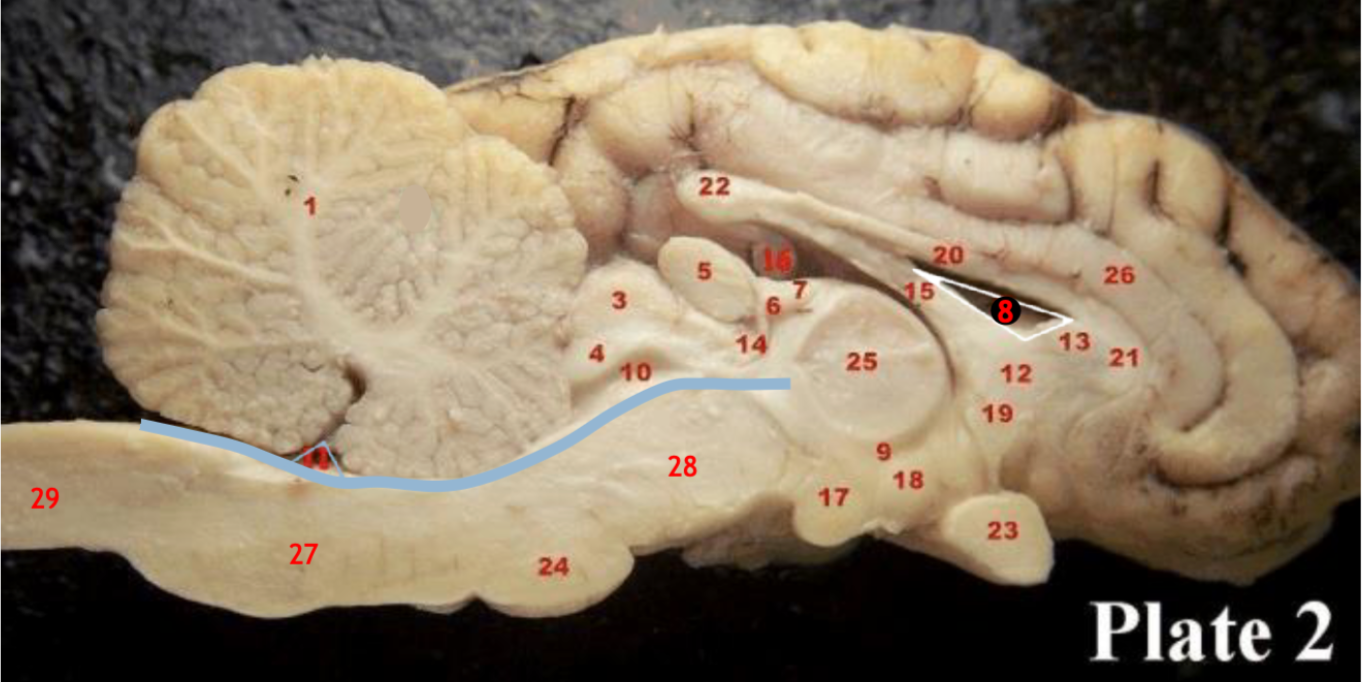
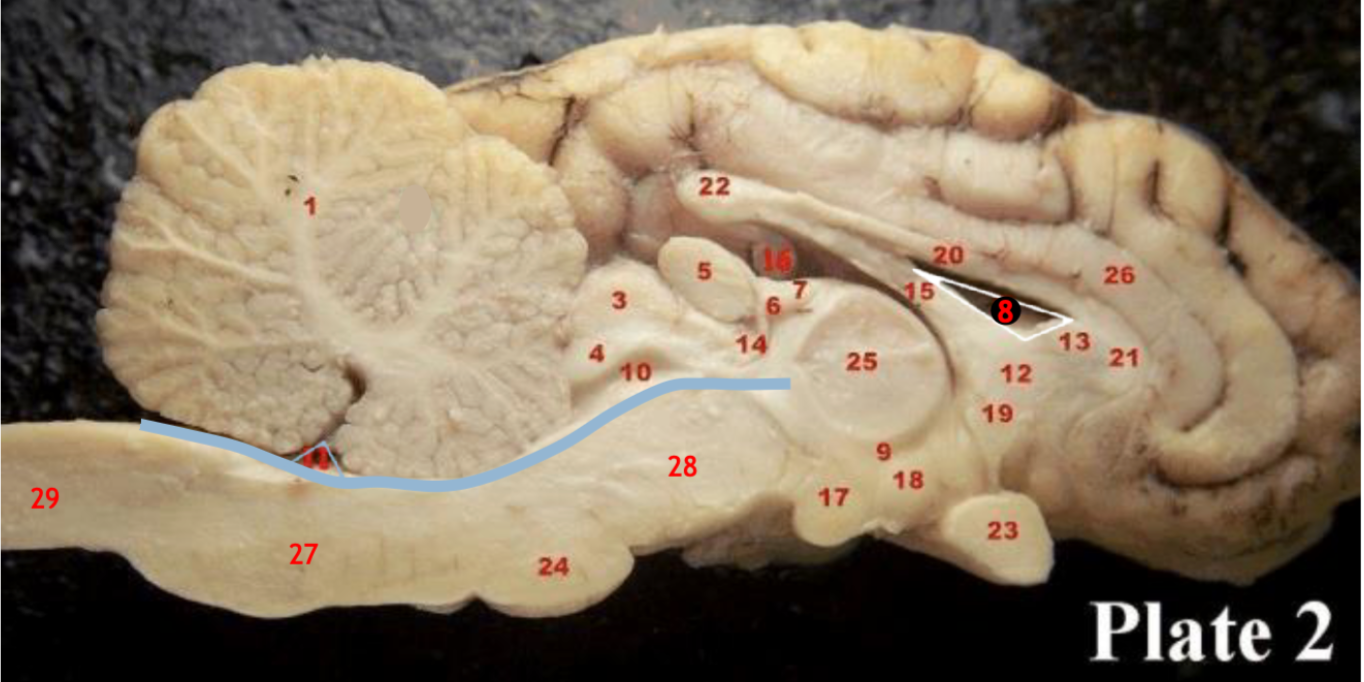
(inbetween two #25 structures)
3rd ventricle
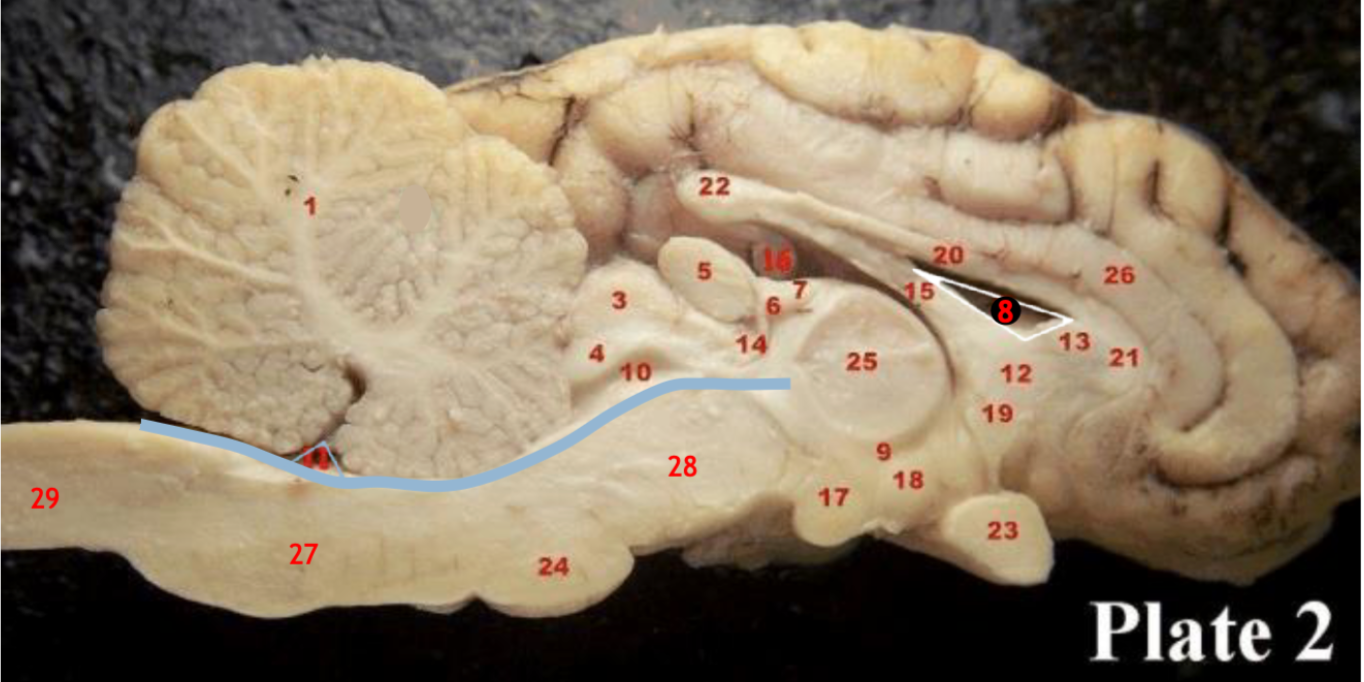
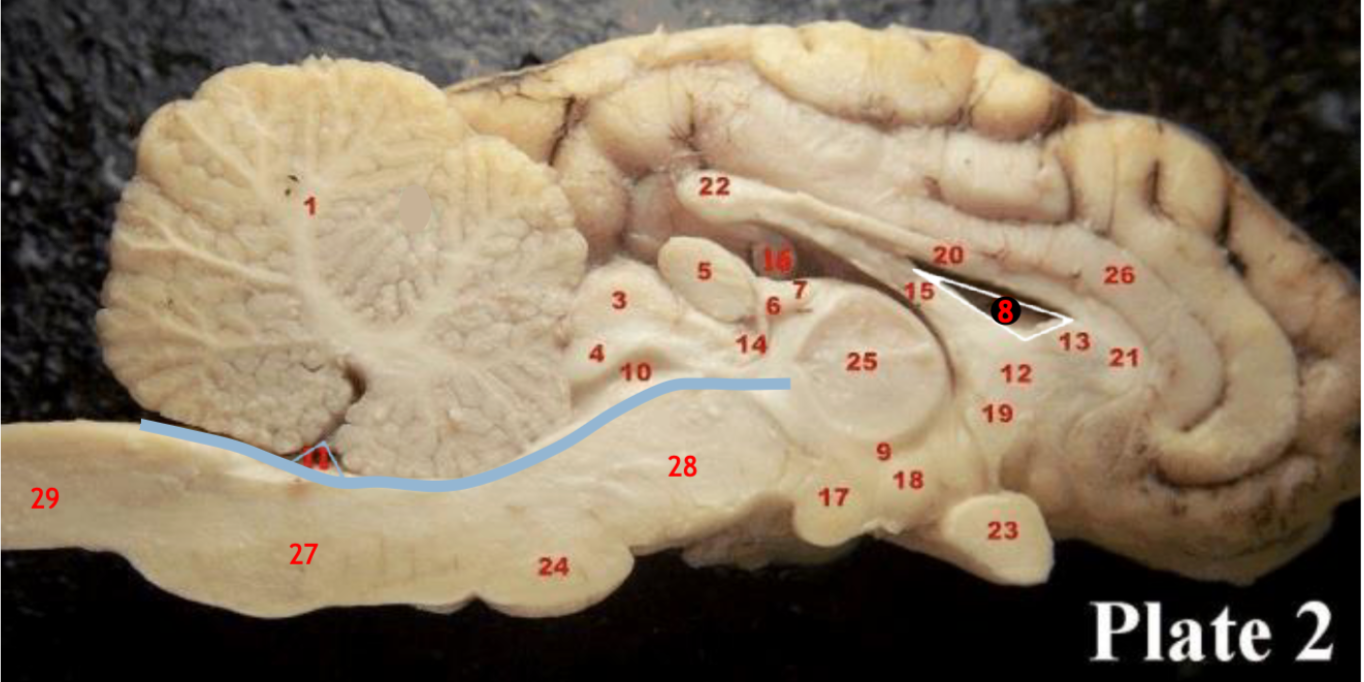
(11)
4th ventricle
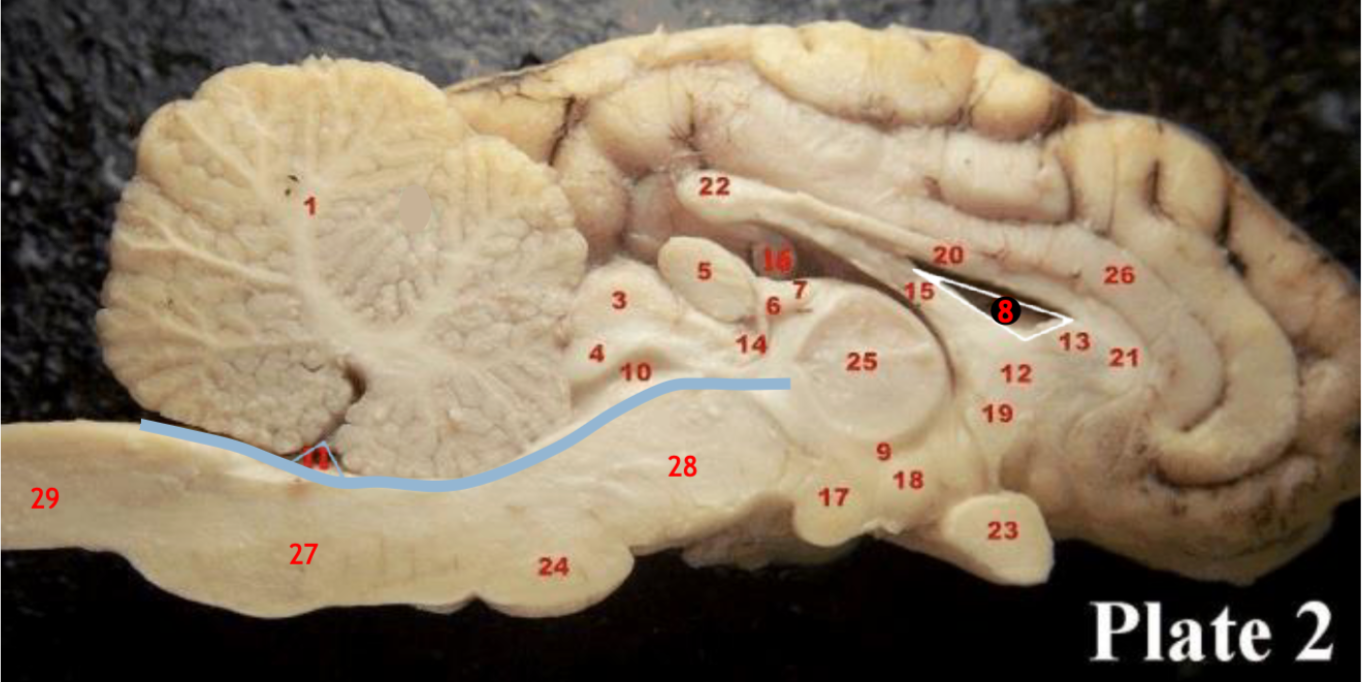
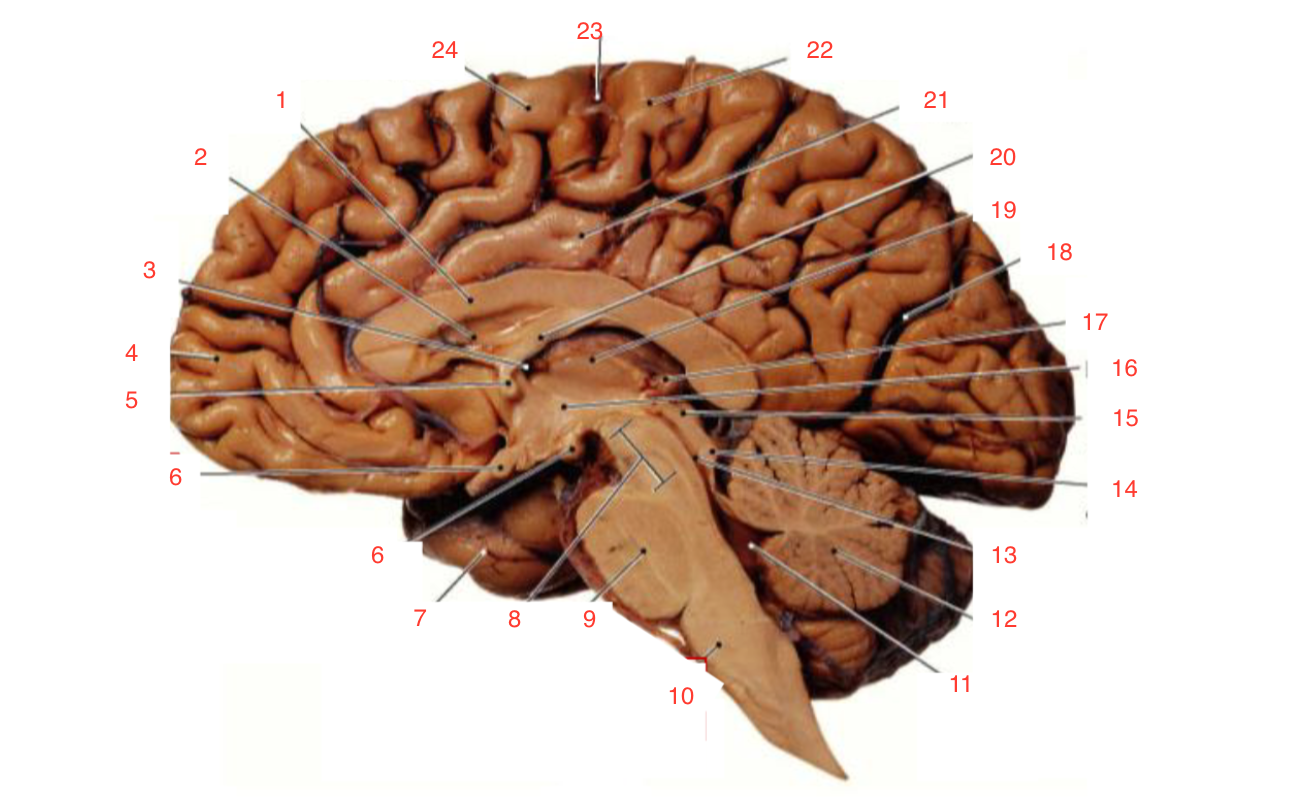
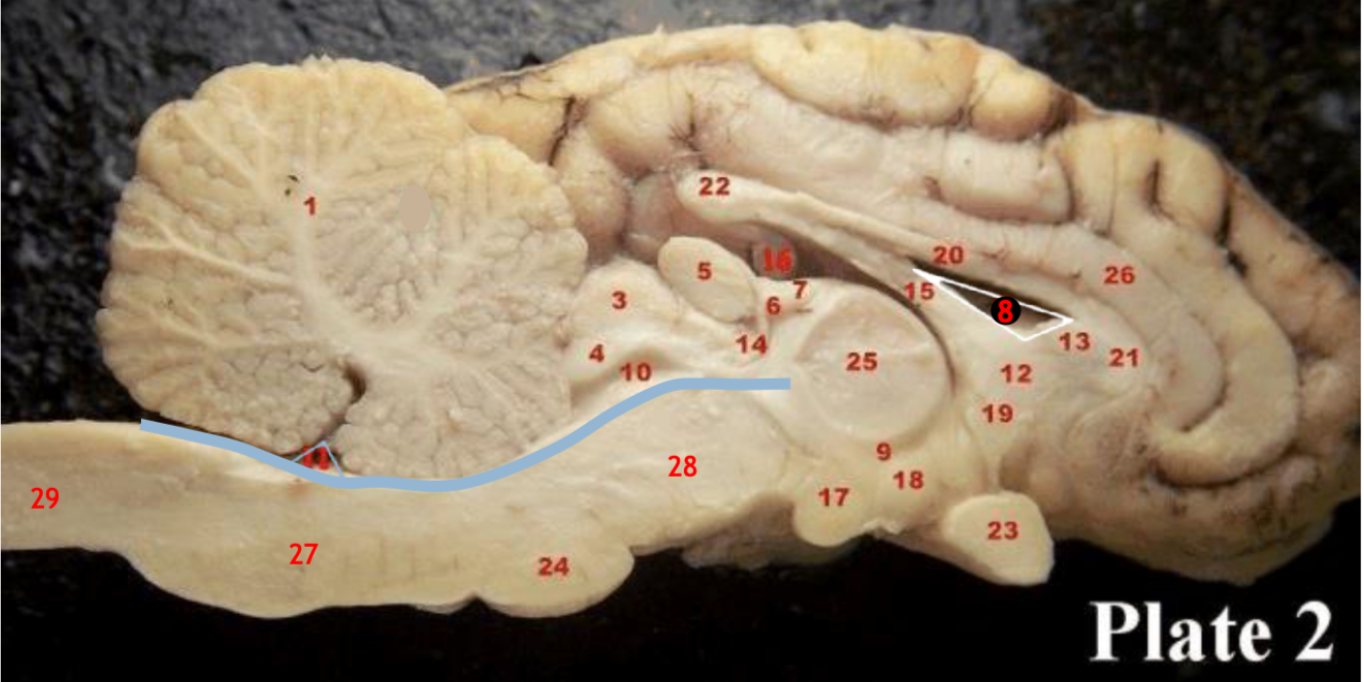
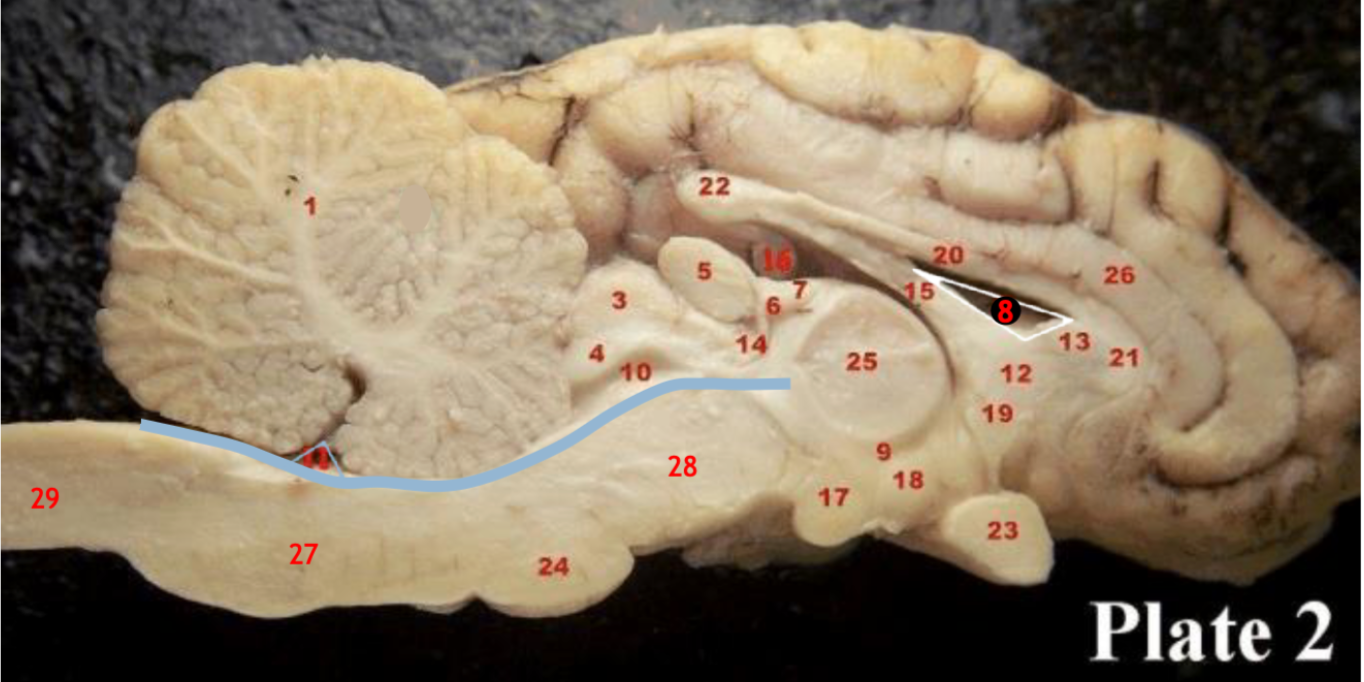
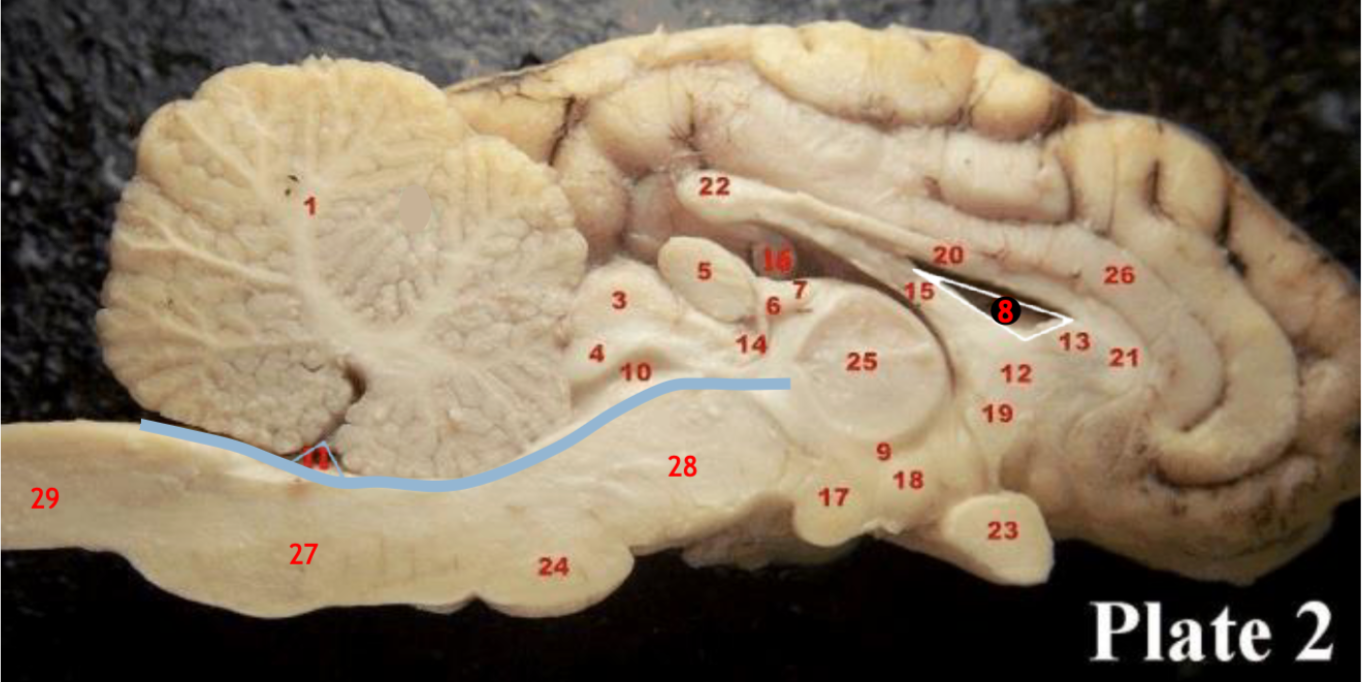
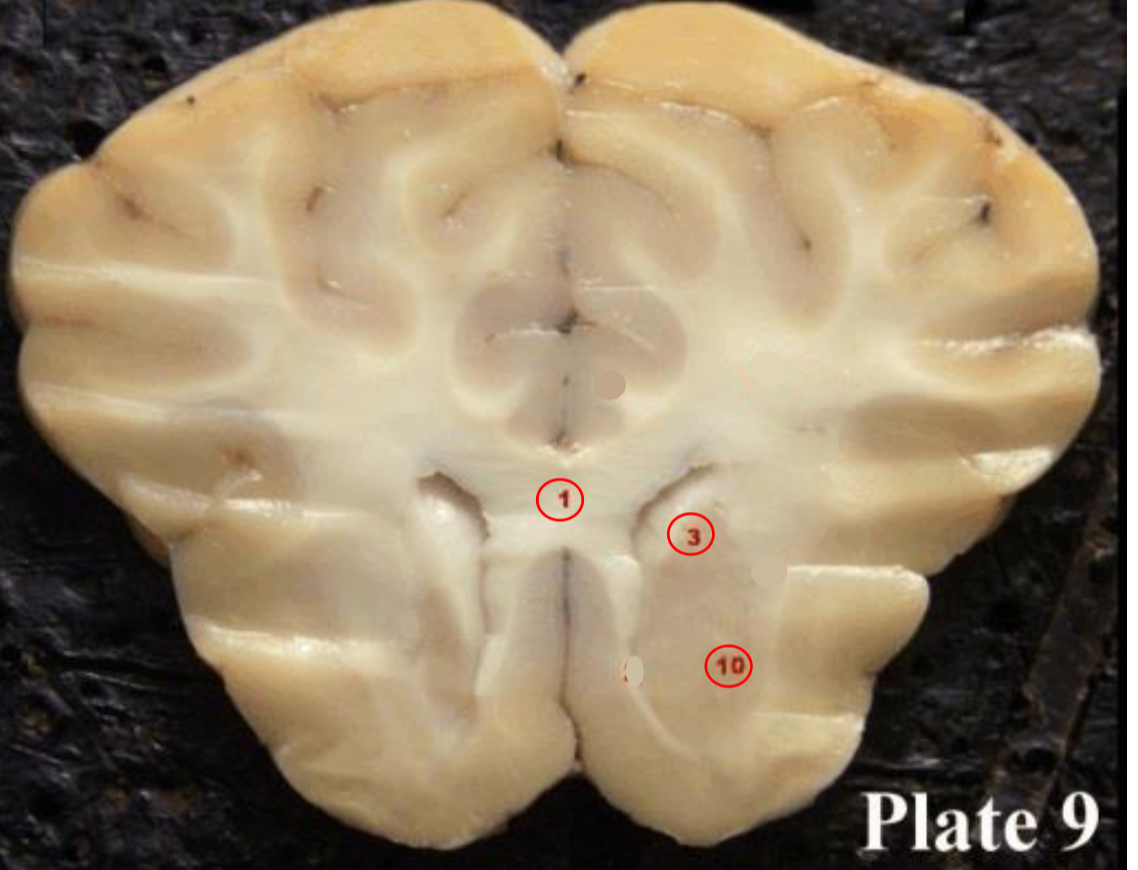
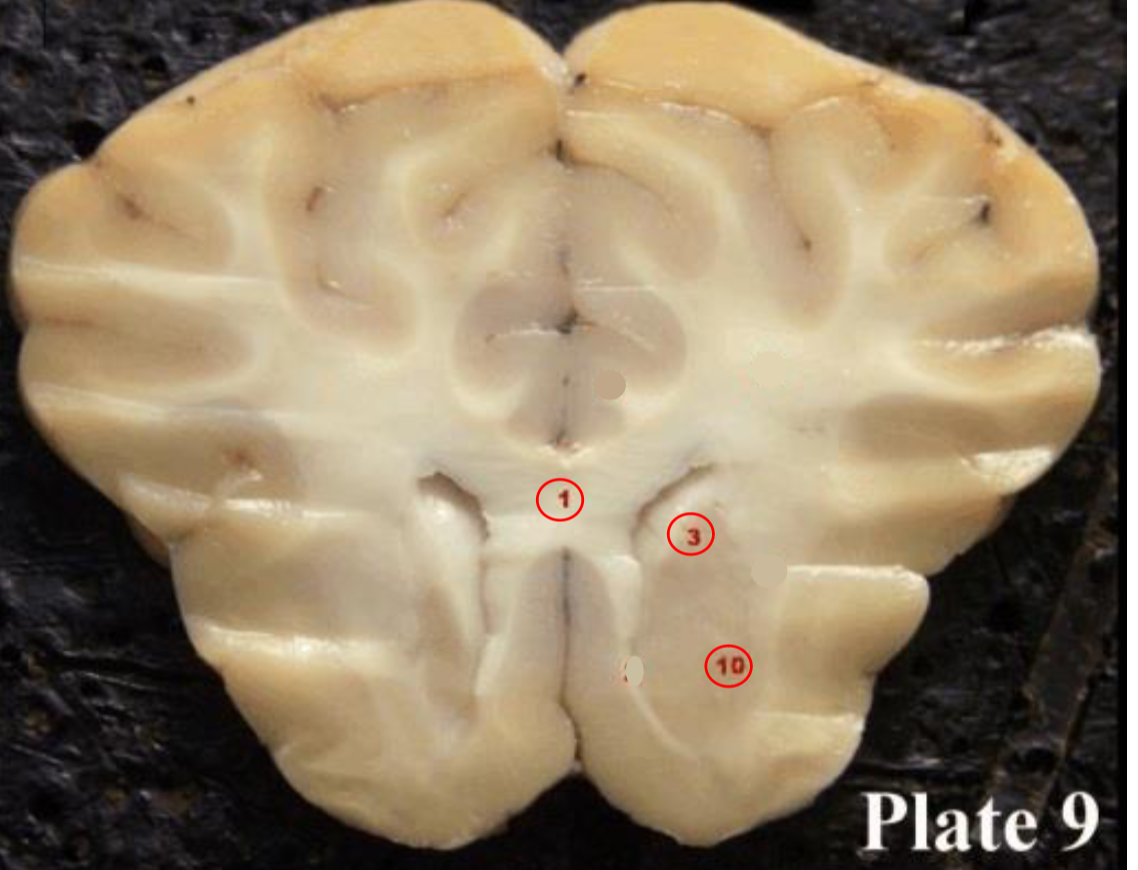
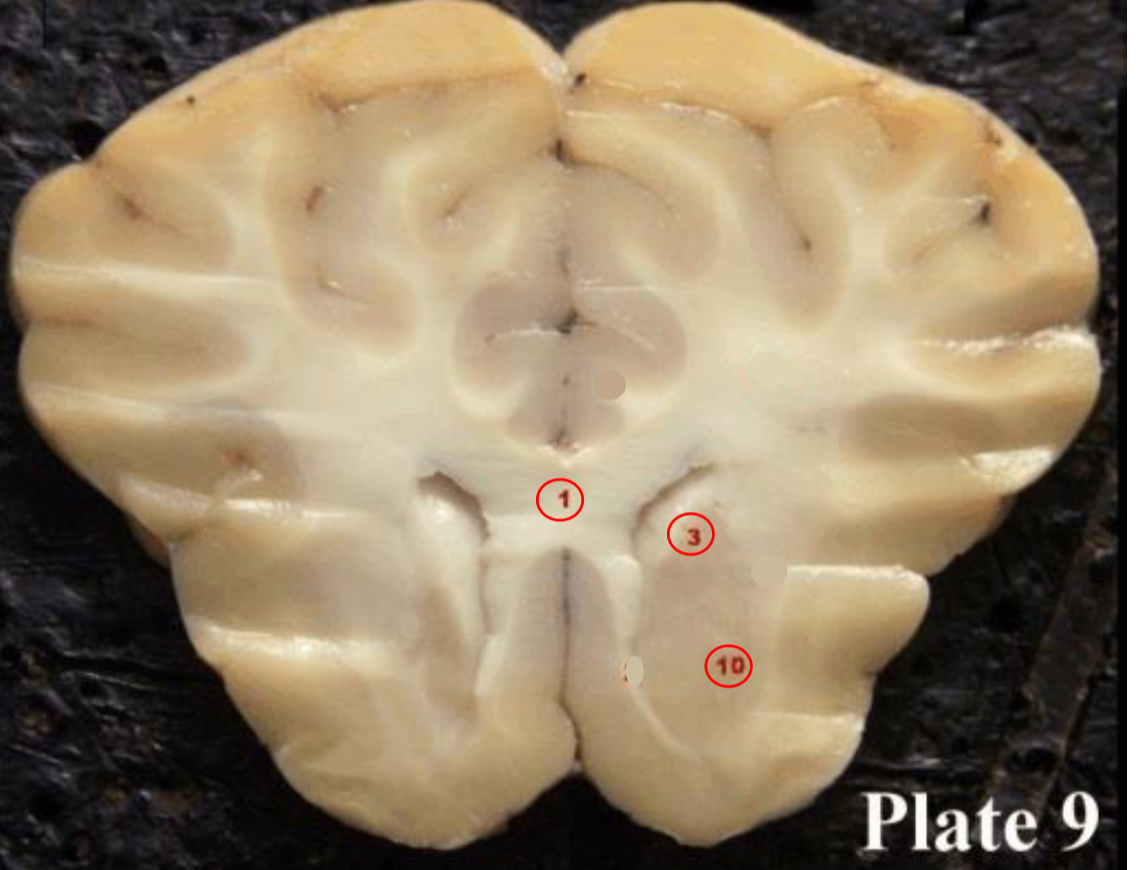
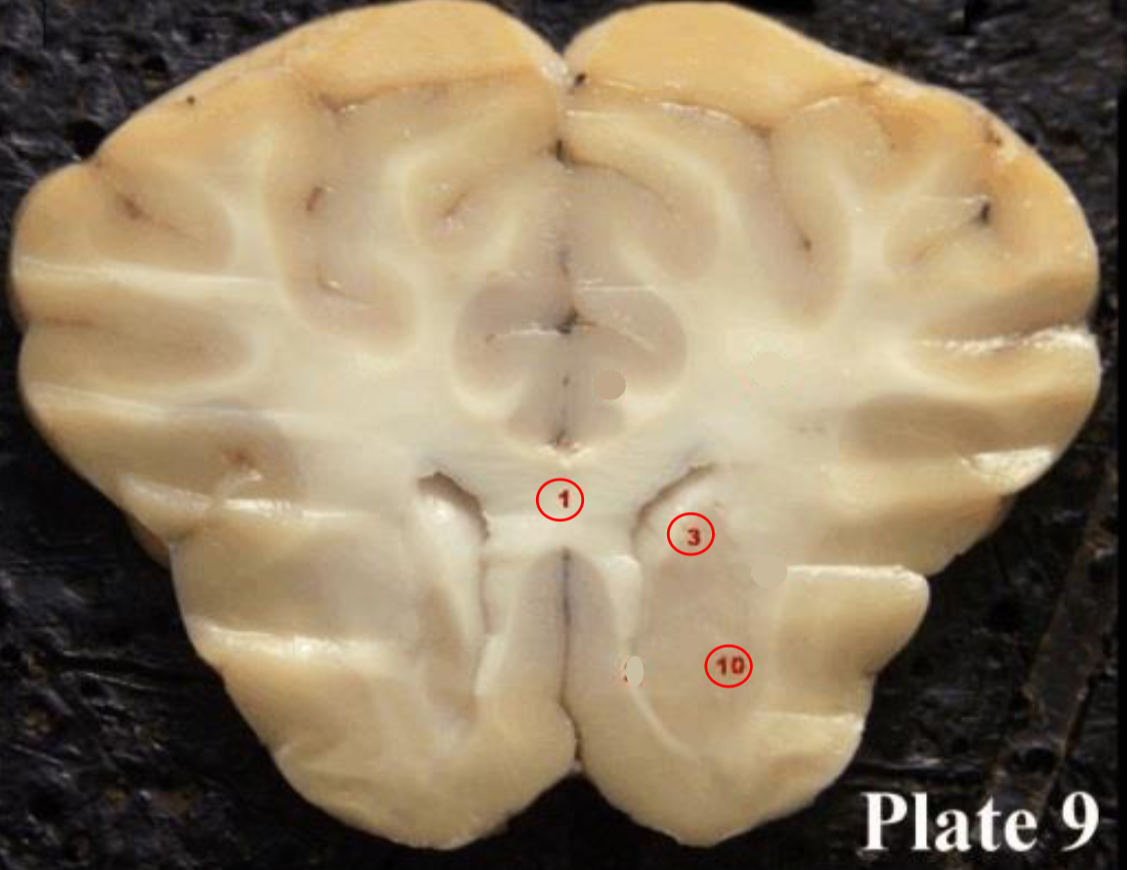
1
Corpus callosum
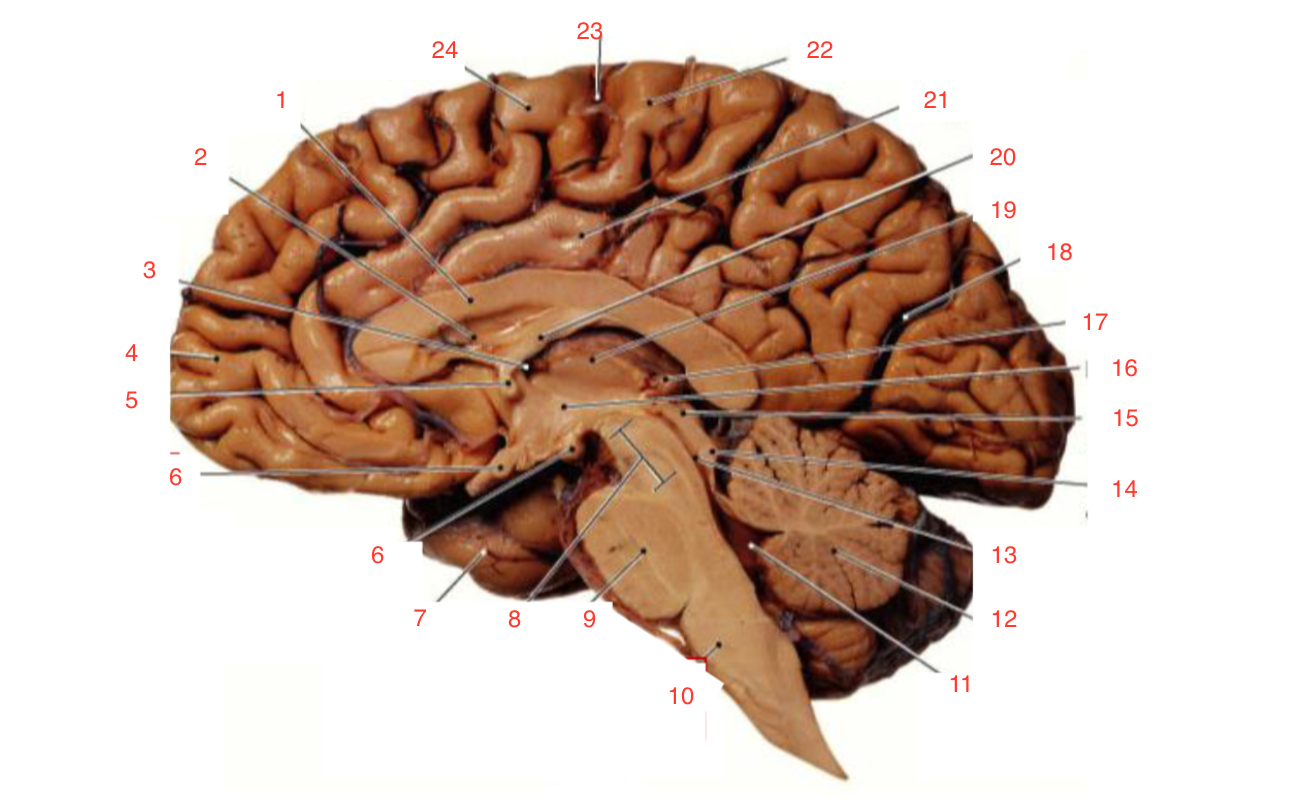
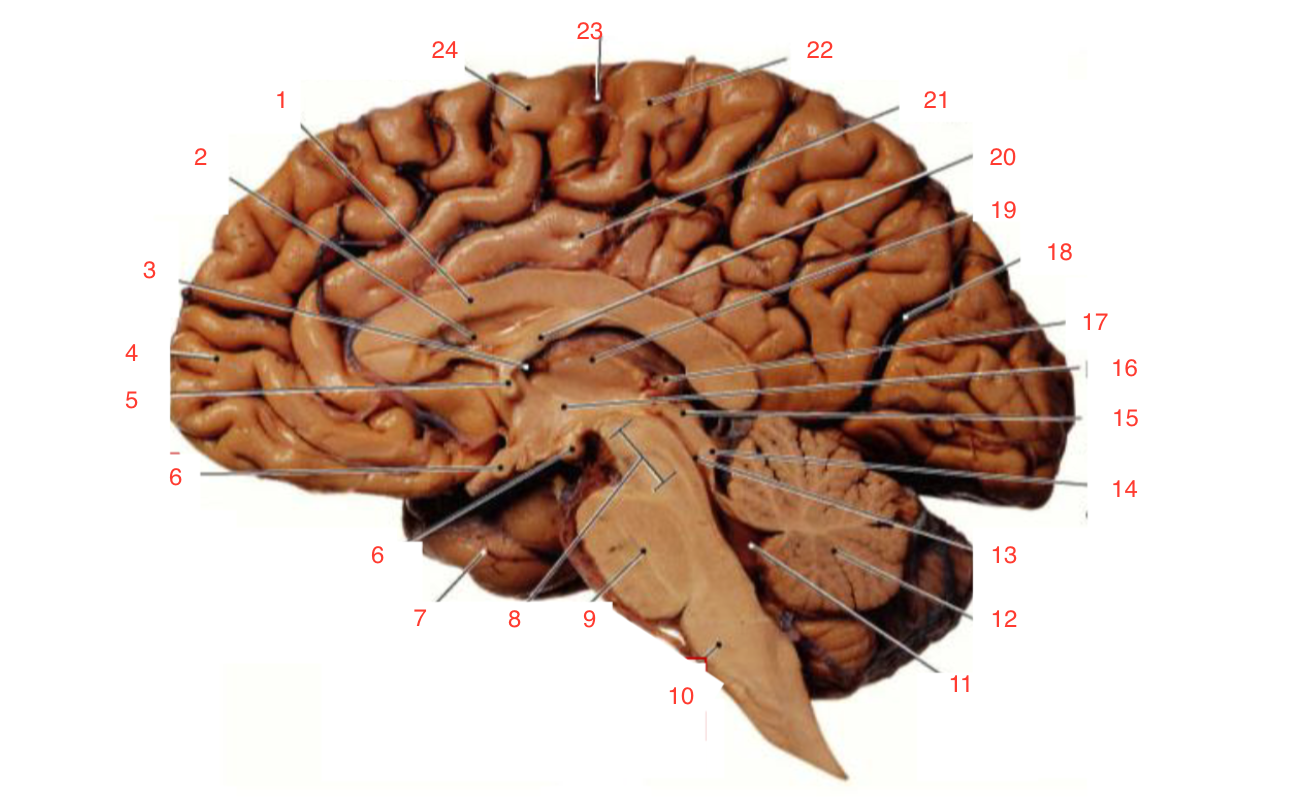
2
Lateral ventricle
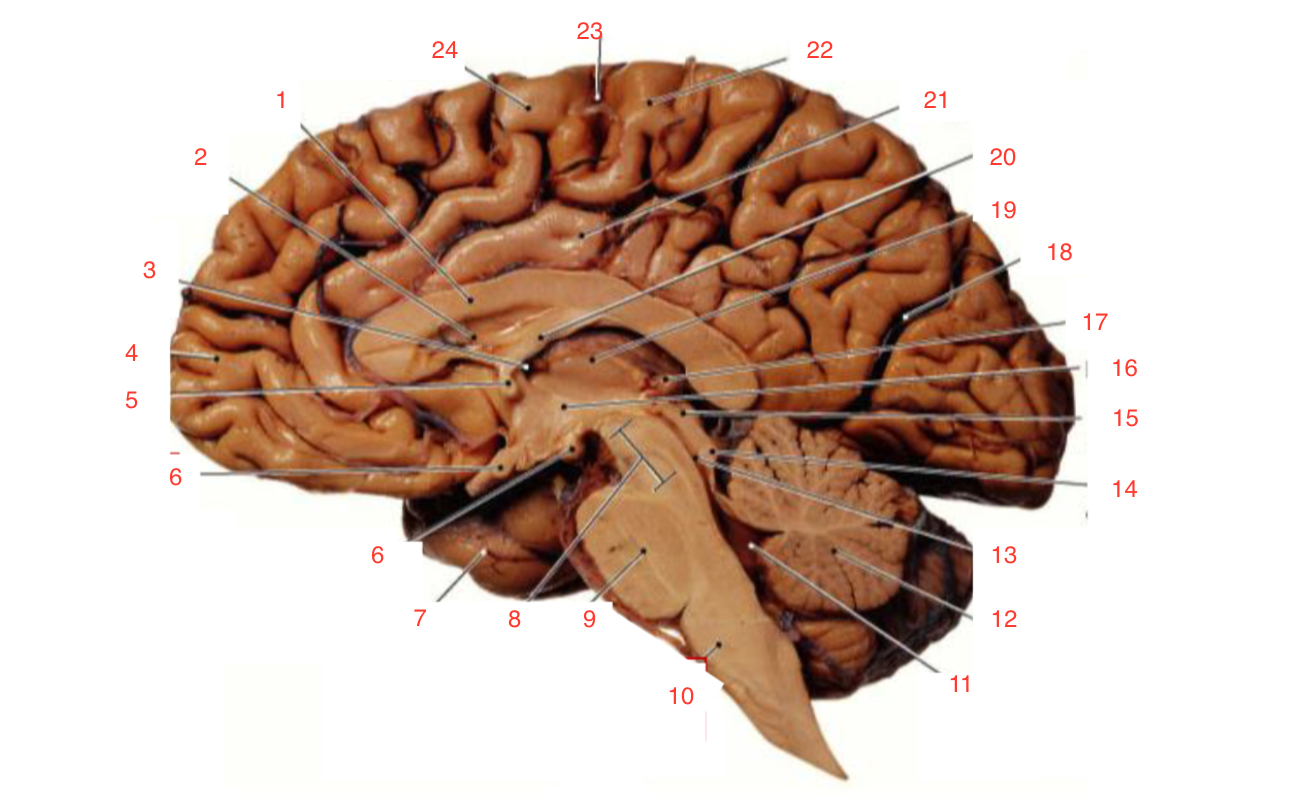
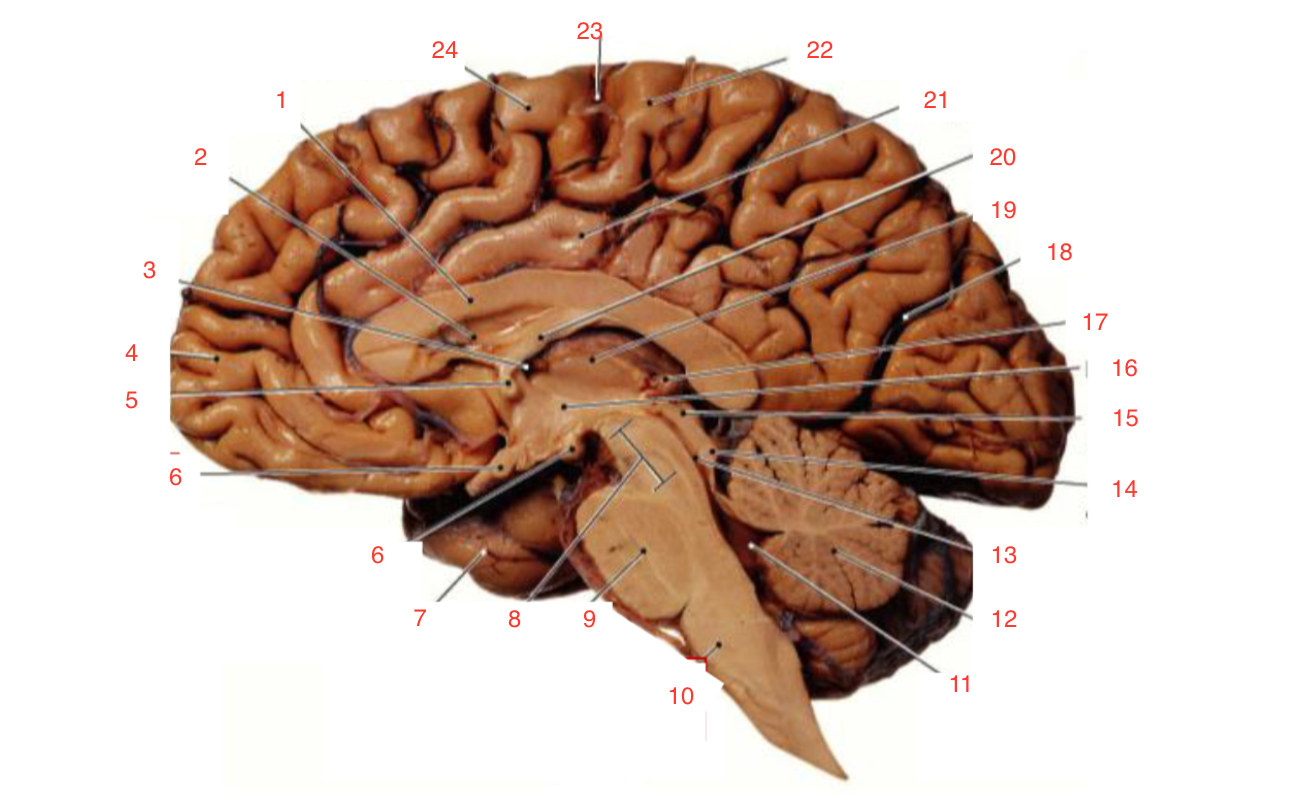
6
optic chiasm
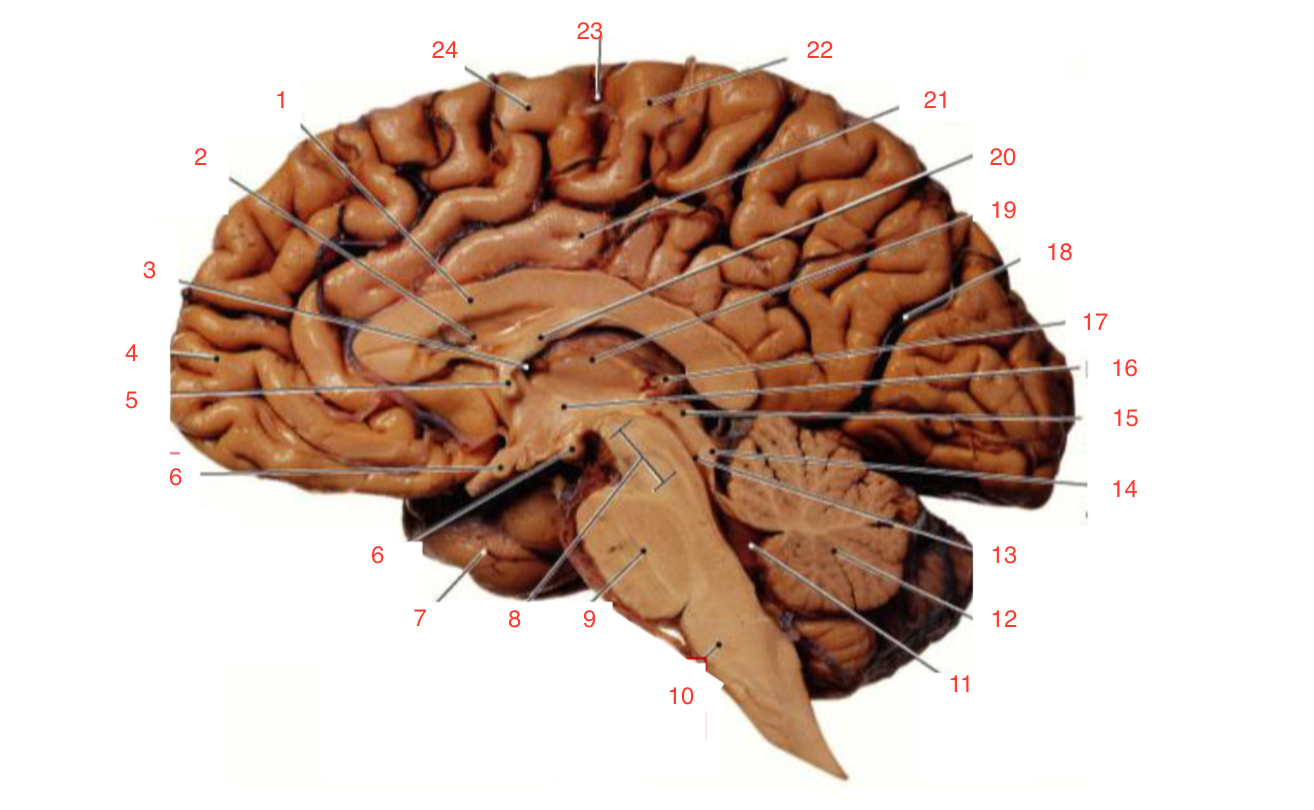
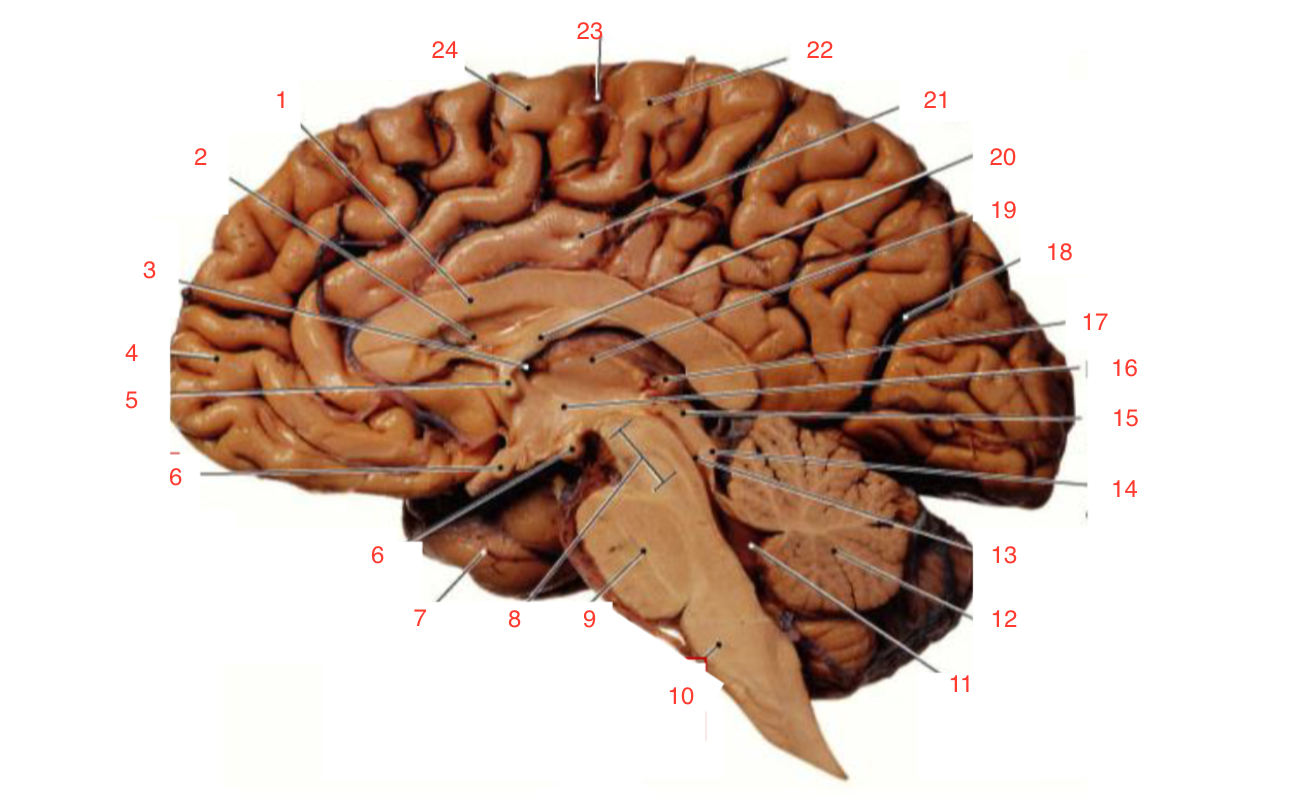
8
Midbrain (Mesencephalon)
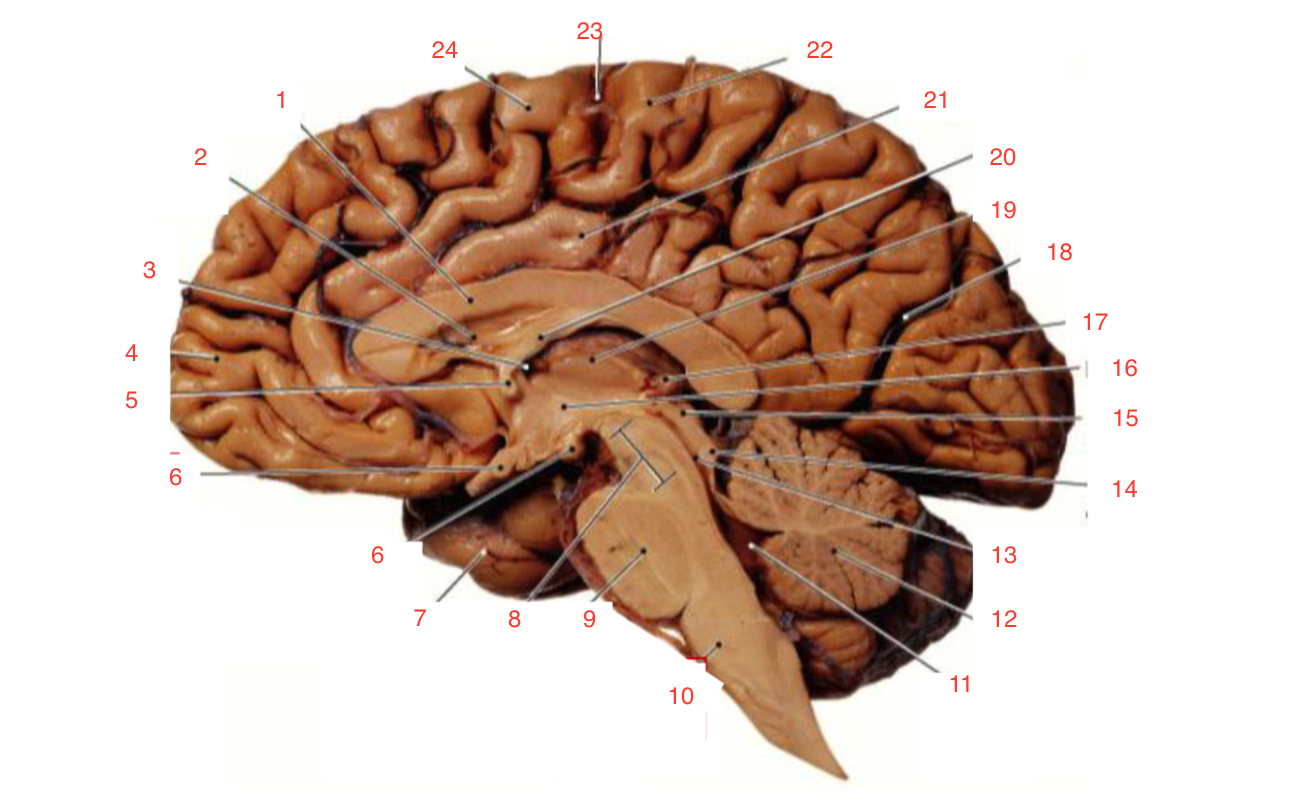
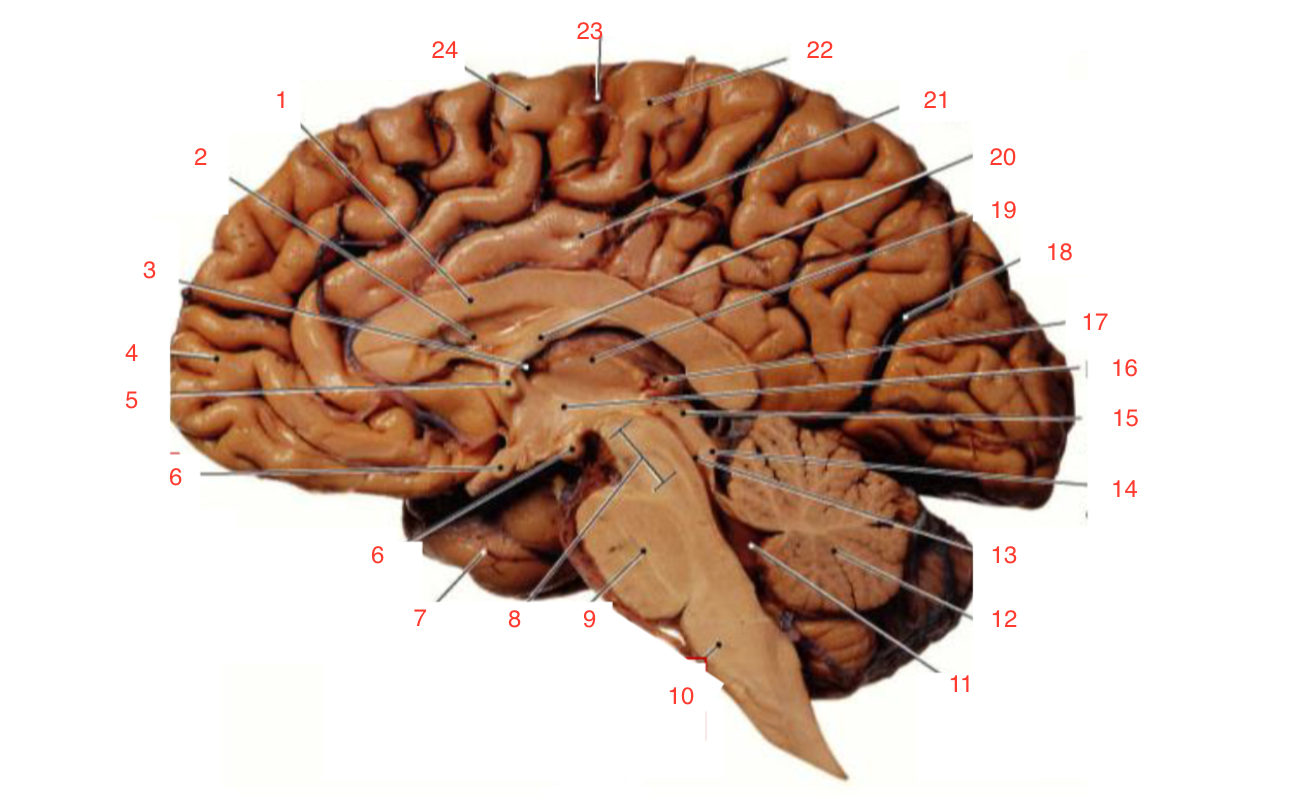
9
Pons
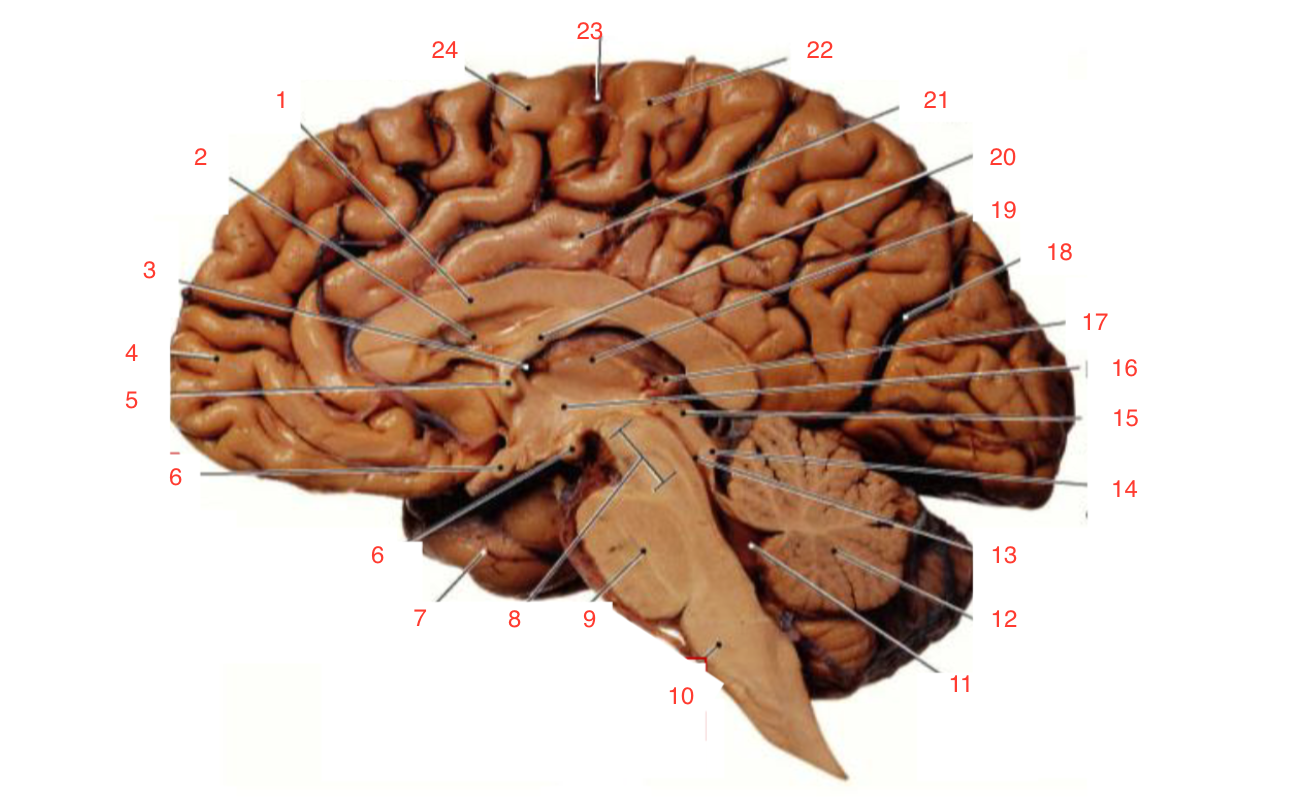
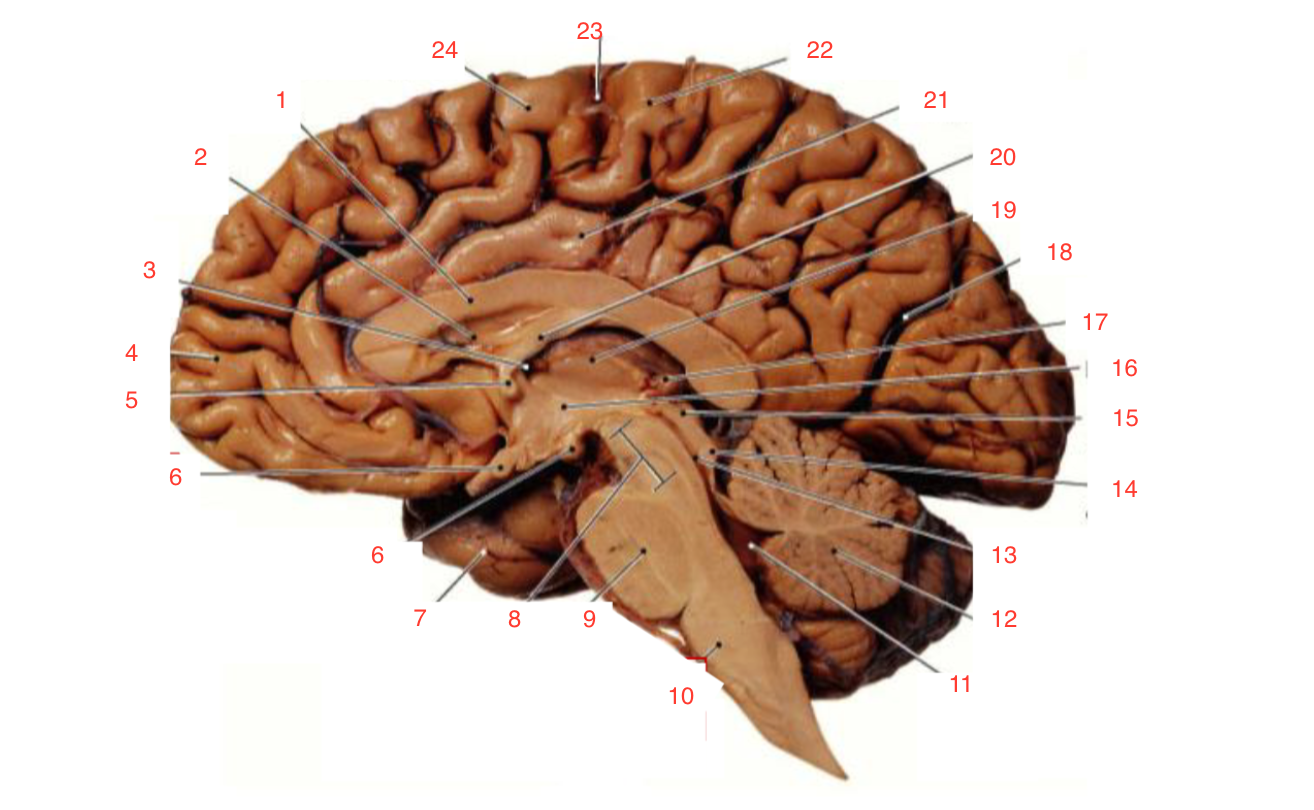
10
Medulla
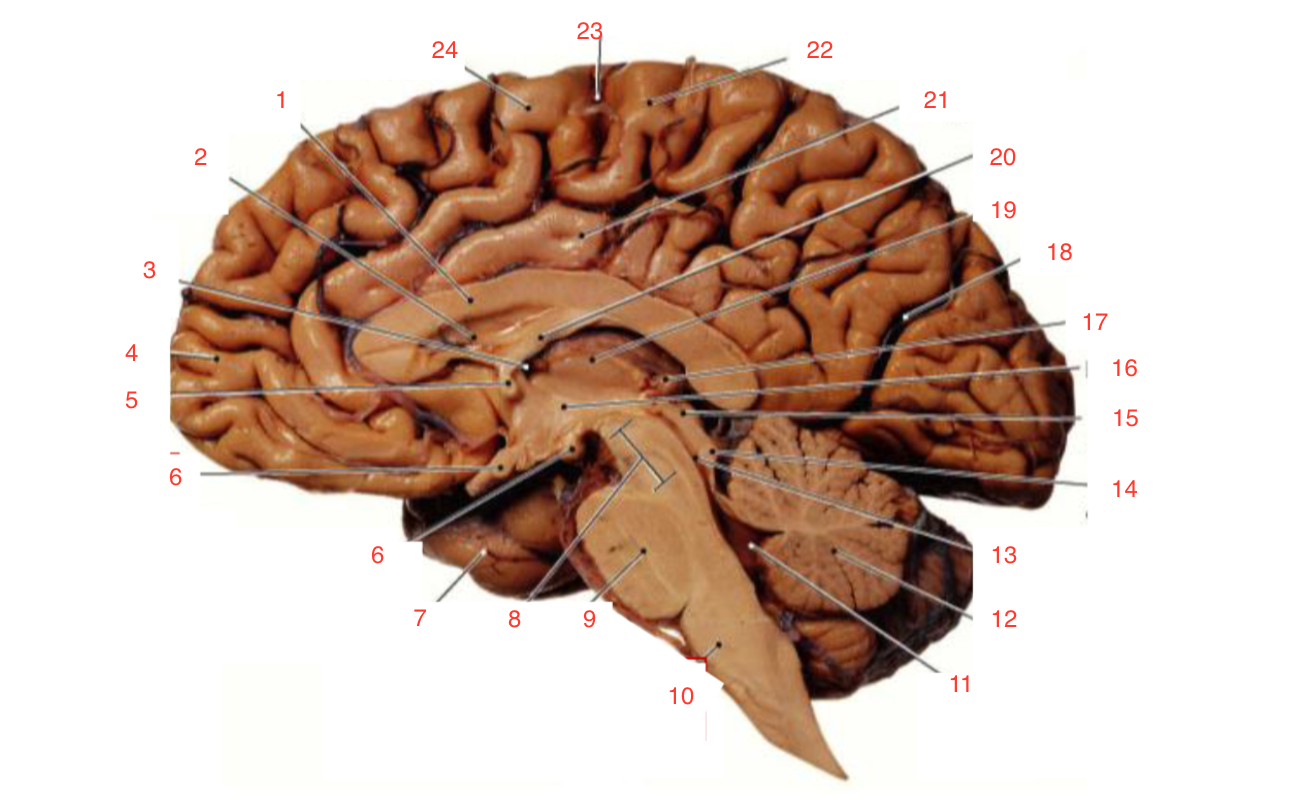
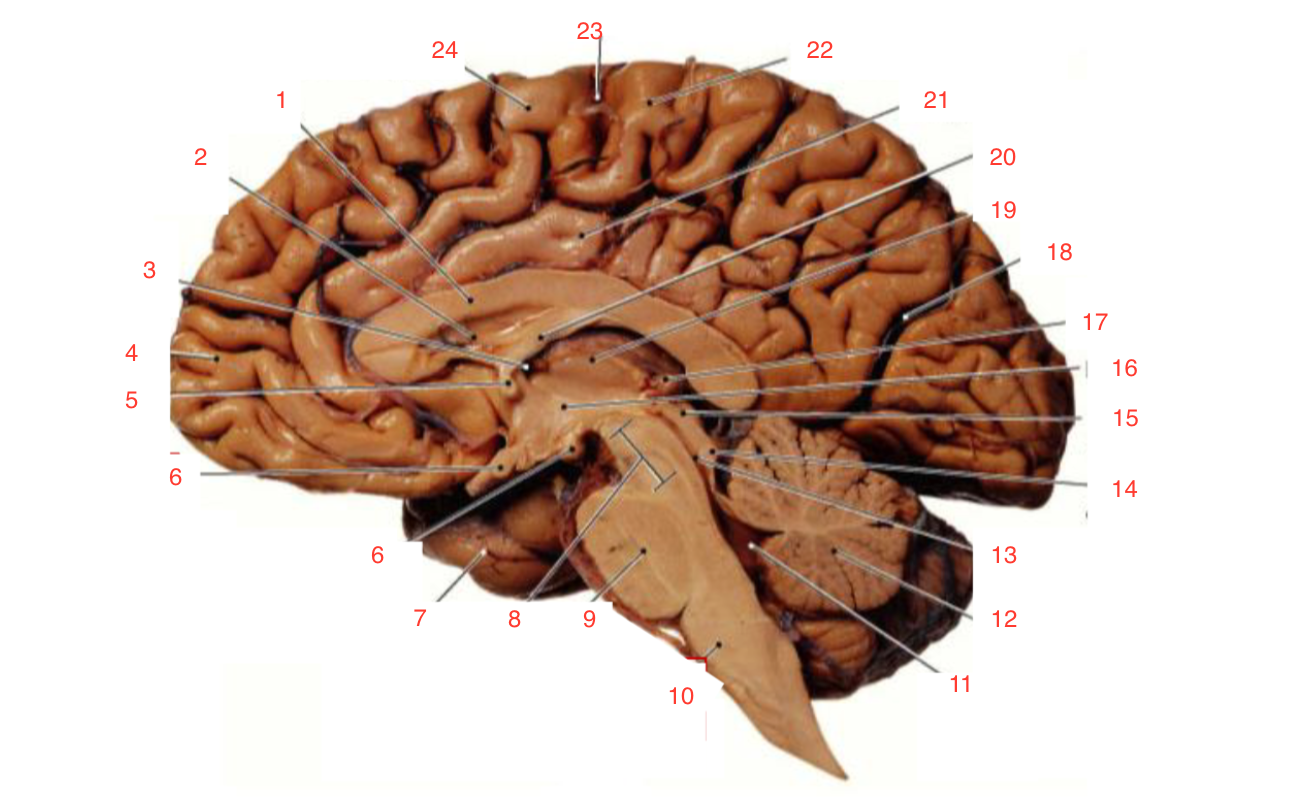
11
fourth ventricle
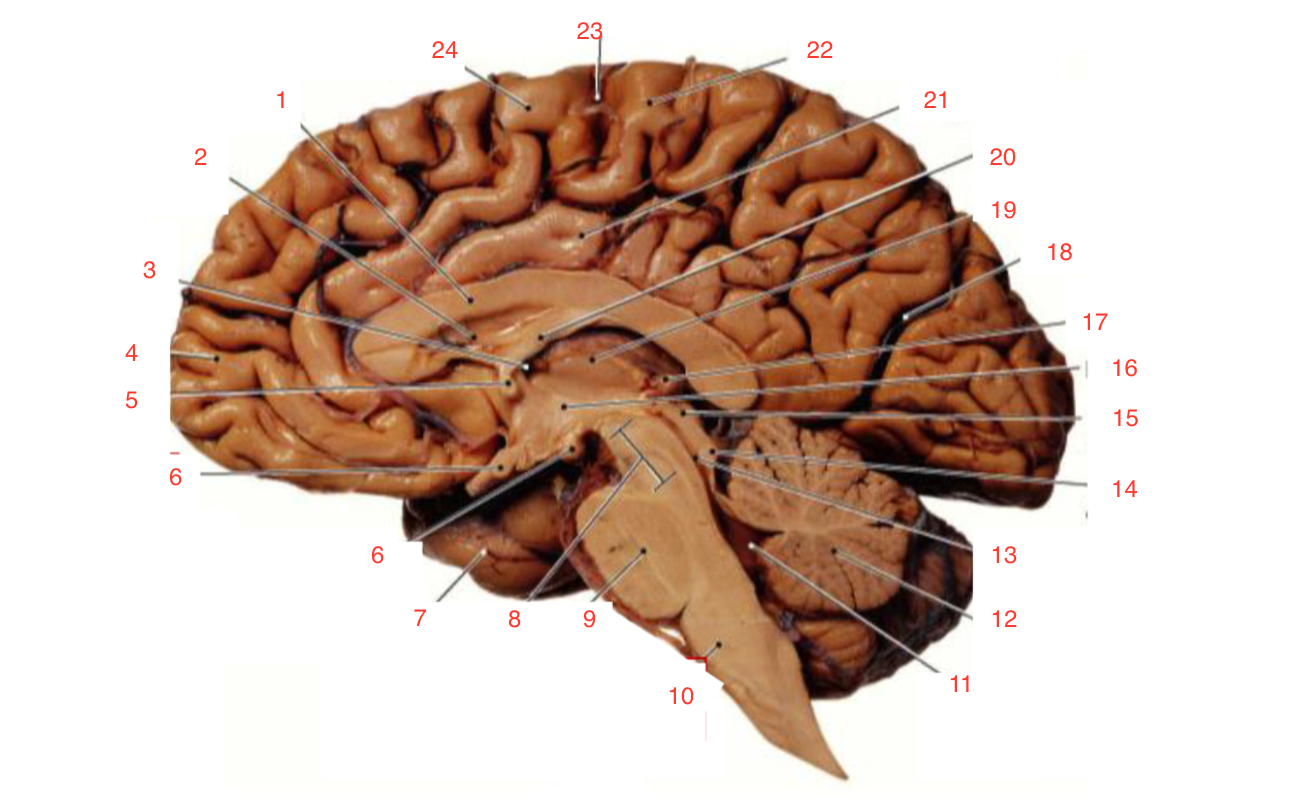
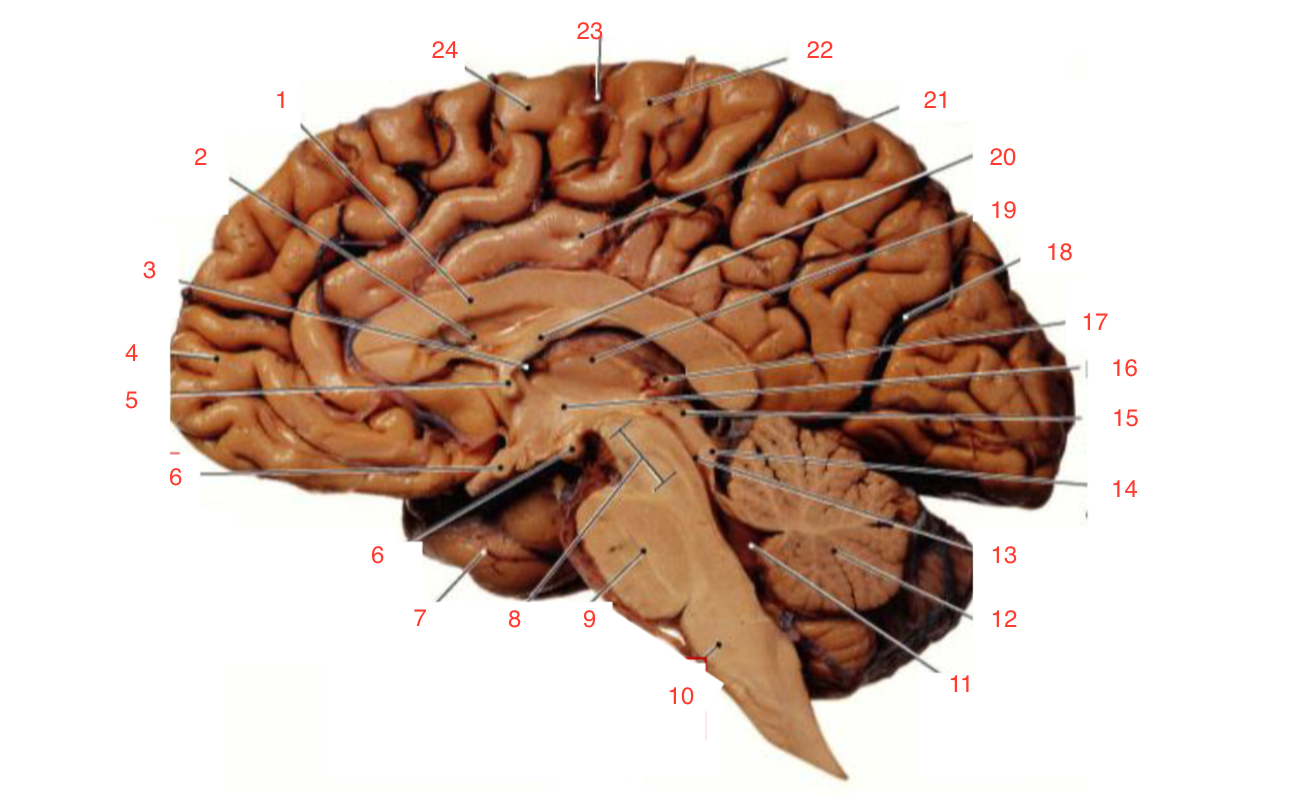
12
Cerebellum
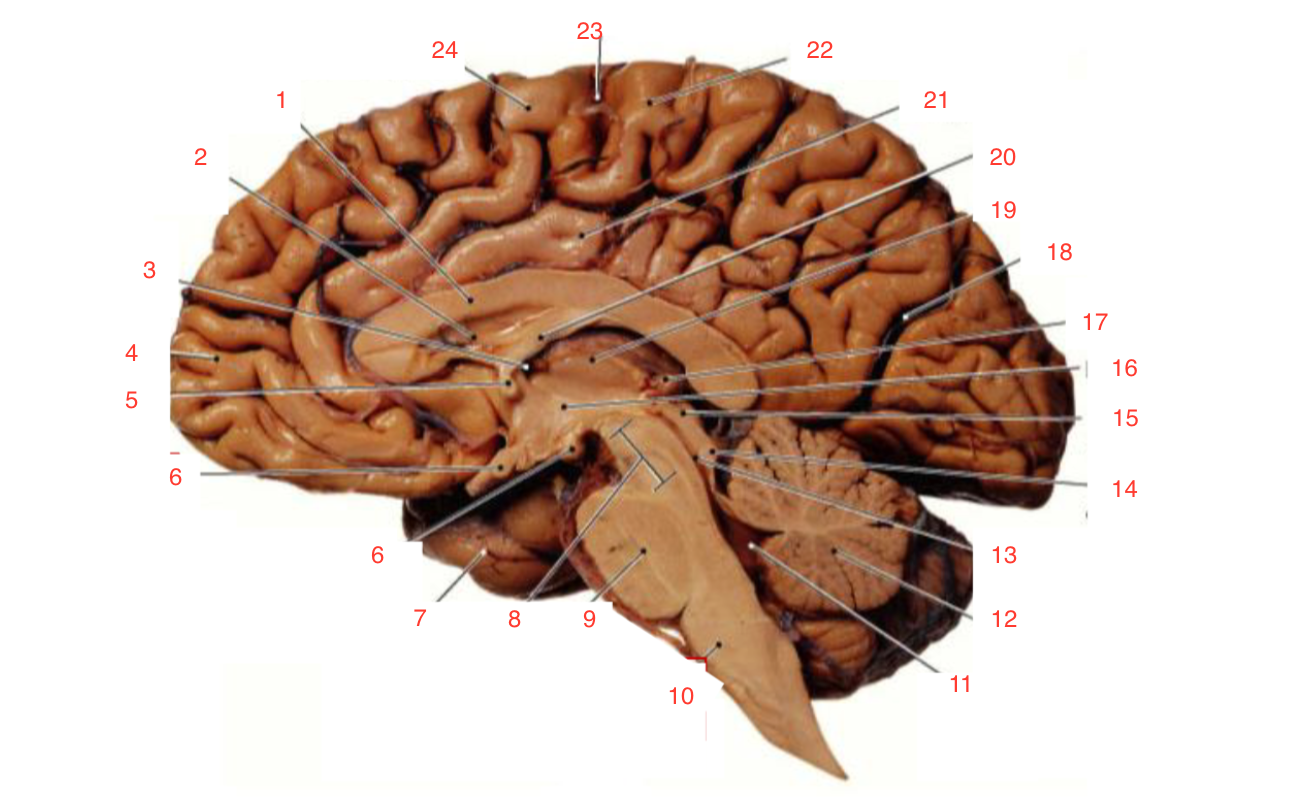
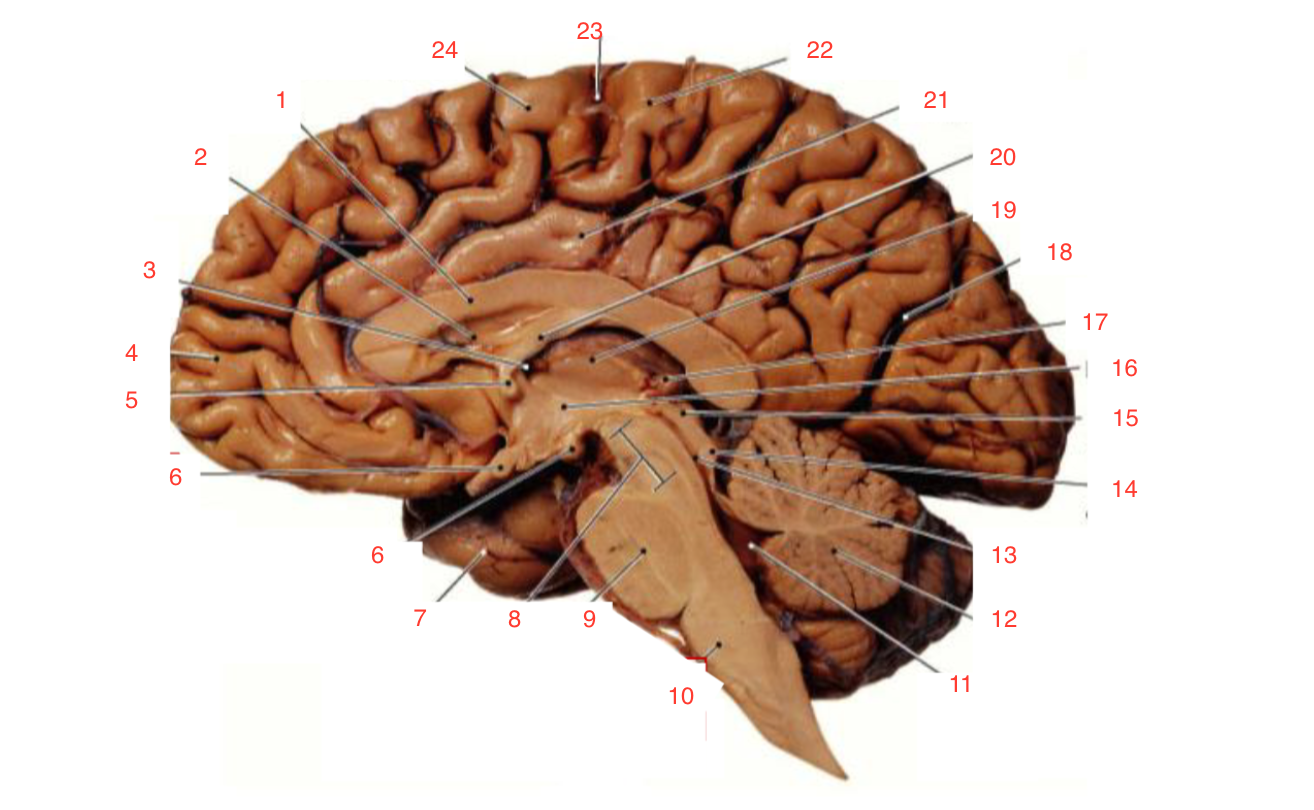
13
Cerebral aqueduct
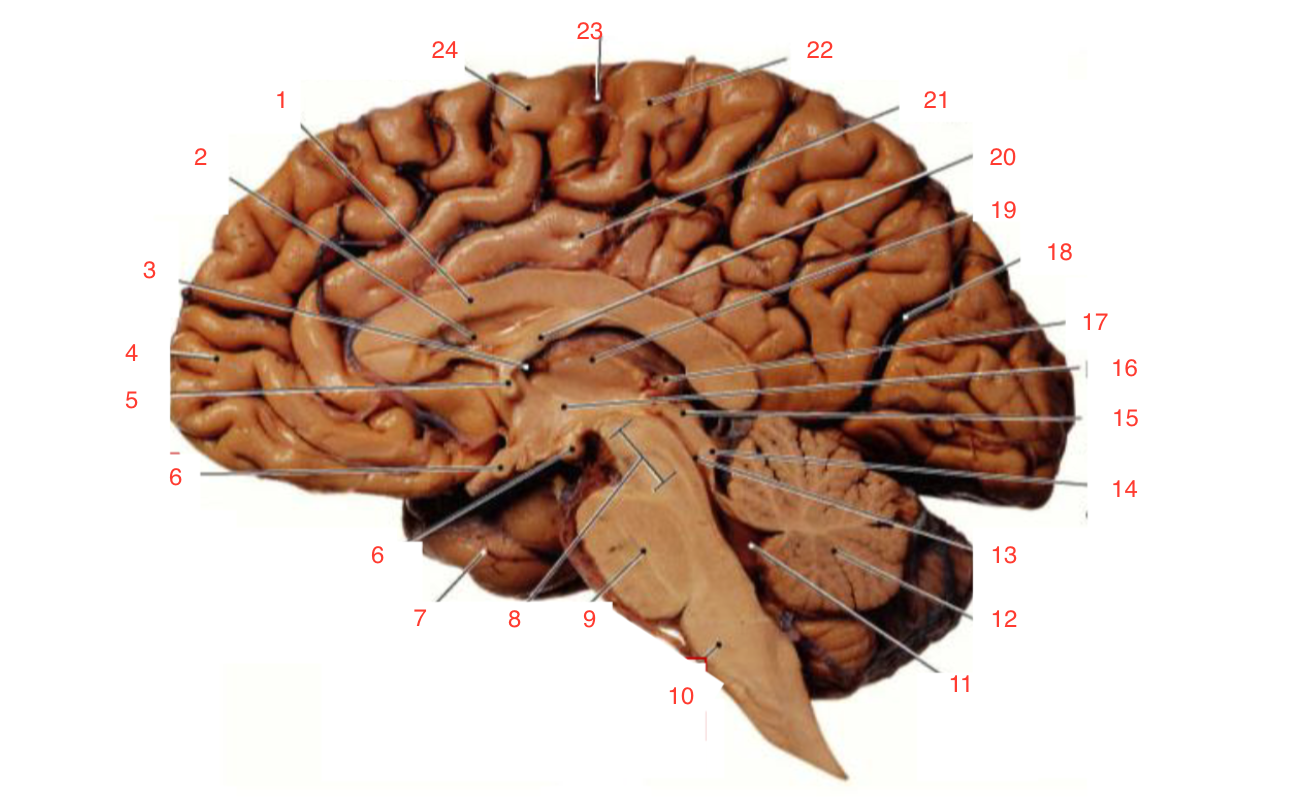
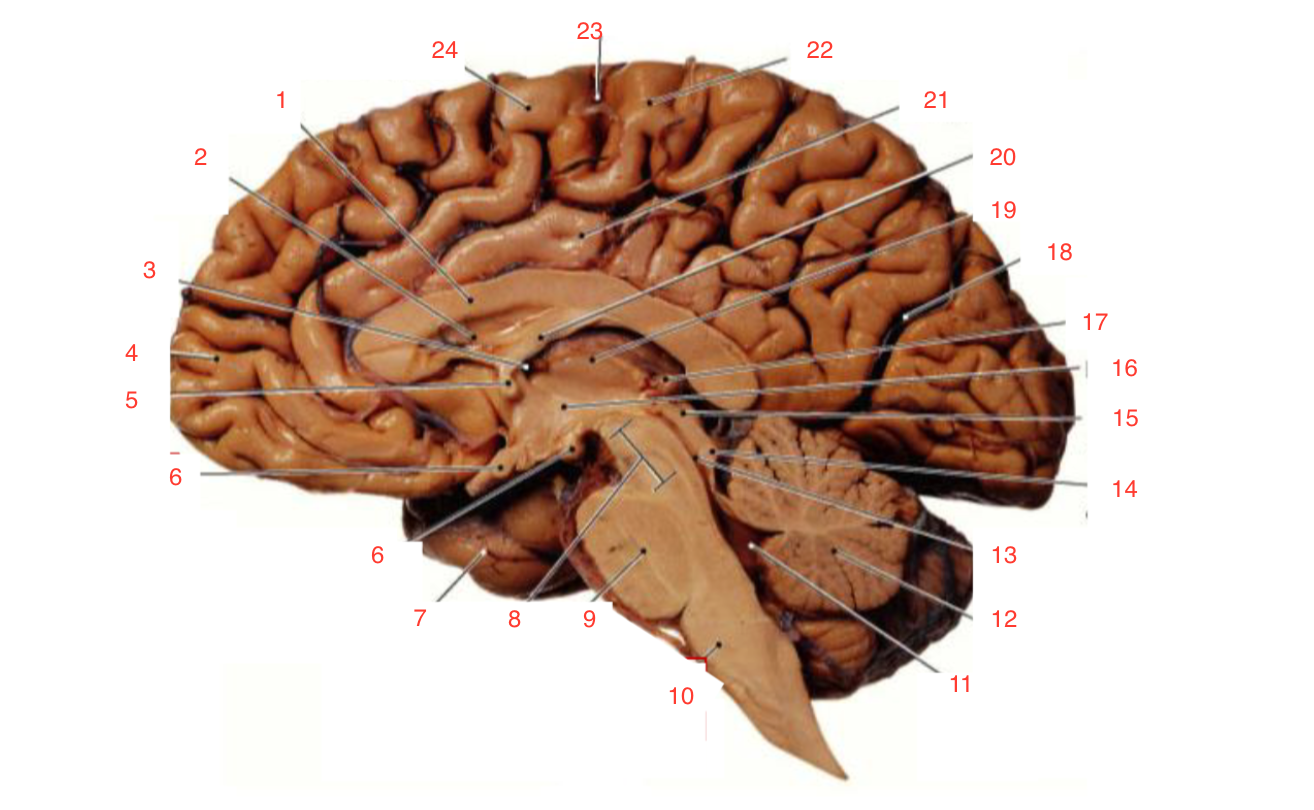
14
Inferior colliculi
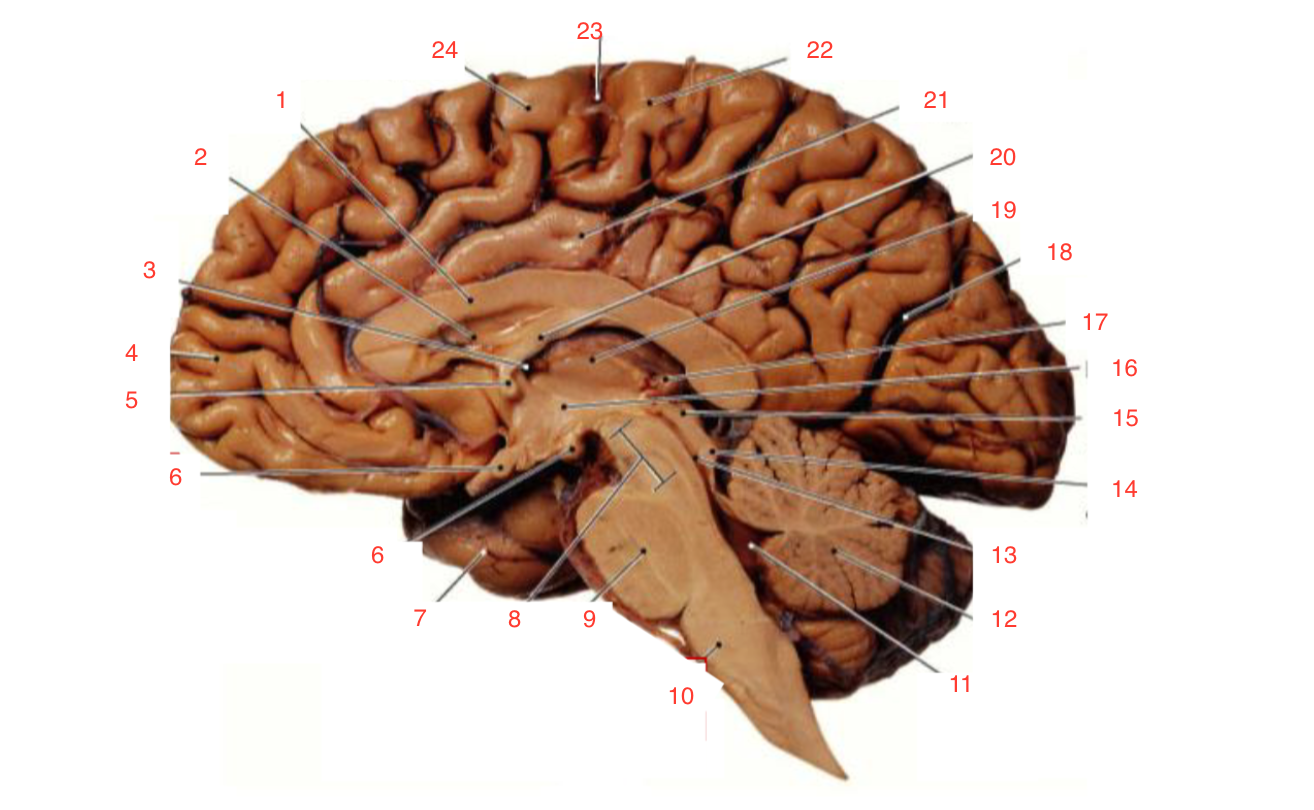
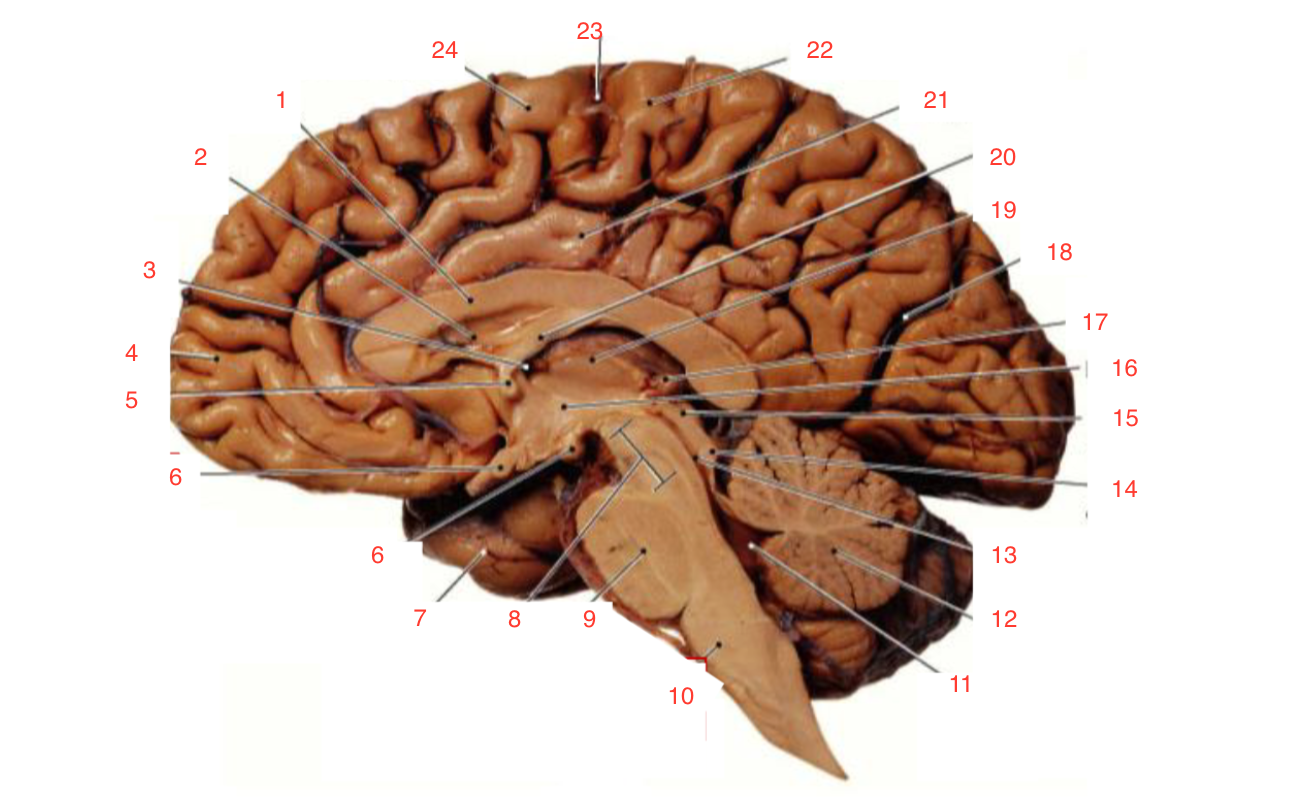
15
Superior colliculi
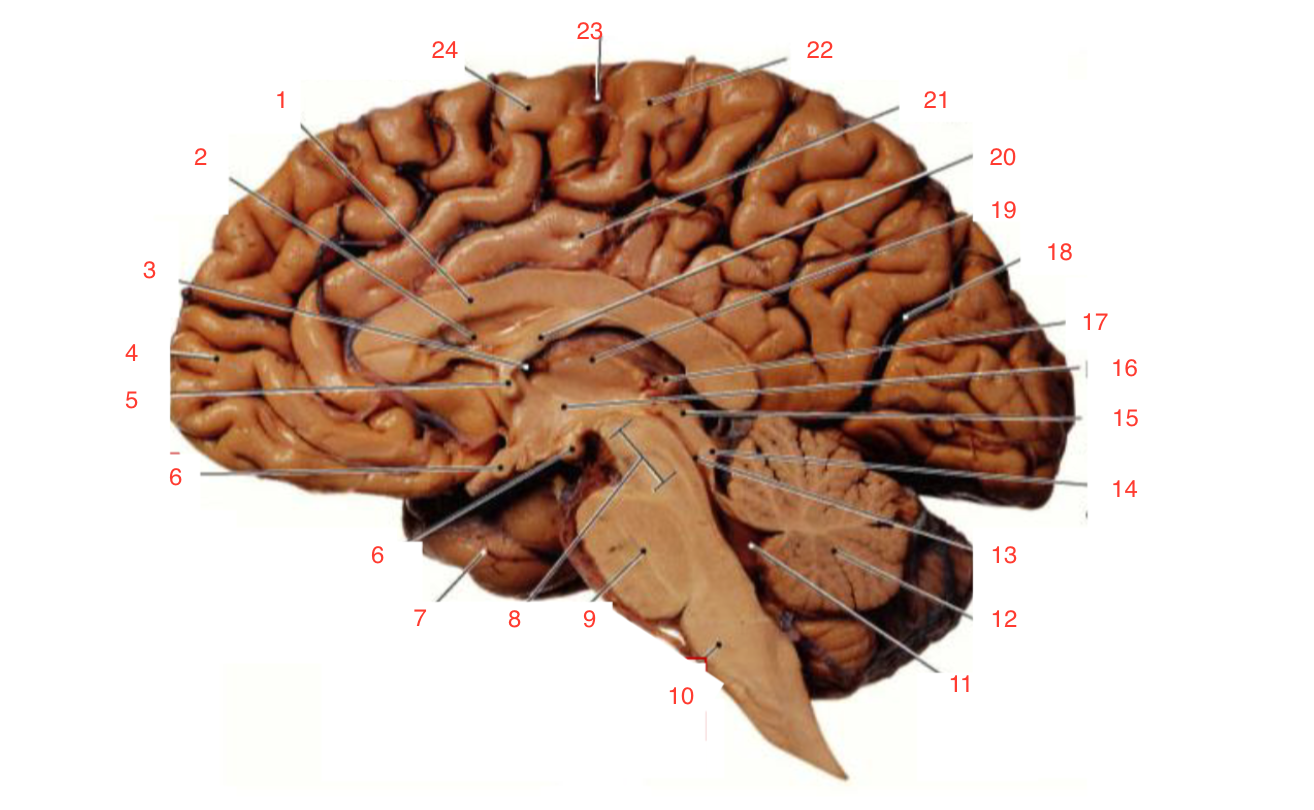
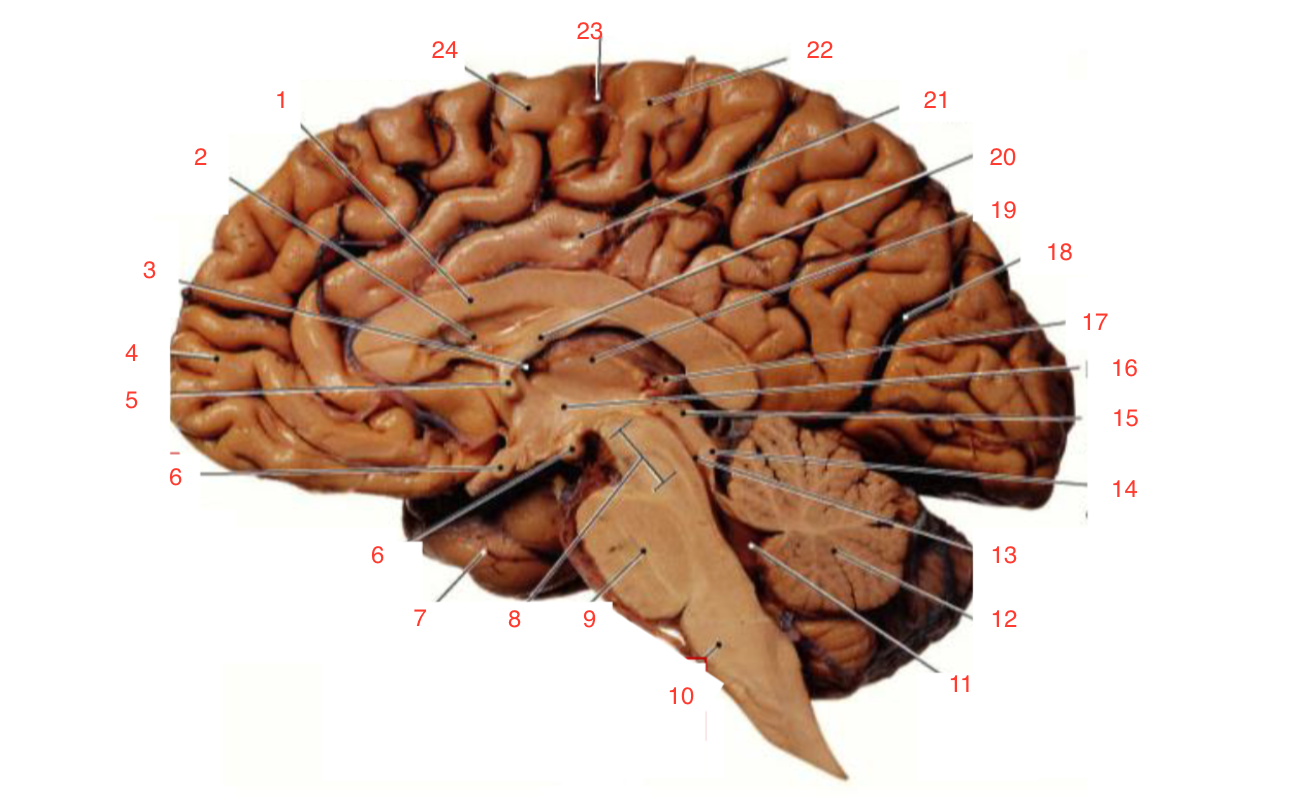
17
Pineal gland
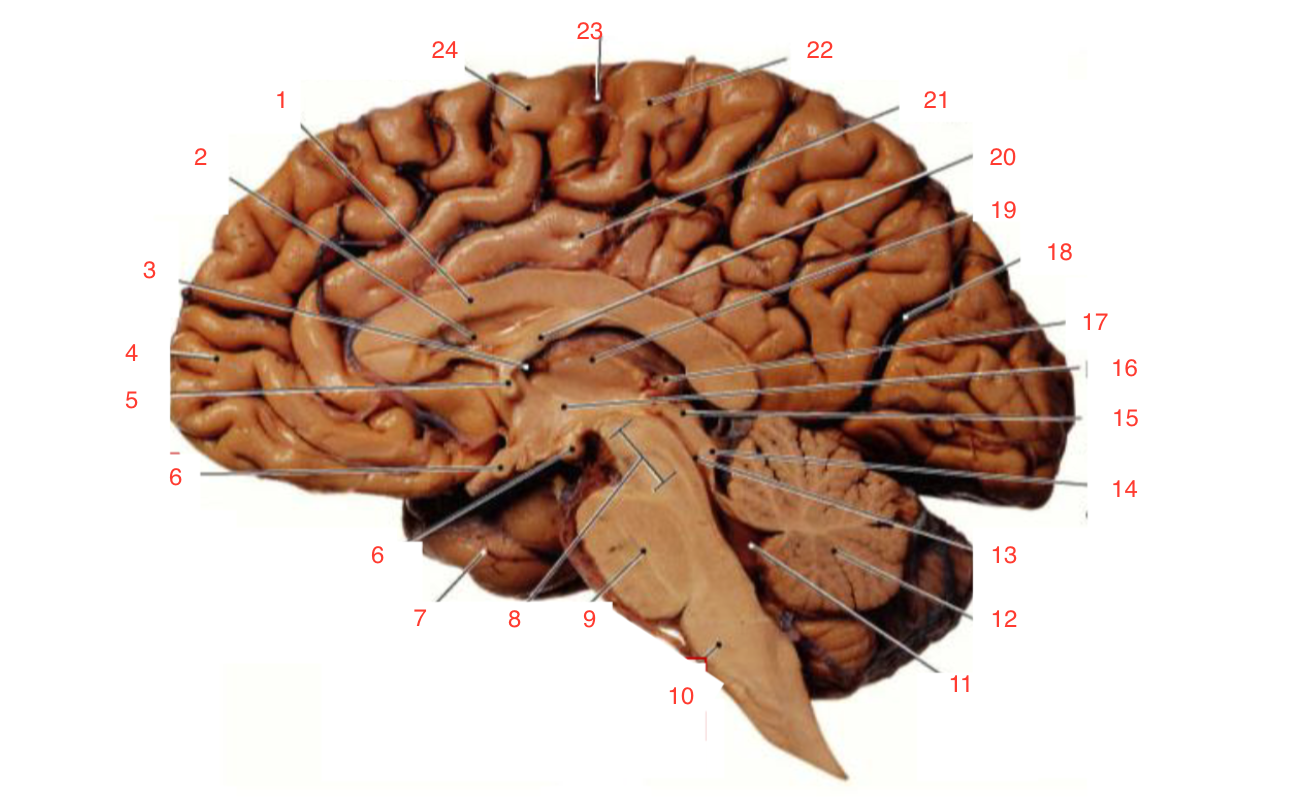
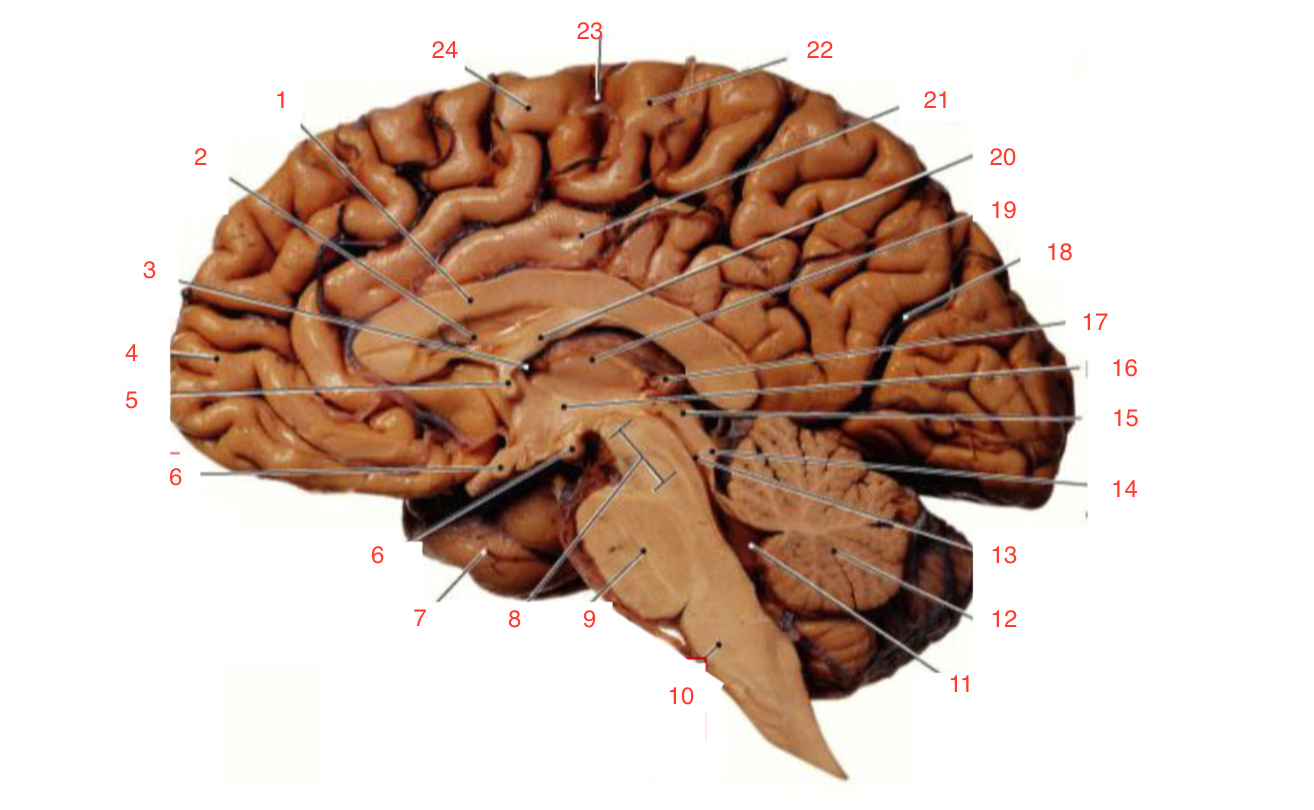
19
Right Thalamus
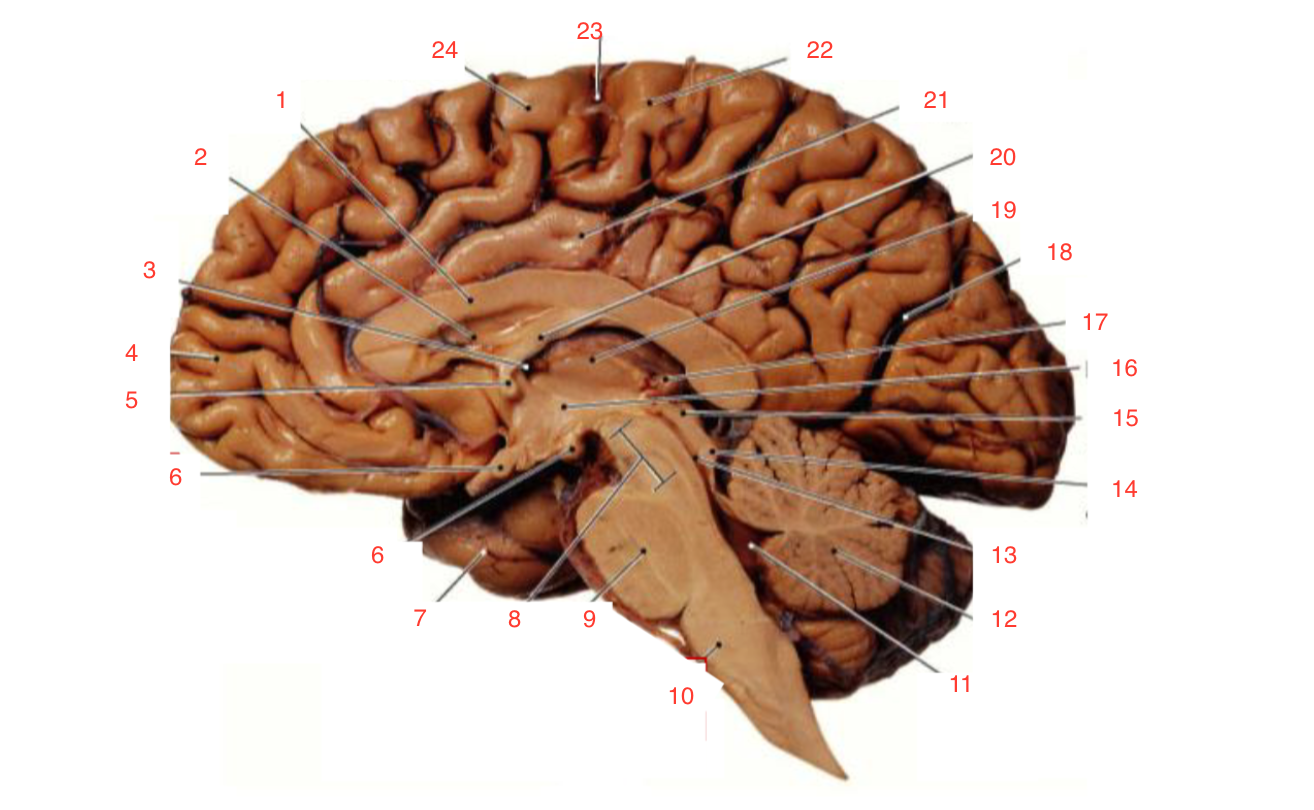
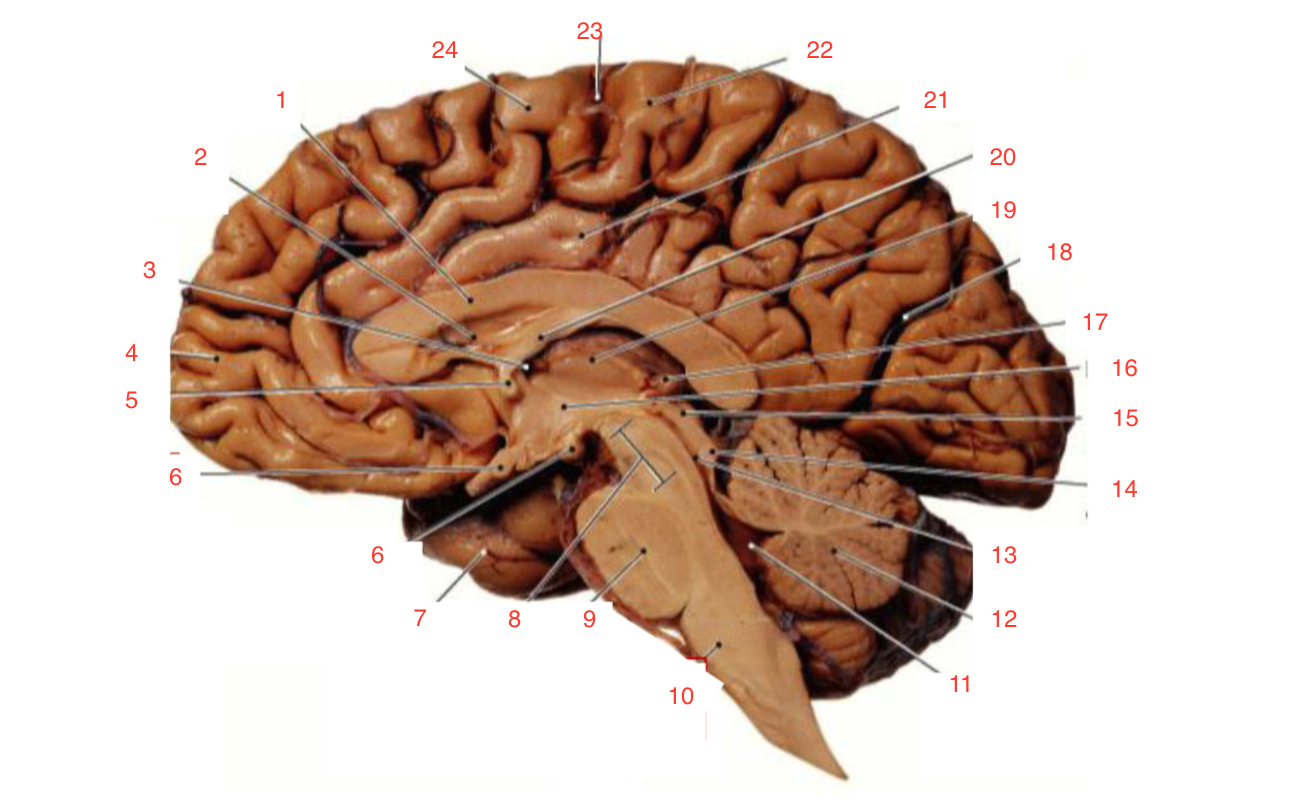
23
Central Sulcus
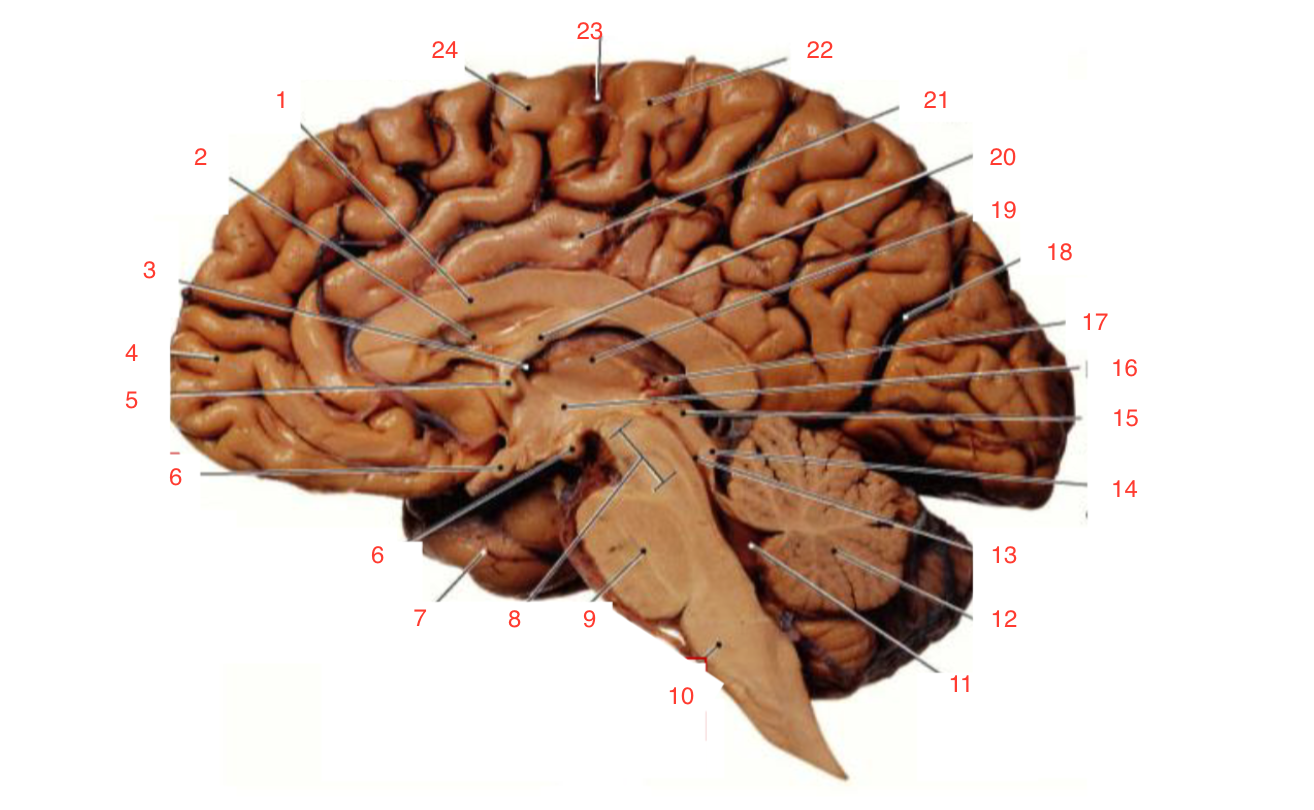
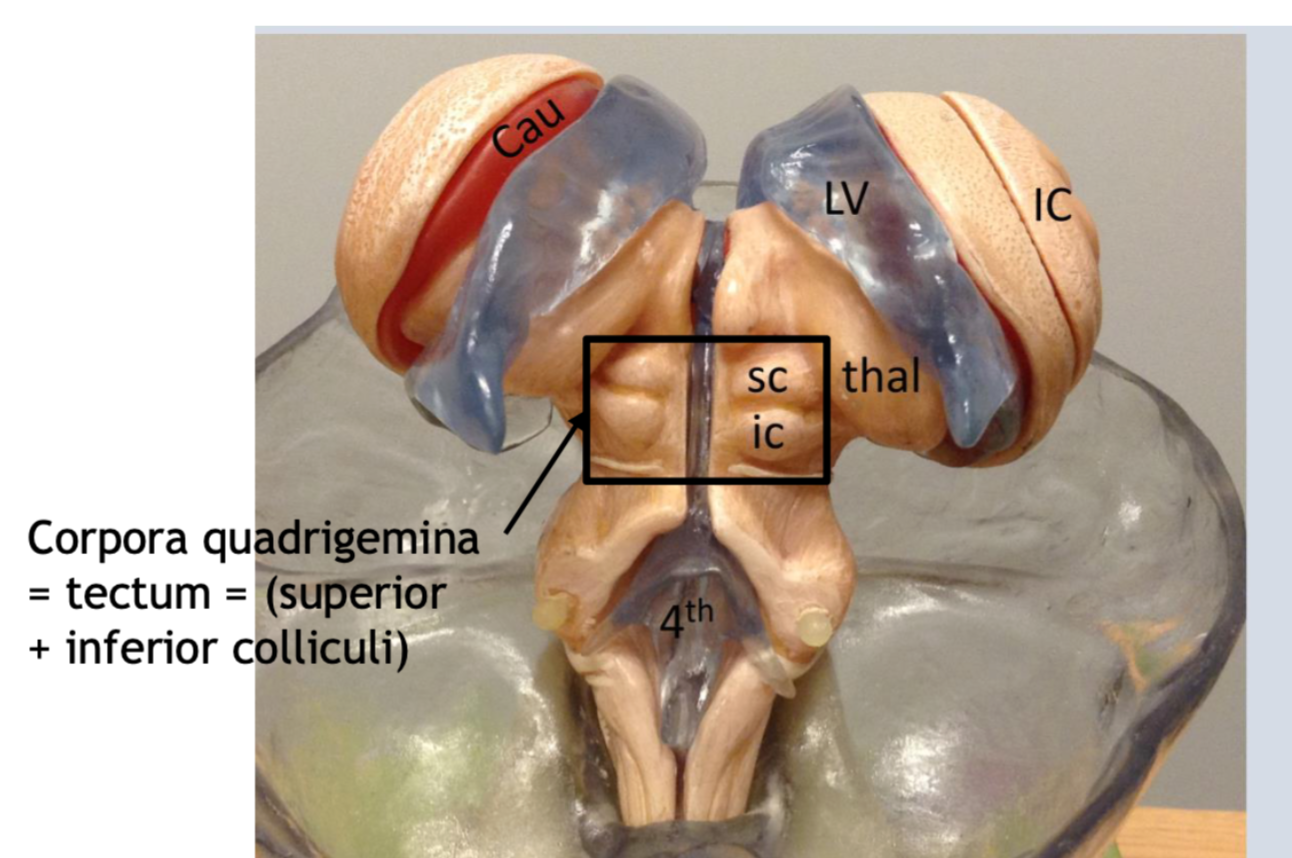
The inferior and superior colliculi
form the tectum which is part of the
midbrain (mesencephalon) involved in vision and hearing

pineal gland
It is part of the endocrine system
and produces melatonin, which helps maintain
circadian rhythm and regulates reproductive hormones
ventricular system
Includes the cerebellum and 4th ventricle. circulates the cerebrospinal fluid throughout the brain and spinal cord.
cerebrum
cerebrum is subdivided into lobes with specialized functions. As a whole it is responsible for controlling voluntary
actions, emotions, hearing, vision, personality and much more.
cerebellum
plays an important
role in motor control and cognitive functions such as attention, language, and emotional responses
brain stem
This area is made up of the medulla, pons, and midbrain (midbrain also known as the
mesencephalon). controls breathing, swallowing, heart rate, blood pressure, and wakefulness.
Infundibulum
part of the endocrine system and produces hormones that control metabolism, growth, sexual function, sleep, and
mood
olfactory bulbs
everal important
parts of the visual system are visible in the central view of the brain: optic nerve meet in the optic chiasm. After
the optic chiasm, visual information proceeds along the optic tract towards the visual cortex
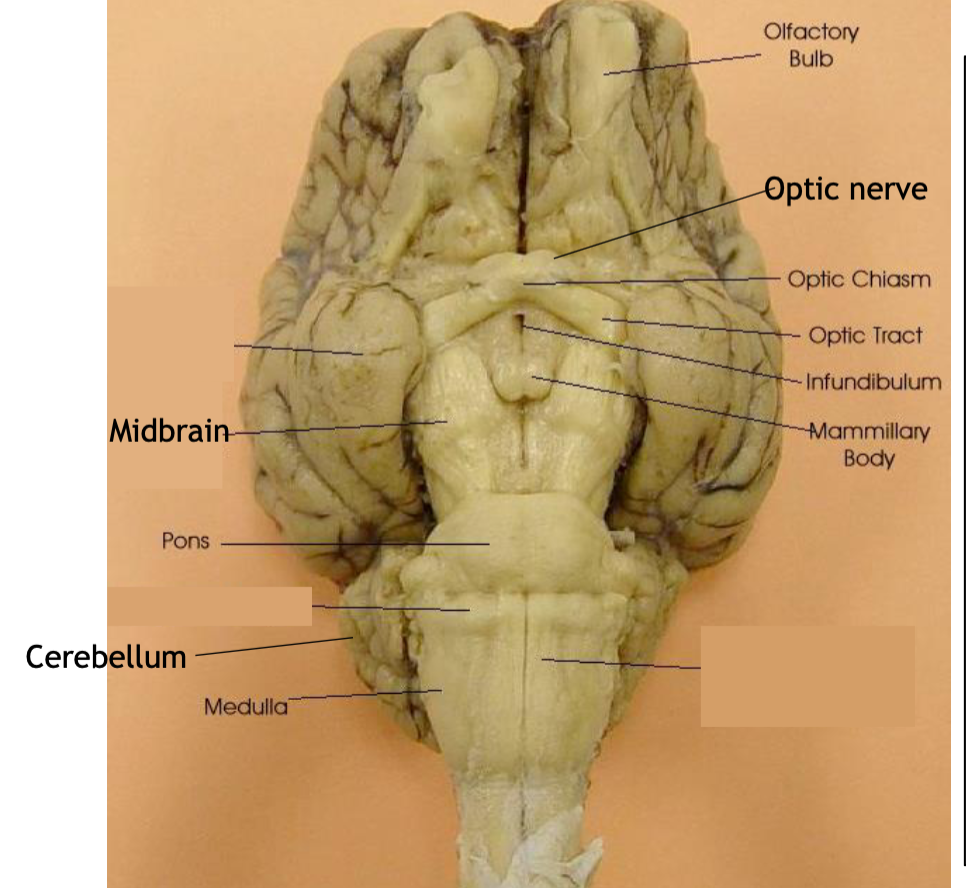
mammillary bodies
part of the limbic system and play a
role in memory.
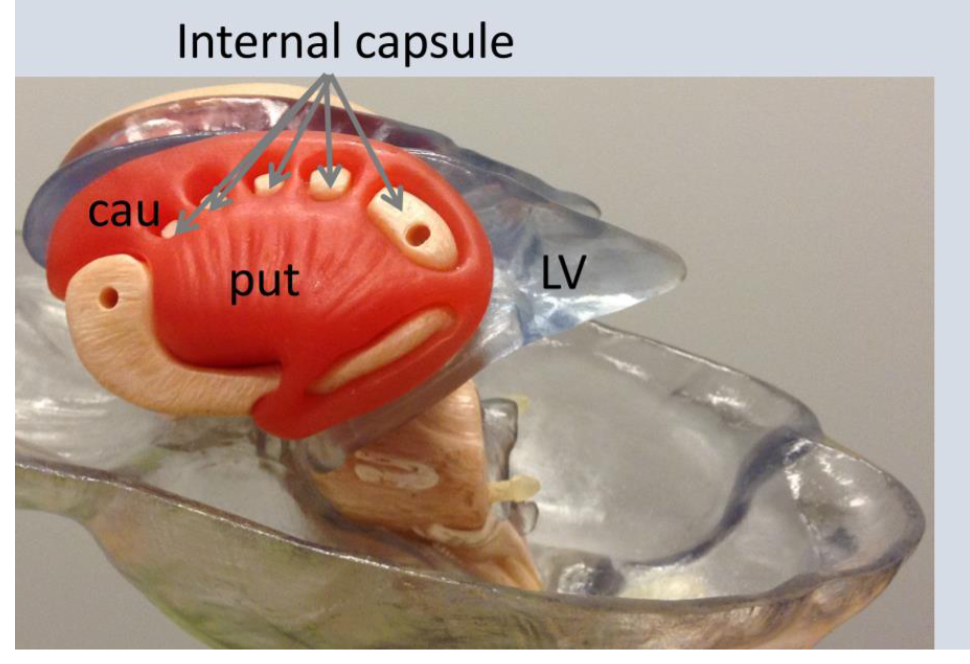
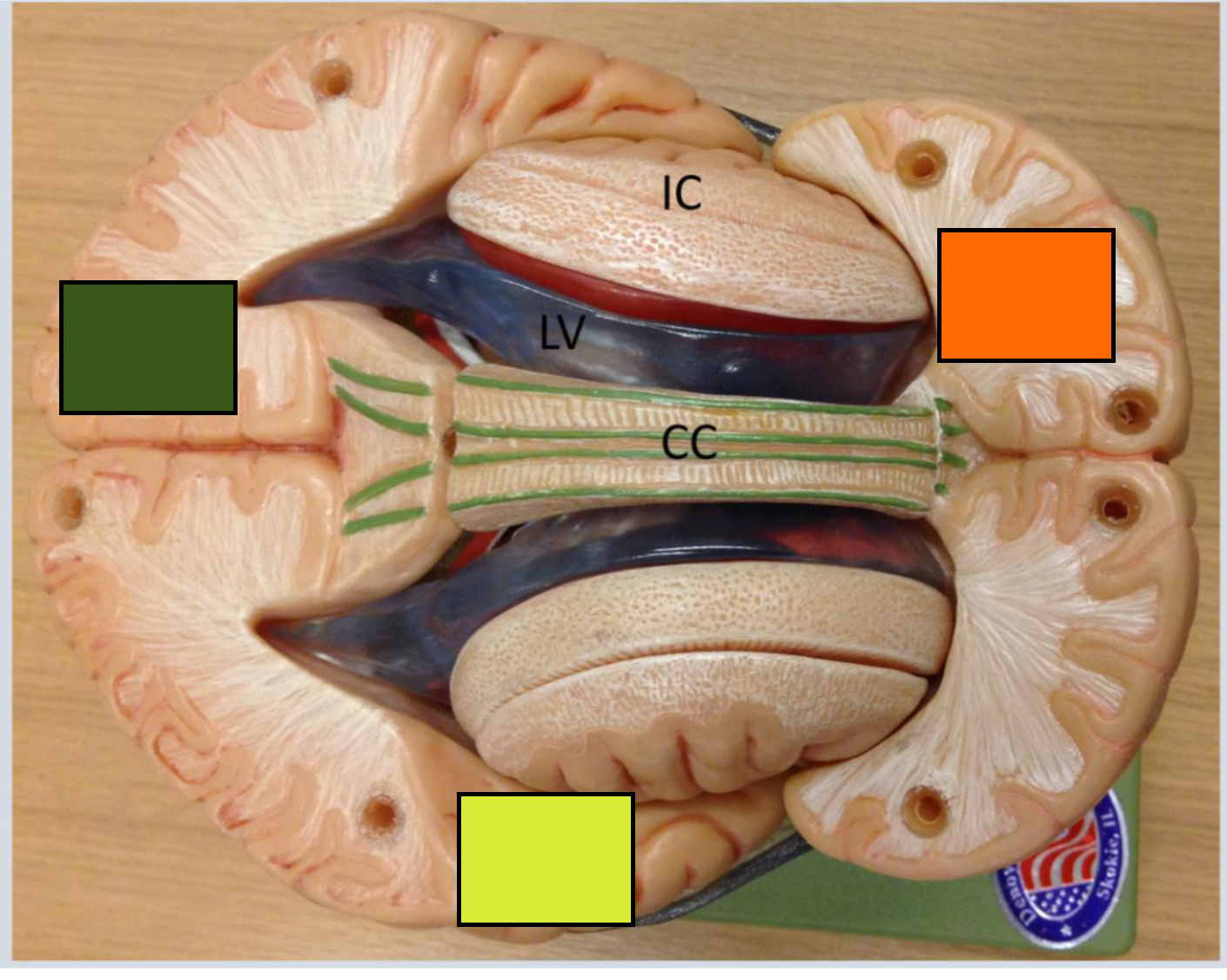
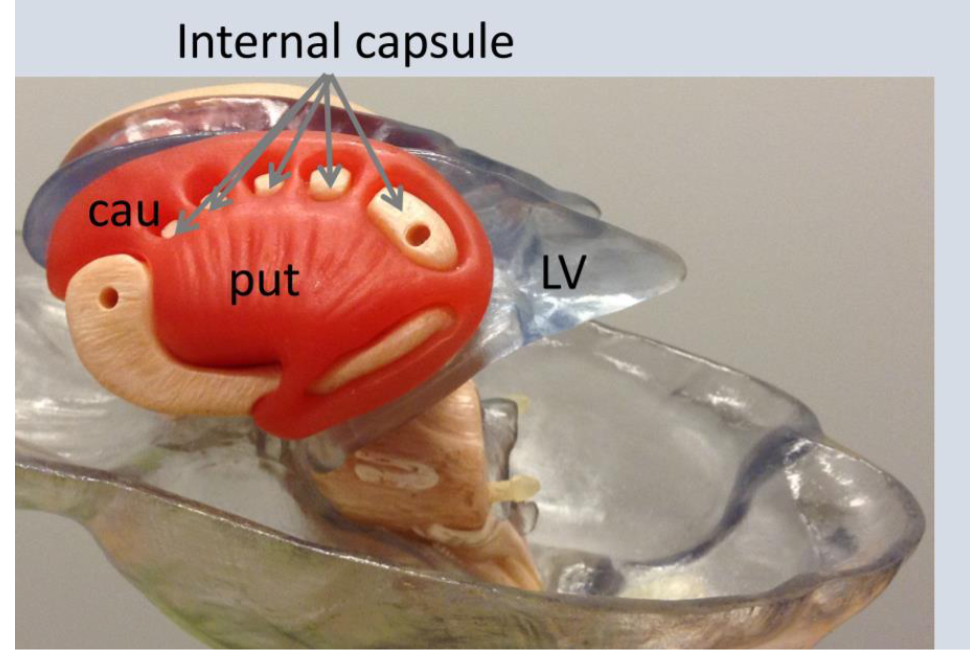
what is CAU?
Caudite nucleus
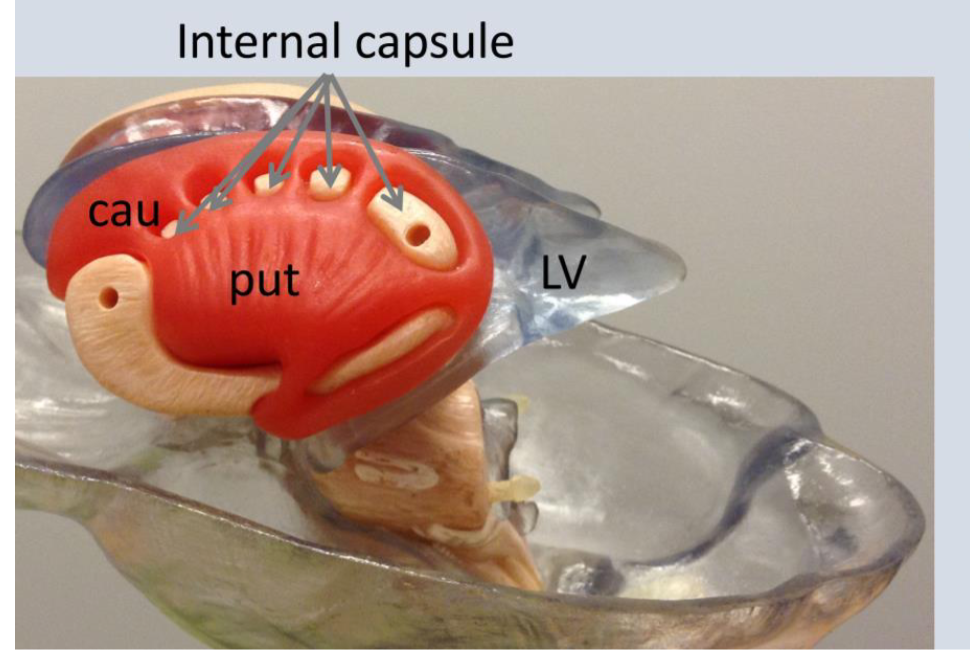
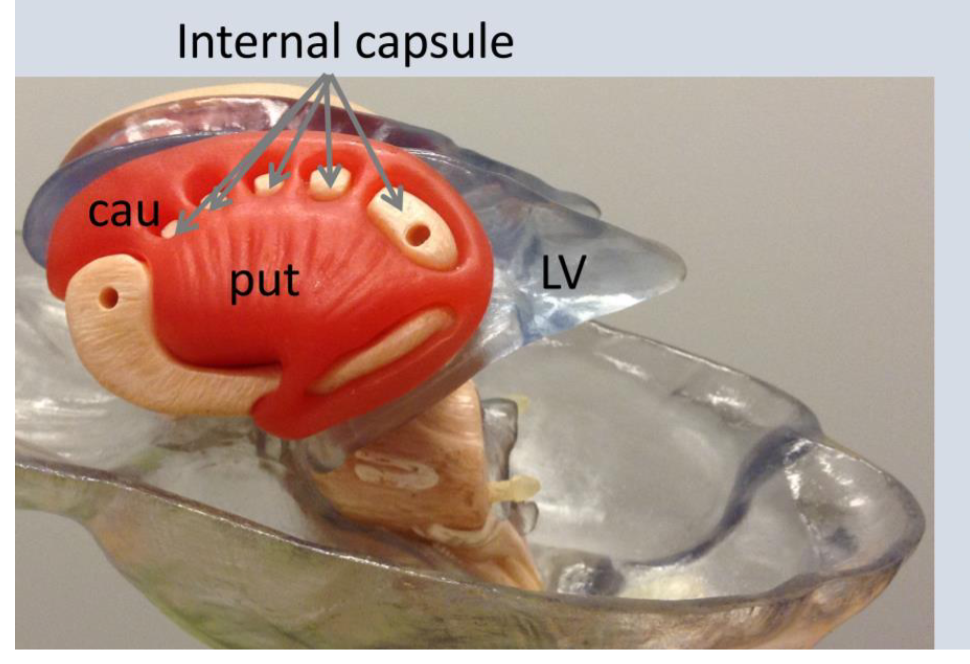
What is LV?
Lateral ventricles
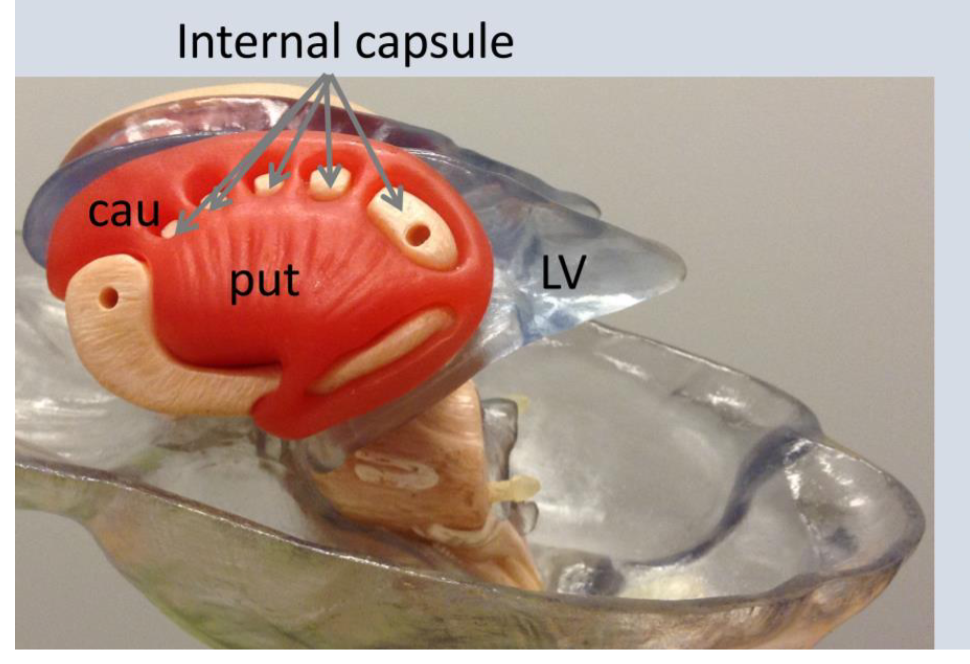
What is 3rd
The 3rd ventricle
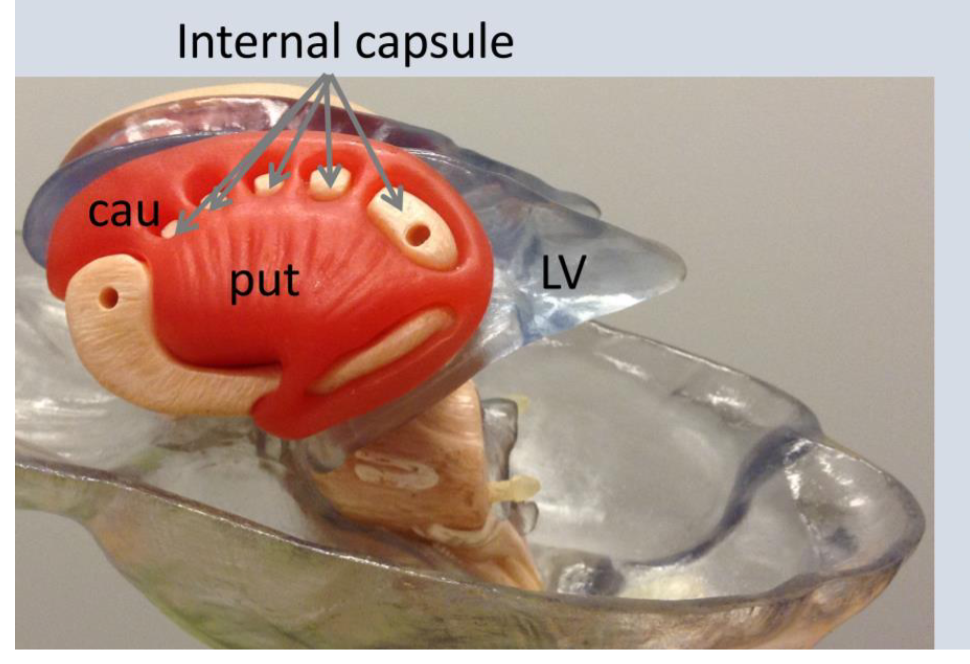
What is IC?
insular cortex
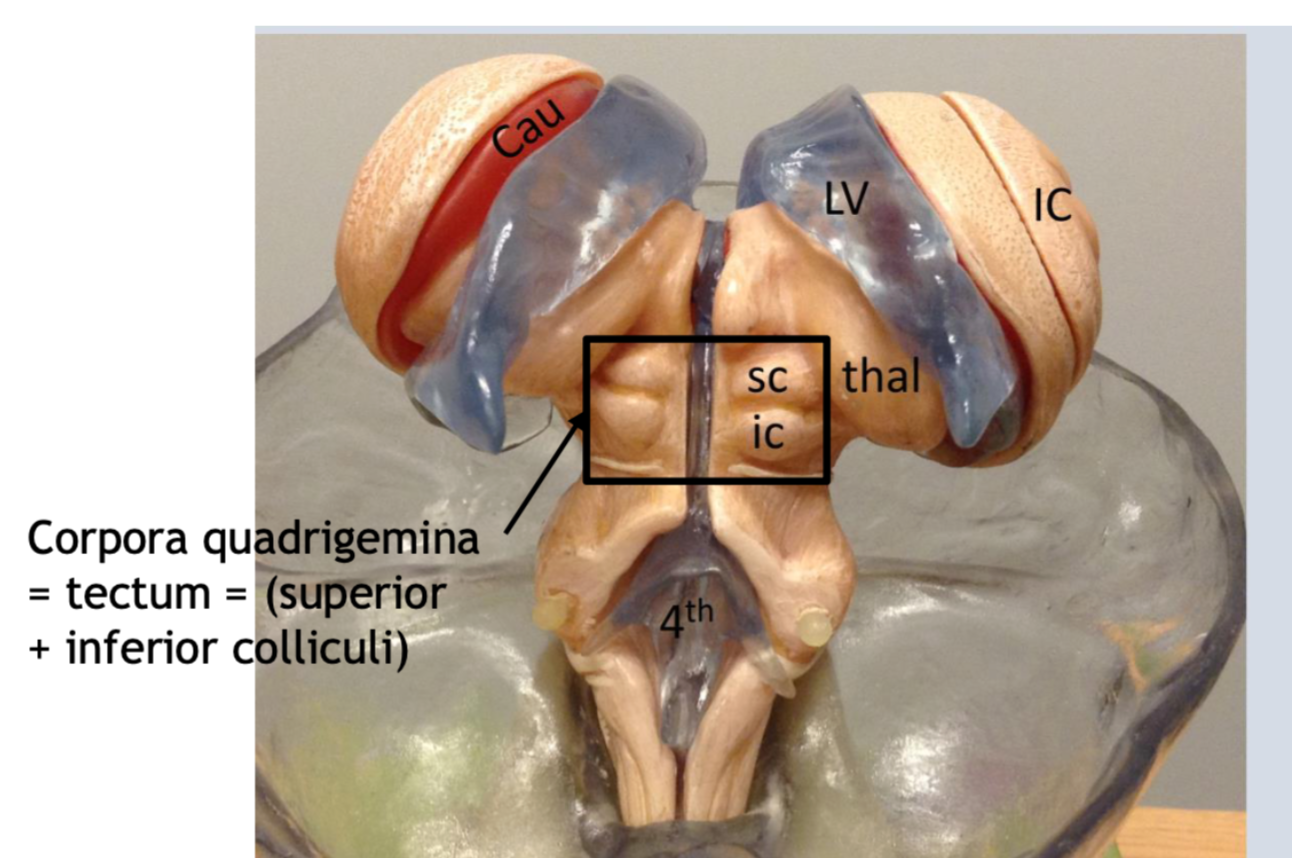
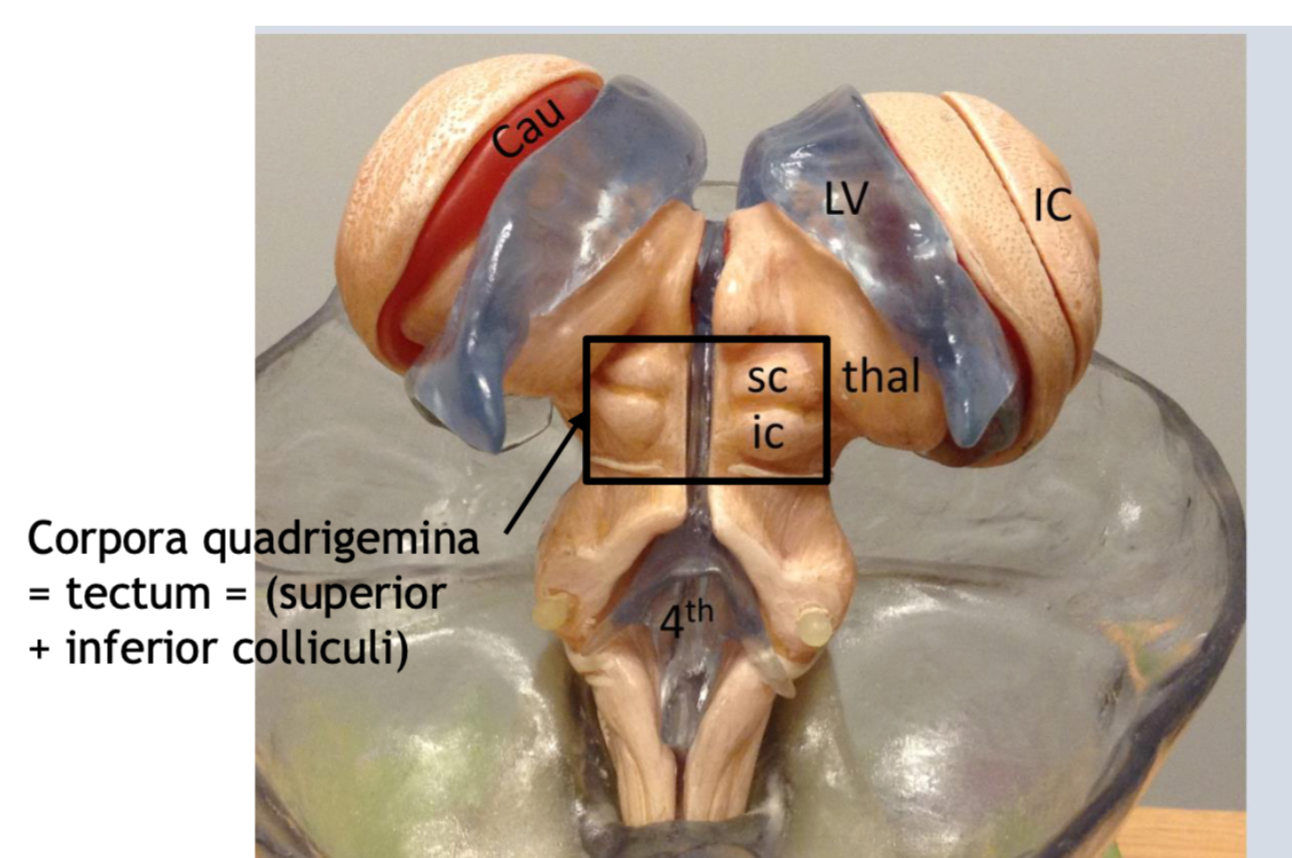
What is thal?
the thalamus
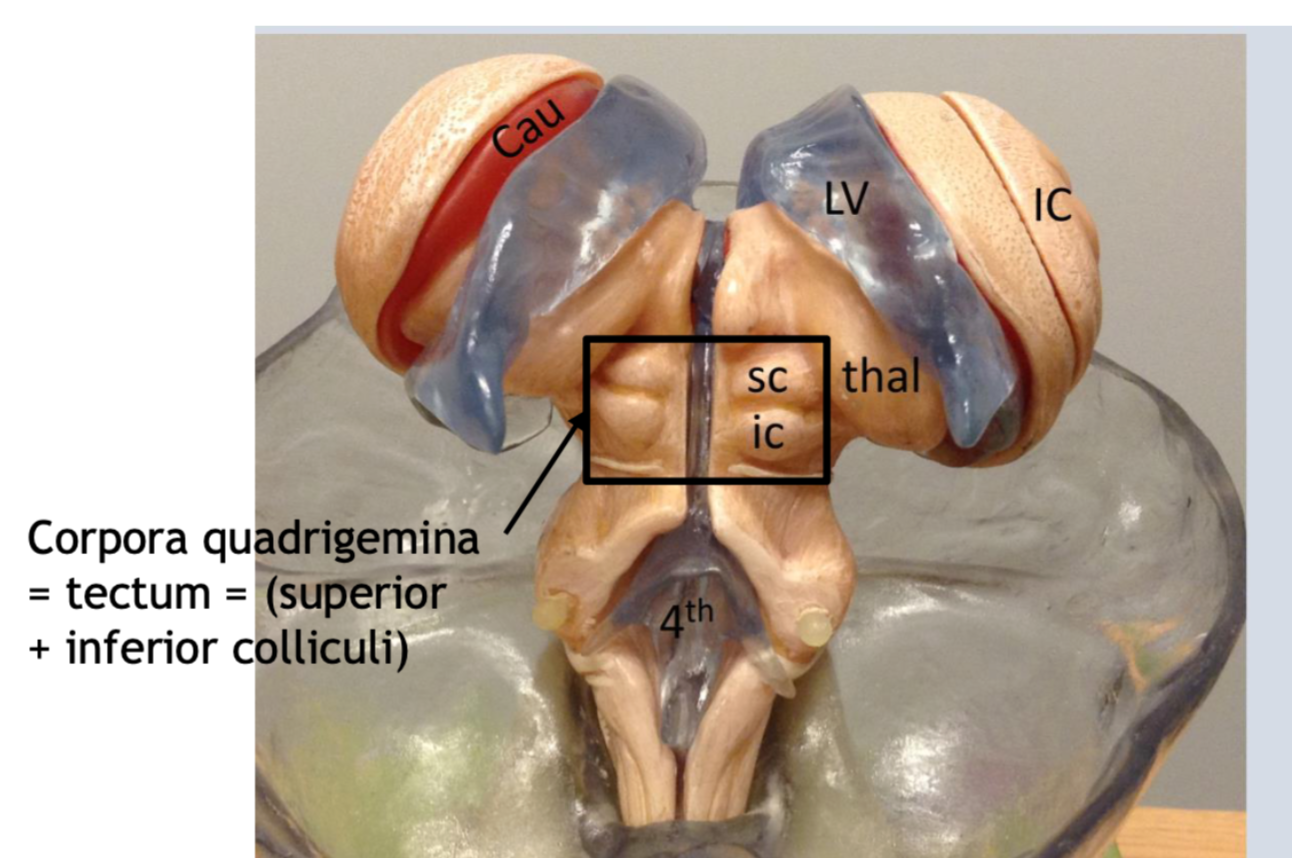
Insular cortex functions include
sensory processing
○ feelings and emotions
○ motor control
○ risk prediction
○ decision-making
○ bodily self-awareness
○ complex social functions like
empathy
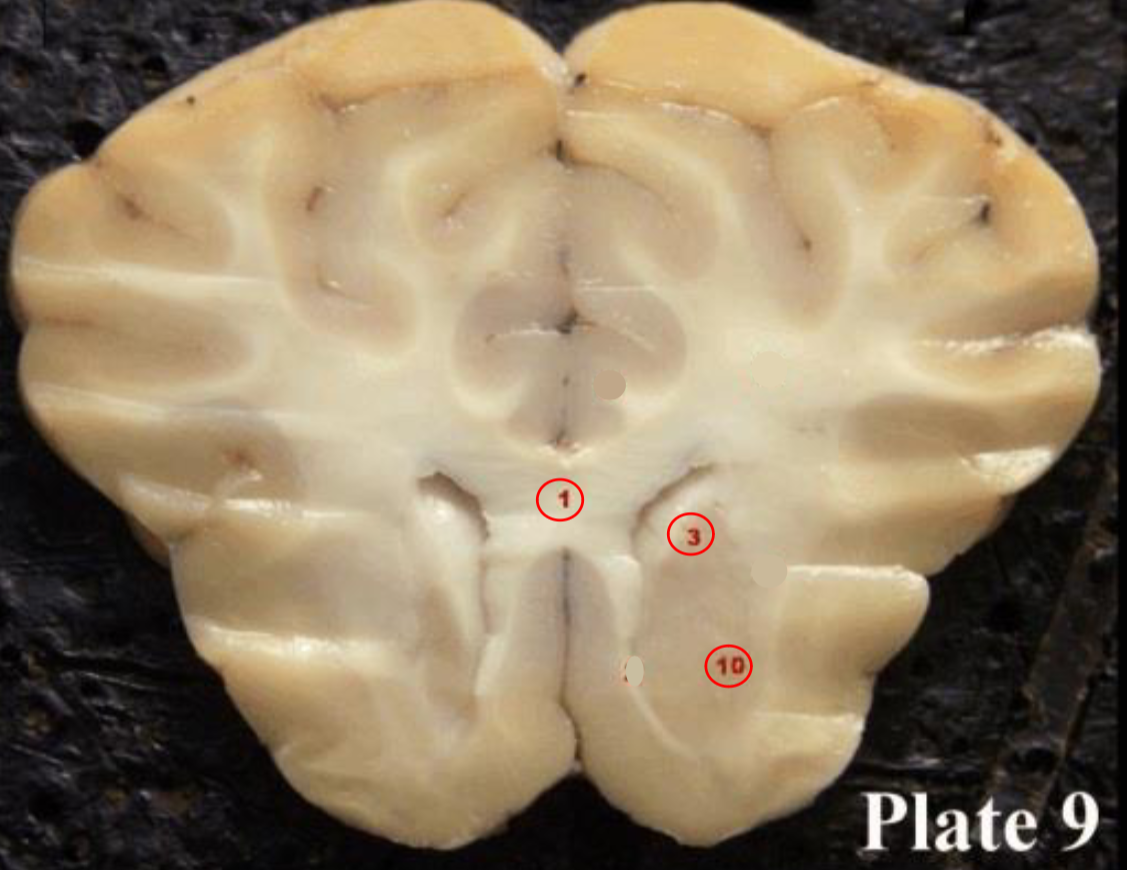
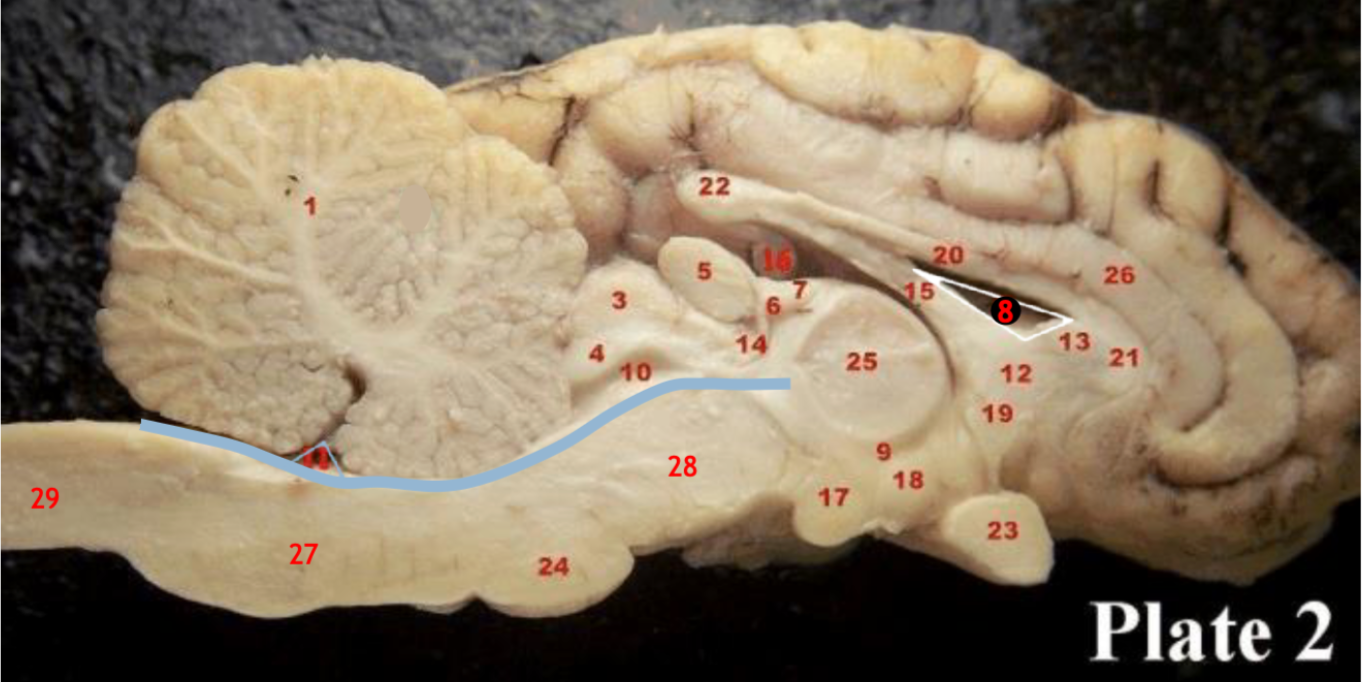
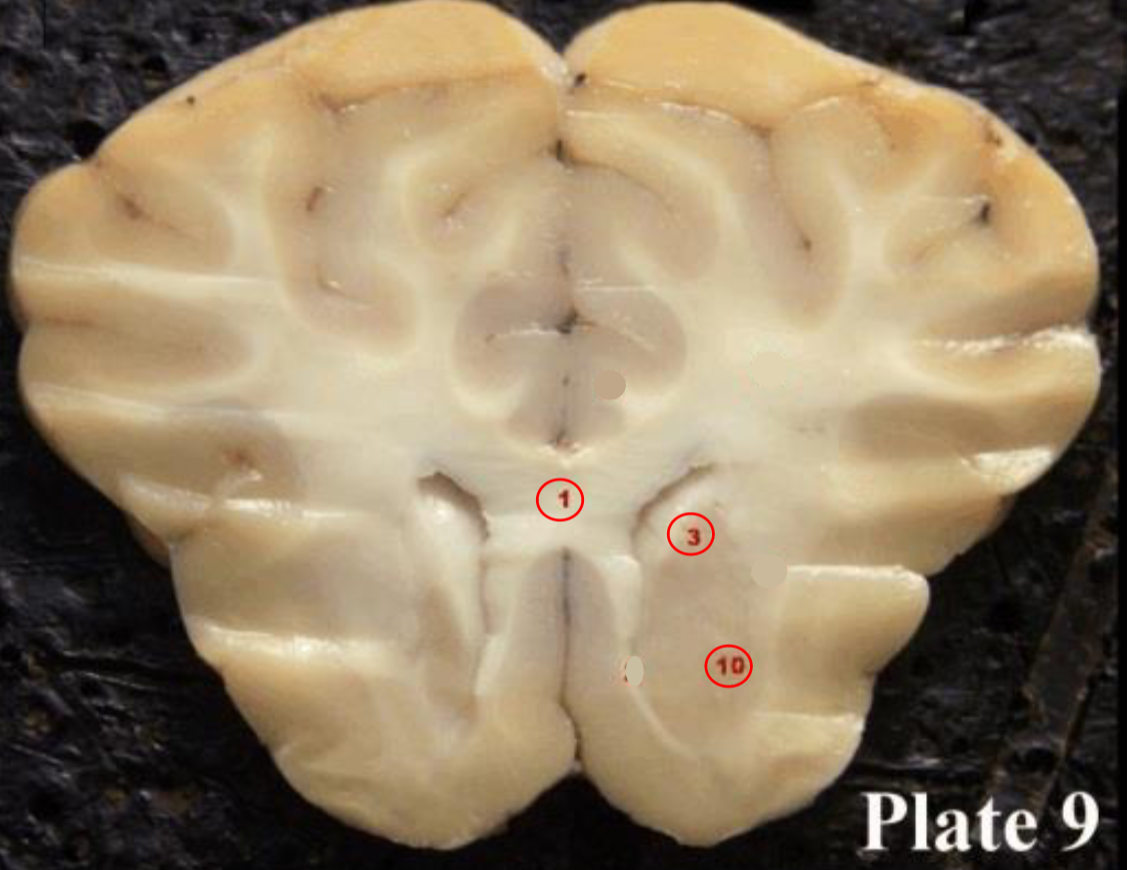
corpus callosum
(1) large band of myelinated axon fibers that cross from one side of the brain to the other, joining the two hemispheres of the brain.
caudate nucleus
(3) deep brain structure that is part of the basal ganglia that plays a role in motor functions, learning, and reward systems
putamen
10) a deep brain structure of the basal
ganglia that plays a role in stages of movement (preparation, execution, etc.) and also influences various types of learning.
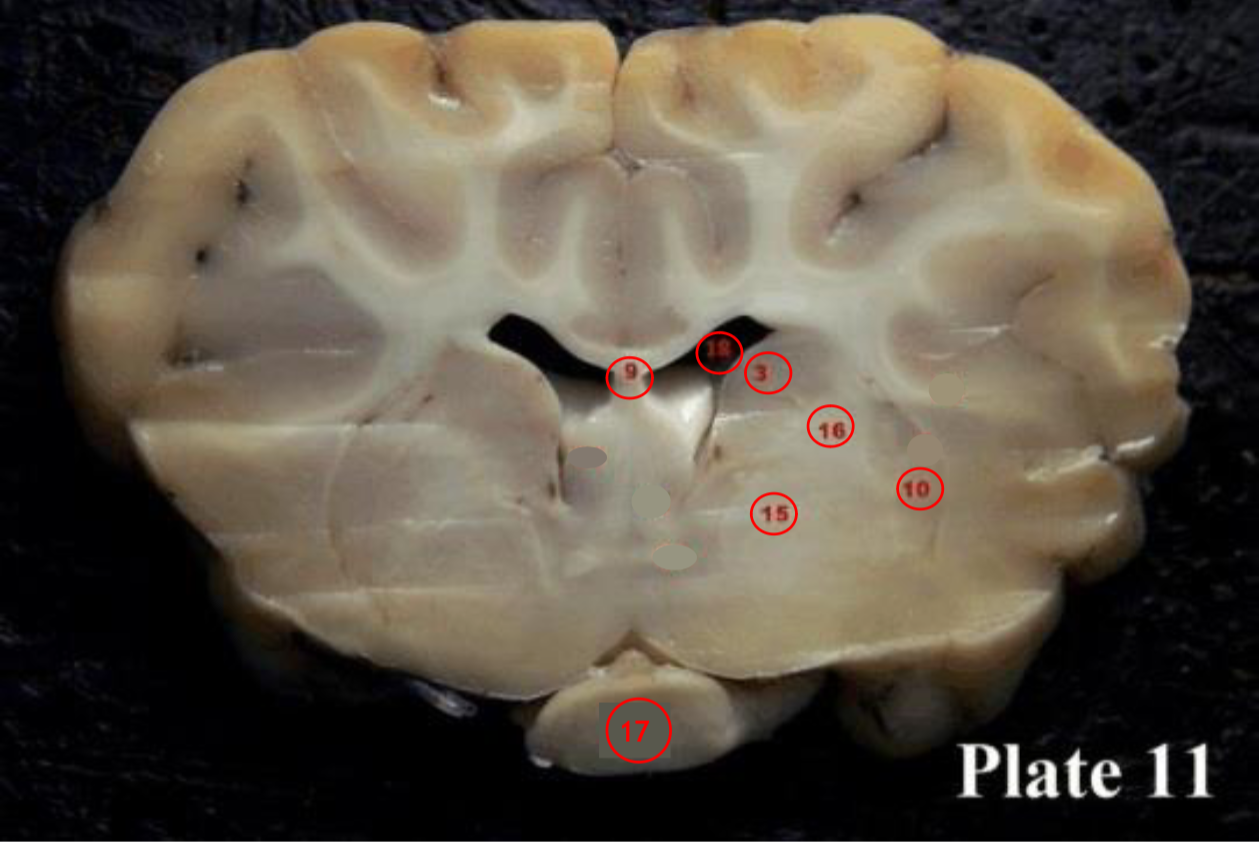
optic chiasm
(17) is the X-shaped structure formed at the point below the brain where the two optic nerves cross over each other.
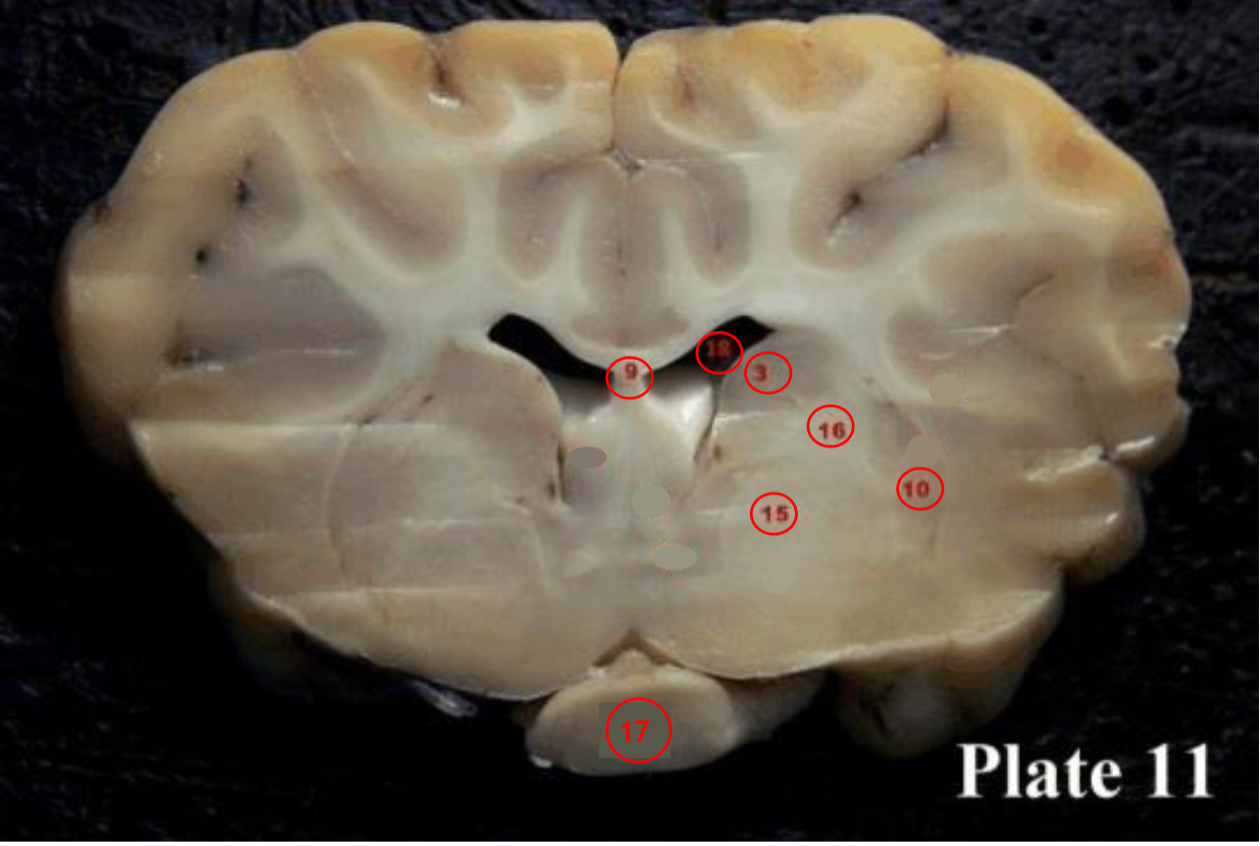
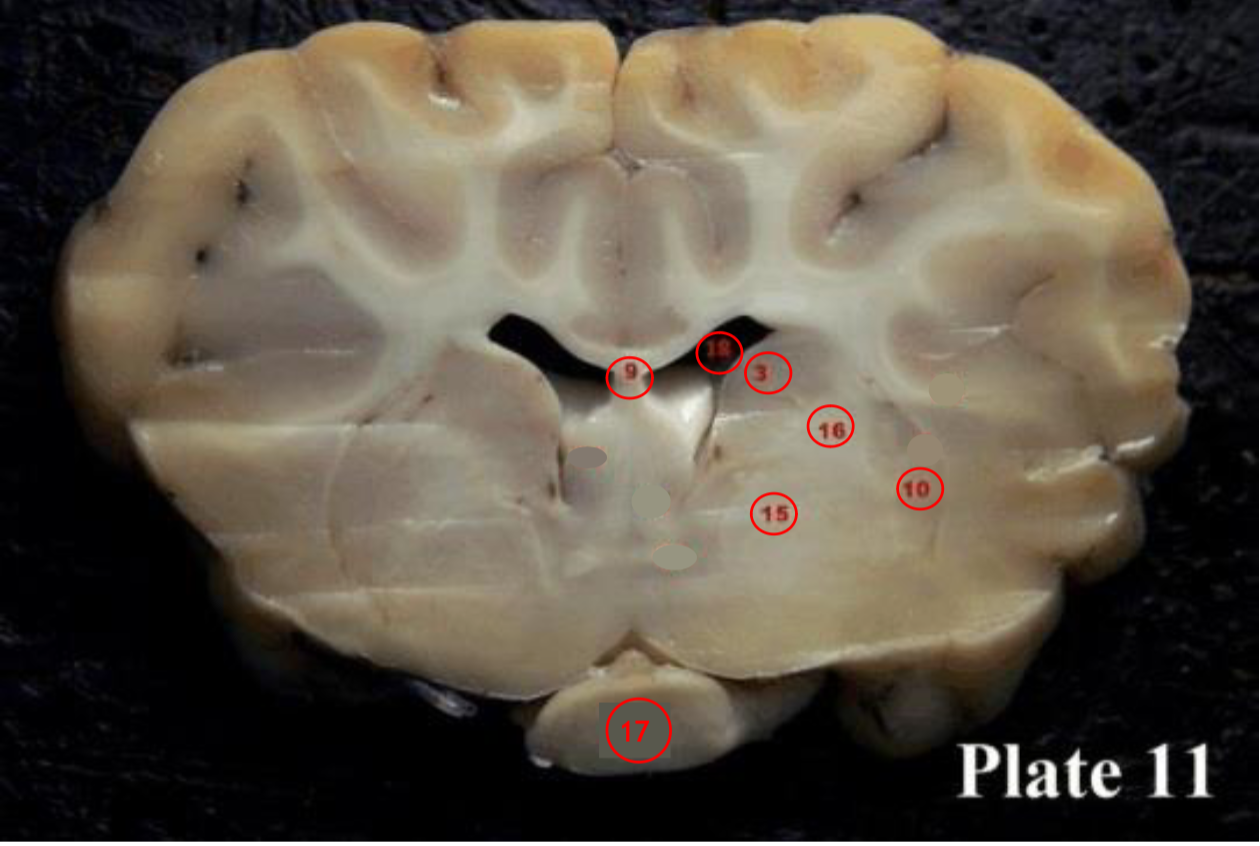
lateral ventricles
(18) are
the two largest cavities of the
ventricular system of the brain
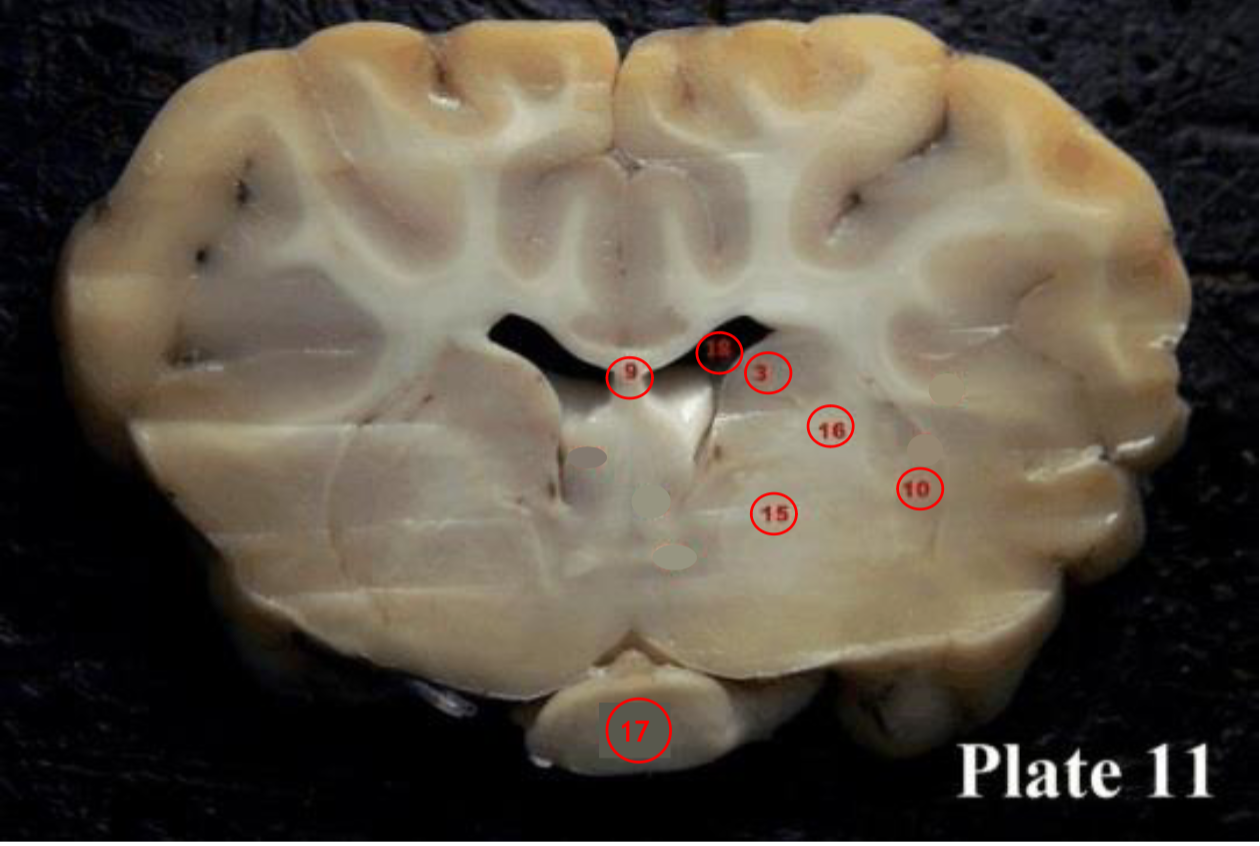
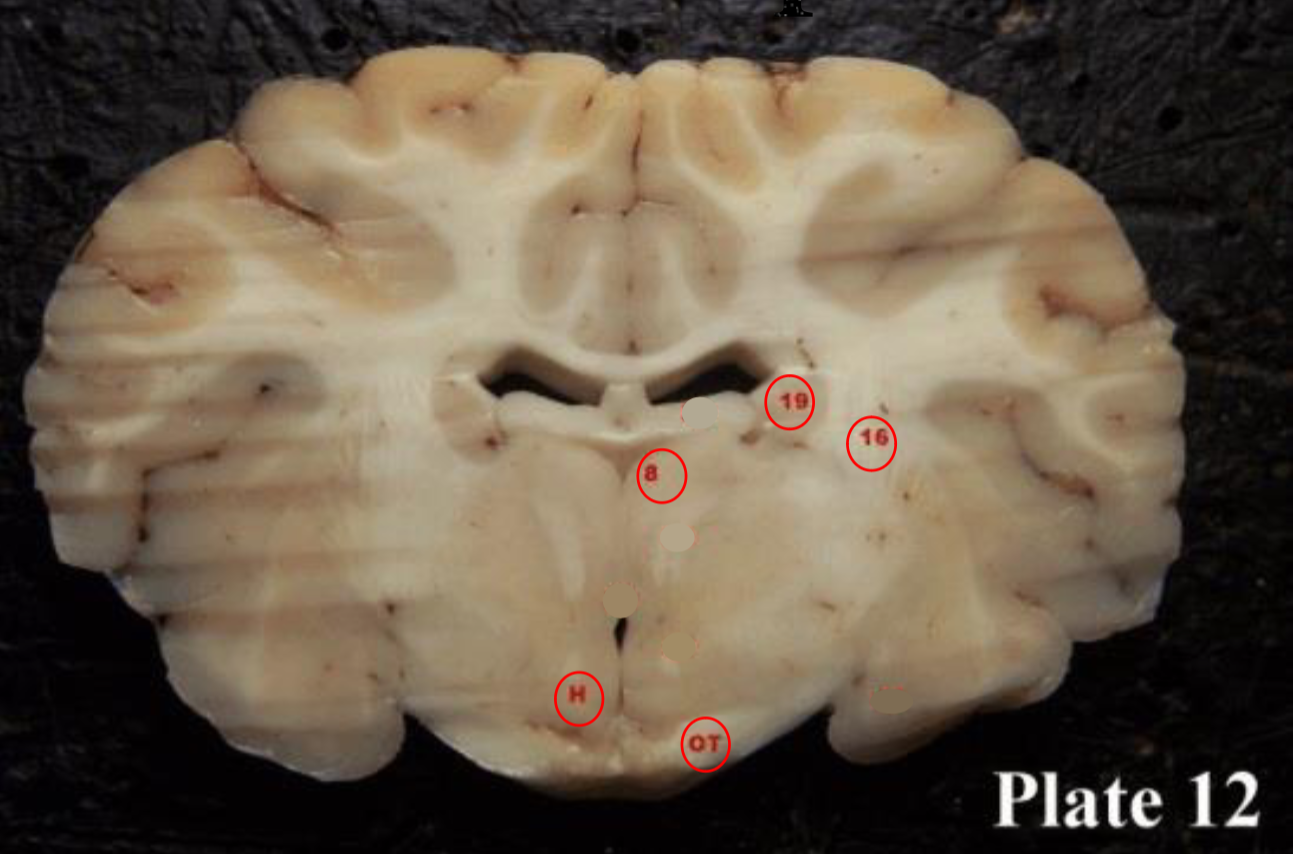
Optic tracts
(OT) are part of the visual system in the brain and
are the posterior continuation of the optic nerves after the medial (temporal lobe) fibers decussate at the optic chiasm.
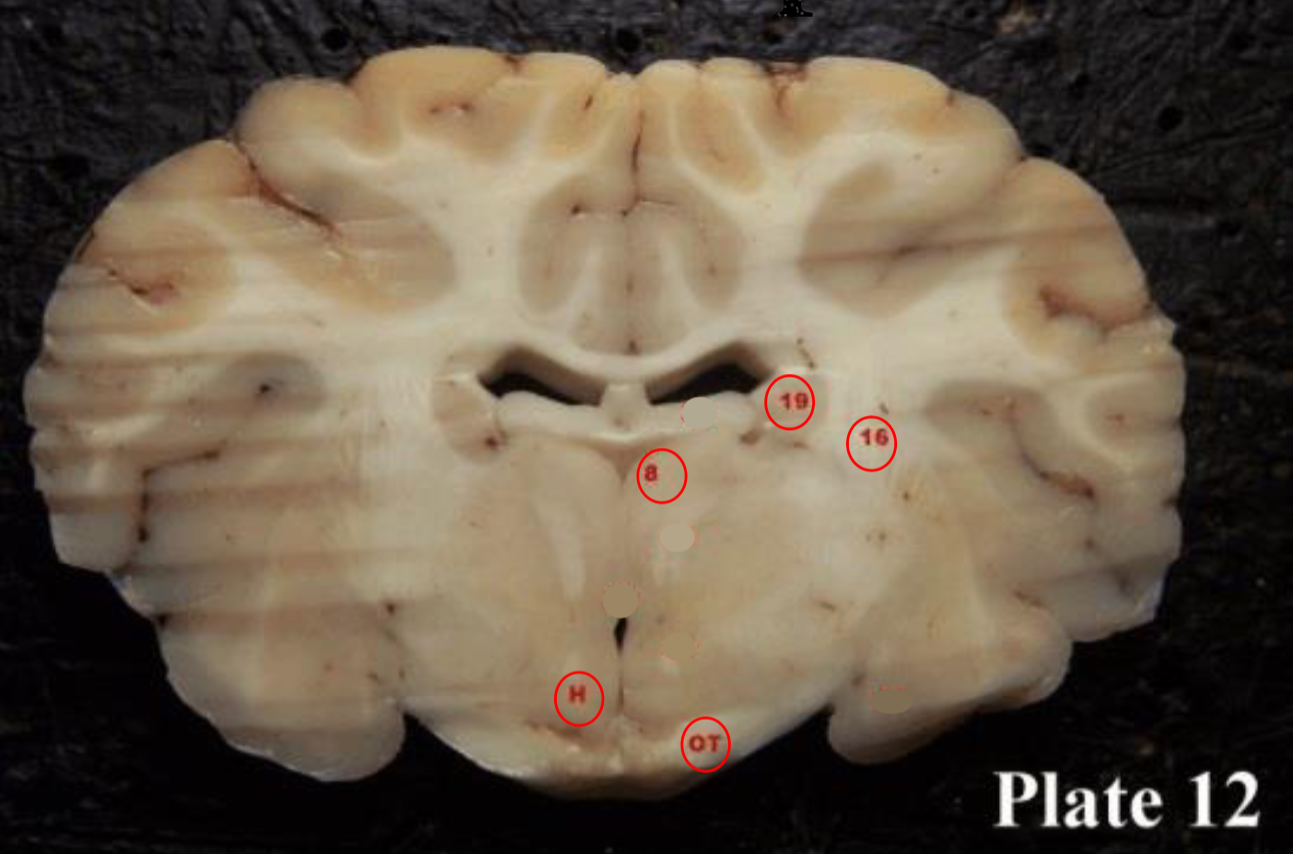
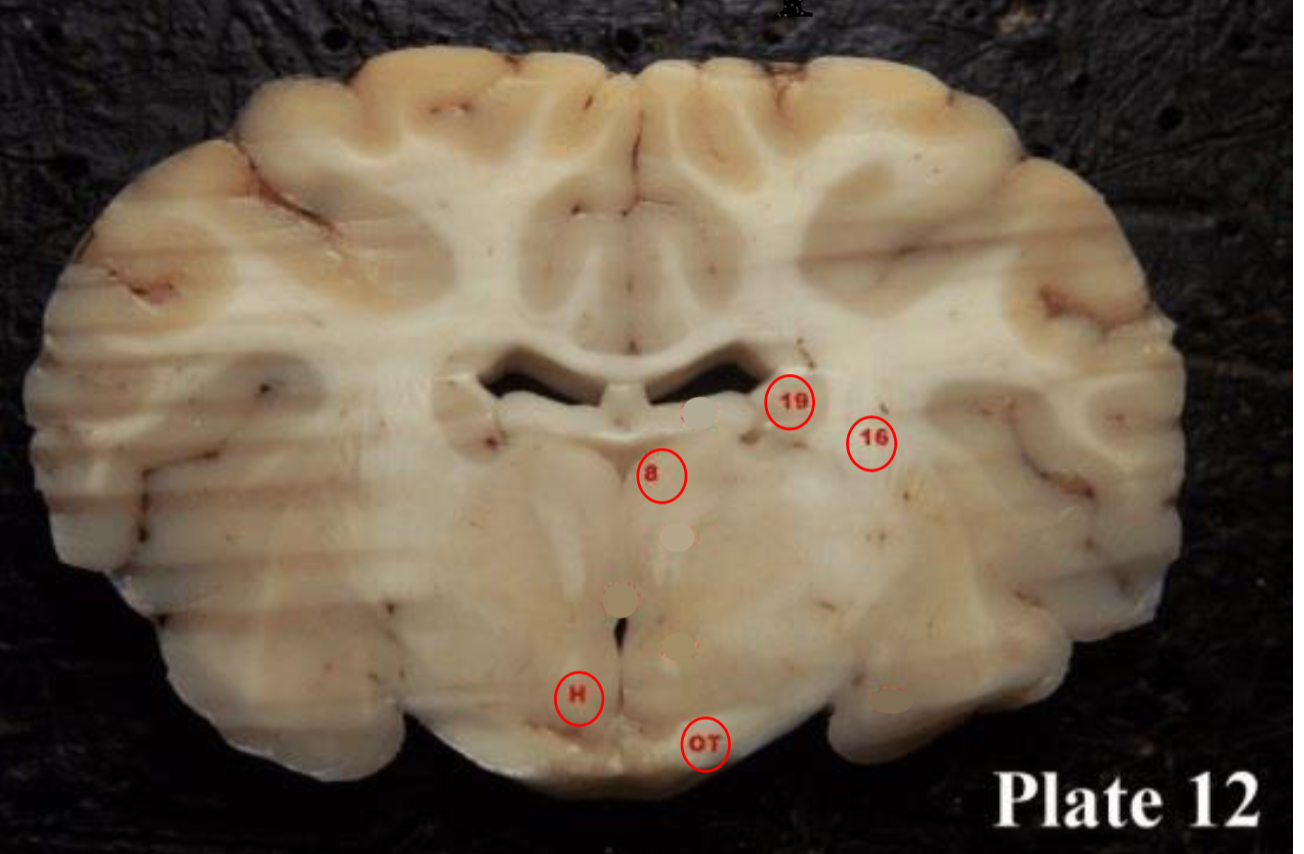
thalamus
(8) plays a role in the regulation of consciousness and sleep.
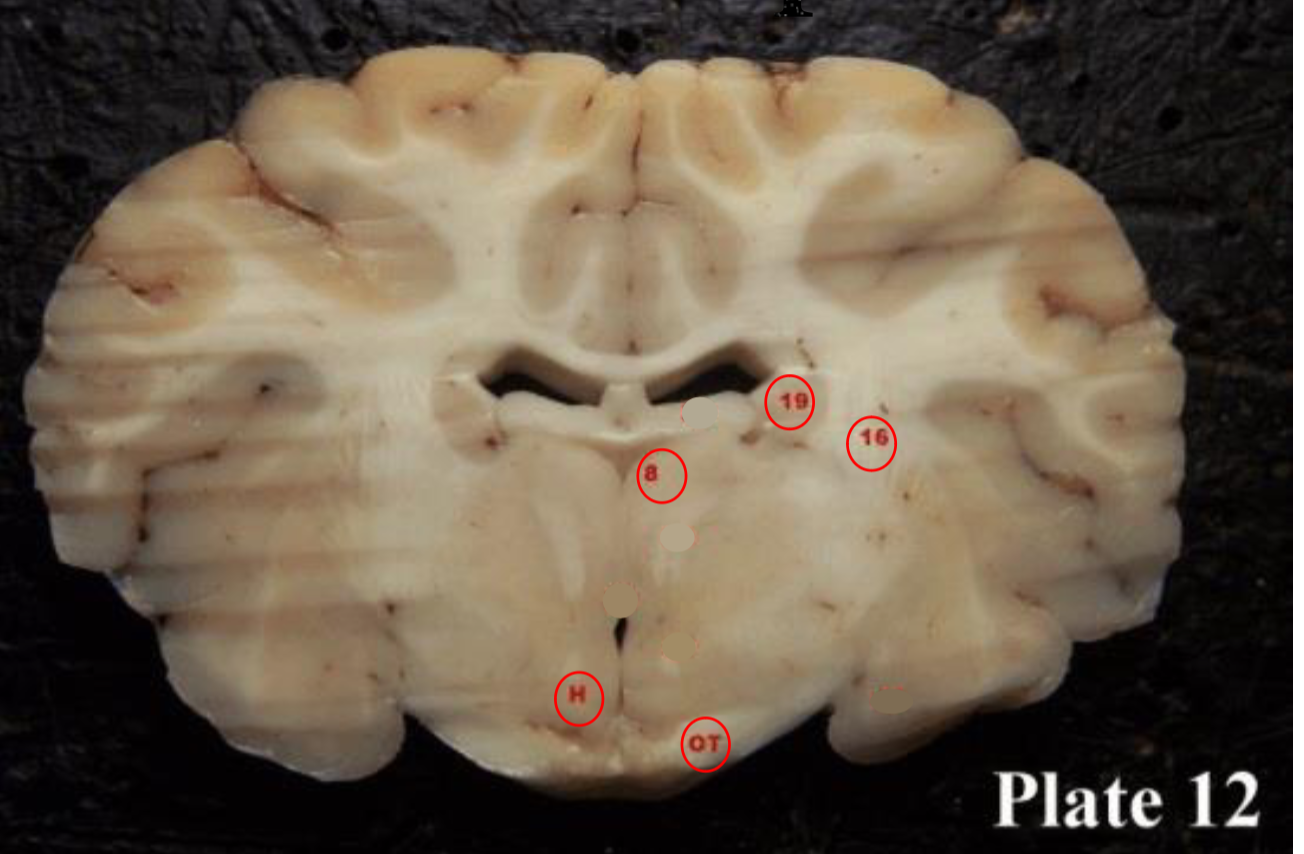
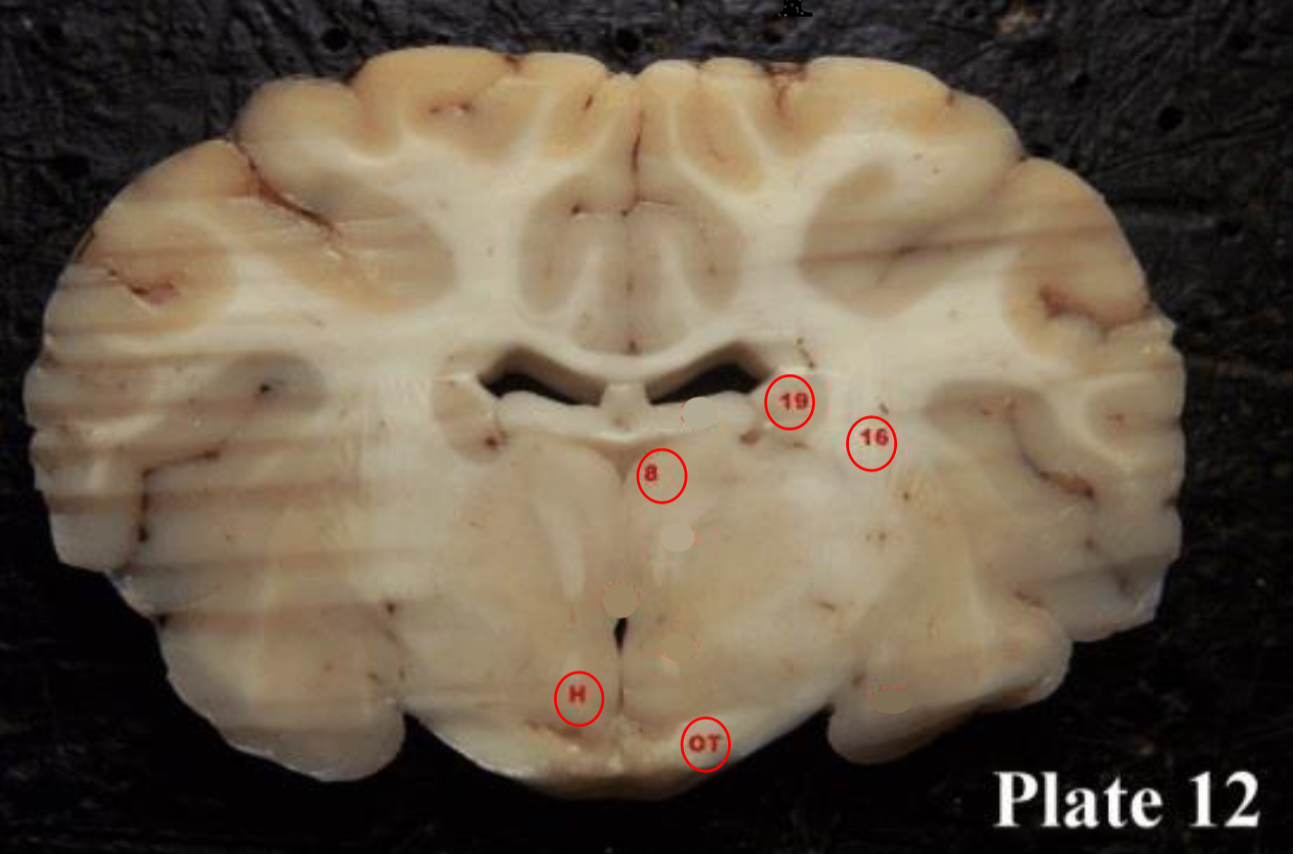
hypothalamus
(H)plays a role in the regulation of body temperature, thirst, sleep/wake cycle, hunger, sexual behaviors, heart rate, blood pressure, and more.
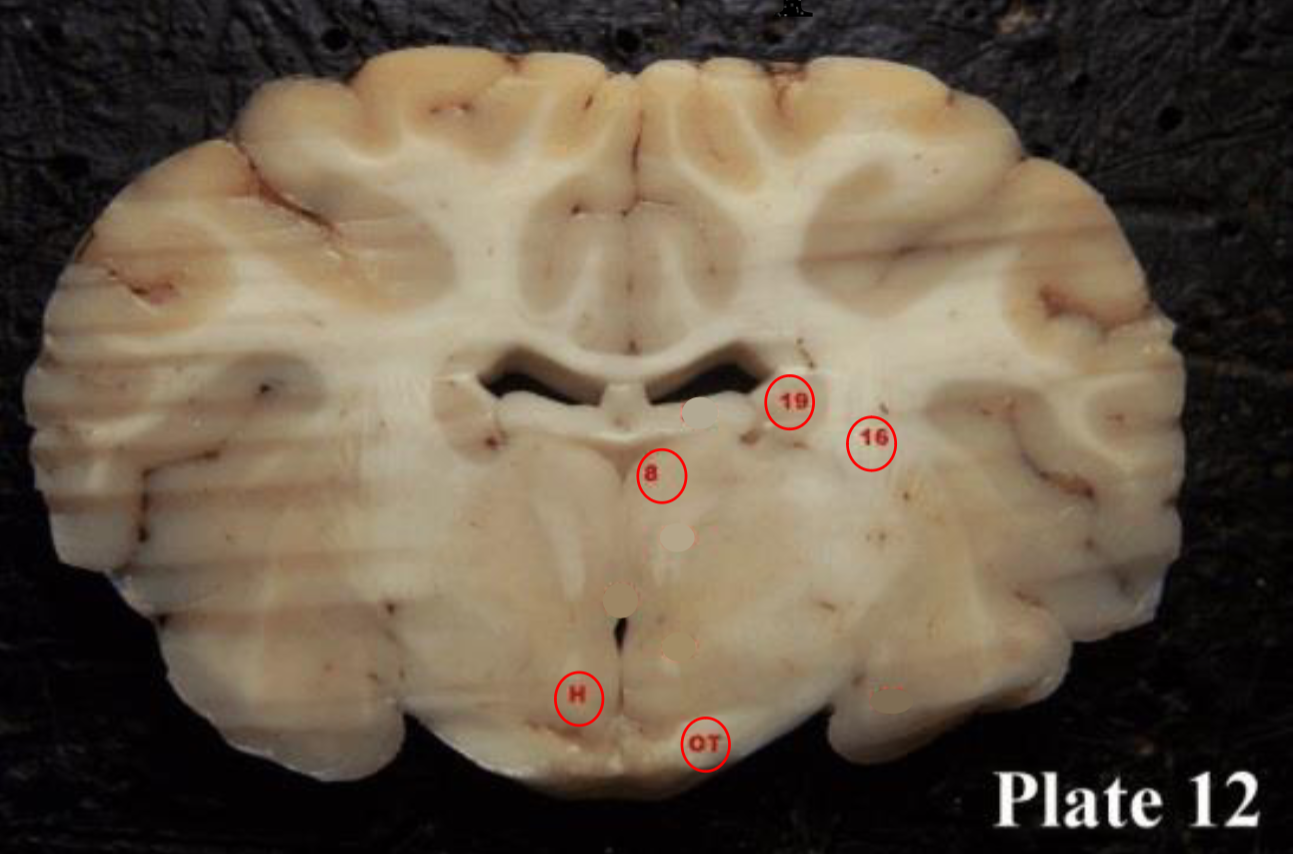
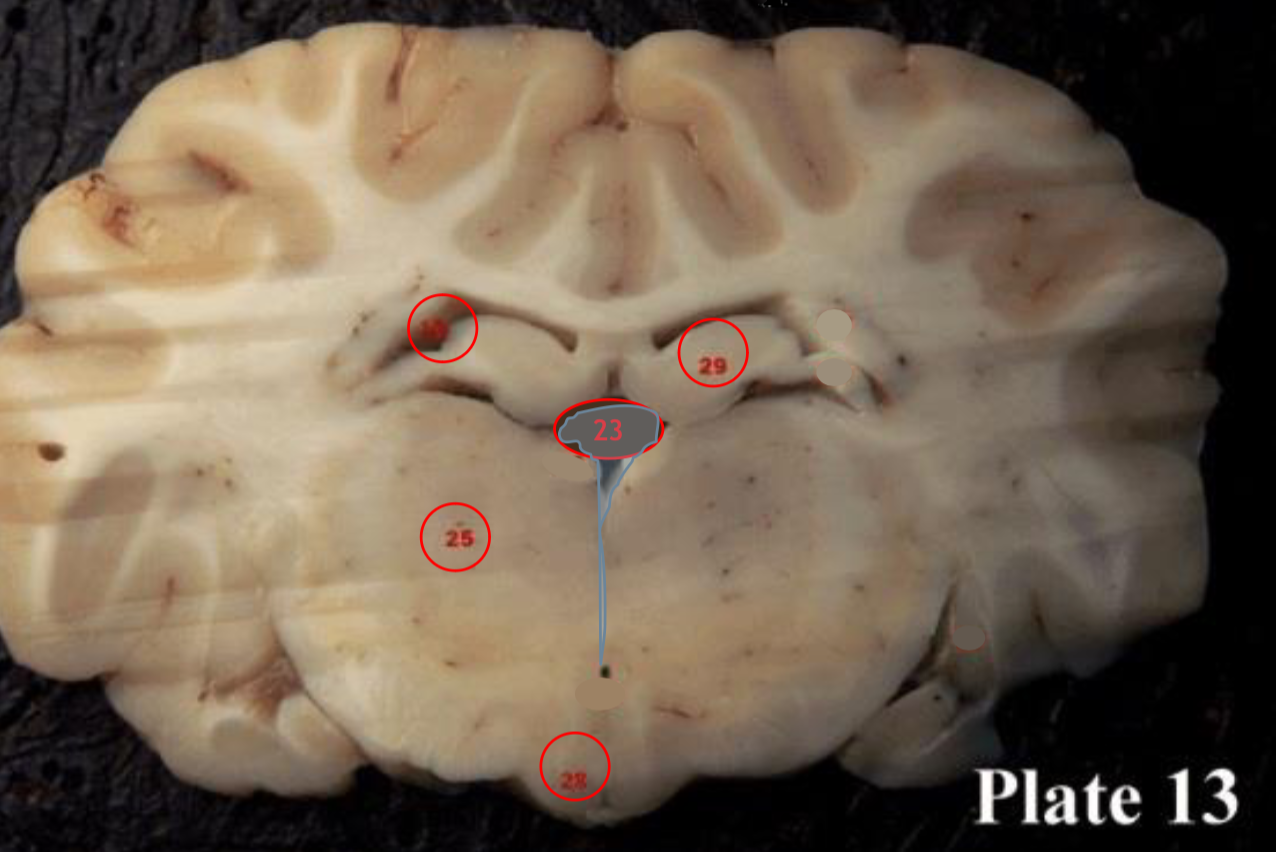
mammillary bodies
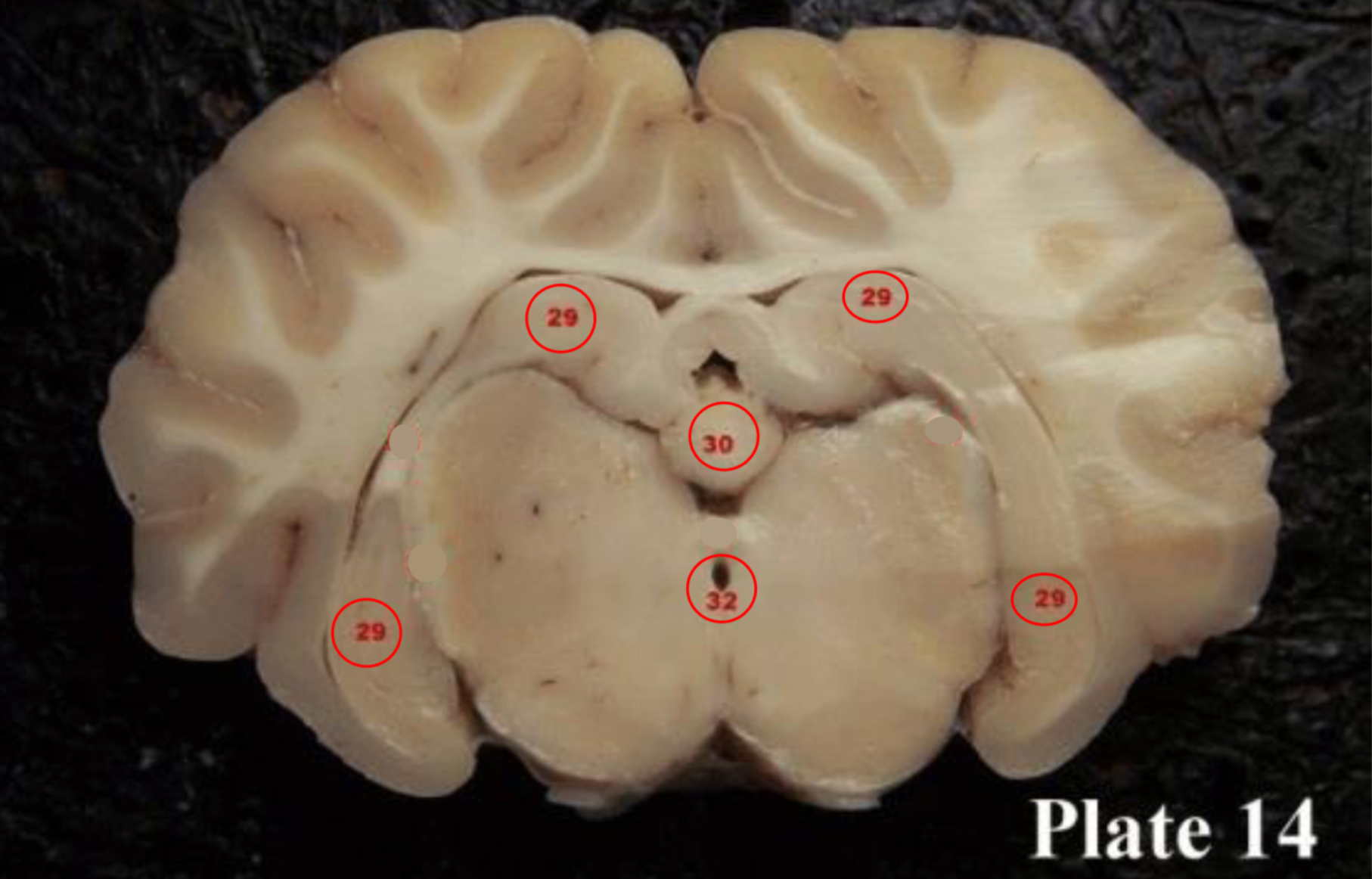
(28) They act as a relay for information coming from the amygdala and hippocampus, via the mamillo-thalamic tract to the thalamus. The play a roll in memory
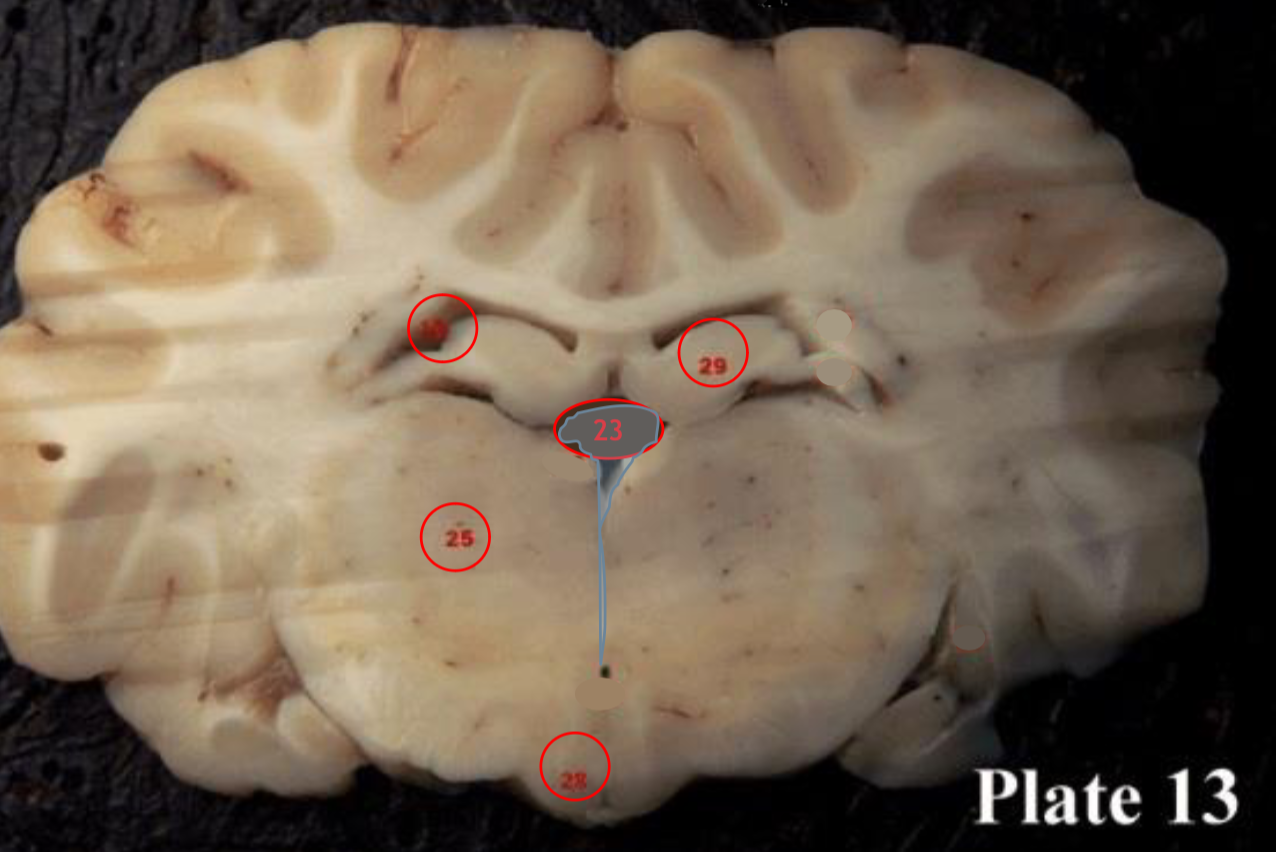
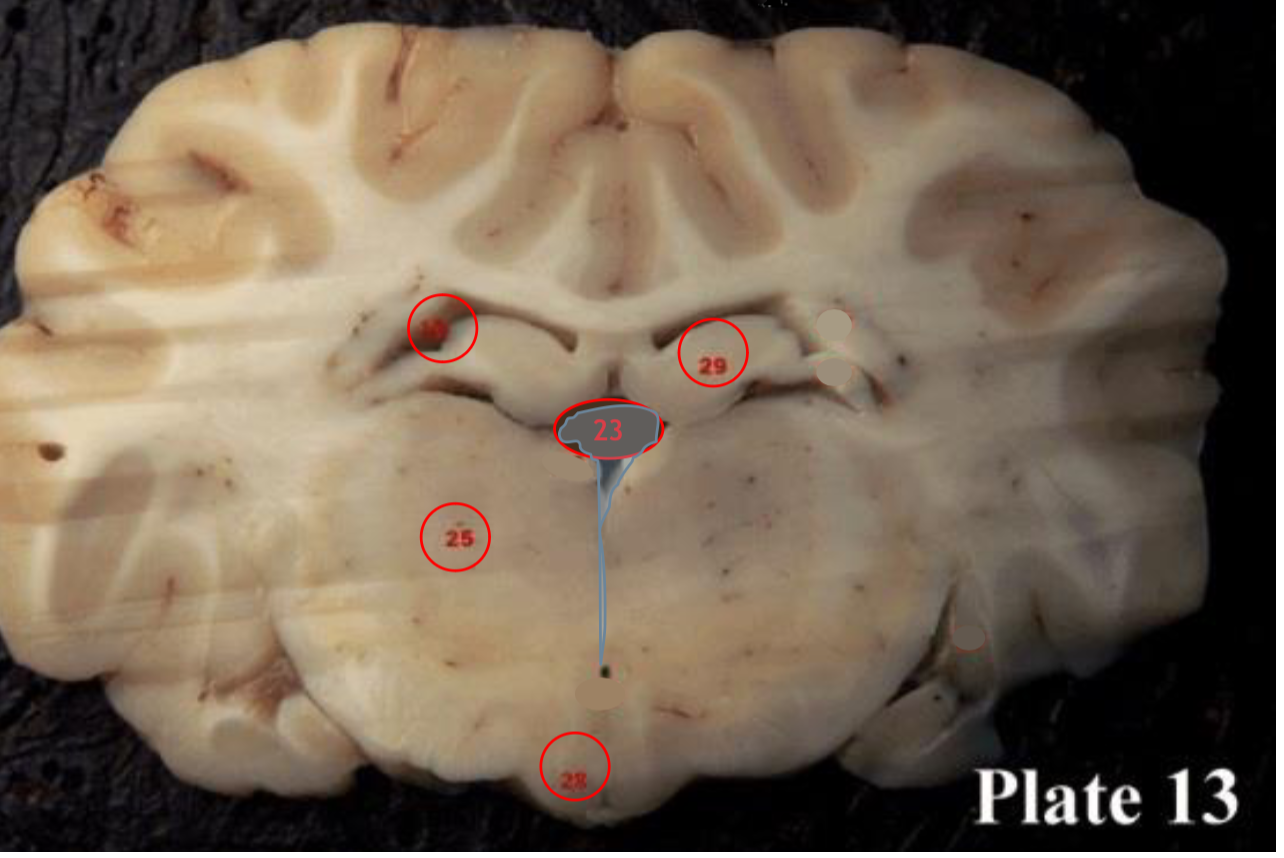
hippocampus
(29) is located within the brain's
medial temporal lobe is associated primarily with
memory, in particular the transfer or short-term (working) memory to long-term memory.
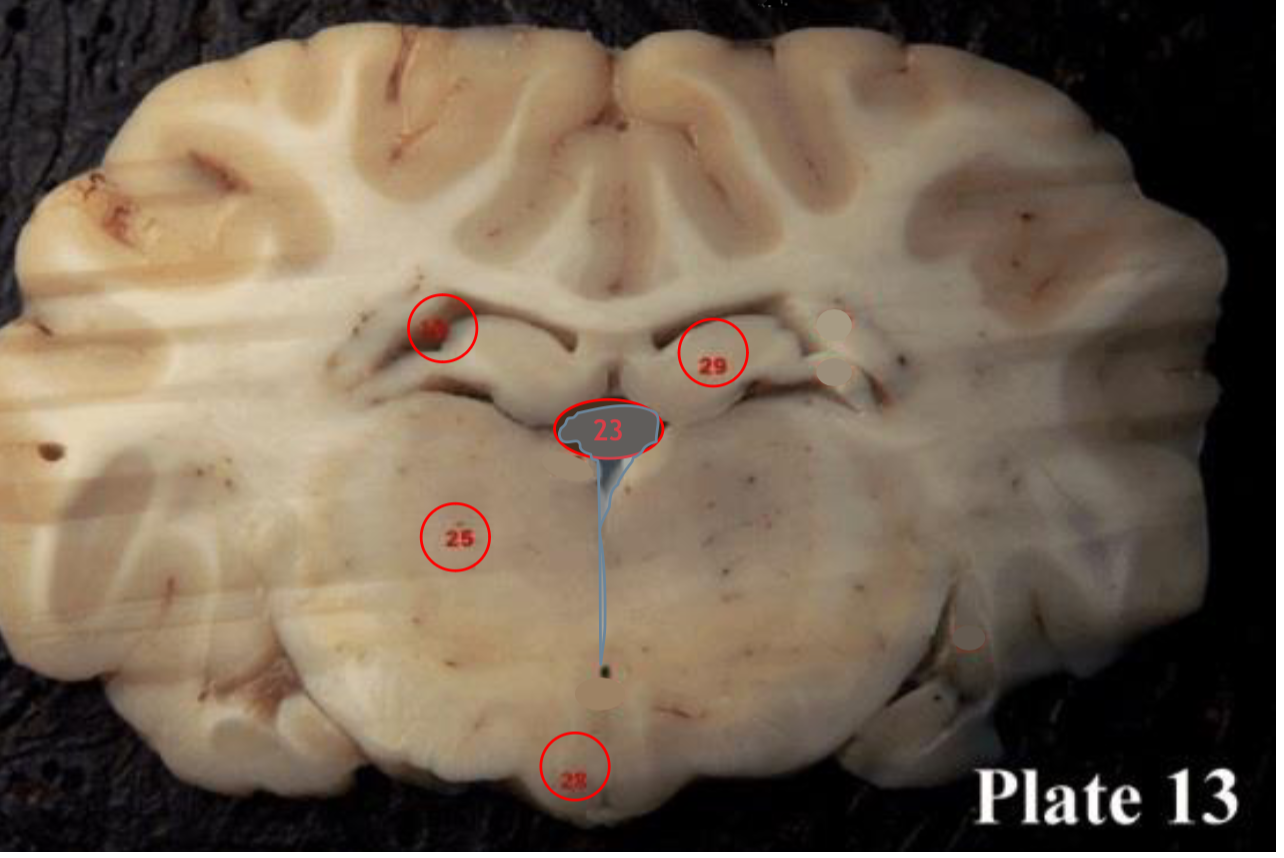
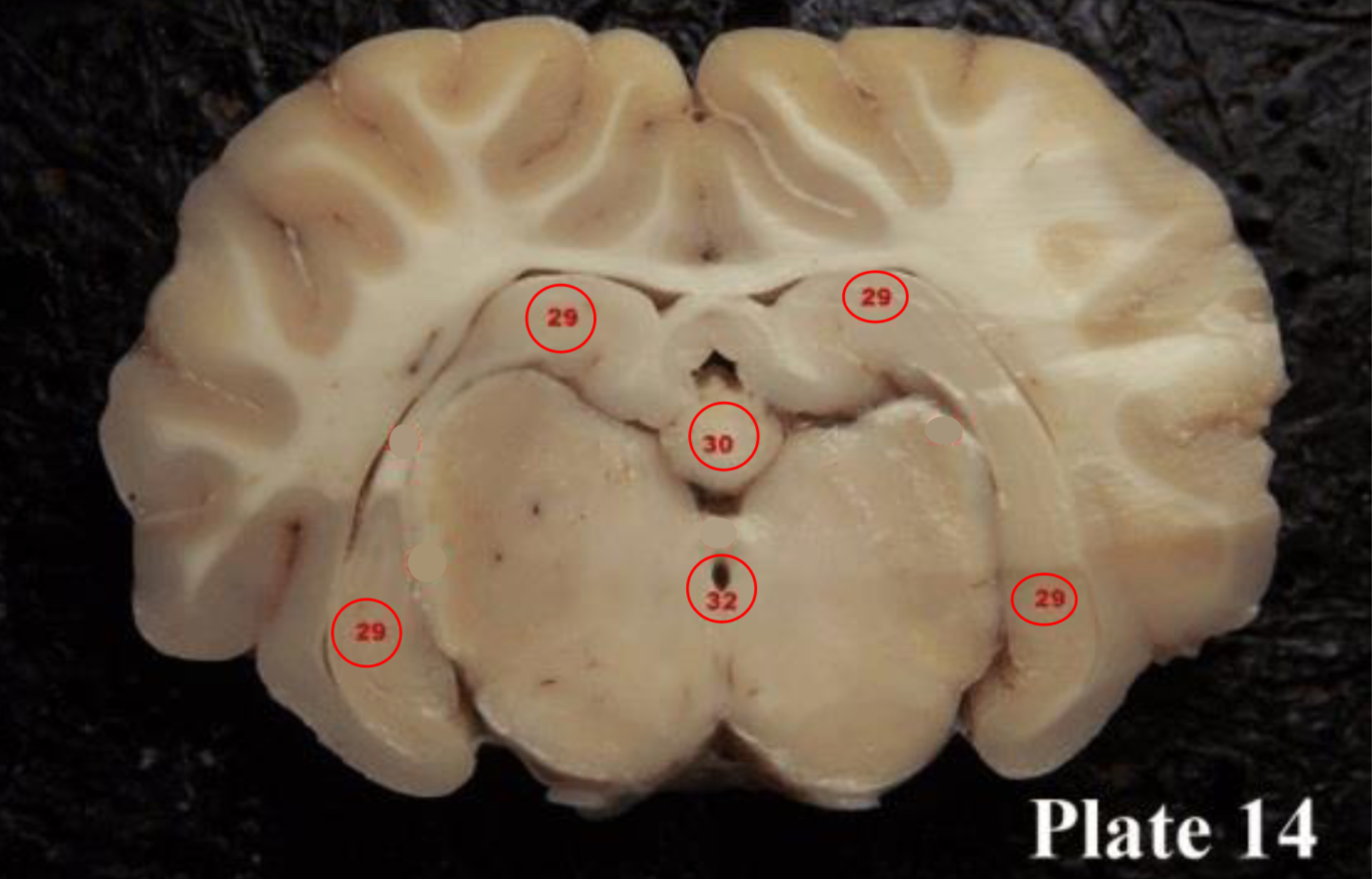
Pineal gland
(30) produces melatonin, a serotonin- derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cycles.
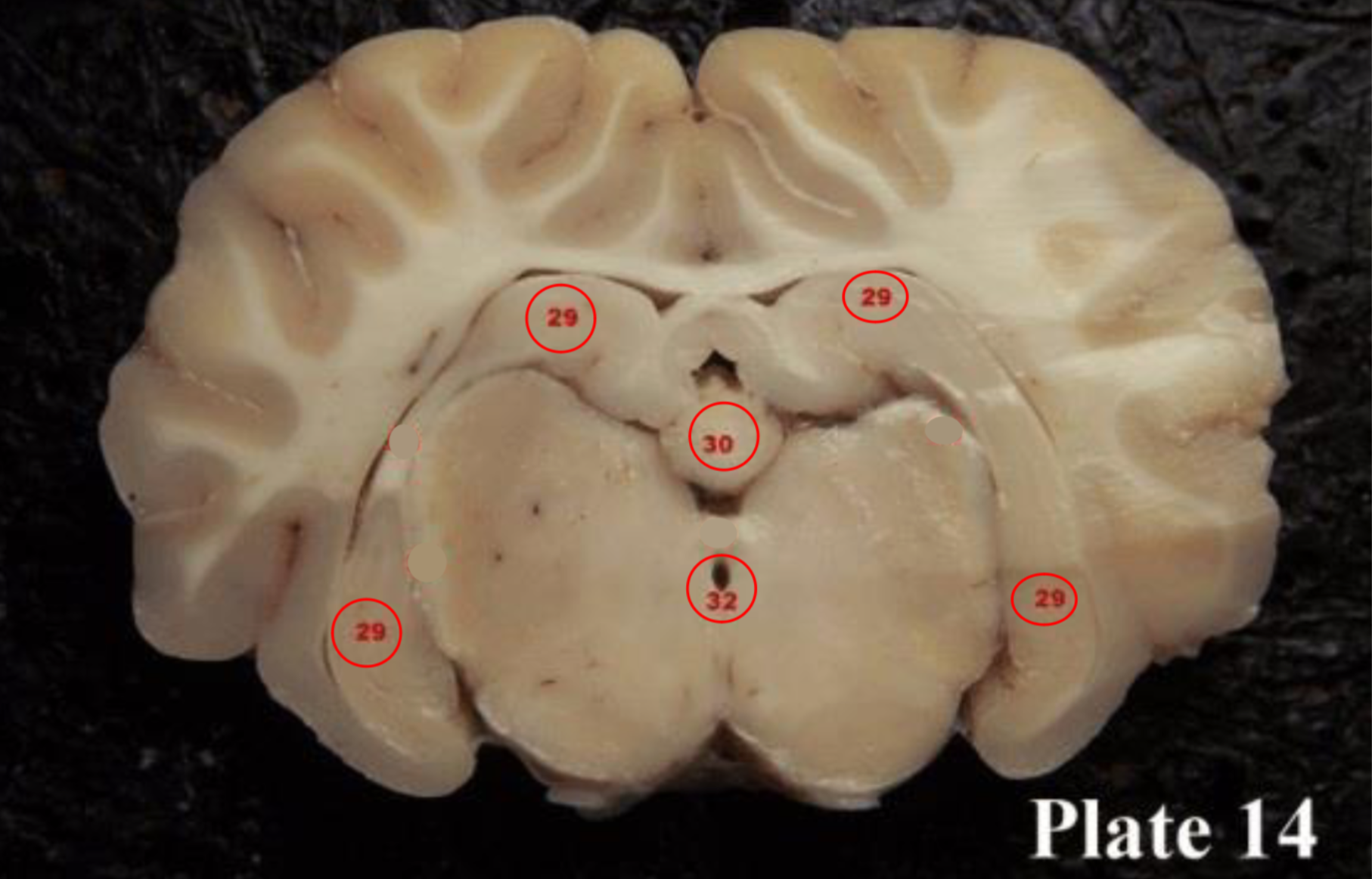
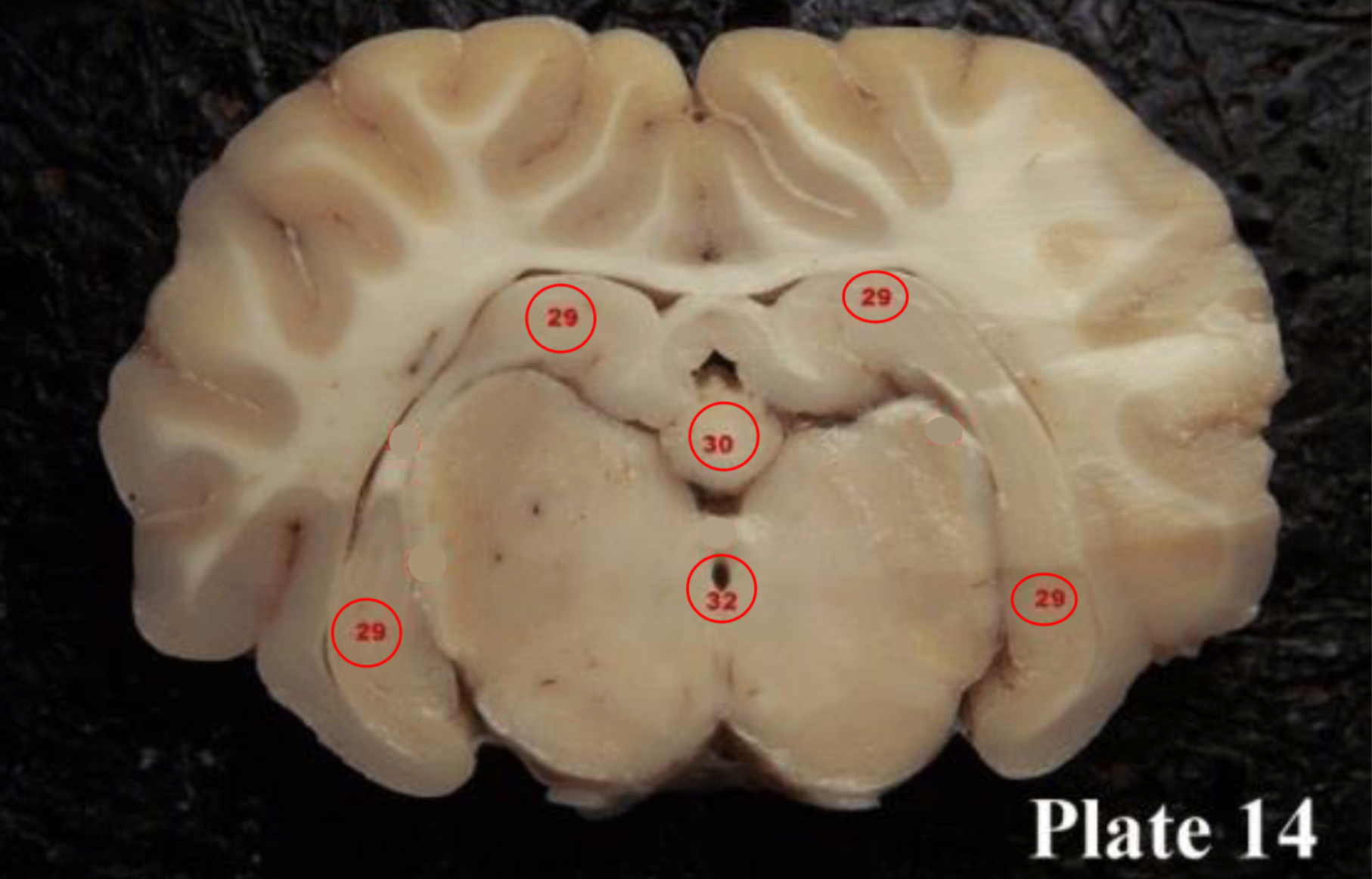
cerebral aqueduct
(32)
is part of the ventricular
system located within the
mesencephalon (or
midbrain) and contains CSF.
arachnoid and pia mater
blood vessels are found between what two meninges layers? (the subarachnoid space)
Ventral structures
-Brainstem
-infundibulum
-olfactory bulbs
-optic tract/chaism/nerve
-mamillary bodies
Dorsal structures
-cerebrum
-sulci
-gyri
-longitudinal fissure
-cerebellum
-spinal cord
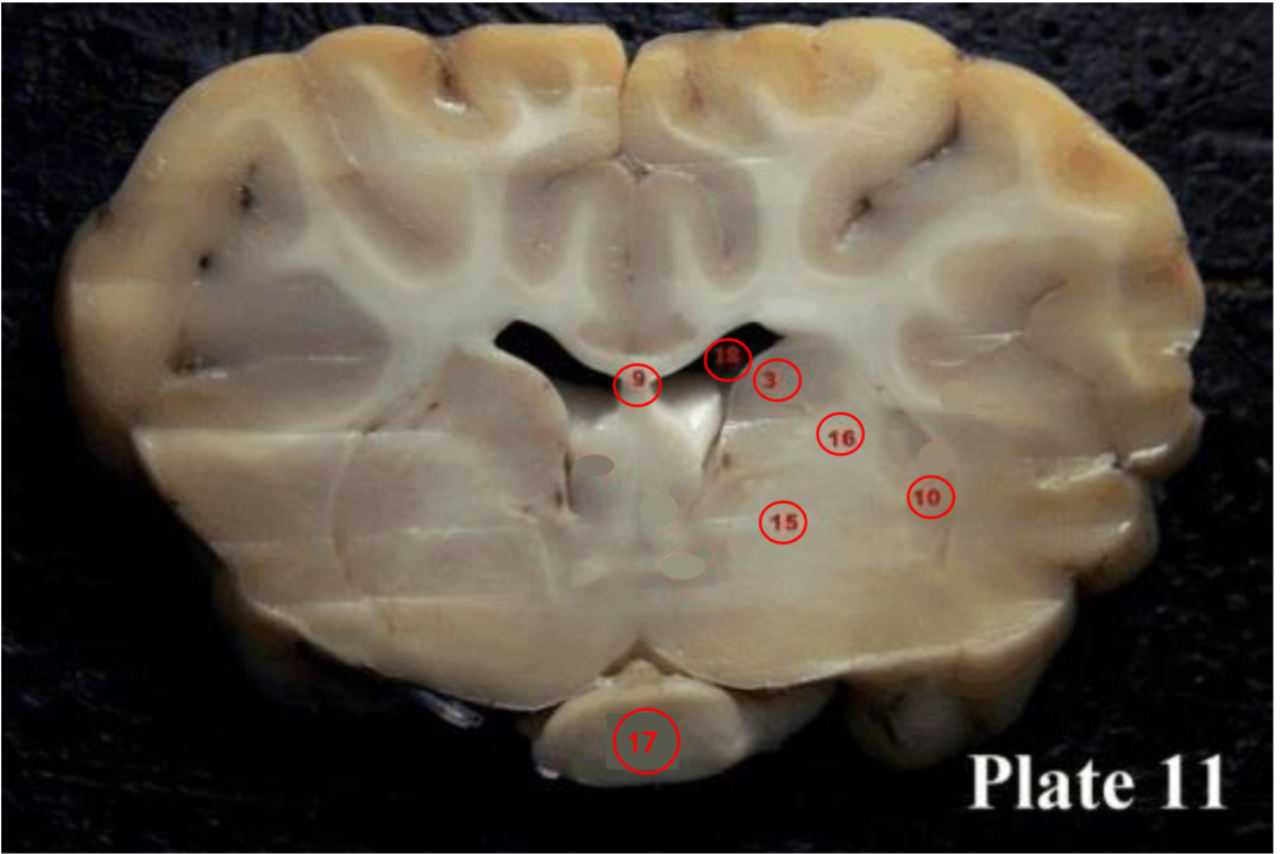
Globus pallidus
(15) plays a role in voluntary movement
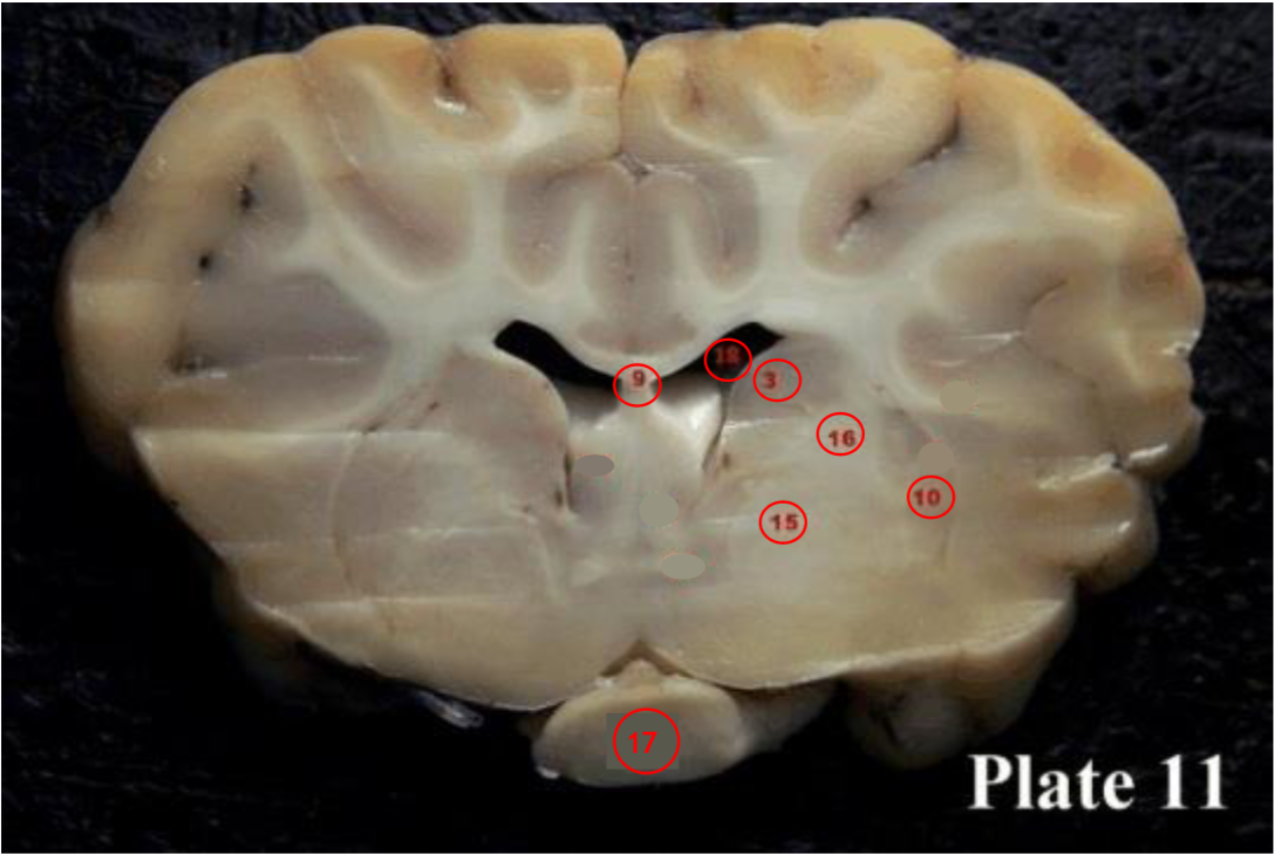
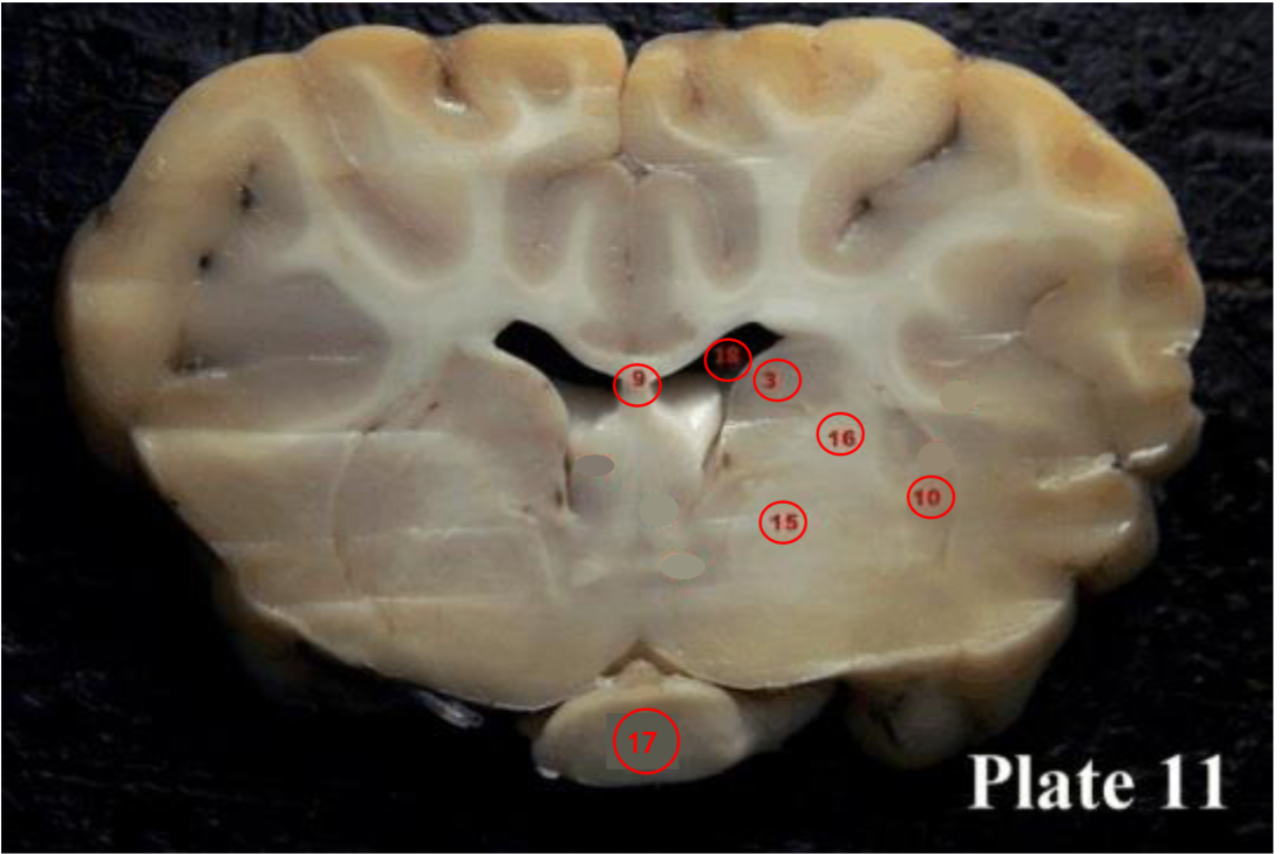
Internal capsule
(16) contains ascending and descending axons from the cerebral cortex through the thalamus
-seperate caudate nucleus from putamen and globus pallidus
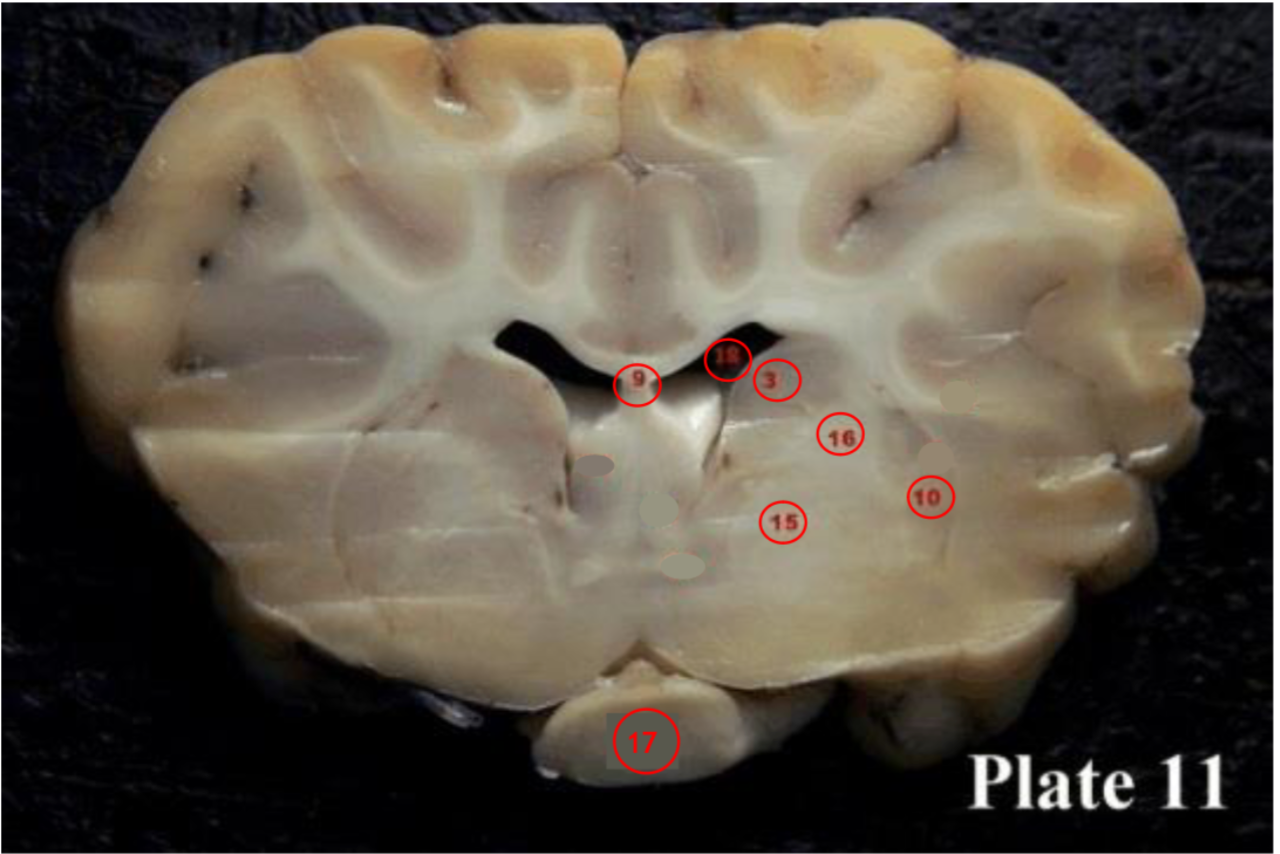
Third ventricle
directly between the left and right thalamus. located in the midbrain diencephalon
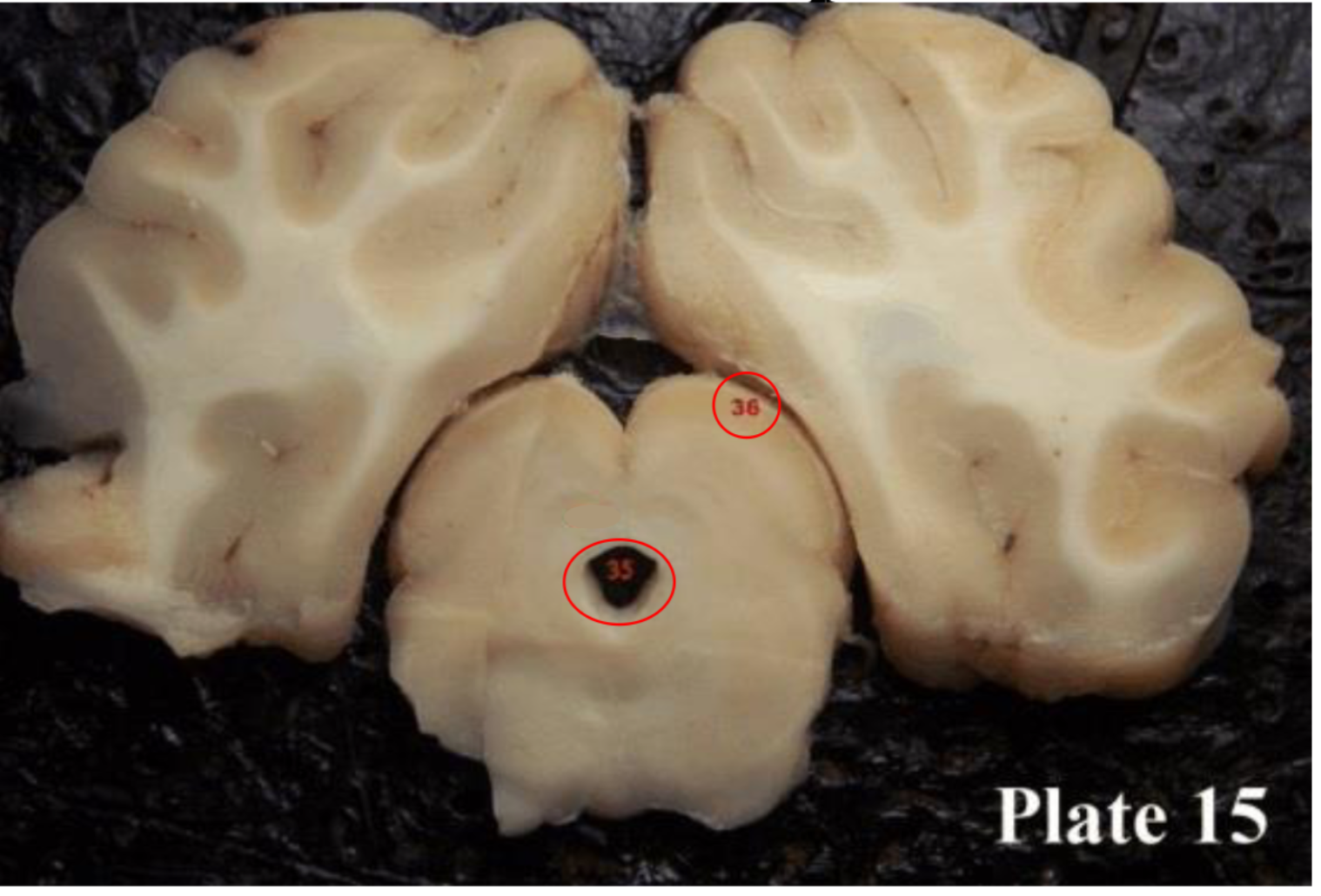
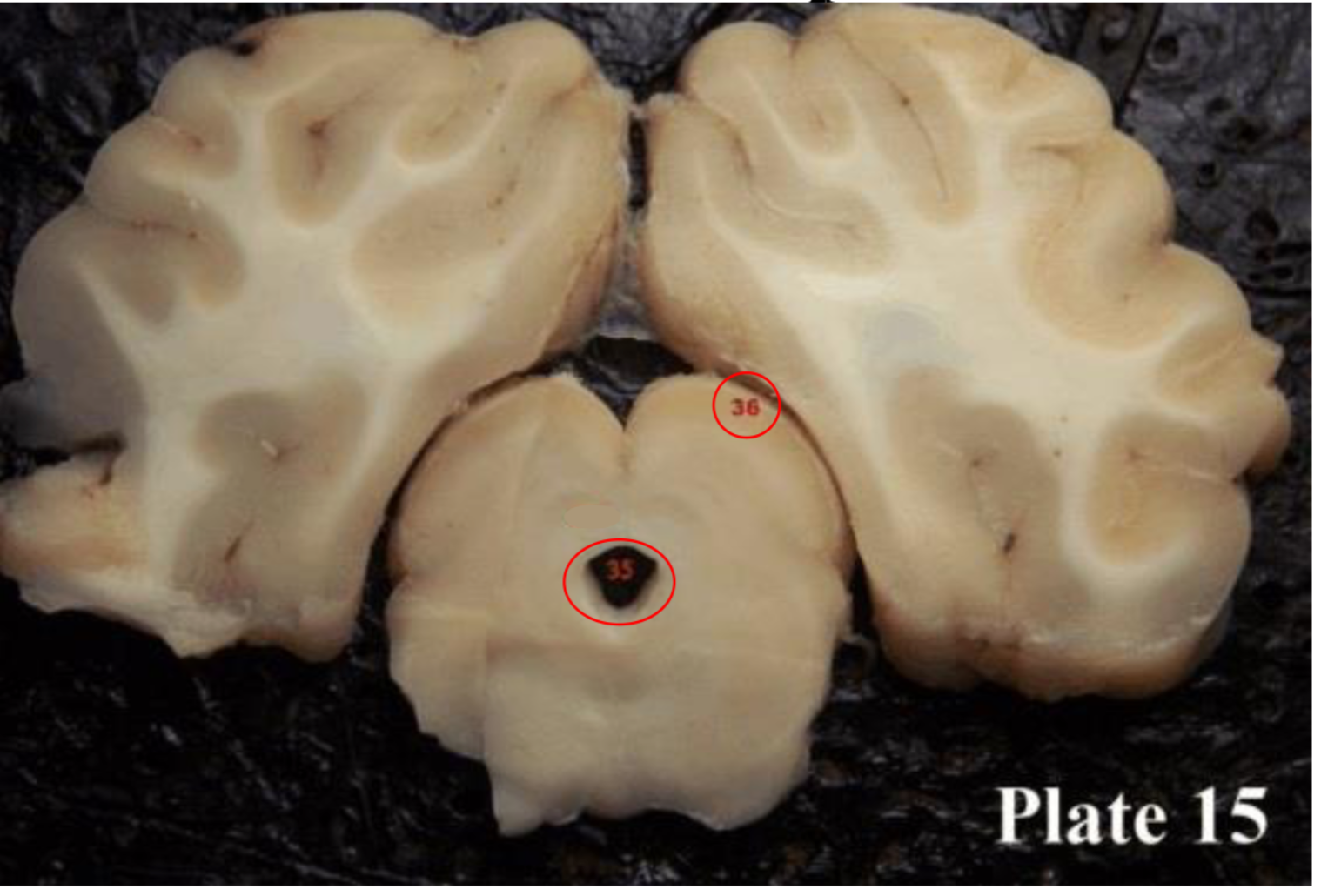
Superior colliculi
(36) paired with the inferior colliculi to form the tectum or corpora quadregema
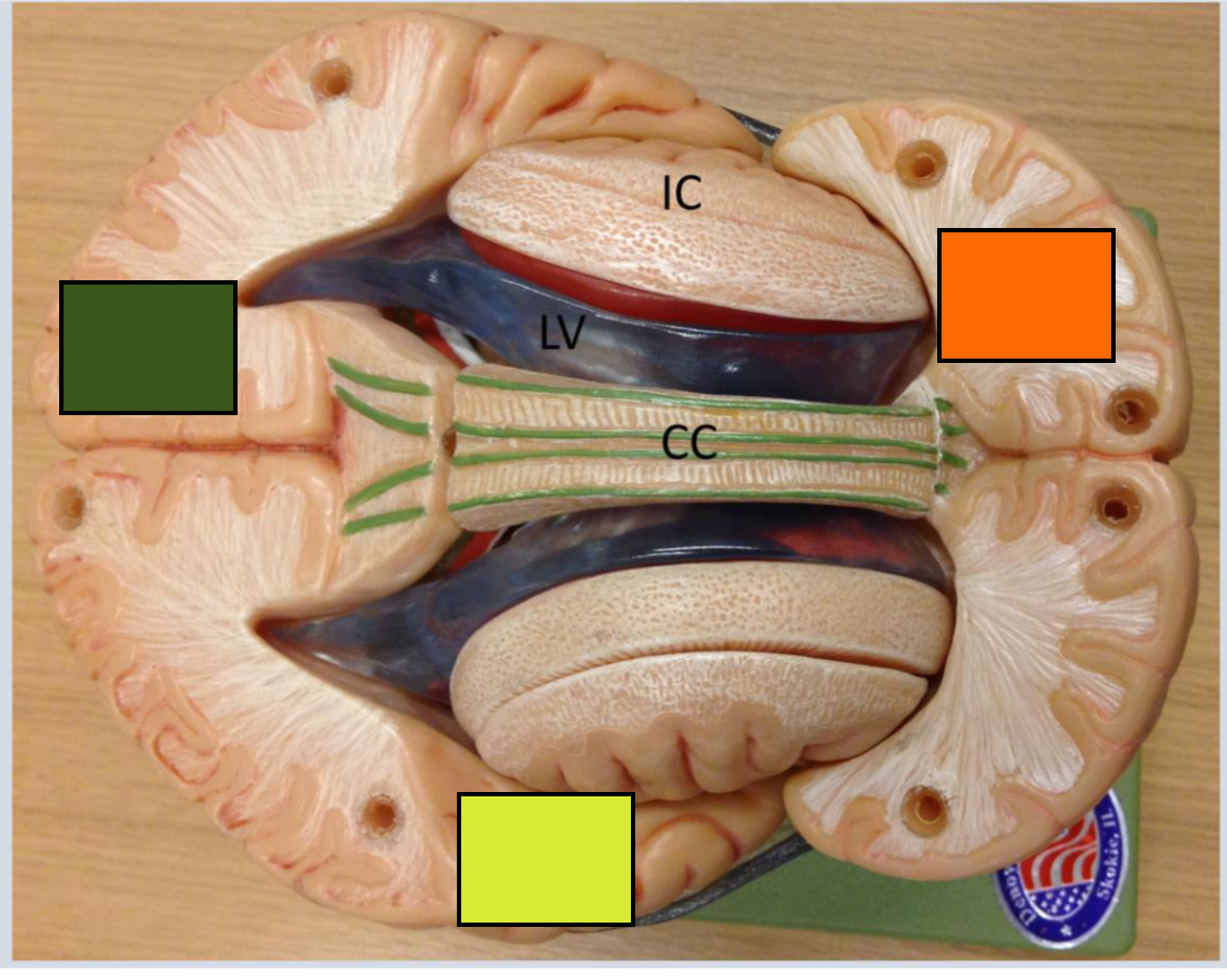
What is the green square
Occipital cortex
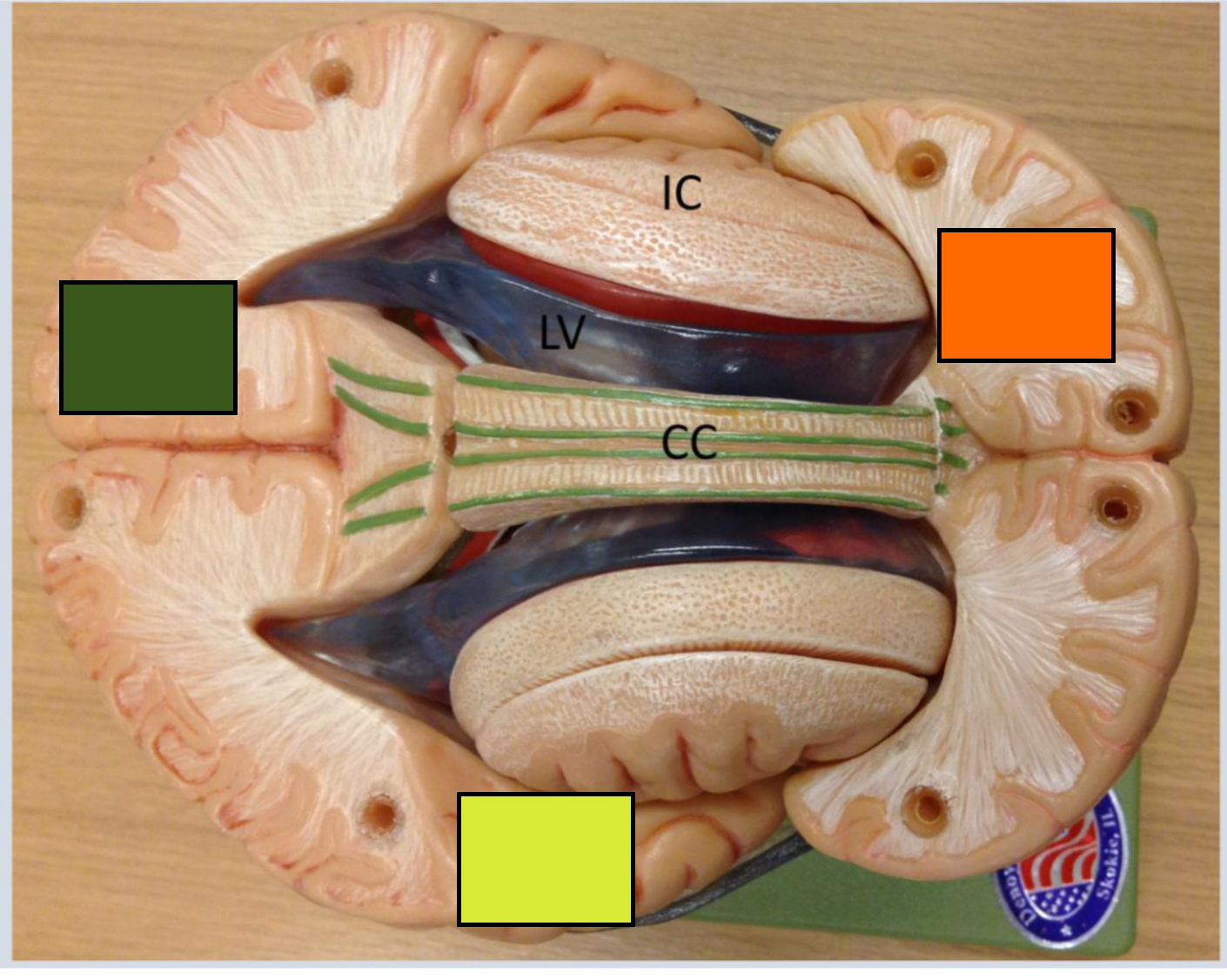
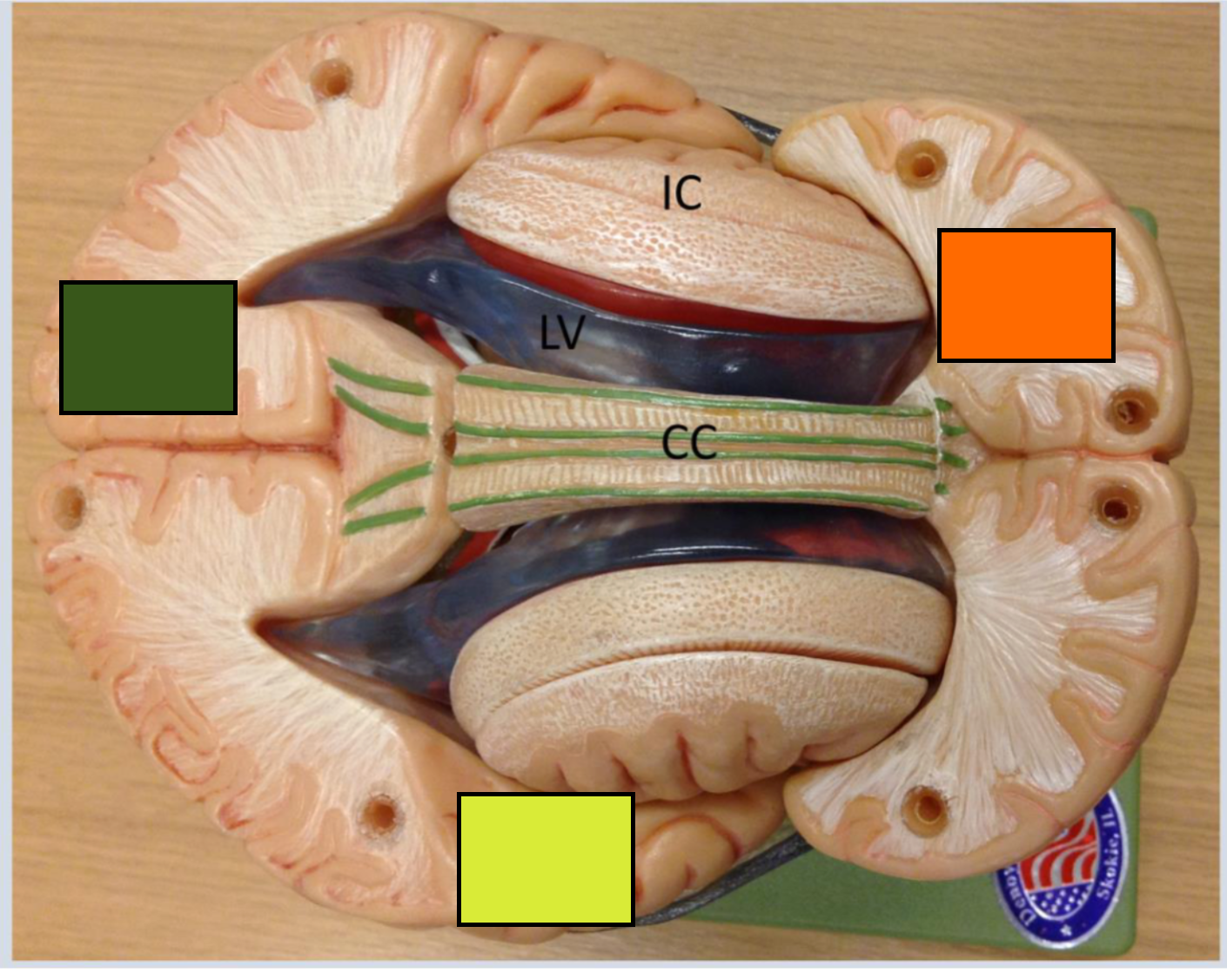
What is the yellow square
Temporal lobe
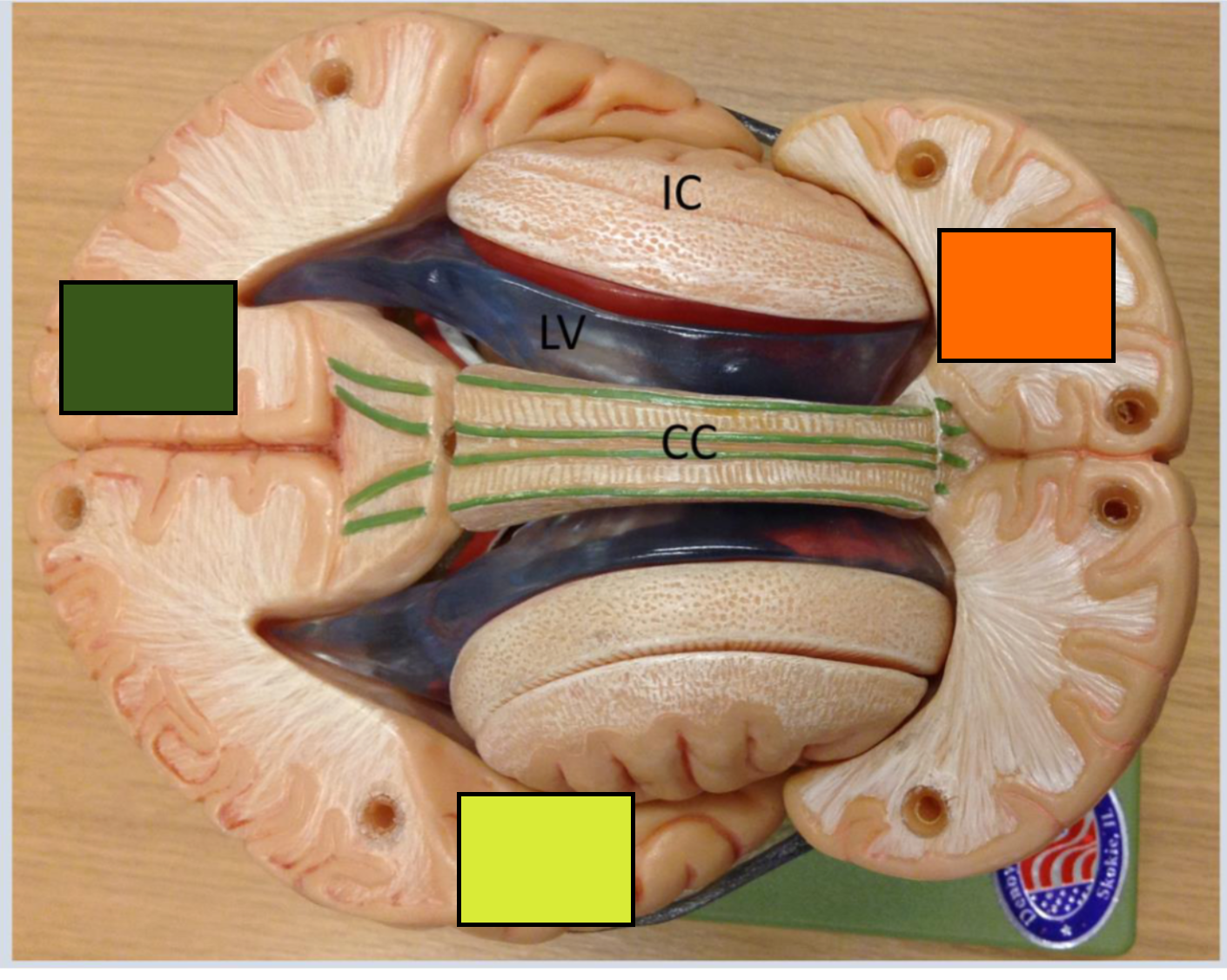
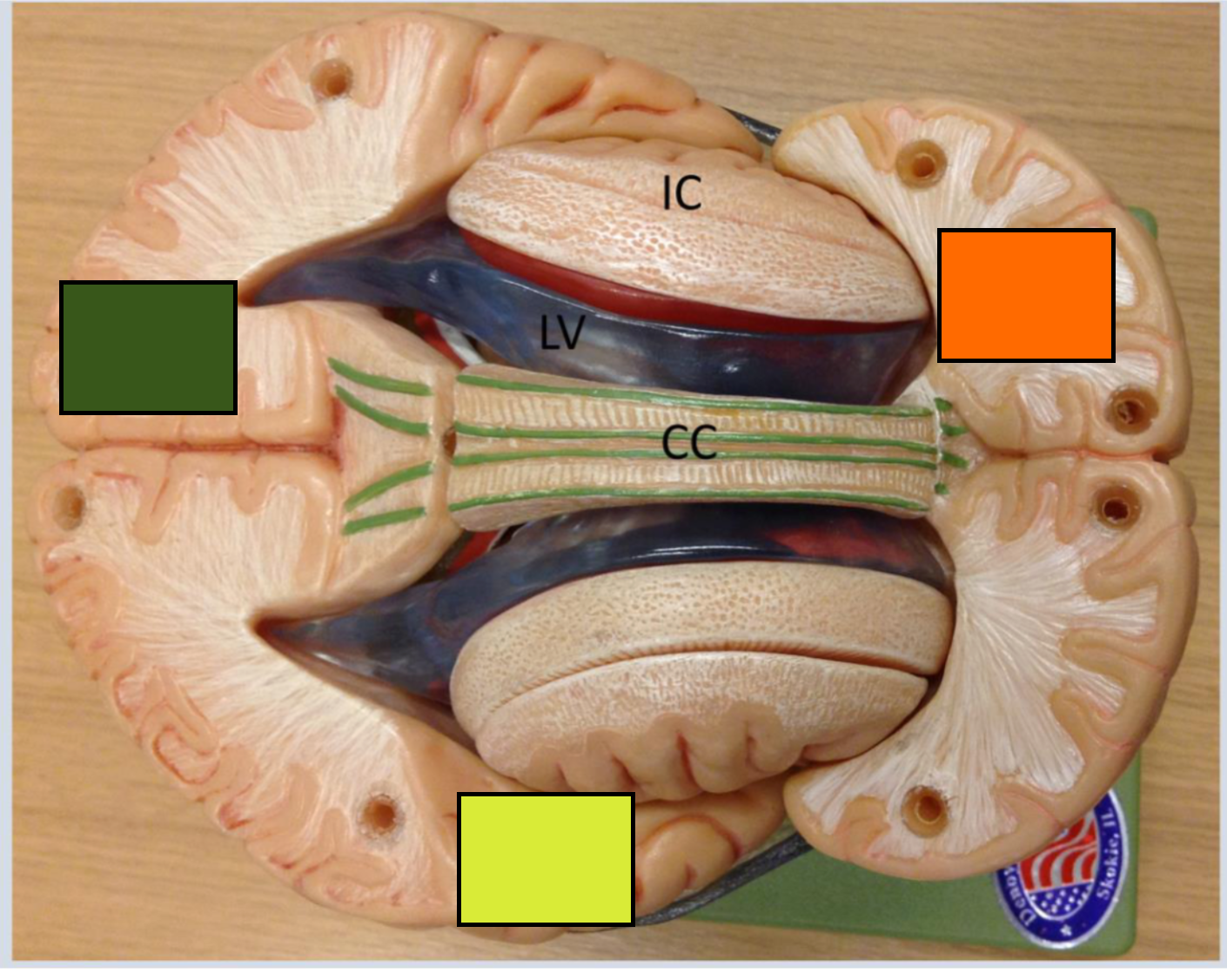
What is the orange square
Frontal cortex