Respiratory anatomy
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:03 PM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
1
New cards
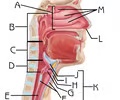
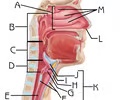
External Nares (Nostrils)
L
Function: channel air into and out of the nasal cavity
Function: channel air into and out of the nasal cavity
2
New cards
Nasal septum
Location: between the nostrils
Function: divides the nasal cavity
Function: divides the nasal cavity
3
New cards
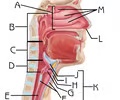
Nasal cavity
A
Function: filter, warm and moisten air; produce mucus; resonance chamber for speech
Function: filter, warm and moisten air; produce mucus; resonance chamber for speech
4
New cards
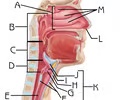
Nasal Conchae (superior, middle, inferior)
M
Function: inferior-responsible for the majority of airflow direction, humidification, heating, and filtering of air inhaled through the nose; middle-act as buffers to protect the sinuses from coming in direct contact with pressurized nasal airflow; superior-serve to protect the olfactory bulb
Function: inferior-responsible for the majority of airflow direction, humidification, heating, and filtering of air inhaled through the nose; middle-act as buffers to protect the sinuses from coming in direct contact with pressurized nasal airflow; superior-serve to protect the olfactory bulb
5
New cards
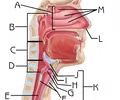
Nasopharynx
B
Subdivision of the Pharynx
Function: passageway for air from nasal cavity
Subdivision of the Pharynx
Function: passageway for air from nasal cavity
6
New cards
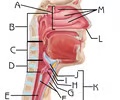
Oropharynx
C
Subdivision of the Pharynx
Function: Passageway for food and air
Subdivision of the Pharynx
Function: Passageway for food and air
7
New cards
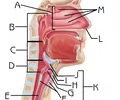
laryngopharynx
D
Subdivision of the Pharynx
Function: Passageway for food and air
Subdivision of the Pharynx
Function: Passageway for food and air
8
New cards
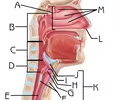
Larynx
K
Function: air passageway; prevents food from entering lower respiratory tract; voice production
Function: air passageway; prevents food from entering lower respiratory tract; voice production
9
New cards
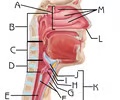
Thyroid cartilage
H
Function:serves to protect the vocal folds; attachment for several laryngeal muscles
Function:serves to protect the vocal folds; attachment for several laryngeal muscles
10
New cards
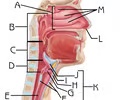
Epiglottis
J
Function: prevent food from entering lower respiratory system;
Function: prevent food from entering lower respiratory system;
11
New cards
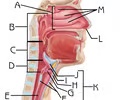
Cricoid Cartilage
F
Function:provide attachments for the cricothyroid muscle, posterior cricoarytenoid muscle and lateral cricoarytenoid muscle muscles, cartilages, and ligaments involved in opening and closing the airway and in speech production
Function:provide attachments for the cricothyroid muscle, posterior cricoarytenoid muscle and lateral cricoarytenoid muscle muscles, cartilages, and ligaments involved in opening and closing the airway and in speech production
12
New cards
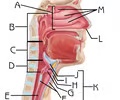
Vestibular Folds
I
Function: keeping food and drink out of the airway, breathing, and speech
Function: keeping food and drink out of the airway, breathing, and speech
13
New cards
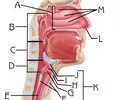
Vocal folds
G
Function: voice production
Function: voice production
14
New cards
Trachea
E
Function: air passageway; filters, warms and moistens air
Function: air passageway; filters, warms and moistens air
15
New cards
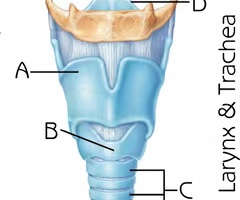
Thyroid cartilage (View 2)
A
Function:serves to protect the vocal folds; attachment for several laryngeal muscles
Function:serves to protect the vocal folds; attachment for several laryngeal muscles
16
New cards
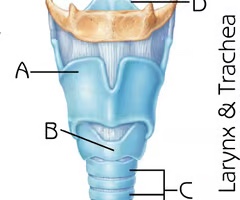
Cricoid Cartilage (View 2)
B
Function:provide attachments for the cricothyroid muscle, posterior cricoarytenoid muscle and lateral cricoarytenoid muscle muscles, cartilages, and ligaments involved in opening and closing the airway and in speech production
Function:provide attachments for the cricothyroid muscle, posterior cricoarytenoid muscle and lateral cricoarytenoid muscle muscles, cartilages, and ligaments involved in opening and closing the airway and in speech production
17
New cards
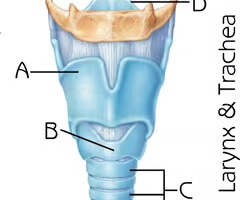
Epiglottis (View 2)
D
Function: prevent food from entering lower respiratory system
Function: prevent food from entering lower respiratory system
18
New cards
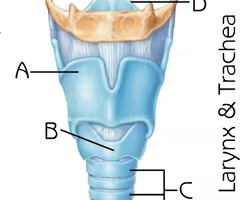
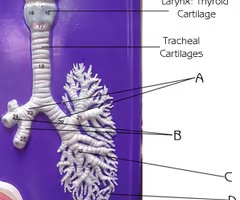
Tracheal cartilages
C
Function: maintain structure of the airway of the trachea
Function: maintain structure of the airway of the trachea
19
New cards
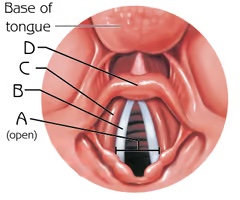
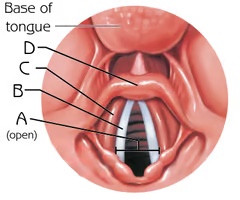
Glottis (open)
A
combination of the vocal folds (vocal cords) and the space in between the folds
Function: voice production
combination of the vocal folds (vocal cords) and the space in between the folds
Function: voice production
20
New cards
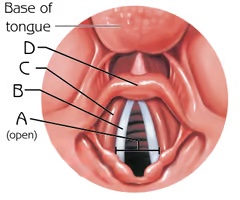
Vocal Folds (View 2)
B
Function: voice production
Function: voice production
21
New cards
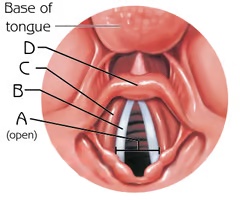
Vestibular Folds (View 2)
C
Function: keeping food and drink out of the airway, breathing, and speech
Function: keeping food and drink out of the airway, breathing, and speech
22
New cards
Epiglottis (View 3)
D
Function: prevent food from entering lower respiratory system
Function: prevent food from entering lower respiratory system
23
New cards
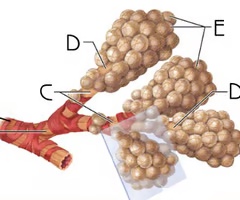
terminal bronchiole
A
the most distal segment of the conducting zone
Function: passage of air to respiratory zone; secretion of surfactant which reduces surface tension, allowing for bronchioles to expand during inspiration and keeping the bronchioles from collapsing during expiration
the most distal segment of the conducting zone
Function: passage of air to respiratory zone; secretion of surfactant which reduces surface tension, allowing for bronchioles to expand during inspiration and keeping the bronchioles from collapsing during expiration
24
New cards
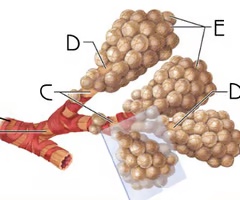
bronchiole
B
branches no longer contain cartilage or glands in their submucosa
Function: passage of air to terminal bronchioles; secretion of surfactant which reduces surface tension, allowing for bronchioles to expand during inspiration and keeping the bronchioles from collapsing during expiration
branches no longer contain cartilage or glands in their submucosa
Function: passage of air to terminal bronchioles; secretion of surfactant which reduces surface tension, allowing for bronchioles to expand during inspiration and keeping the bronchioles from collapsing during expiration
25
New cards
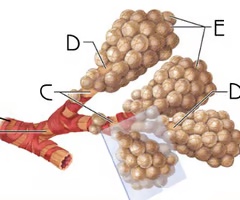
respiratory bronchiole
C
Function: passage of air to alveolar ducts
Function: passage of air to alveolar ducts
26
New cards
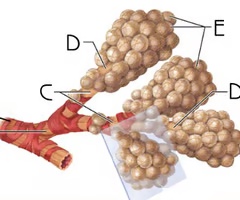
Alveolar ducts
D
Function: passage of air to alveoli
Function: passage of air to alveoli
27
New cards
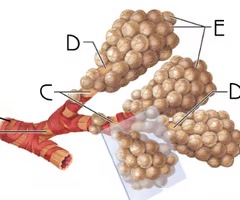
Alveoli
E
Function: gas exchange with blood- giving oxygen to blood and taking carbon dioxide
Function: gas exchange with blood- giving oxygen to blood and taking carbon dioxide
28
New cards
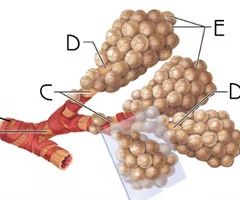
Alveolar sac
F
Function: contain groups of alveoli for gas exchange
Function: contain groups of alveoli for gas exchange
29
New cards
Primary bronchi
A
branch off the trachea
Function:passageway for air
branch off the trachea
Function:passageway for air
30
New cards
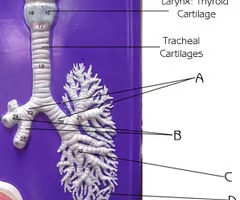
Secondary bronchi
B
Branch off the primary bronchi
Function:passageway for air
Branch off the primary bronchi
Function:passageway for air
31
New cards
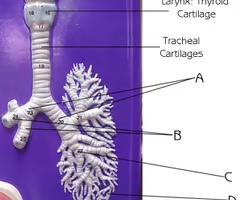
Tertiary bronchi
C
Branch off secondary bronchi
Function:passageway for air
Branch off secondary bronchi
Function:passageway for air
32
New cards
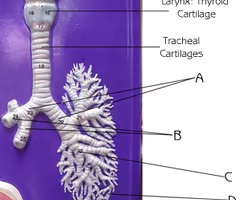
bronchioles (view 2)
D
Branch off tertiary bronchi; branches no longer contain cartilage or glands in their submucosa
Function:passageway for air
Branch off tertiary bronchi; branches no longer contain cartilage or glands in their submucosa
Function:passageway for air
33
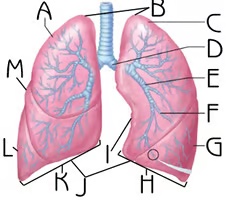
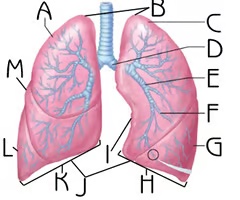
New cards
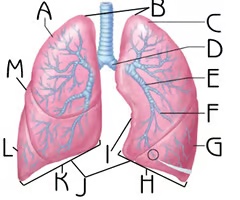
Right Superior Lobe
A
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
34
New cards
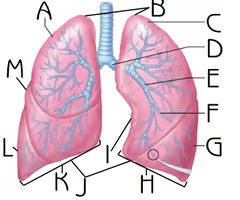
Apex
B
Function: contain uppermost airways
Function: contain uppermost airways
35
New cards
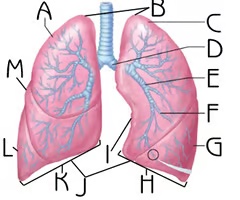
Left Superior Lobe
C
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
36
New cards
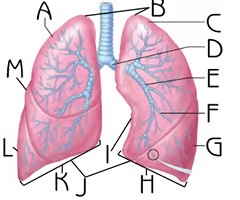
Secondary bronchus (View 2)
E
Branch off the primary bronchi
Function:passageway for air
Branch off the primary bronchi
Function:passageway for air
37
New cards
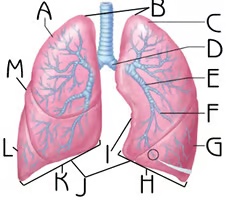
Tertiary bronchus (View 2)
F
Branch off the secondary bronchi
Function:passageway for air
Branch off the secondary bronchi
Function:passageway for air
38
New cards
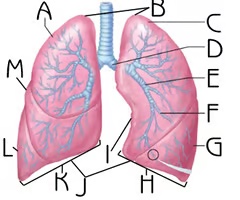
Left Inferior Lobe
G
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
39
New cards
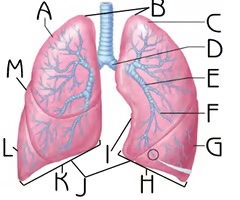
Left Lung
H
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
40
New cards
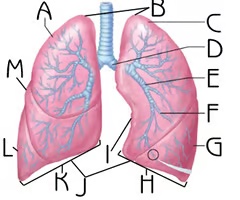
Right Lung
K
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
41
New cards
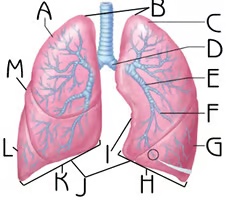
Cardiac notch
I
Function: accommodate the heart
Function: accommodate the heart
42
New cards
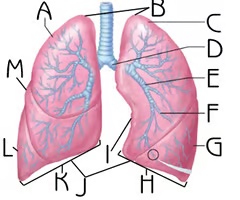
Base of lungs
J
Function: respiration
Function: respiration
43
New cards
Right inferior lobe
l
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
44
New cards
Right middle lobe
M
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
45
New cards
hilus
A
Function: entry to lungs for airways, blood vessels, and lymph vessels
Function: entry to lungs for airways, blood vessels, and lymph vessels
46
New cards
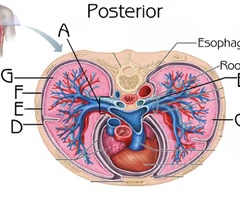
Left primary bronchus (View 2)
B
Function: passageway for air
Function: passageway for air
47
New cards
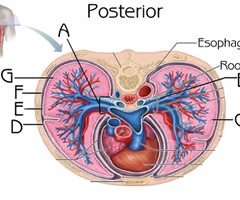
Left Lung (Cross section)
C
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
48
New cards
Pleural cavity
D
Function: aids optimal functioning of the lungs during respiration;contains pleural fluid, which allows the pleurae to slide effortlessly against each other during ventilation
Function: aids optimal functioning of the lungs during respiration;contains pleural fluid, which allows the pleurae to slide effortlessly against each other during ventilation
49
New cards
Visceral pleurae
E
Located next to lungs
Function: cover and protect lungs; create pleural cavity which contains pleural fluid, which allows the pleurae to slide effortlessly against each other during ventilation
Located next to lungs
Function: cover and protect lungs; create pleural cavity which contains pleural fluid, which allows the pleurae to slide effortlessly against each other during ventilation
50
New cards
Parietal Pleurae
F
Located just deep to thoracic wall
Function: cover and protect lungs; create pleural cavity which contains pleural fluid, which allows the pleurae to slide effortlessly against each other during ventilation
Located just deep to thoracic wall
Function: cover and protect lungs; create pleural cavity which contains pleural fluid, which allows the pleurae to slide effortlessly against each other during ventilation
51
New cards
Right Lung (View 2)
G
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
Function: house passageways smaller than primary bronchi
52
New cards
Bronchiole (Histology)
B
Branch off tertiary bronchi; branches no longer contain cartilage or glands in their submucosa
Function:passageway for air
Branch off tertiary bronchi; branches no longer contain cartilage or glands in their submucosa
Function:passageway for air
53
New cards
Alveoli (Histology)
A
Function: gas exchange with blood- giving oxygen to blood and taking carbon dioxide
Function: gas exchange with blood- giving oxygen to blood and taking carbon dioxide
54
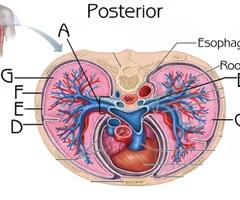
New cards
Dorsal Respiratory Group
C
Function: Quiet inspiration
Function: Quiet inspiration
55
New cards
Ventral Respiratory Group
D
Function: Forceful inspiration and active expiration
Function: Forceful inspiration and active expiration
56
New cards
Pneumotaxic Center
A
Function:Influences inspiration to shut off (inhibits inspiratory & apneustic centers)
Function:Influences inspiration to shut off (inhibits inspiratory & apneustic centers)
57
New cards
Apneustic Center
B
Function: Prolongs inspiration (stimulates inspiratorycenter); deeper, slower pattern of breath
Function: Prolongs inspiration (stimulates inspiratorycenter); deeper, slower pattern of breath
58
New cards
Mucosa (Histology)
A
Function: lining and secretion of mucus
Function: lining and secretion of mucus
59
New cards
Submucosa
B
Function: contain blood supply; secrete mucus
Function: contain blood supply; secrete mucus
60
New cards
Hyaline Cartilage (Trachea)
C
Function: maintain opening of airway
Function: maintain opening of airway
61
New cards
Adventitia
D
Function: loose connective tissue that binds trachea to surrounding tissues
Function: loose connective tissue that binds trachea to surrounding tissues
62
New cards
Goblet cells
E
Function: secrete mucus
Function: secrete mucus
63
New cards
Mucus Glands
F
Function: secrete mucus
Function: secrete mucus
64
New cards
Chondrocyte in lacuna
G
Function: maintain matrix of cartilage
Function: maintain matrix of cartilage
65
New cards
Cilia
A
Function: Move mucus toward throat
Function: Move mucus toward throat
66
New cards
Arytenoid cartilage
C
Function: moving vocal folds
Function: moving vocal folds
67
New cards
Corniculate cartilage
B
Function: moving vocal folds
Function: moving vocal folds
68
New cards
Cuneiform cartilage
A
Function: moving vocal folds
Function: moving vocal folds
69
New cards
Chemoreceptors (respiratory)
What receptors are stimulated more by increased CO2 levels than by decreased O2 levels and stimulate Rhythmicity Area for respiration?
70
New cards
Aorta and Carotid Arteries
What is the location of the peripheral chemoreceptors of the respiratory system?
71
New cards
Medulla oblongata
What is the location of the central chemoreceptors of the respiratory system?
72
New cards
Type I alveolar cell (simple squamous)
A
Function: gas exchange
Function: gas exchange
73
New cards
Type II alveolar cells
B
Function: produce surfactant that keeps alveoli from collapsing and sticking together by decreasing surface tension
Function: produce surfactant that keeps alveoli from collapsing and sticking together by decreasing surface tension
74
New cards
Nasal Bone
A
Function: provide structure to external nose
Function: provide structure to external nose
75
New cards
Middle Nasal concha
B
Part of ethmoid bone
Function: create channel for middle nasal meatus
Part of ethmoid bone
Function: create channel for middle nasal meatus
76
New cards
perpendicular plate
C
Part of ethmoid bone
Function: separate the two sides of the nose (septum)
Part of ethmoid bone
Function: separate the two sides of the nose (septum)
77
New cards
Inferior nasal concha
D
part of maxilla
Function: create channel for inferior nasal meatus
part of maxilla
Function: create channel for inferior nasal meatus
78
New cards
Vomer
E
Function: provide part of nasal septum and hard palate
Function: provide part of nasal septum and hard palate
79
New cards
Ethmoid sinus
B
Function: decreasing weight of skull; increasing resonance of voice; humidifying and warming air
Function: decreasing weight of skull; increasing resonance of voice; humidifying and warming air
80
New cards
Frontal sinus
A
Function: decreasing weight of skull; increasing resonance of voice; humidifying and warming air
Function: decreasing weight of skull; increasing resonance of voice; humidifying and warming air
81
New cards
Sphenoid sinus
C
Function: decreasing weight of skull; increasing resonance of voice; humidifying and warming air
Function: decreasing weight of skull; increasing resonance of voice; humidifying and warming air
82
New cards
Maxillary sinus
D
Function: decreasing weight of skull; increasing resonance of voice; humidifying and warming air
Function: decreasing weight of skull; increasing resonance of voice; humidifying and warming air