Anatomy Lab Midterm
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
Chin
The mental region refers to where?
Ear
The otic region refers to where?
Calf
The sural region refers to where?
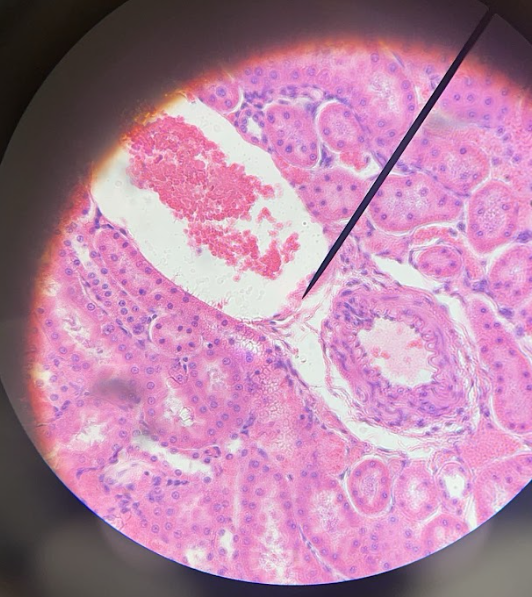
Simple cuboidal epithelial
What kind of tissue?
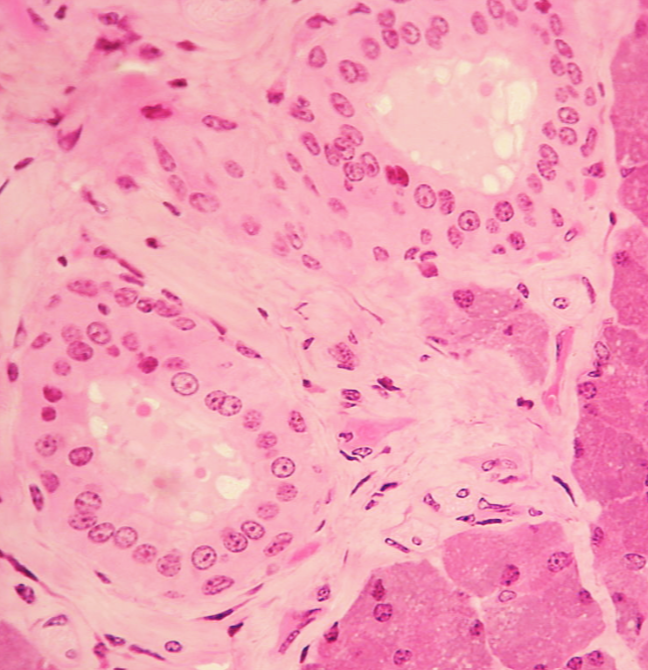
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
What kind of tissue?
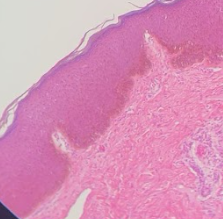
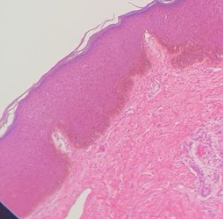
Stratified squamous keratinized
What kind of epithelium?
Dense irregular connective tissue
What kind of tissue?
Stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium
What kind of tissue?
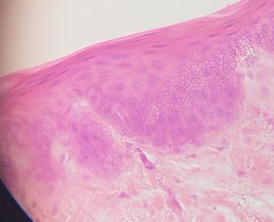
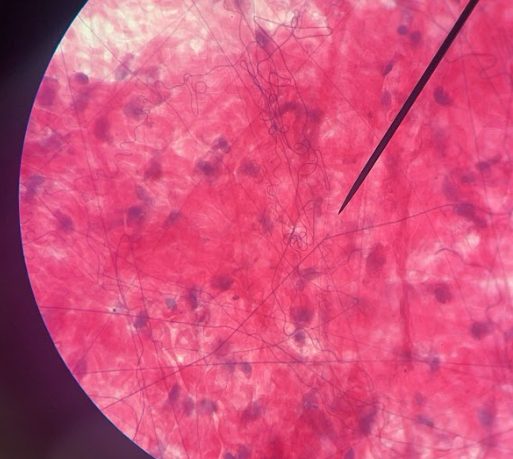
Loose areolar connective tissue
What kind of tissue?
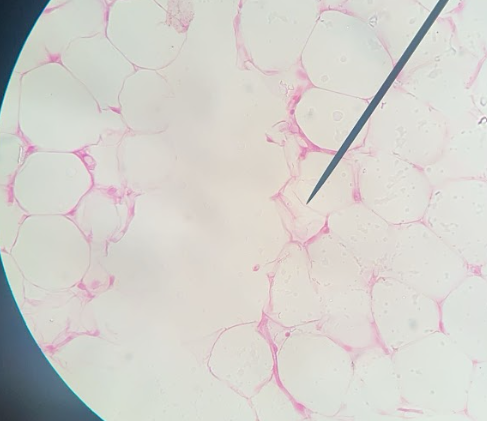
Adipose
What kind of tissue?
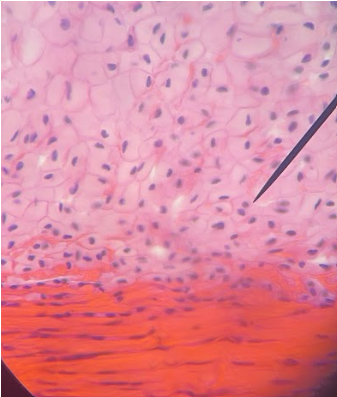
Dense regular collagenous CT
What kind of tissue?
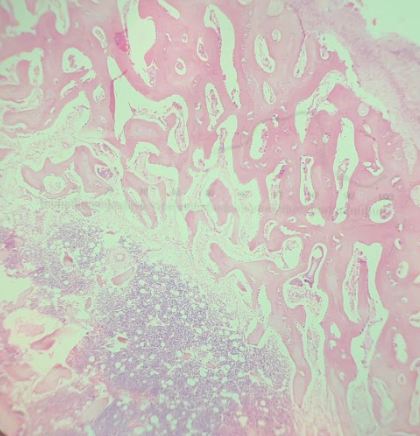
Spongy bone
What kind of tissue?
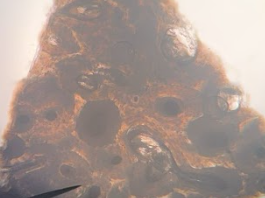
Compact bone
What kind of tissue?
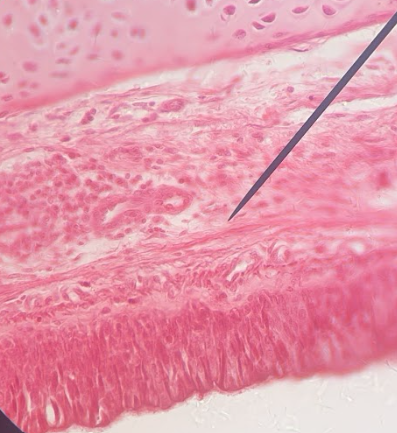
Hyaline cartilage
What kind of tissue?
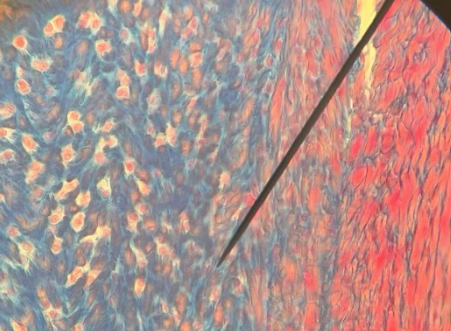
Fibrocartilage
What kind of tissue?
fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
Types of joints: f_____, c________, s_______
Primary tissues
Epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous are all types of ____ _____
simple, stratified, pseudostratified
3 main subdivisions of epithelium
Areolar
Loose connective tissue is also known as what?
Connective tissue proper
Loose (areolar) CT, dense regular CT, dense irregular CT, reticular CT, and adipose tissue are the types of ____ ____ _____
regular, irregular
Dense connective tissue has two categories: _____ and ______
hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, elastic cartilage
The types of cartilage CT are: h_____ ______, f___________, e______ _____
Periosteum
Most superficial tissue of a bone
Osteon
Repeating subunit of bone
Central canal
Runs down the center of each osteon
Lamellae
Rings of bone similar to tree rings that surround the central canal
Lacunae
Small cavities in bone
Perforating canals
Run perpendicular to the lamellae and carry blood vessels from deep in the bone to the periosteum
Trabeculae
Spongy bone is made of what?
depressions
The markings: facet, fossa, fovea, groove, and sulcus are all _____
Facet
Shallow indented surface where two bones meet to form a joint
Fossa
Deeper indented surface in a bone that usually allows a rounded surface of another bone to fit inside of it
Fovea
Shallow pit; often the site of attachment for a ligament
Groove
Allows a blood vessel to travel along the bone’s surface
Sulcus
Also known as a groove
Openings
Canals, fissures, foramen, meatus are all types of ____
Meatus
Another name for a canal in a bone
Condyle
Round end of a bone that fits into a fossa or facet of another bone at a joint
Crest
Ridge along a bone, generally a site of muscle attachment
Epicondyle
Small projection usually proximal to a condyle
Head
Rounded end of the bone that fits into a fossa to form a joint
Line
Ridge along a bone where a muscle attaches
Process
Any bony projection
Protuberance
An outgrowth from a bone due to repetitive pull from a muscle
Trochanter
Large bony projection, only example is in femur
Tubercle
Small rounded projection
Tuberosity
Larger tubercle
Fibrous
Type of joint where the bones are joined by short collagen fibers (most are synarthroses). Include sutures, gomphoses, and syndesmoses.
Cartilaginous
Symphyses and synchondroses are types of ____ joints
Synovial
Planes, saddles, hinges, and ball-and-socket joints are all kinds of ____ joints
Plane
The bones of this kind of joint have flat articular surfaces that allow the bones to glide past one another
Condyloid
This kind of joint consists of one bone that fits into the concave surface of another bone, such as the radiocarpal or metacarpophalangeal joints
Saddle
Similar to condyloid joints but permit a greater ROM
Pivot
Type of synovial joint where one bone rotates around another bone
Protraction
Movement anteriorly away from the body (such as the jaw in an underbite)
Retraction
Movement posteriorly towards the body (such as the jaw in an overbite)
Mastoid process
Structure of the temporal bone that is palpable behind the ear
Styloid process
Large, inferiorly pointing structure of the temporal bone
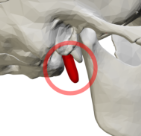
Jugular
What foramen
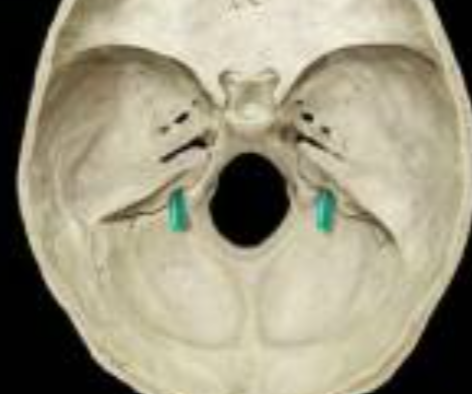
Mandibular fossa
depression in the temporal bone that forms the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
squamous, petrous
The two parts of the temporal bone are the ___ and ____ parts
Occipital condyle
Paired structure of the occipital bone on both sides of the foramen magnum
Foramen magnum
Largest cranial foramen
Optic canal
Most anterior foramen of sphenoid bone
Sella turcica
Saddle on sphenoid bone
Crista galli
What is the ridge of the cribriform plate called
Alveolar process
Structure of the maxilla that supports the teeth
Mental foramen
Foramen near the chin
Mandibular condyle
The head of the mandible
Coronoid process
The other projection on the mandible besides the mandibular condyle
Mandibular notch
In between mandibular condyle and coronoid process
Ramus
Ridge on the body of the mandible
Inferior nasal conchae
Side bones of nasal cavity
Vomer
Forms nasal septum
Frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, maxillary
List the sinuses in order from superior to inferior
Atlas
Which is wider, the atlas or axis?
Cervical
What kind of vertebrae has a bifid (forked) spinous process
Thoracic
What kind of vertebrae has a inferiorly pointing spinous process
Lumbar
What kind of vertebrae has a blunt square spinous process L
7, 12, 5,
How many cervical, thoracic, and lumbar?
sacral promontory
Part of sacrum that projects superiorly into the pelvic cavity
Sacral canal
Part of posterior side of sacrum where spinal nerve roots pass through
Manubrium
Top part of the sternum
Body
Middle part of the sternum
coccyx
Bottom part of sacrum
Xiphoid process
Bottom part of sternum
7, 5, 2
How many true, false, and floating ribs are there?
costal cartilage
The cartilage attaching the ribs to the sternum is called what
Sternal
What part of the rib attaches to the costal cartilage
Costal groove
The ridge on the rib is called what
tubercle
The head of the rib is largely identifiable due to this structure close by it:
head
The posterior end of the rib is called what?
Greater and lesser horns
The horns of the hyoid are called the ___ ____ _____ _____
Sternal
The flat end of the clavicle is which end?
Acromial end
The curved rounded end of the clavicle is which end?
Conoid tubercle
The protrusion off of the clavicle is called what
Acromion
The most anterior and lateral part of the scapula is what
Coracoid process
What is below the acromion on the scapula
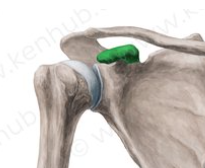
Glenoid cavity
The socket where the shoulder is held is called what
lateral, superior, medial border
The edges of the scapula are called the l_____, s______, and _______ ______