Chapter 26 - Energy
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
metabolism
the total of all the body’s processes
What happens to our metabolism as we get older?
It becomes lower
metabolic rate
The measurement of how much energy you use
basal metabolic rate
The low rate of how much energy you use. It’s usually the lowest when you’re at rest.
mucus
a thick, sticky substance that coats much of the respiratory system
What is the body’s most common source of energy?
sugar glucose
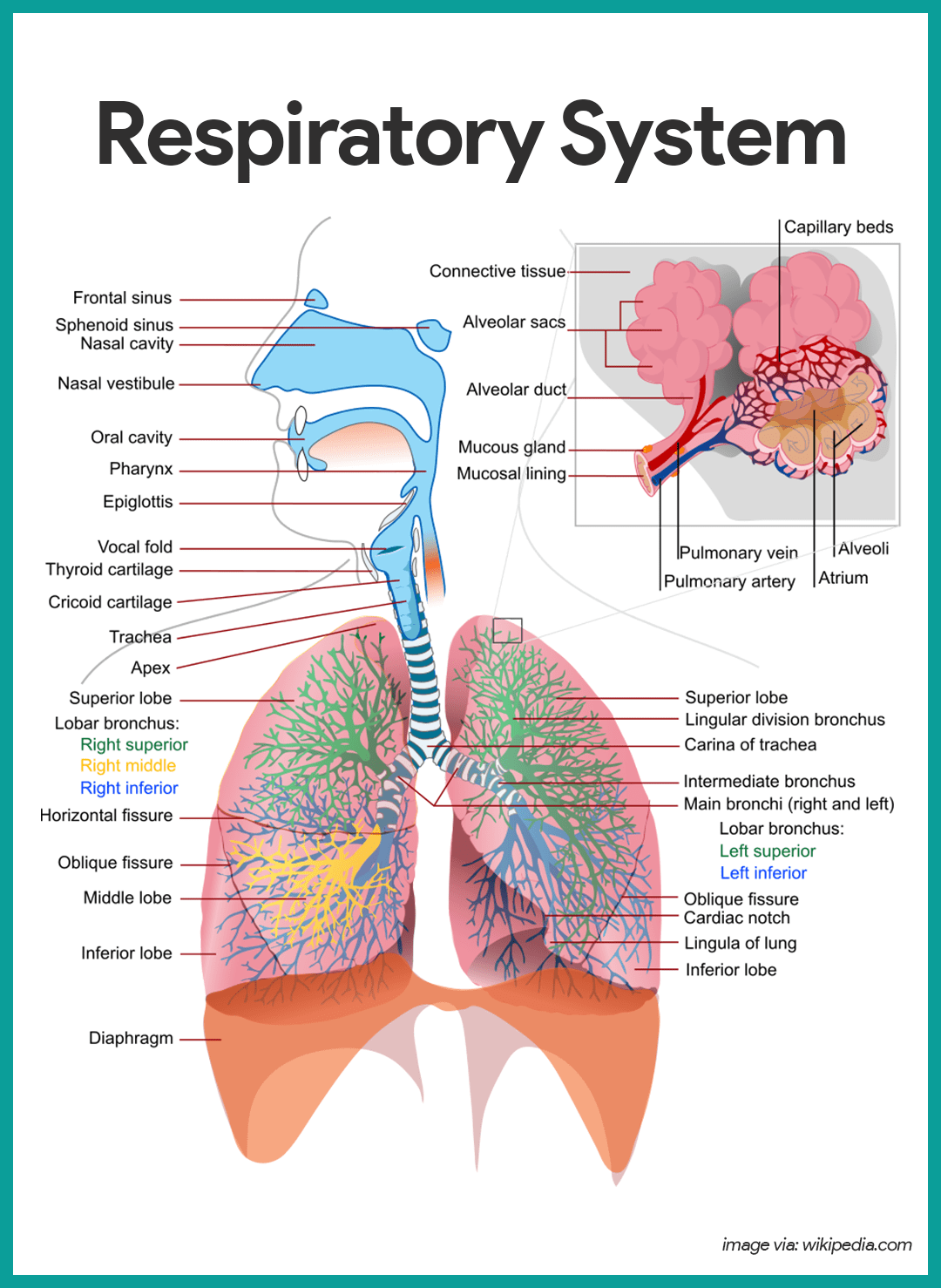
respiratory system’s primary function
to exchange carbon dioxide for a fresh supply of oxygen from the air
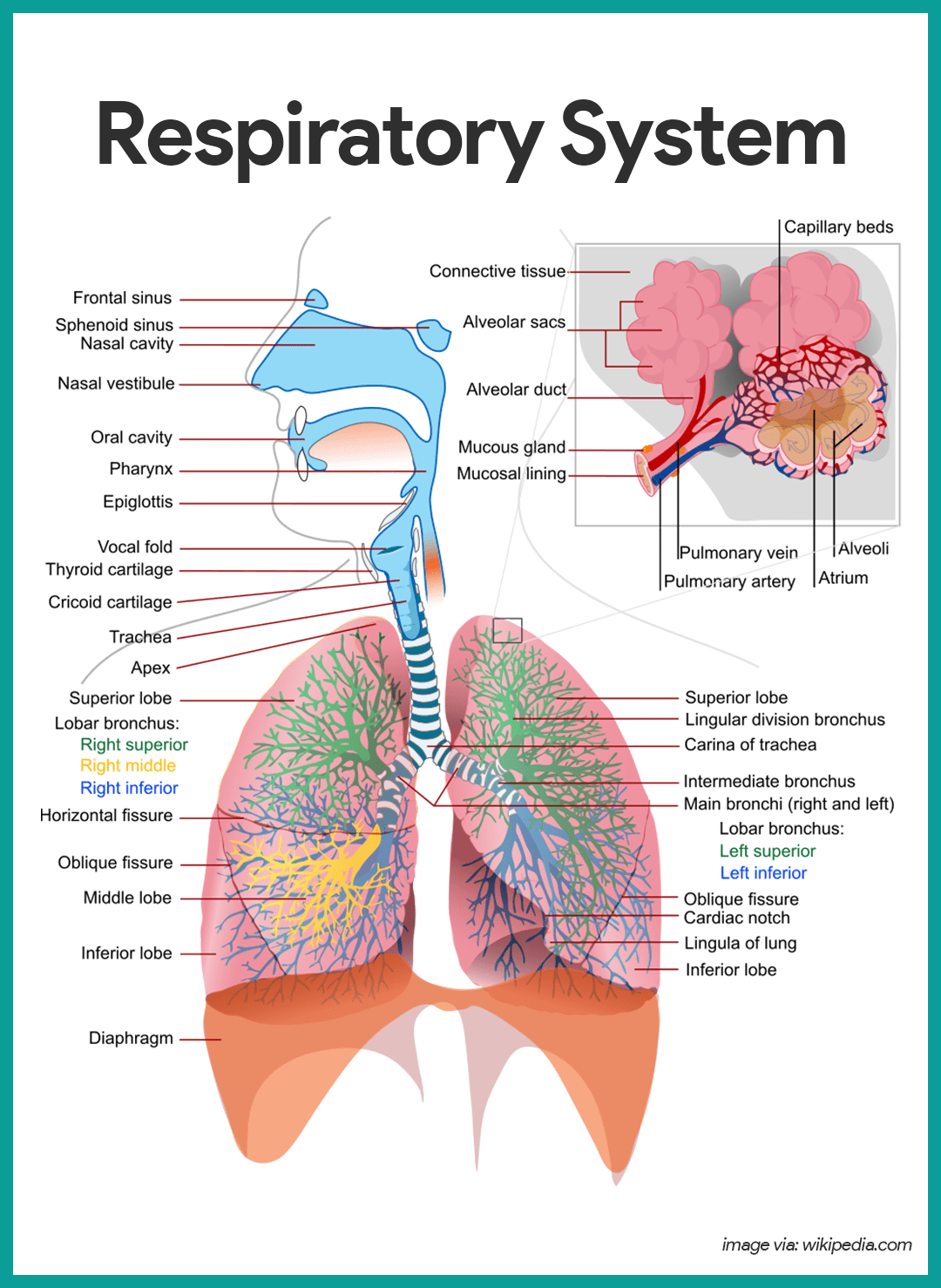
lungs
main organs of the respiratory system
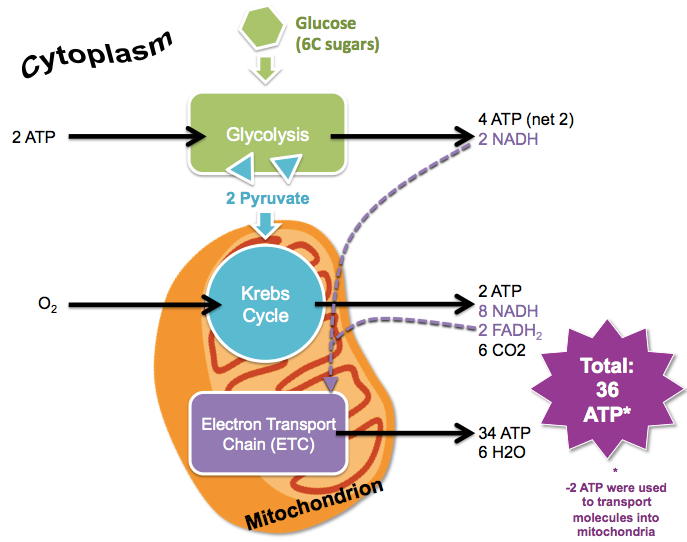
aerobic cellular respiration
The process of combining energy an energy source (sugar) with oxygen (O2) to release energy (ATP) in a form that cells can use.
The respiratory system supplies ____ and the digestive system supplies ____.
respiratory - OXYGEN
digestive - ENERGY
What is the transport system for the body?
blood
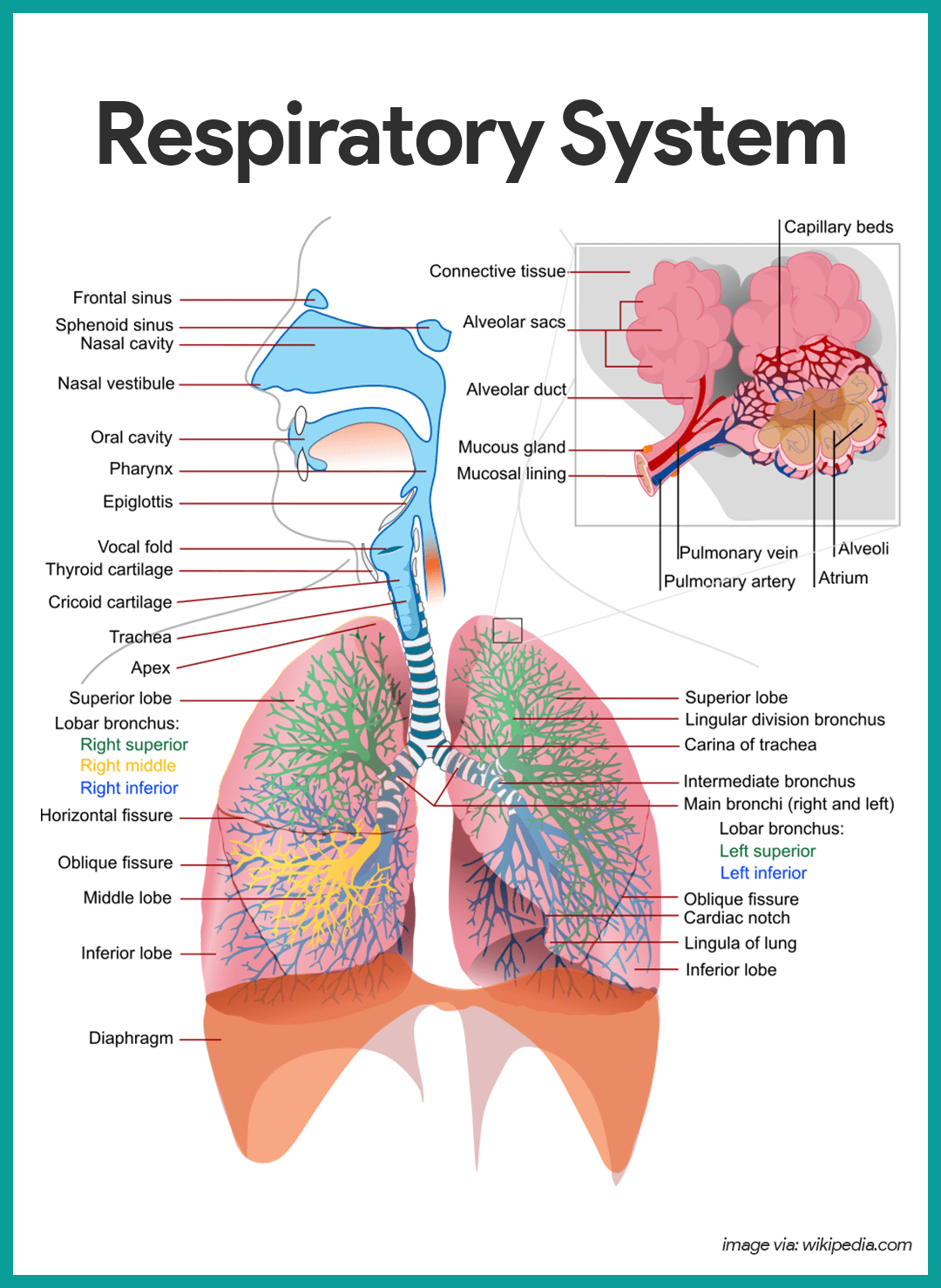
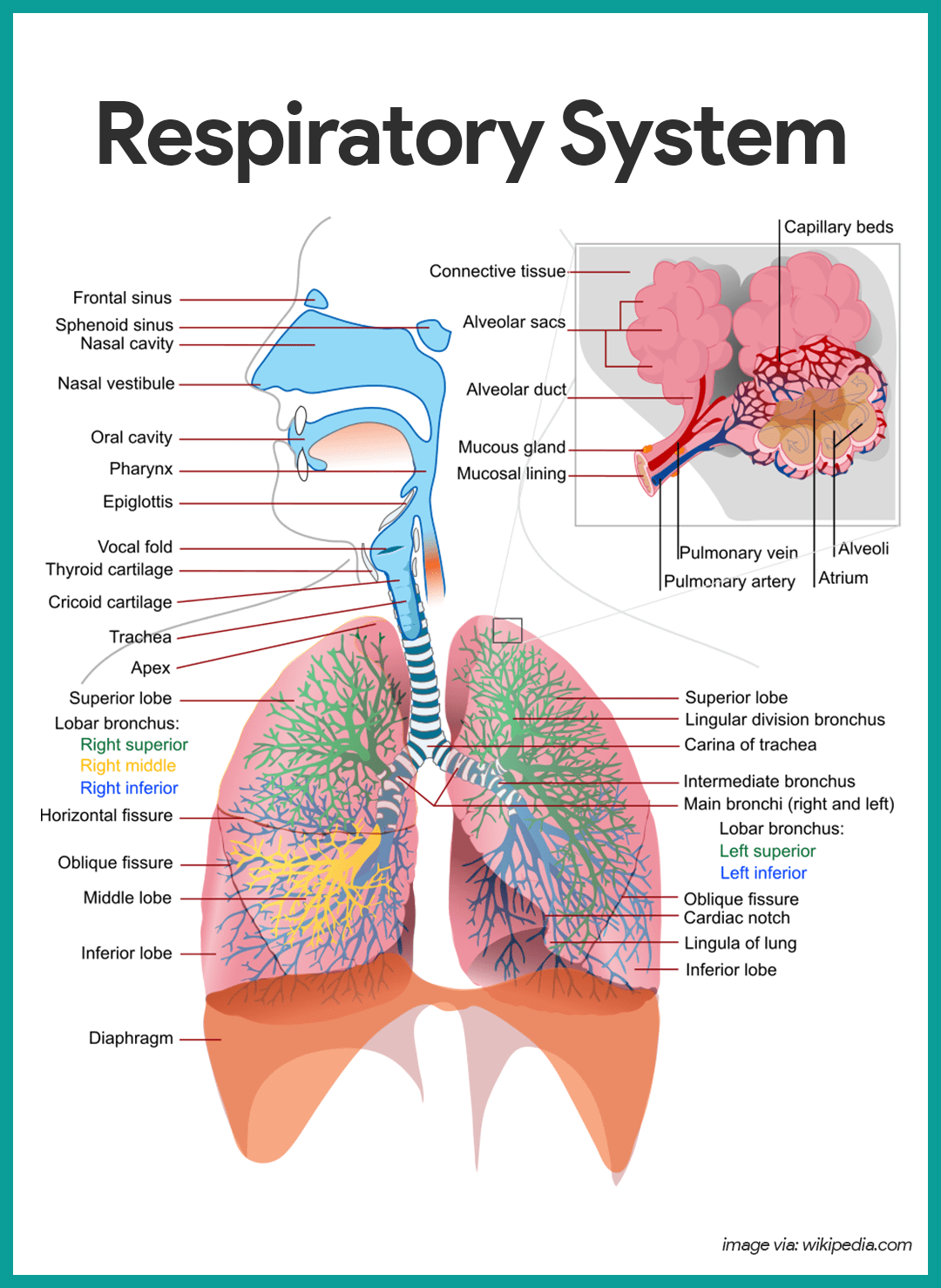
epiglottis (memorize its location too)
structure that prevents food from entering the lungs
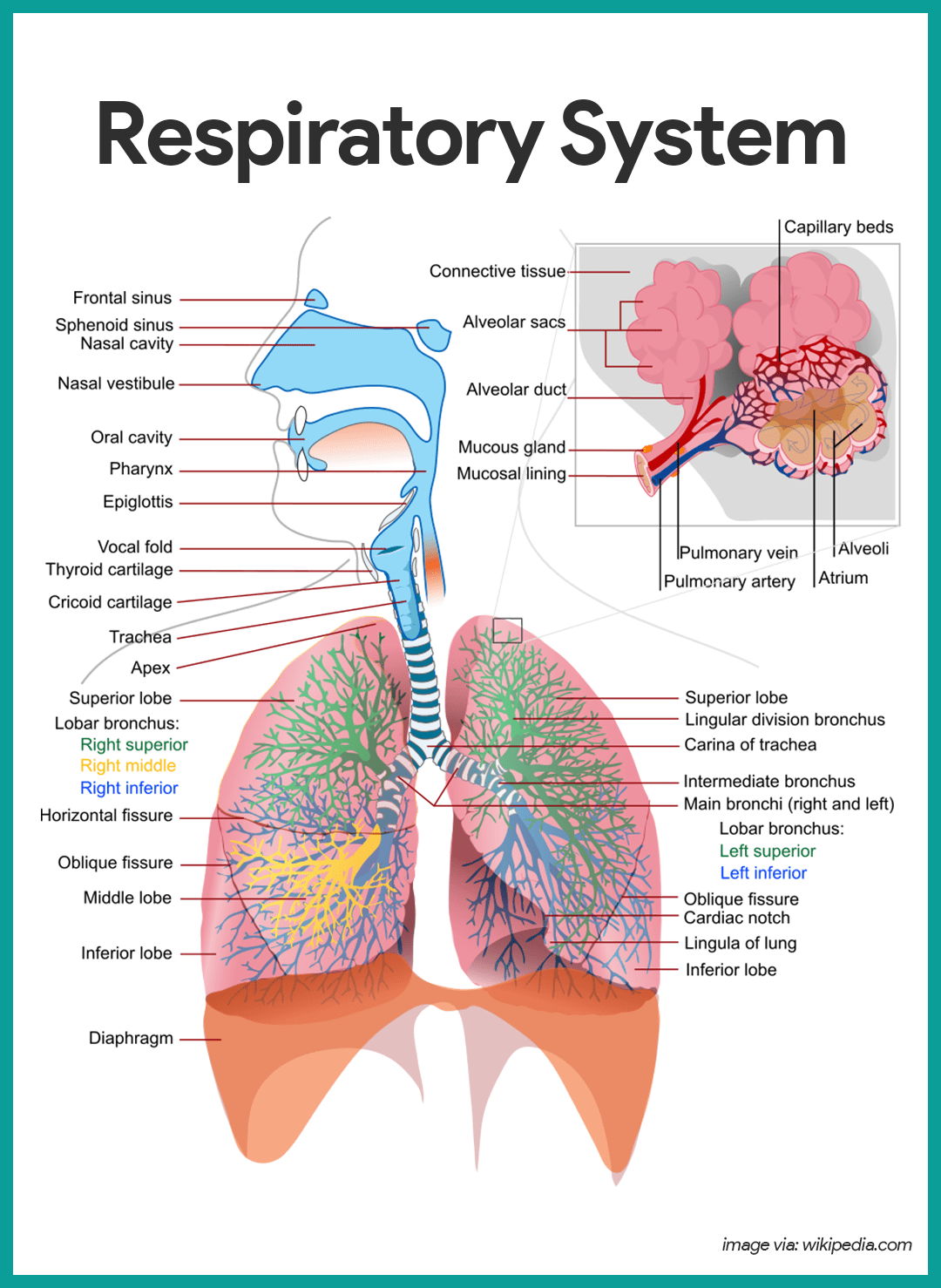
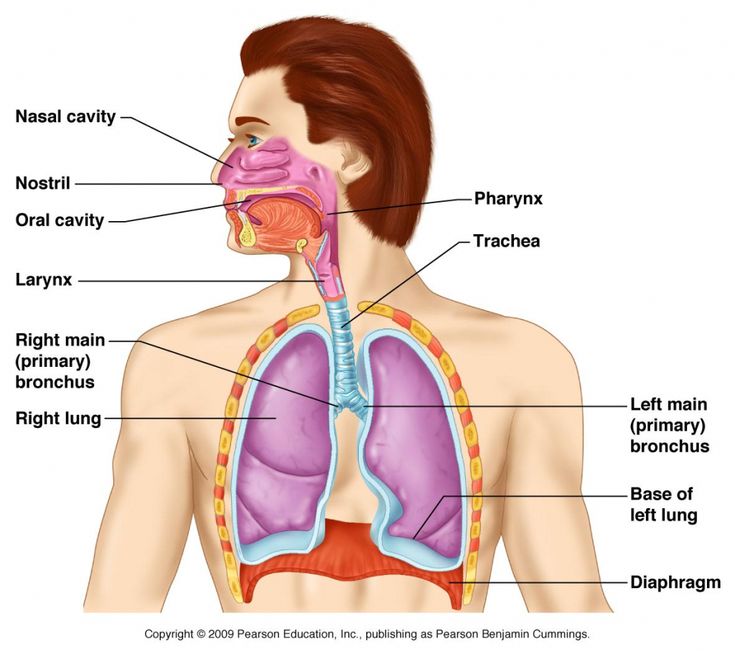
larynx (memorize its location too)
location of the vocal cords
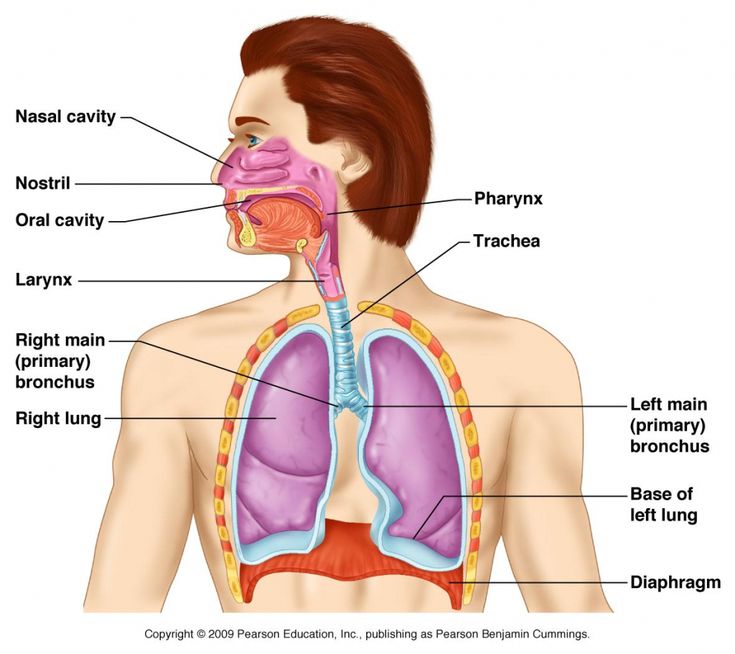
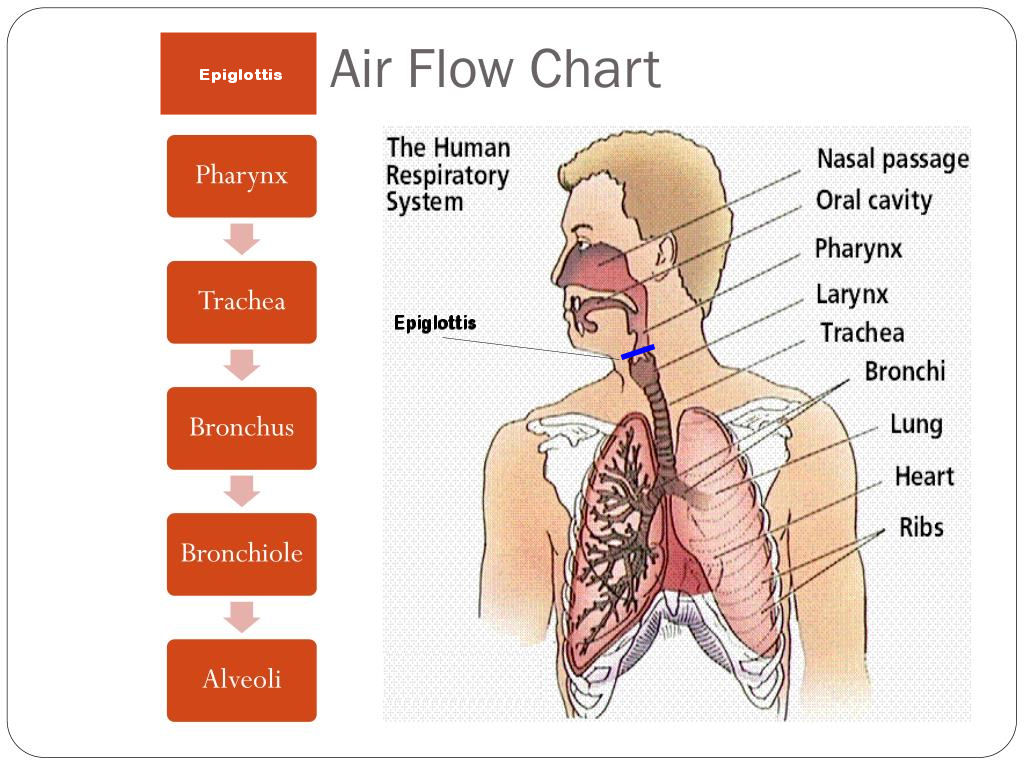
In what order does inhaled air take in your body?
epiglottis
trachea
bronchi (broncos and bronchioles)
alveoli
How does mucus help you?
Lubrication: It serves as a lubricant in different parts of the body.
Protection: Mucus acts as a protective barrier, trapping bacteria, viruses, and allergens to prevent them from spreading.
Moisturizing: It keeps moist organs from drying out.
Filtering: Mucus filters and eliminates inhaled particles and microorganisms.
Immune response: In the lungs, mucus helps trap irritants and allows the body to expel them through coughing, protecting against infection.
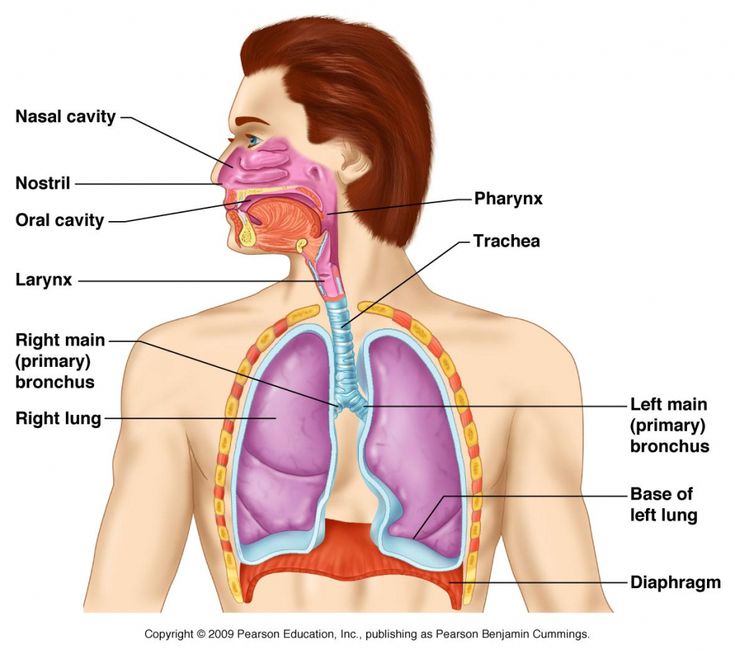
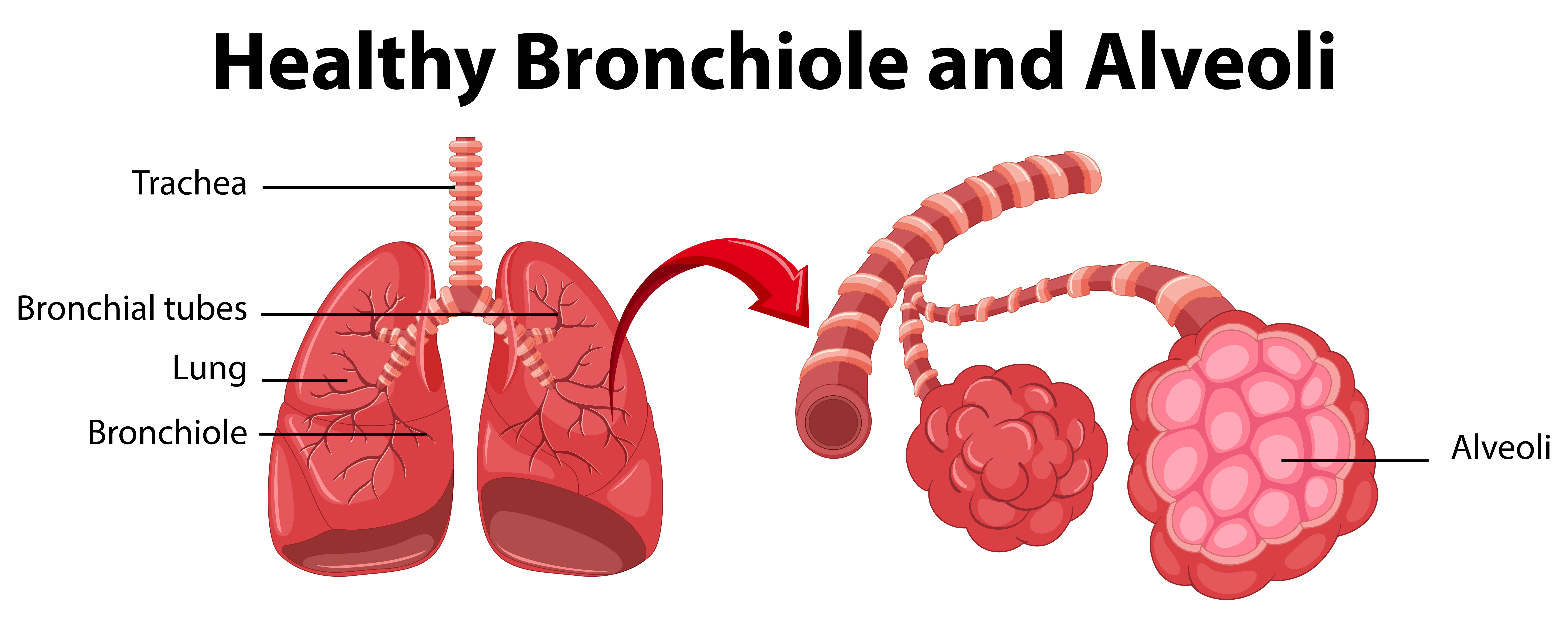
trachea (memorize its location)
Allows air in and out of the lungs
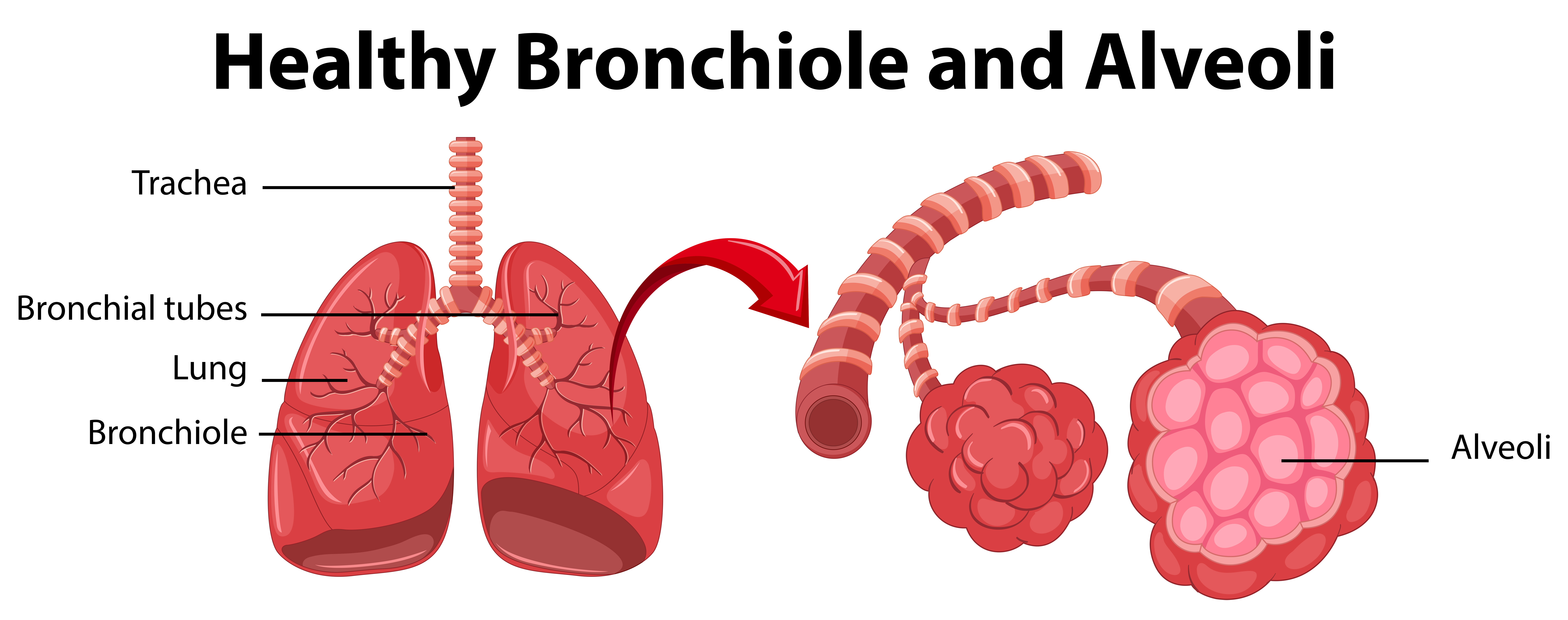
bronchiole (memorize its location)
Delivers air to the 300 million alveoli in the lungs.
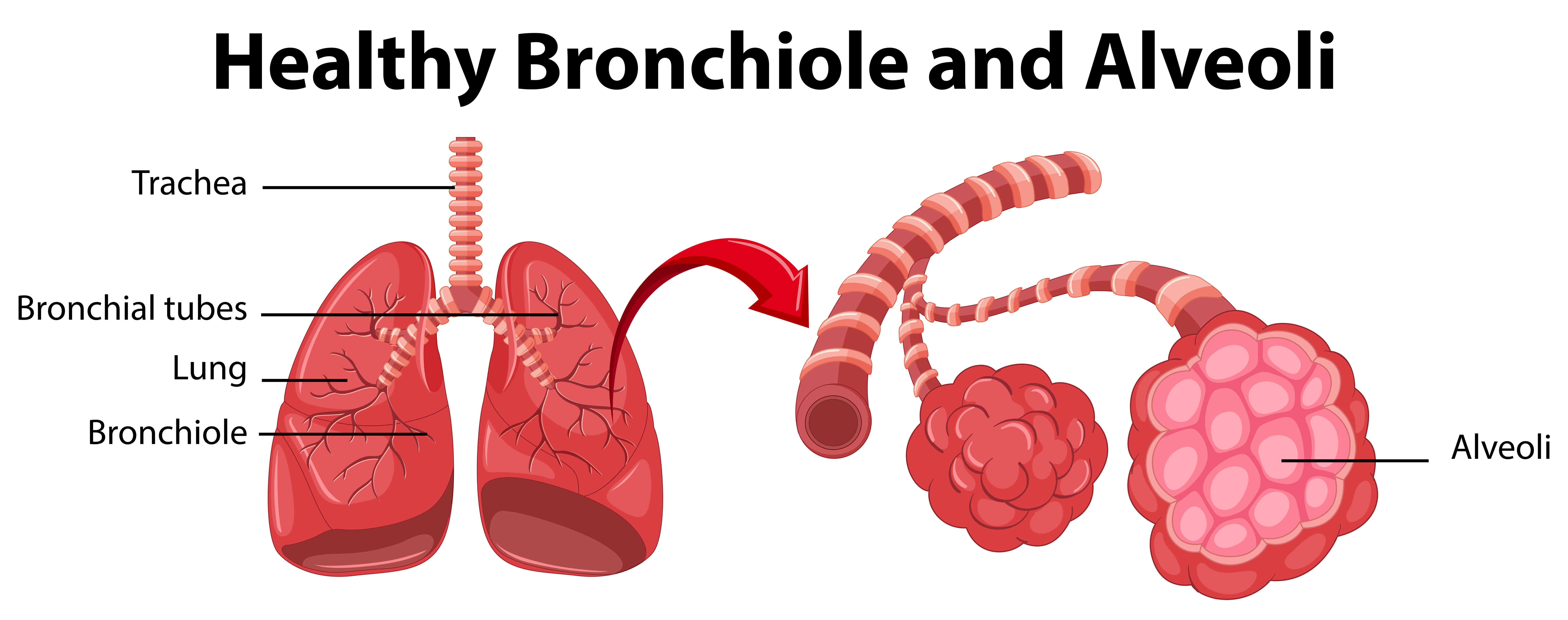
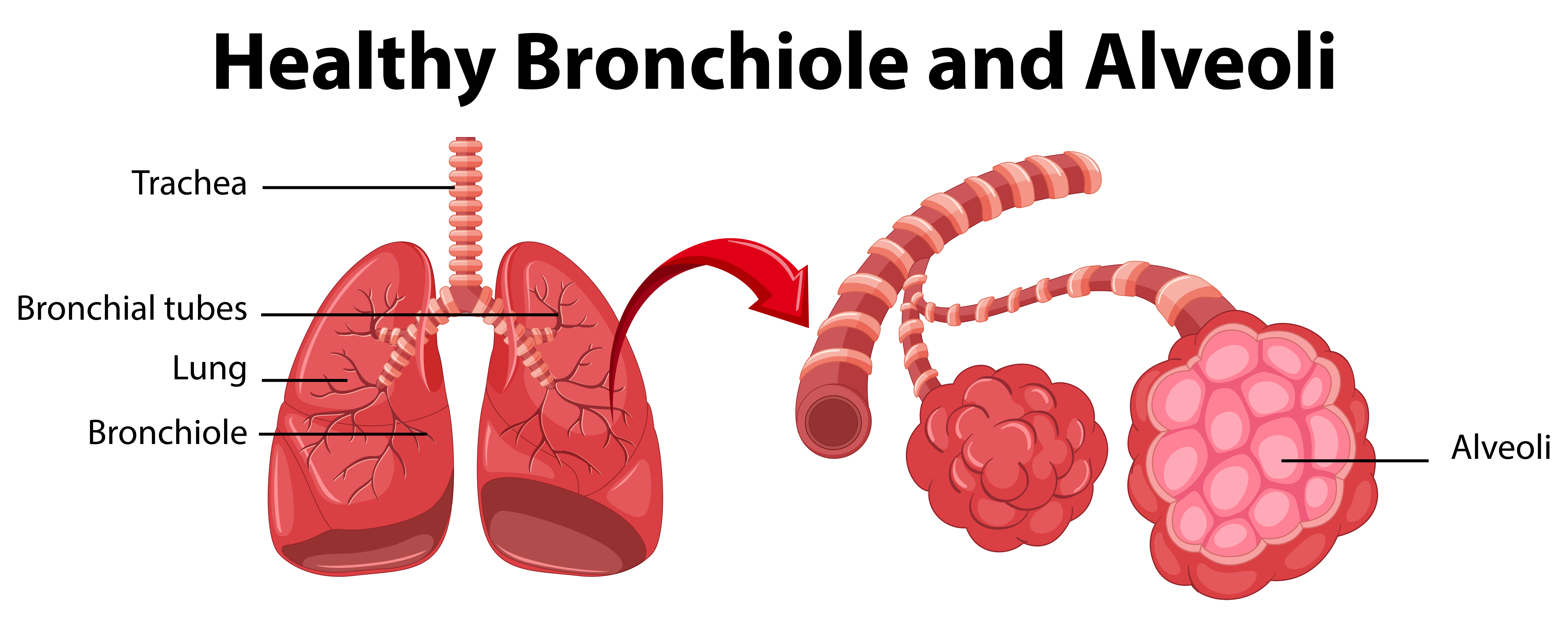
alveoli (memorize its location)
Structure where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between blood and air.
esophagus
An elastic tube that is located behind the larynx and that carries food and liquids to the stomach.
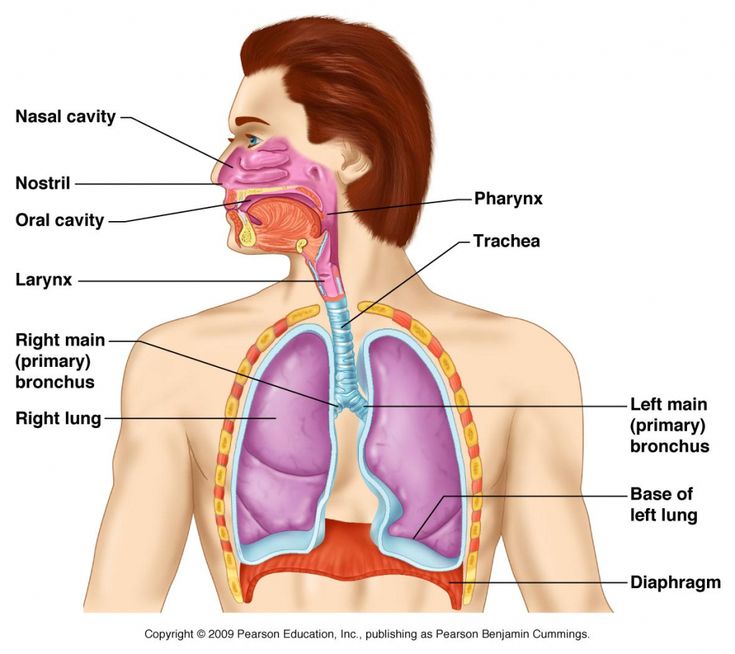
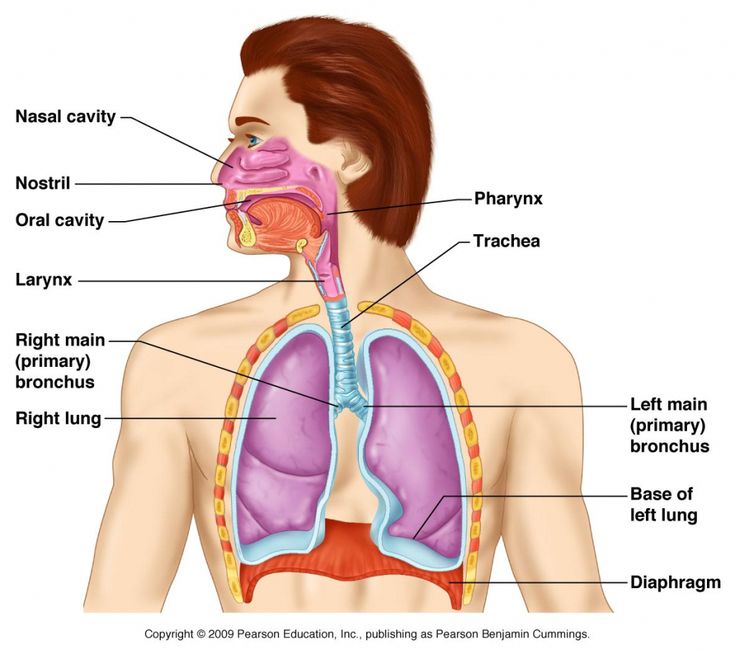
pharynx (memorize its location)
It's part of the conducting zone in the respiratory system, which filters, warms, and moistens air as it travels toward the lungs.
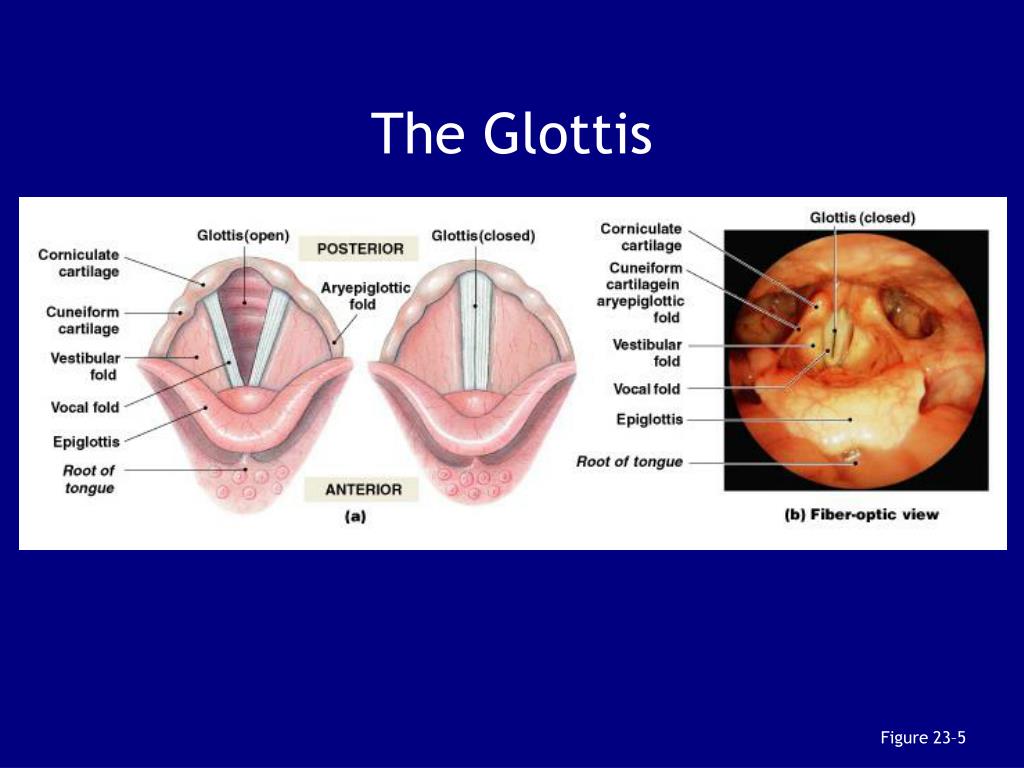
glottis
The space between the folds of the larynx. If something other than air tries to pass through, it folds immediately close.
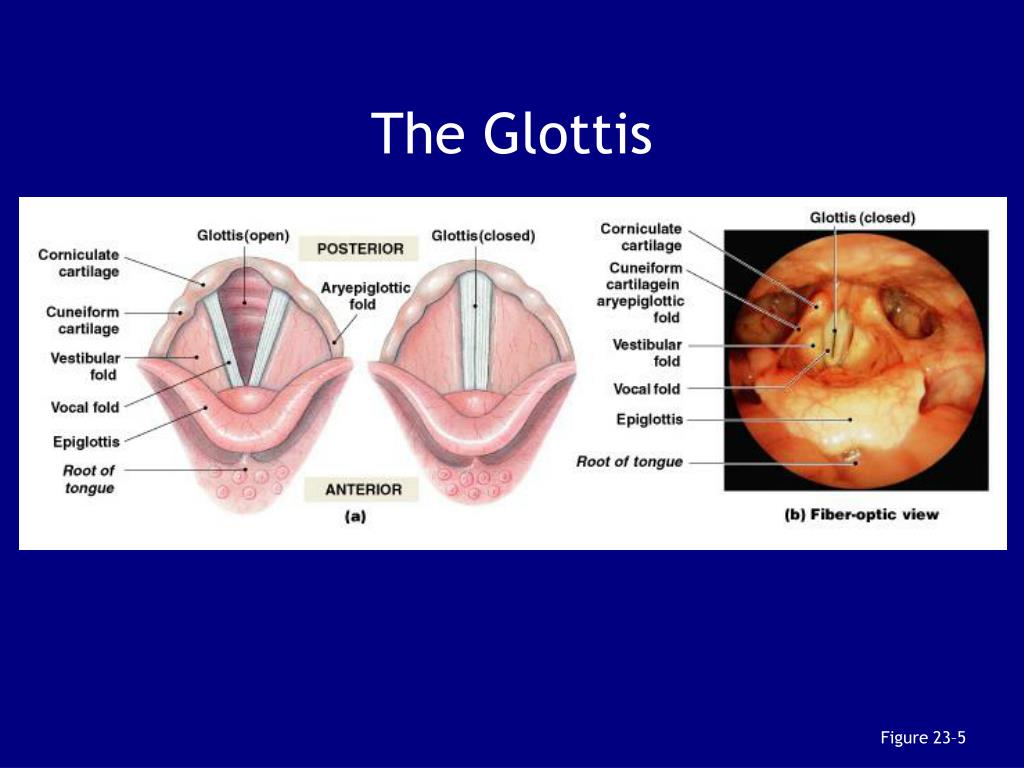
vocal cords
The folds around your glottis.
What can secondhand smoke cause?
bronchitis and pneumonia, allergic coughing and sneezing, and lung cancer.
How many people die every year from smoking (2024)?
5 million
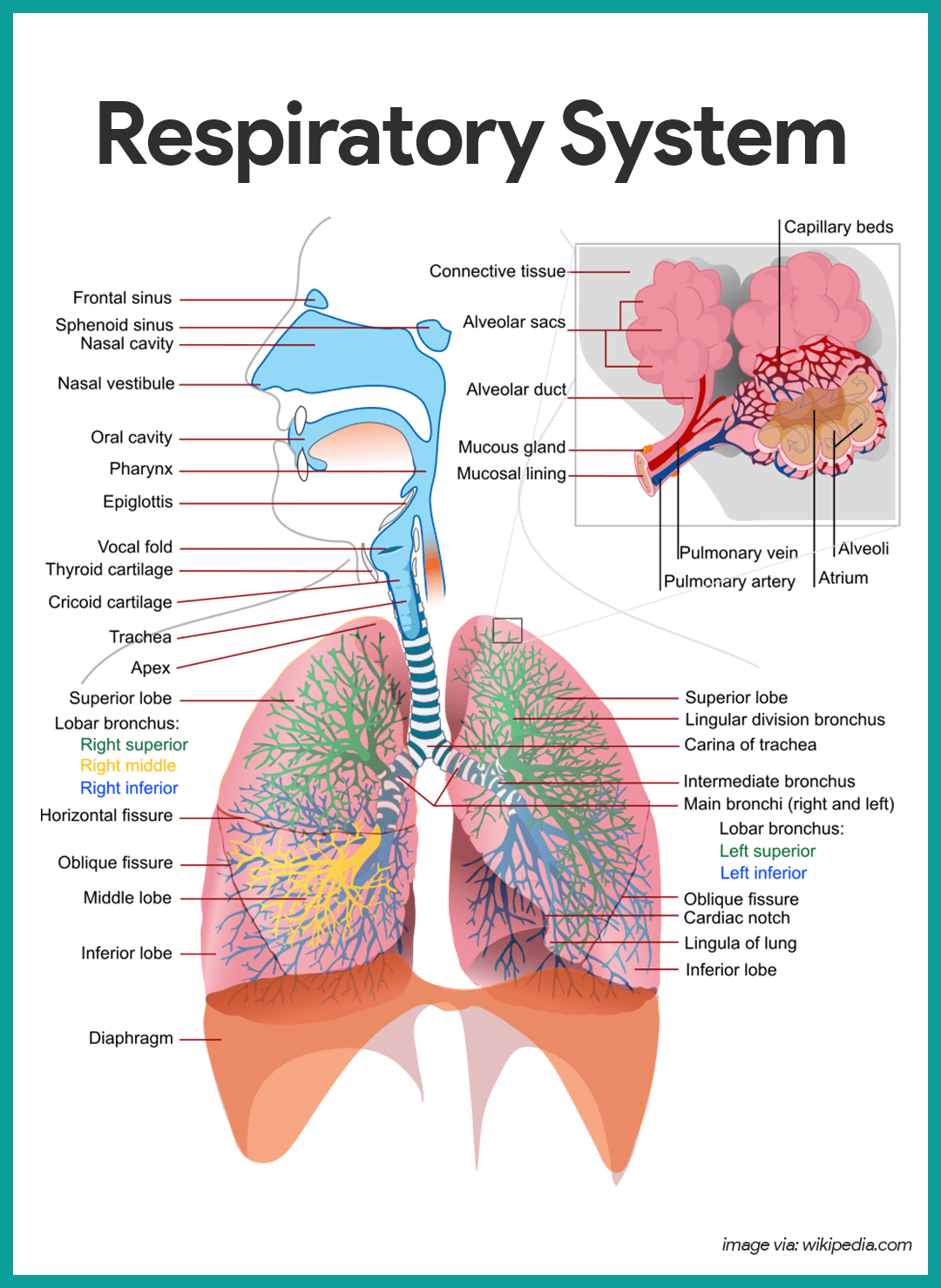
bronchi (Main bronchi, right and left; memorize its location)
The two branches of the trachea
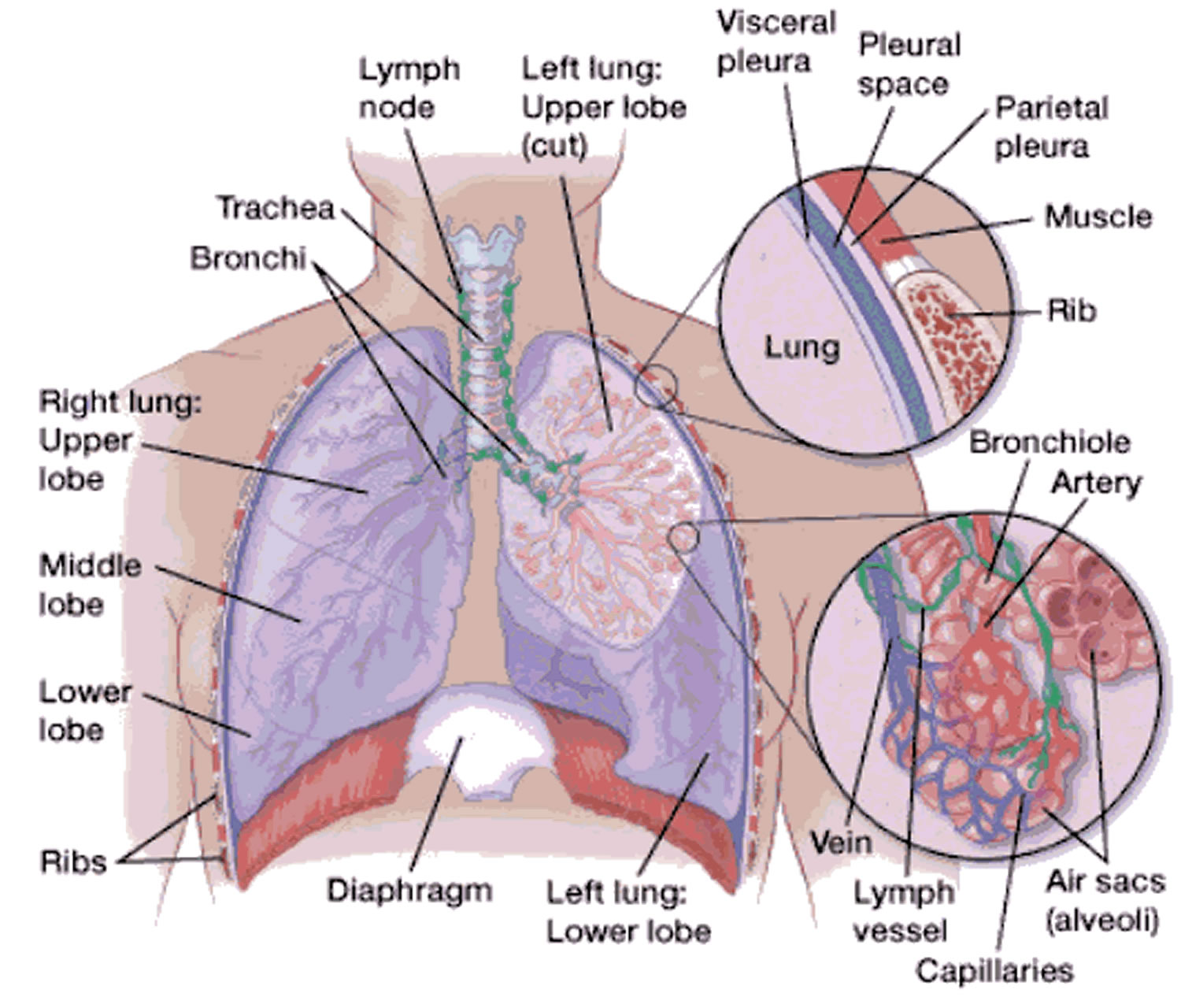
What surround the alveoli?
Capillaries. Here gases in the air pass through the walls of the alveoli and the capillaries to enter the blood.
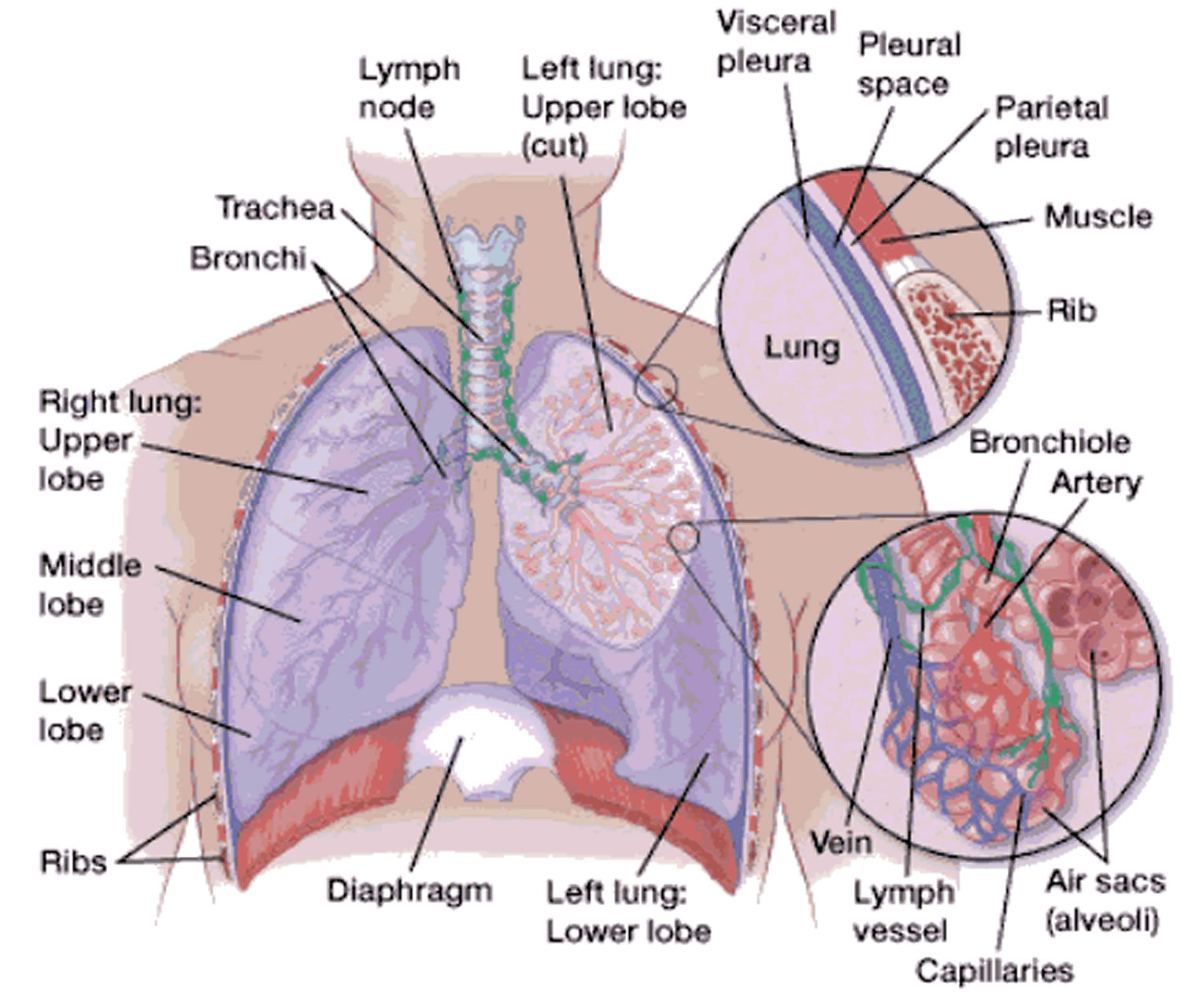
diaphragm
A dome-shaped muscle that attaches to the lower ribs, the backbone and the sternum. When it contracts, you inhale. When it relaxes, you exhale.
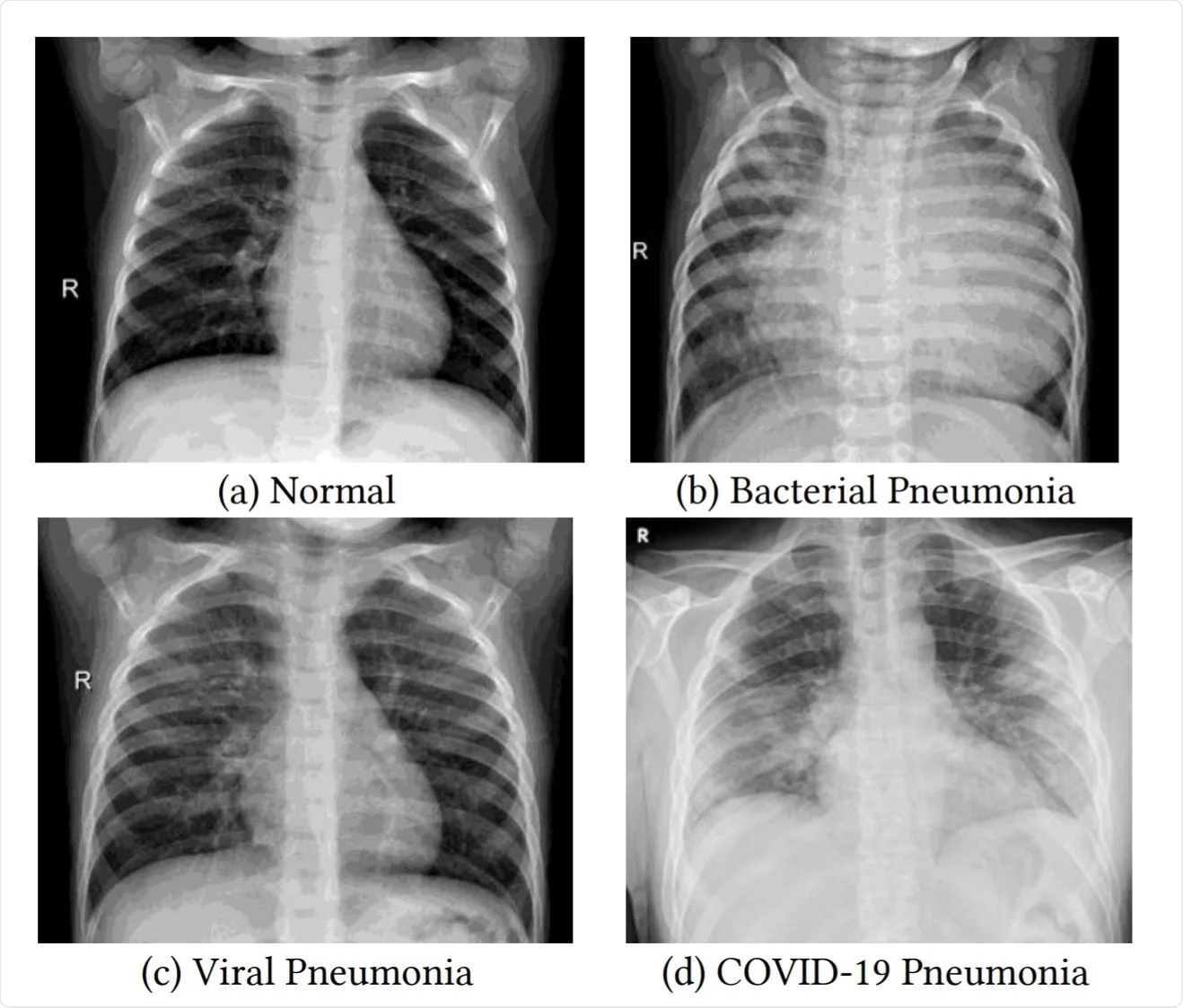
Pnemonia
A disease that causes the alveoli to full with fluid.
tuberculosis
Bacteria growing in the alveoli
emphysemea
A smoking-related lung disease. The smoke causes the alveolar walls to become stiff and less elastic. So when the person coughs hard enough, the alveoli bursts under pressure!
collapsed lung
Results from a hole in the thorax (chest), resulting in fluid entering the chests and collapses the lung.
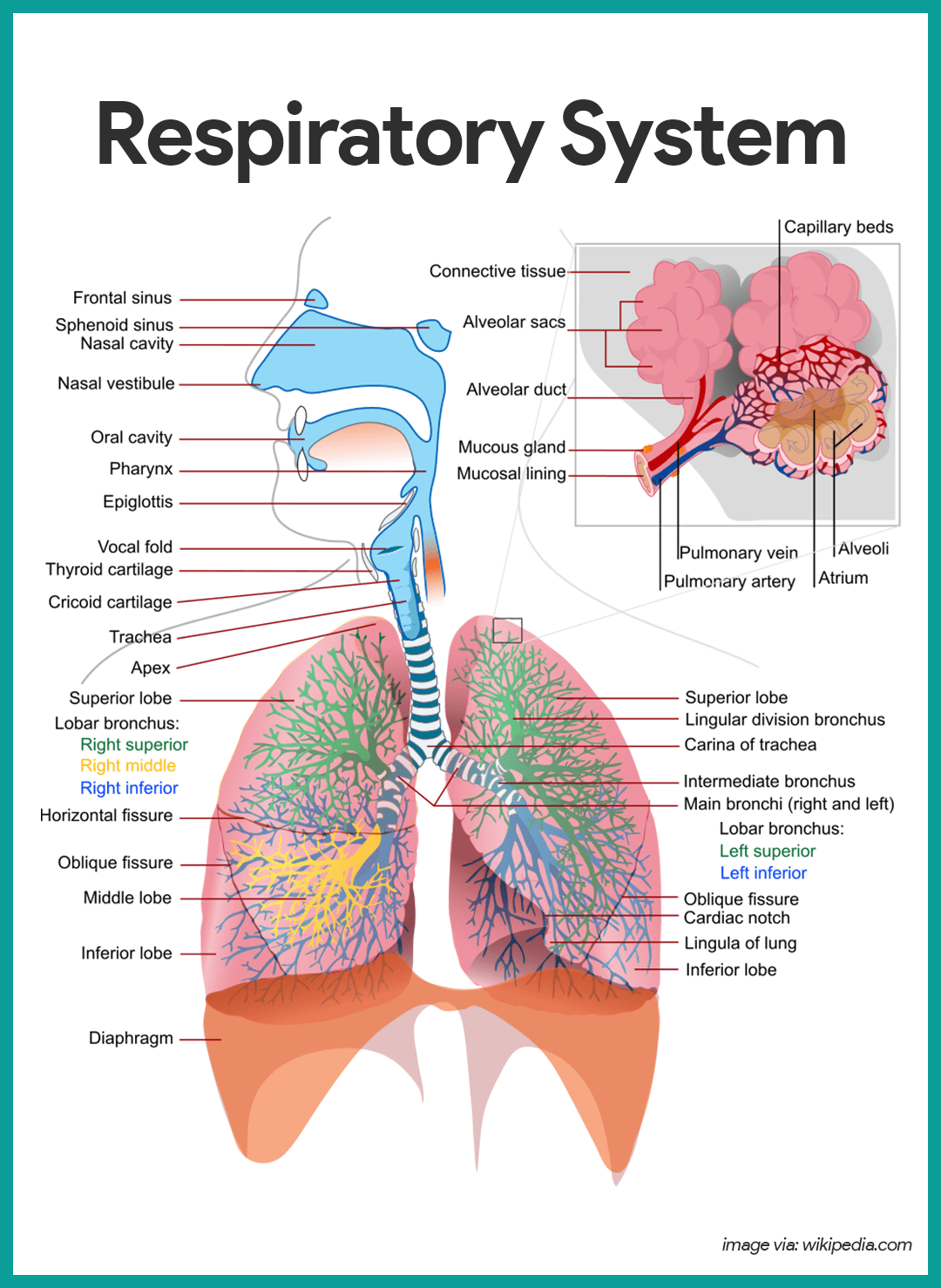
What are the air passage in your lungs called?
bronchioles
diffusion
A process that causes oxygen to enter the blood
What is the maximum amount of air that a typical person can inhale in one breath?
4500mL
assimilation
The process of building living tissues from the digested foods
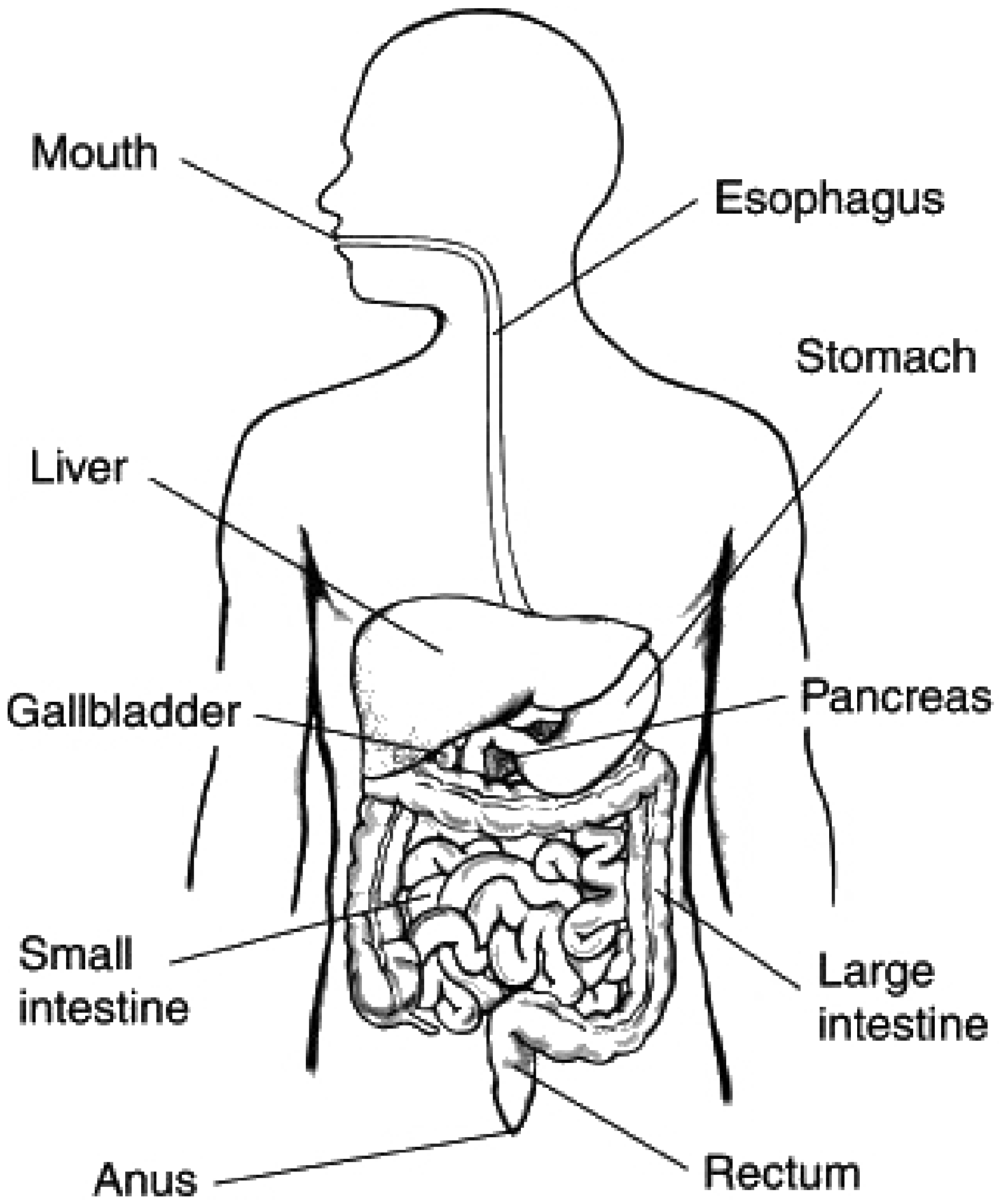
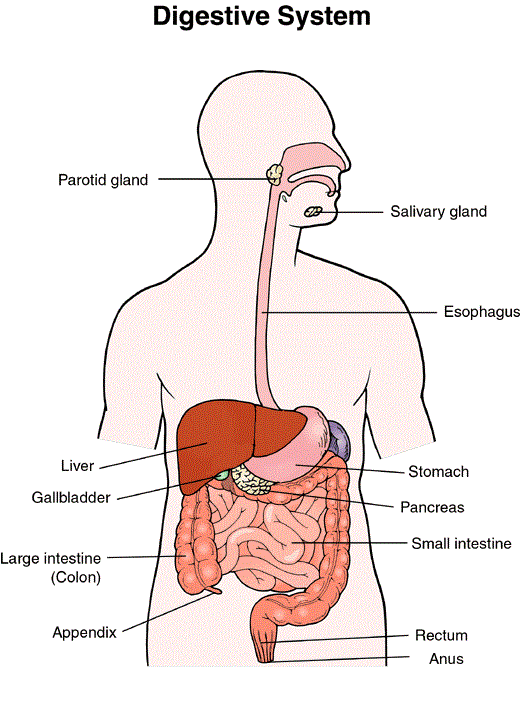
alimentary canal
A long tube that runs from the mouth to the anus. The main organs are the: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, & large intestine.
peristalsis
moving food along the alimentary canal
Which teeth are used for cutting and biting?
incisors
mechanical digestion
involves grinding and mixing
chemical digestion
Chemically breaking down the food into substances the body can use.
accessory organs
Attached to the alimentary canal by tubes, these organs produce the substances necessary for digestion. The main ones are the liver and pancreas.
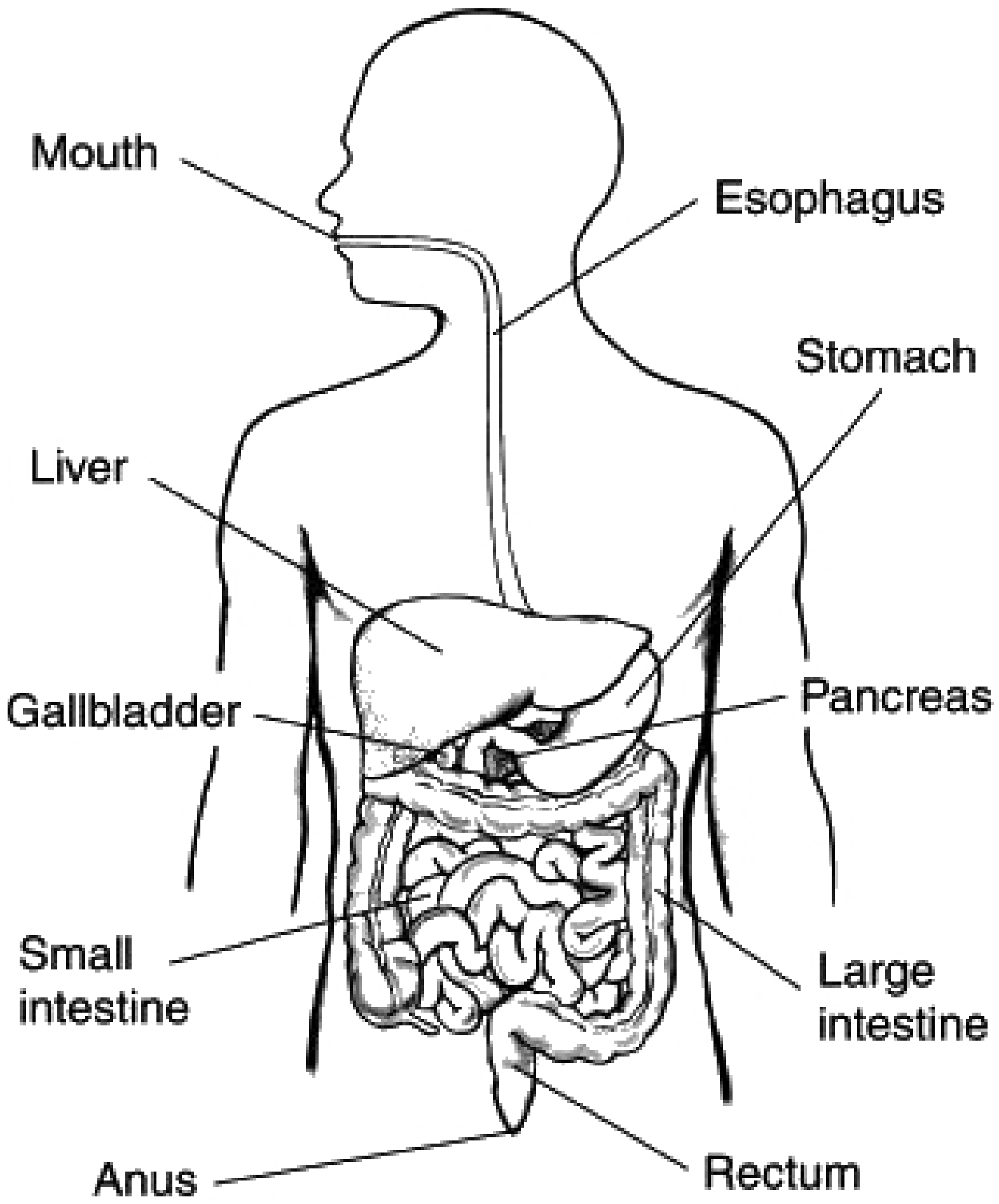
canine teeth
vital in eating to tear and rip apart food when chewing.
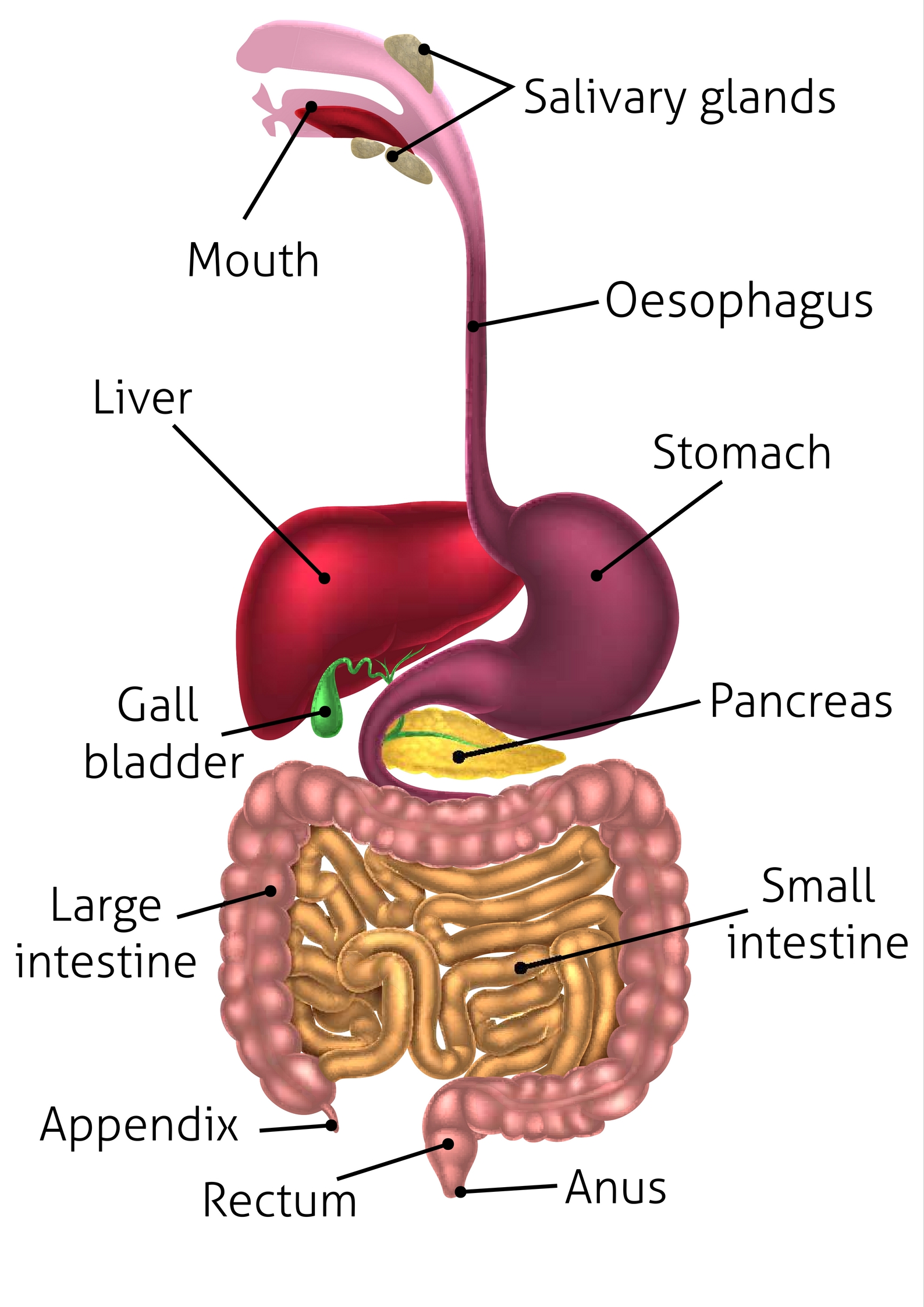
pancreas (memorize its location)
A major accessory digestive organ. It produces pancreatic juice that contains several enzymes that are important for digestion. It also produces sodium bicarbonate to neutralize chyme.
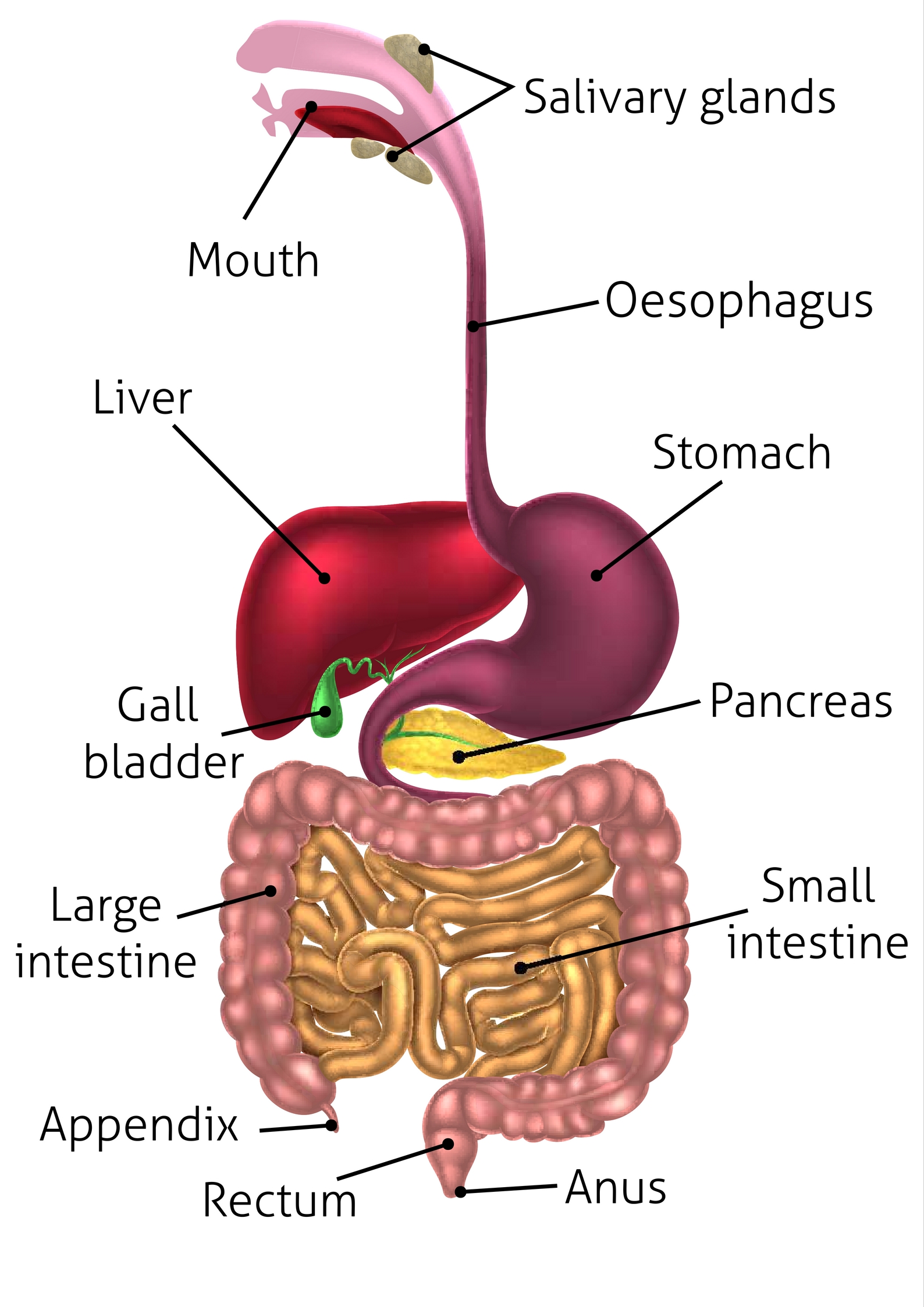
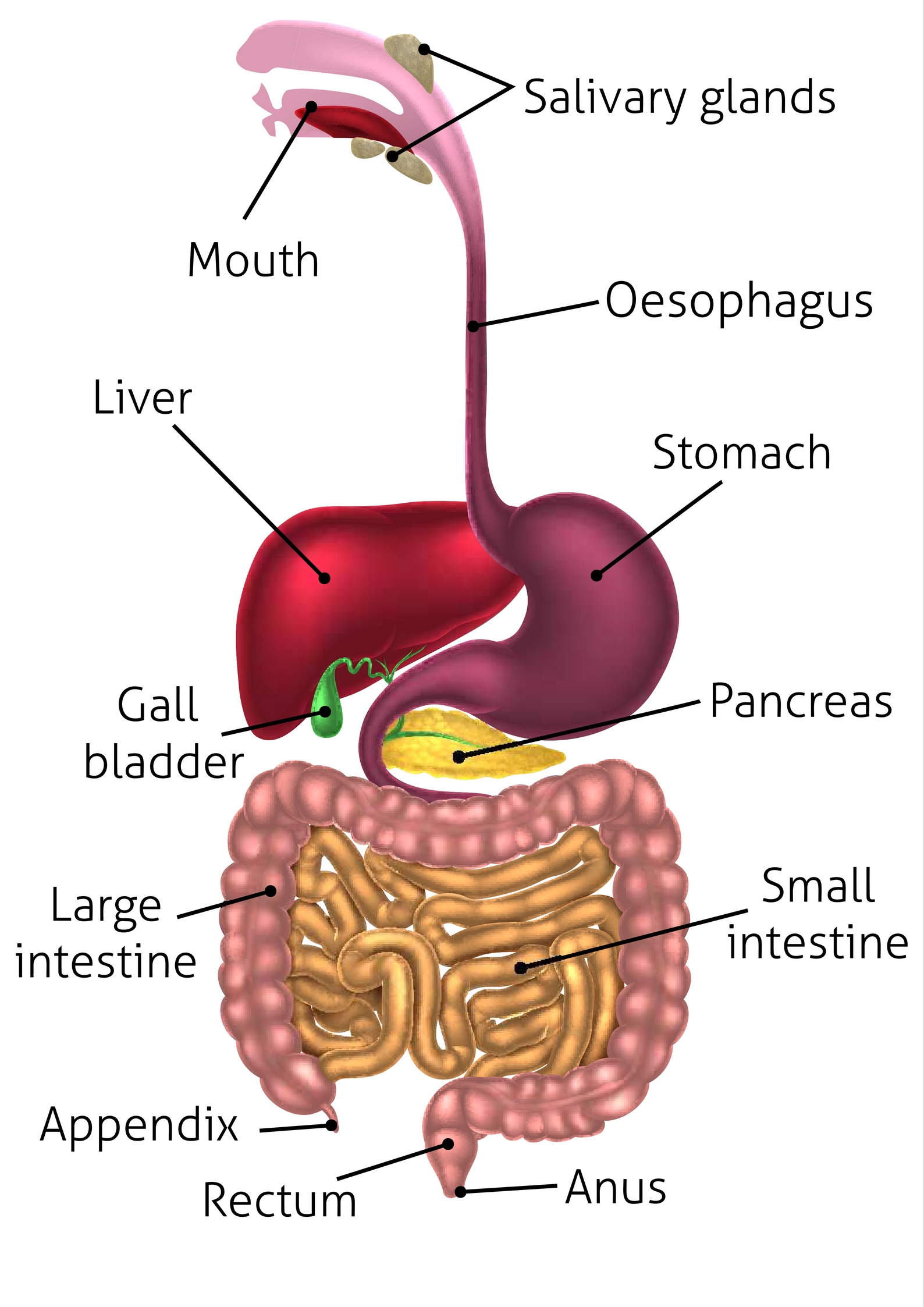
salivary glands (memorize their locations)
salivary glands
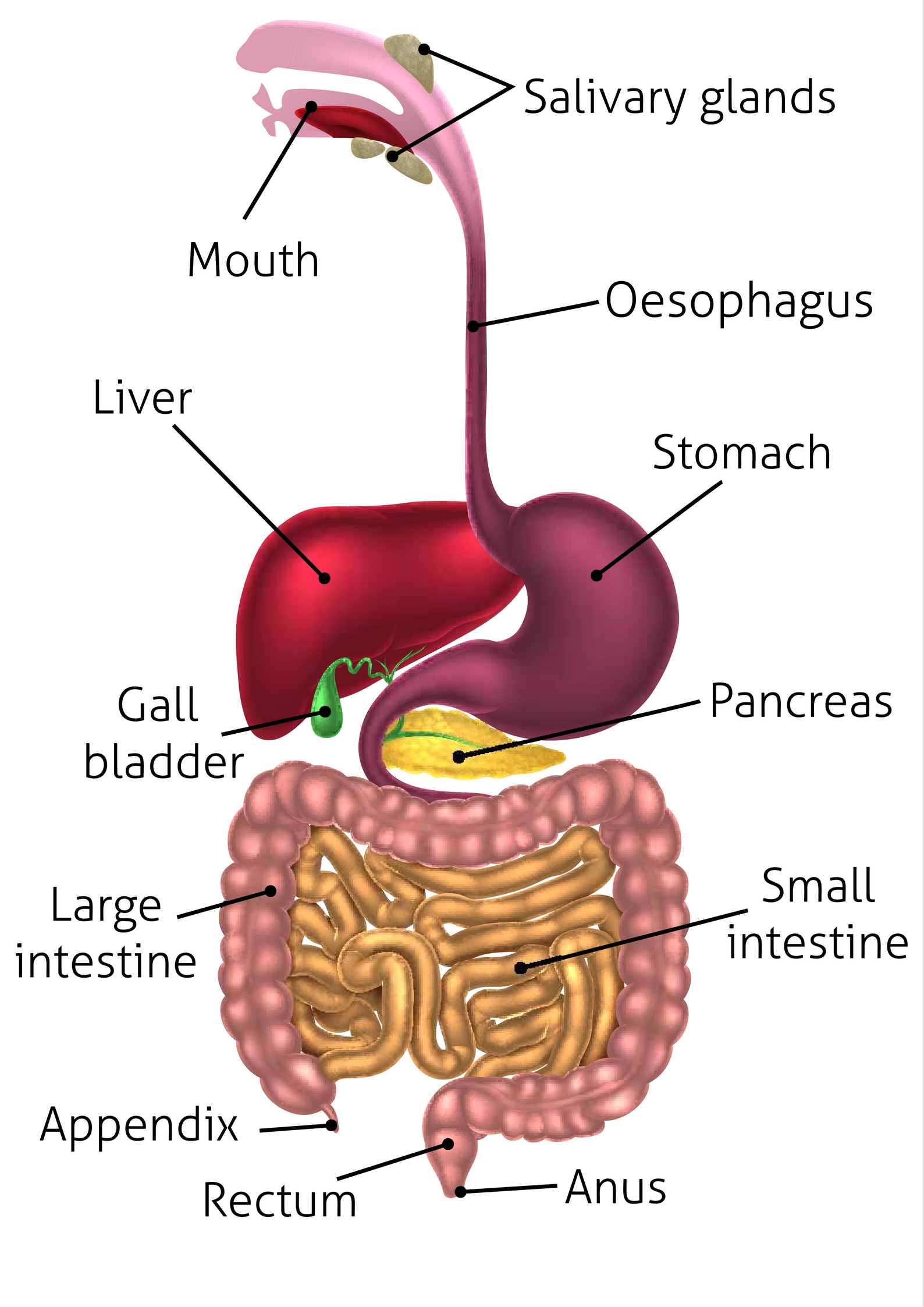
rectum (memorize its location)
rectum
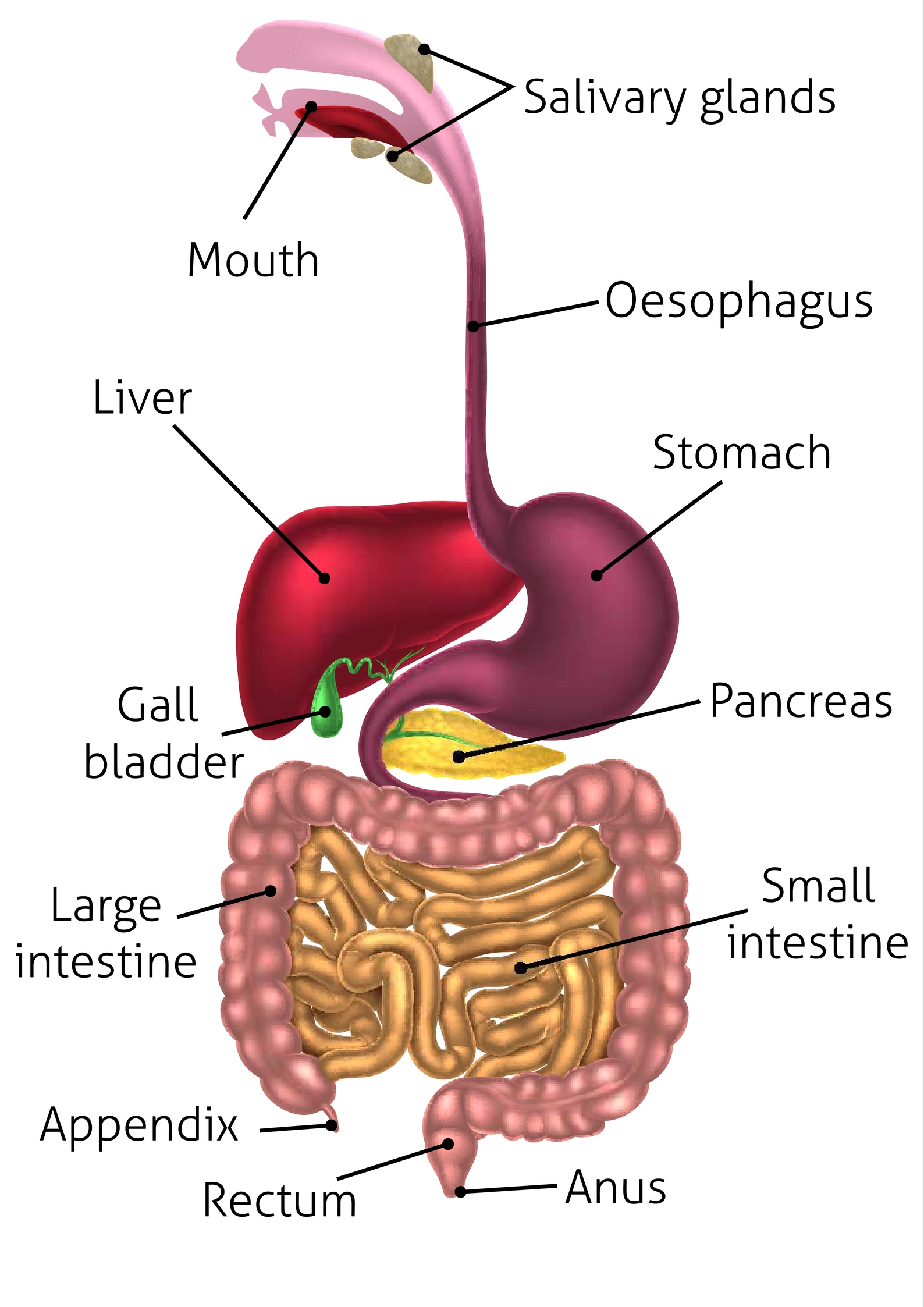
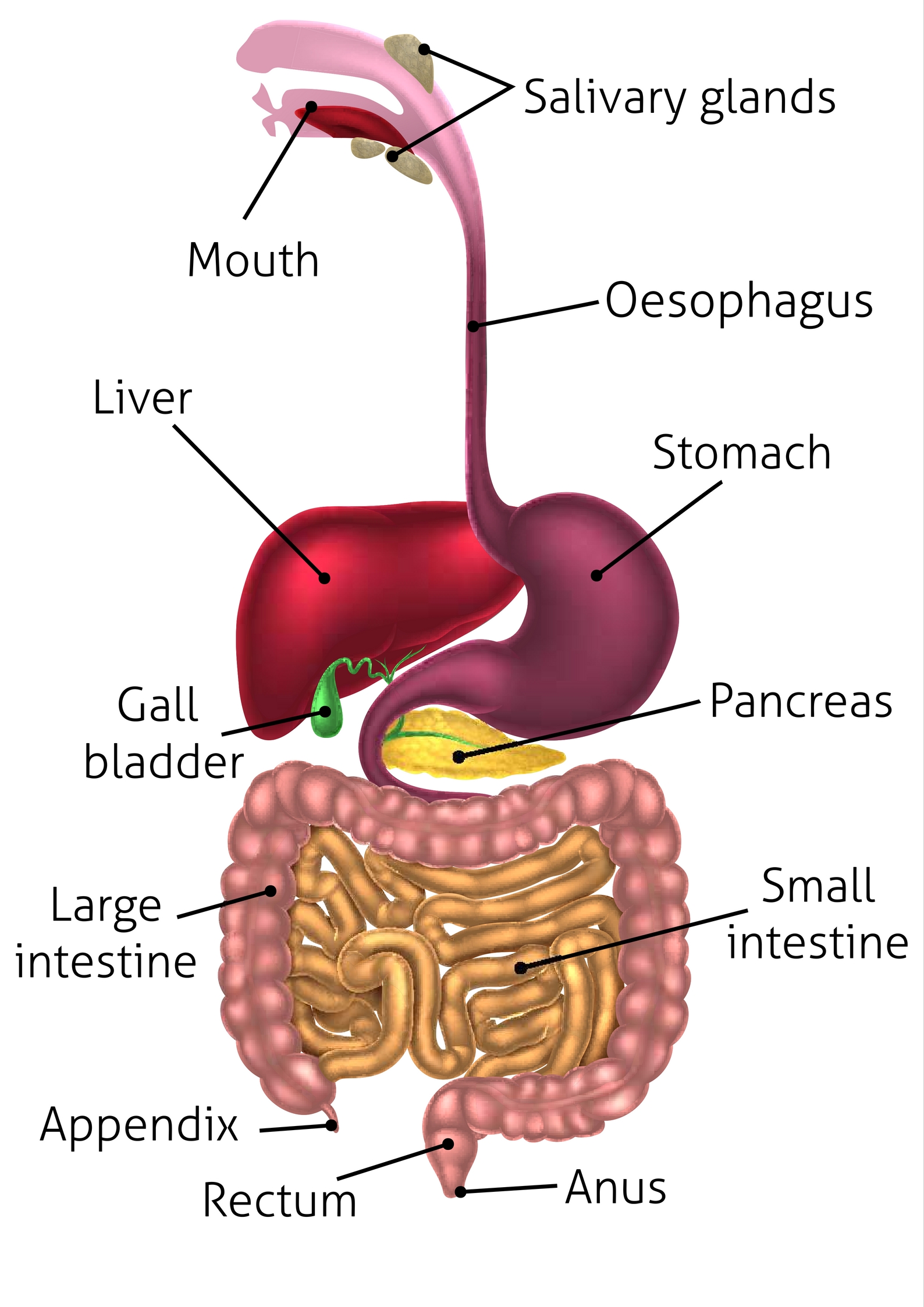
appendix (memorize its location)
An organ attached to the large intestine.
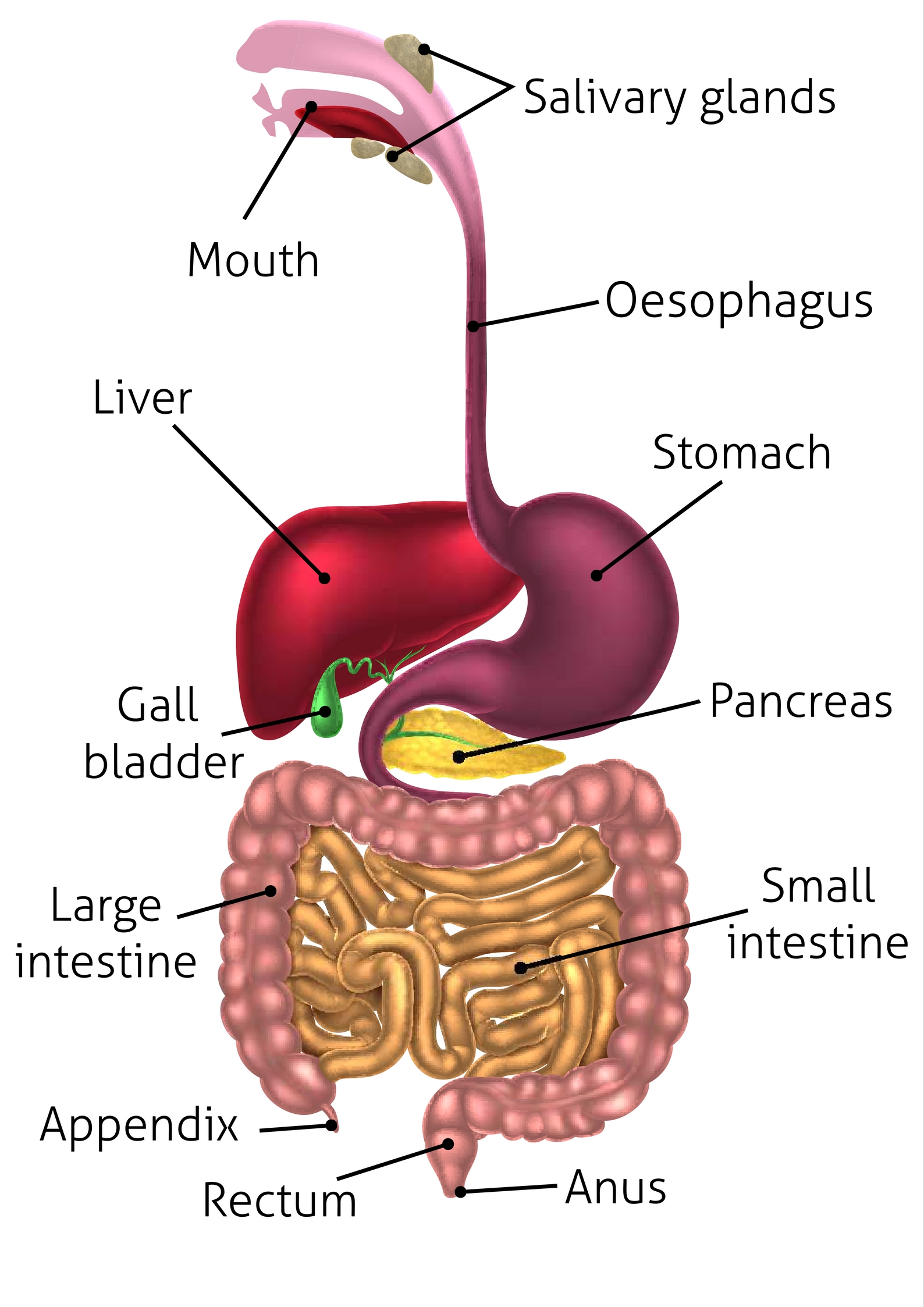
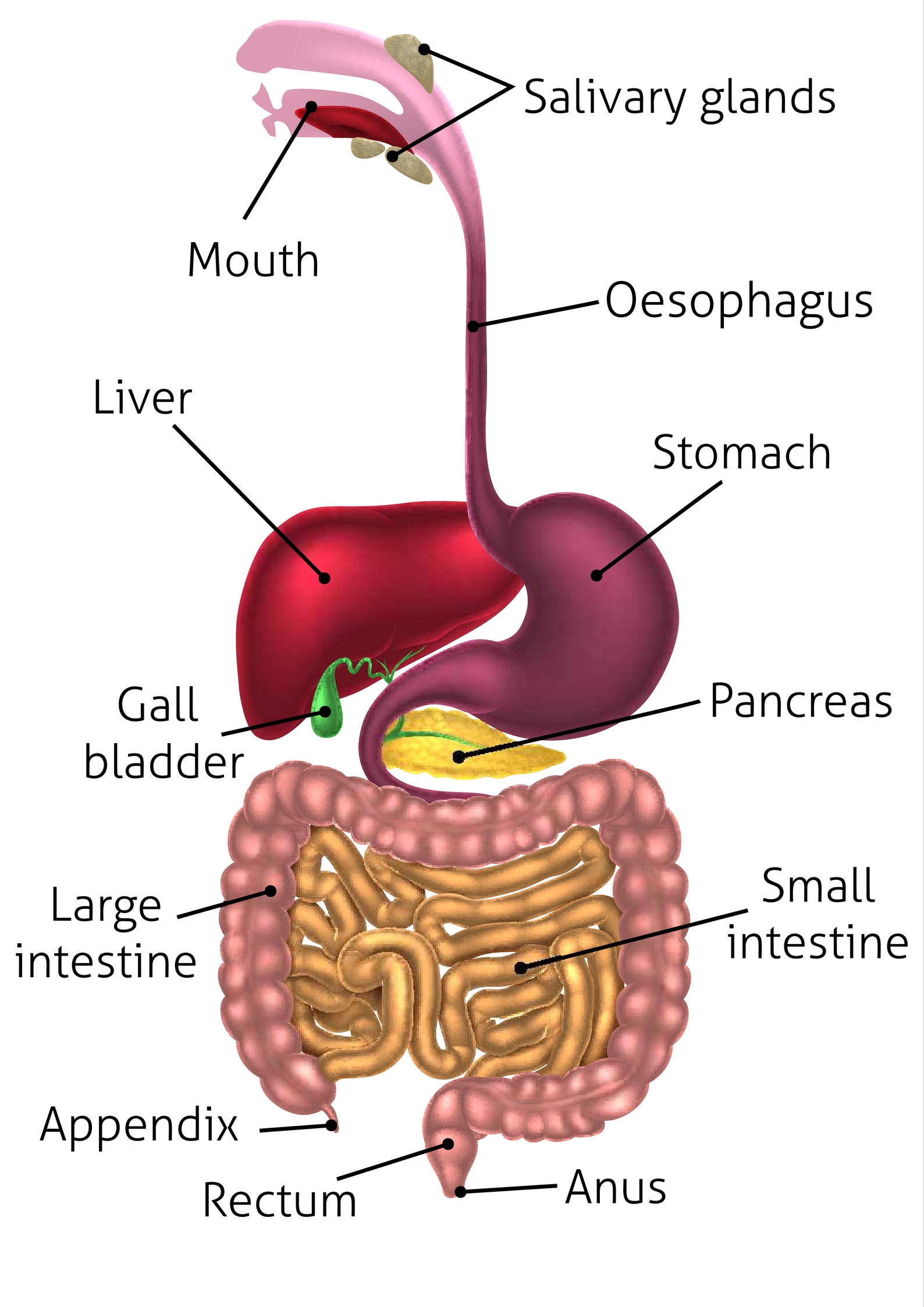
small intestine (memorize its location)
Most of the chemical digestion process takes place in this organ.
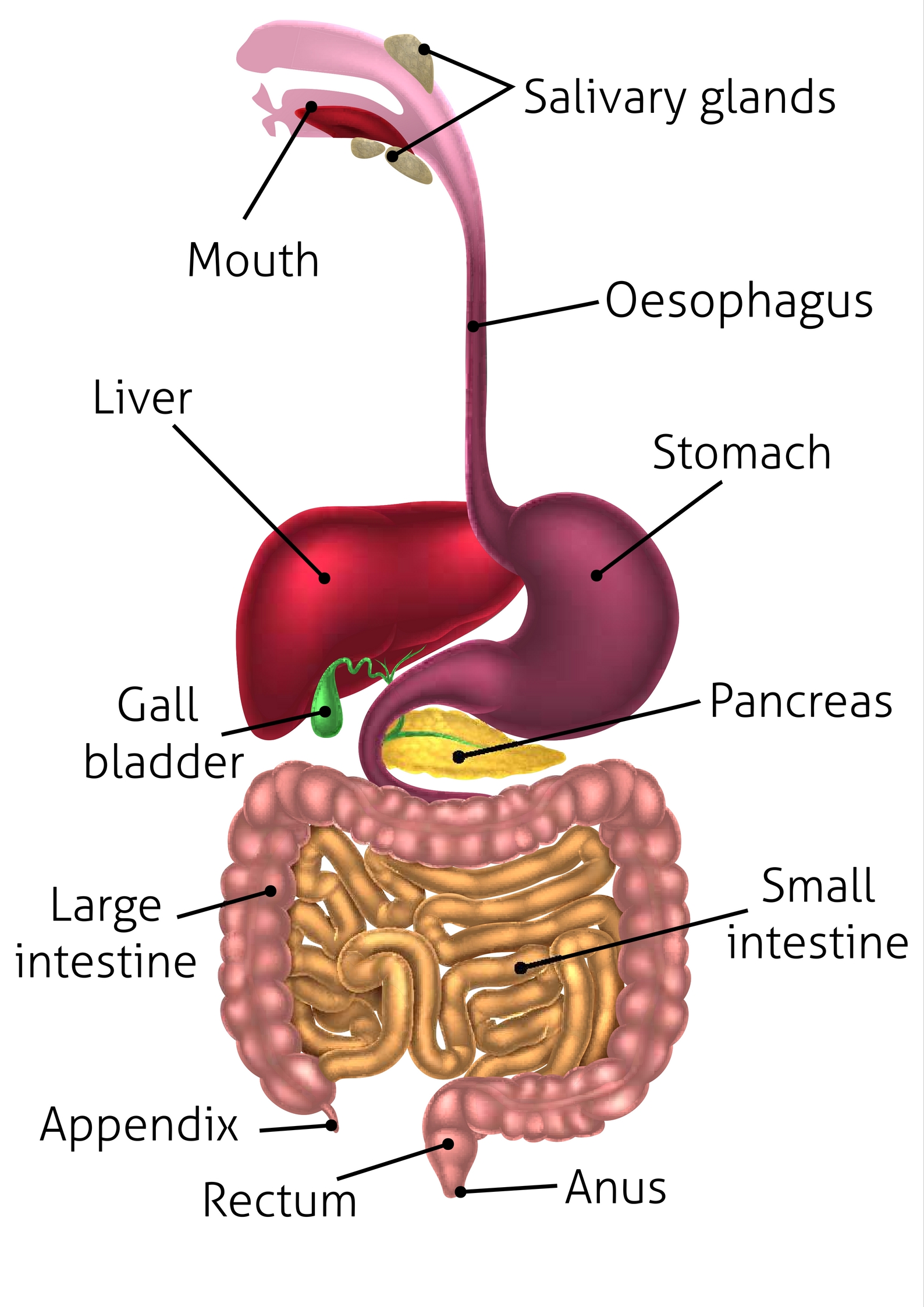
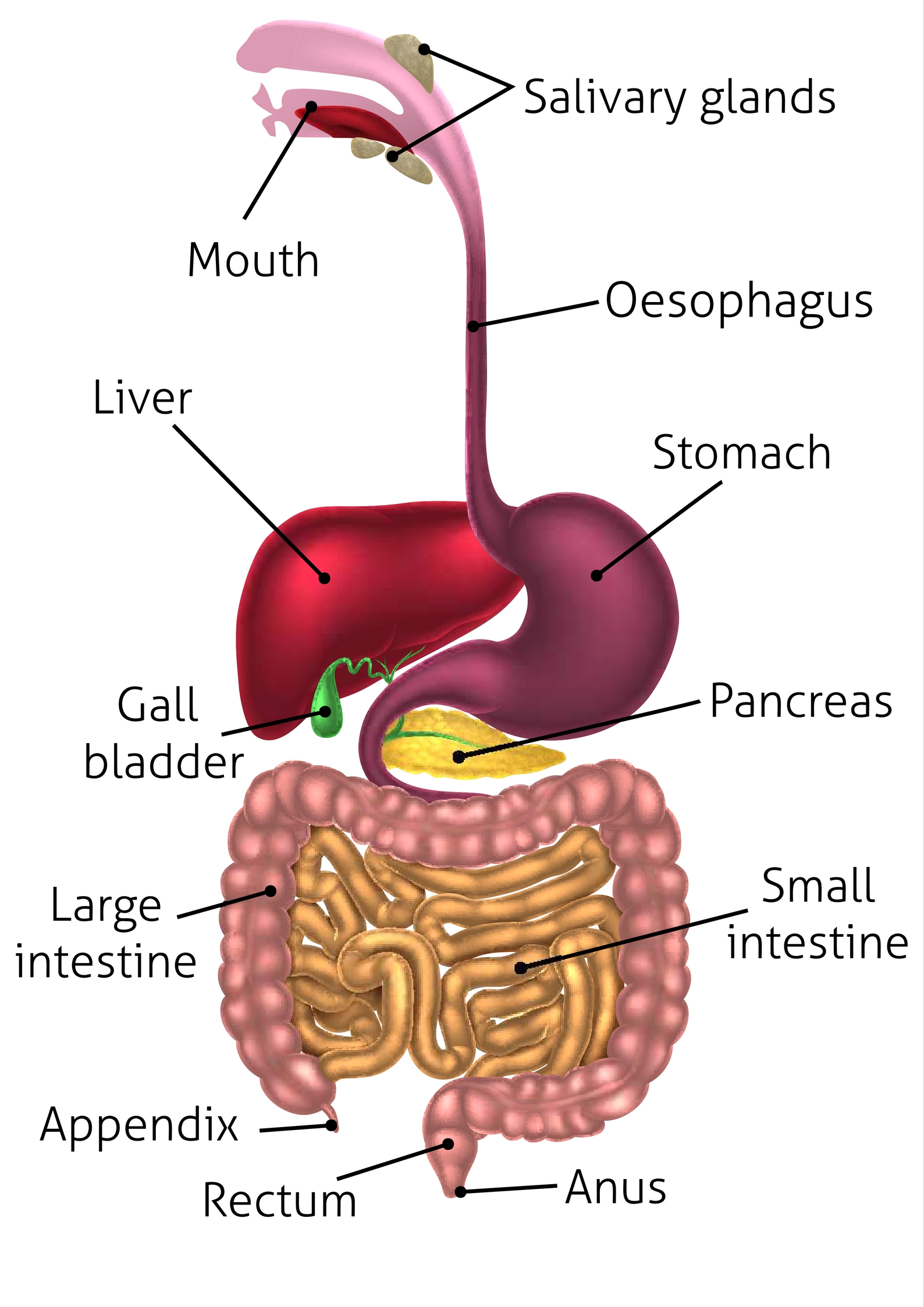
large intestine (memorize its location)
The remaining undigested foods and fluids go here.
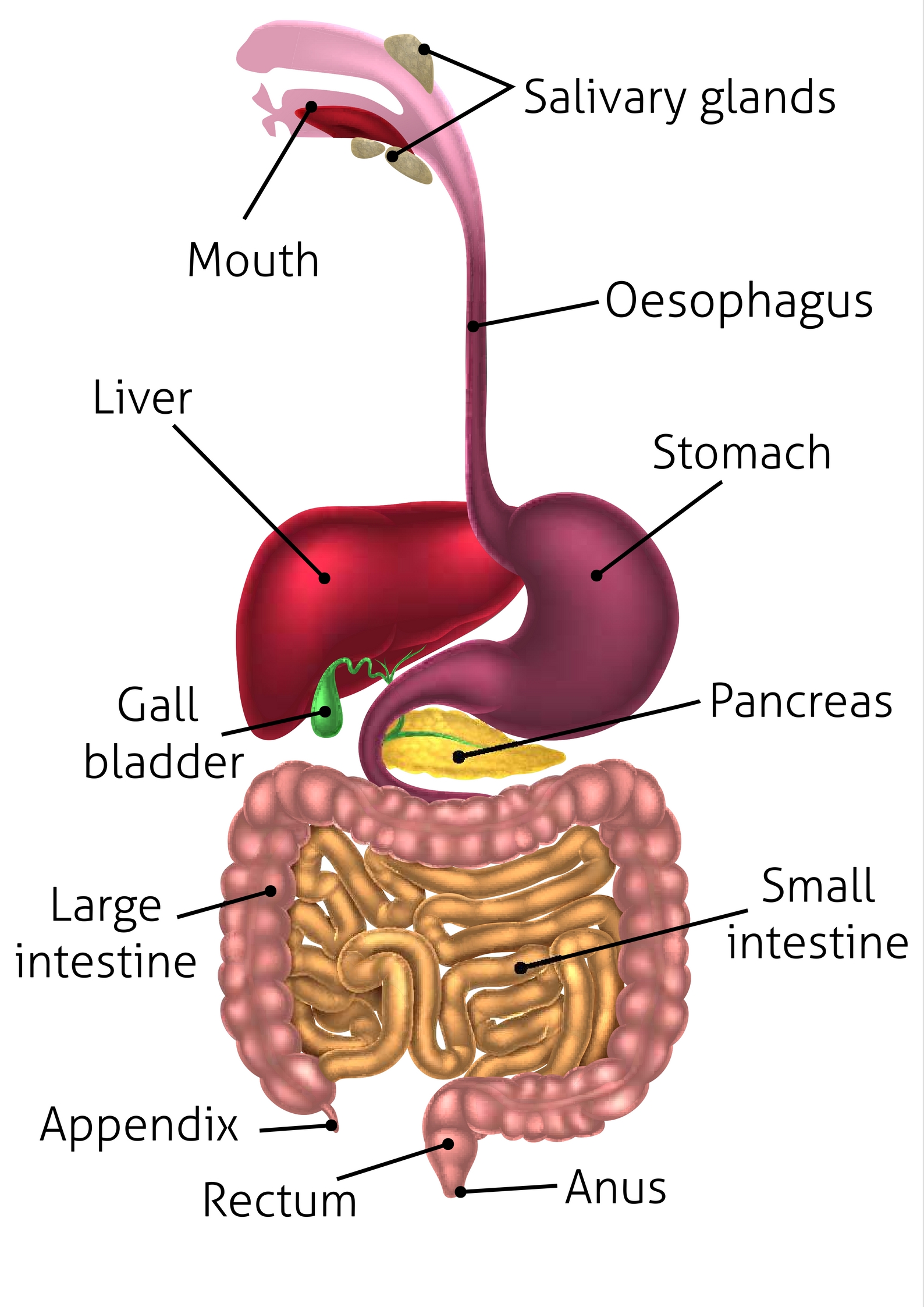
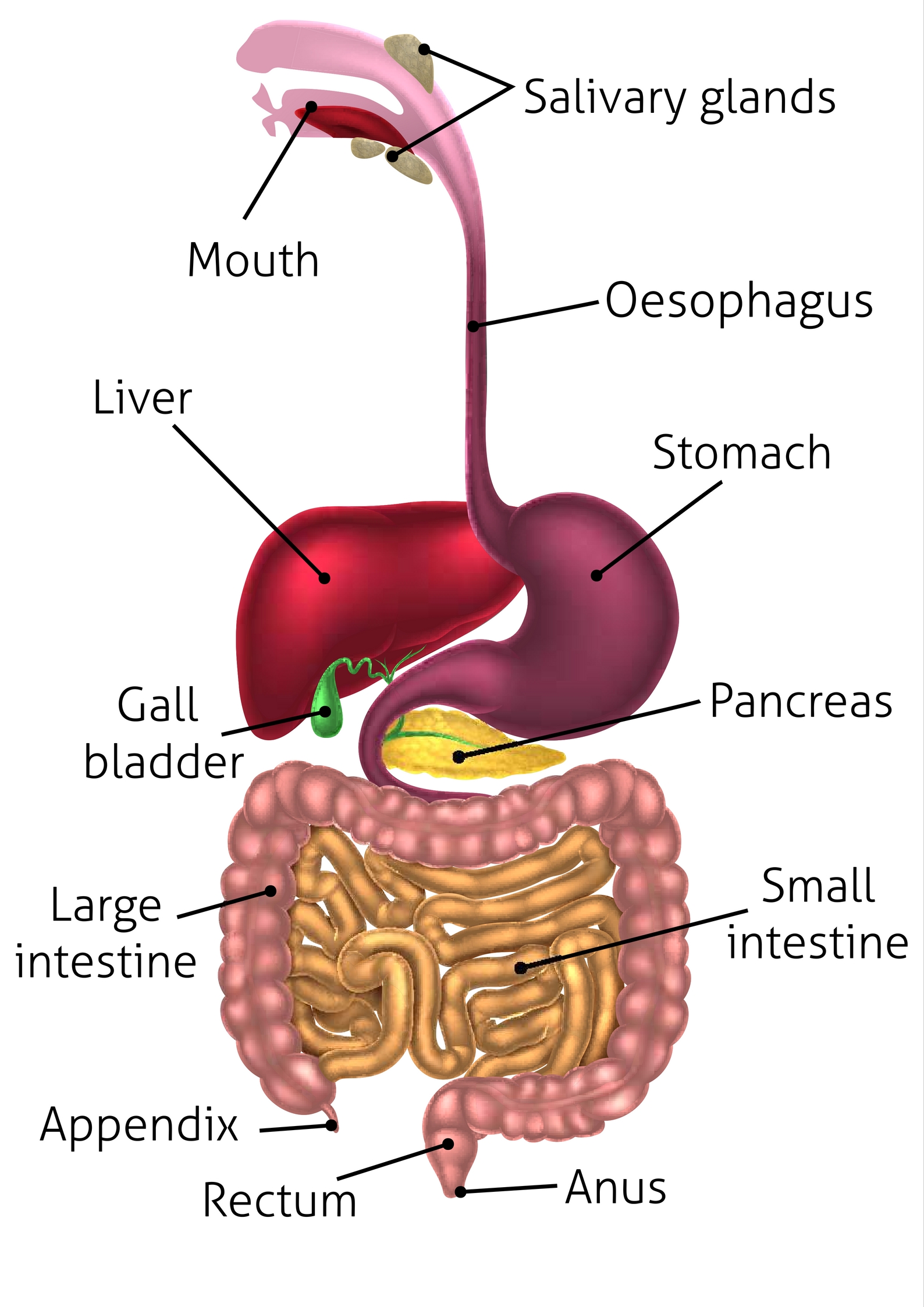
gallbladder (memorize its locaiton)
gallbladder
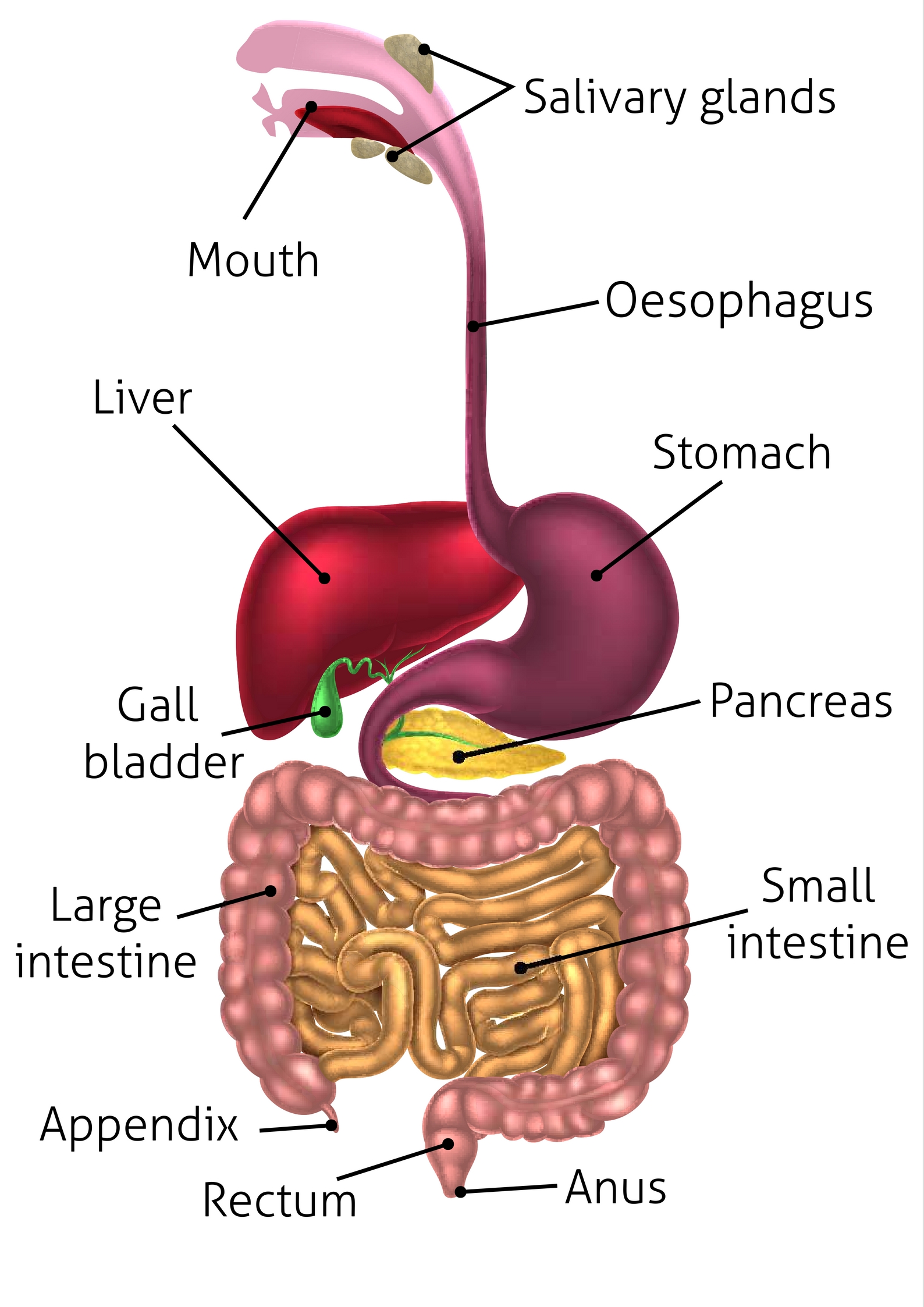
liver (memorize its location)
One of the accessory digestive organs. It produces bile, filters out harmful substances in the blood, helps adjust sugar levels in the blood, filters out old red blood cells, and produces some substances that are important in blood clotting.
What do the 3 pairs of salivary glands produce?
saliva
saliva
watery fluid that contains digestive enzymes
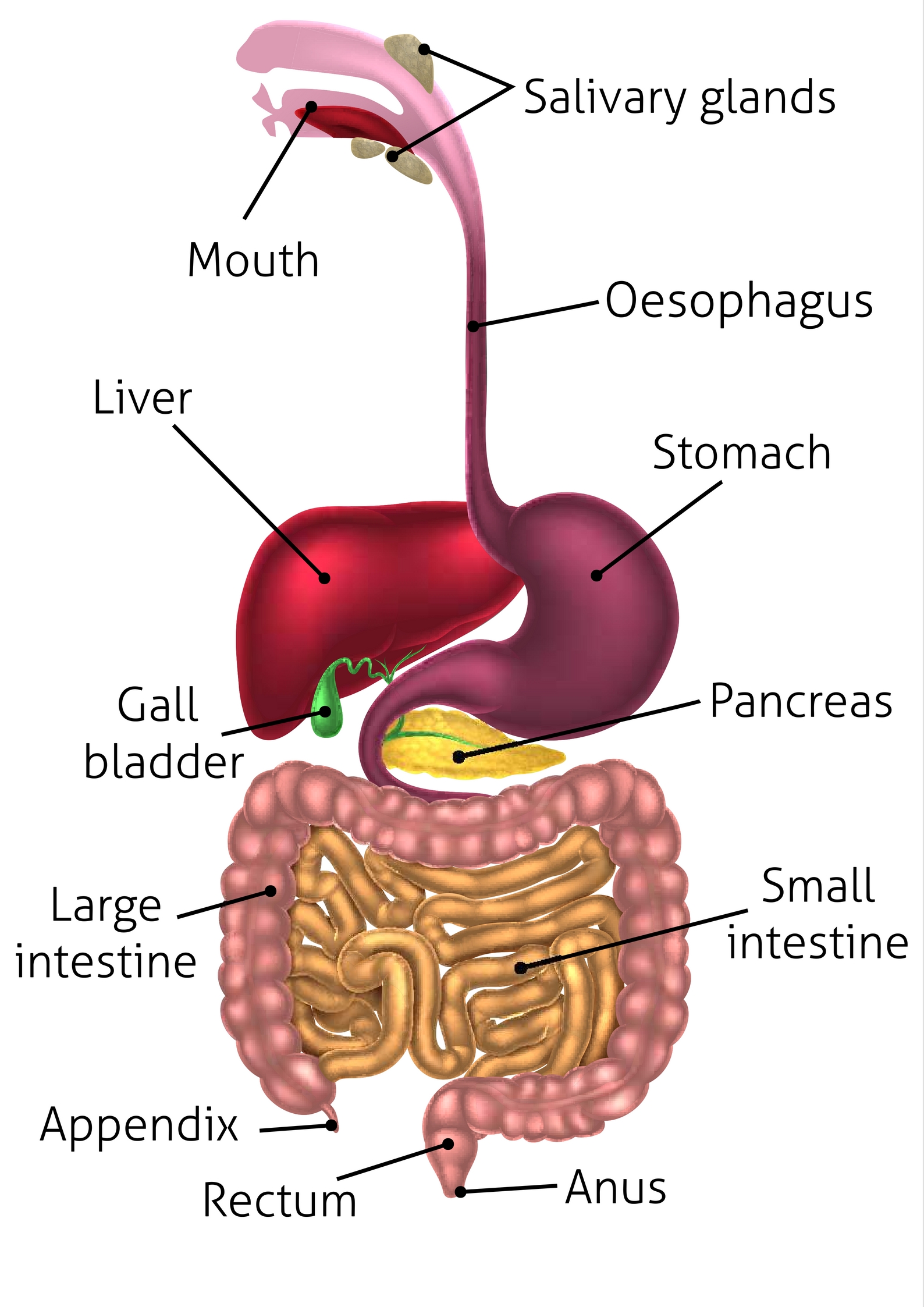
Order that food passes through the body
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
anus
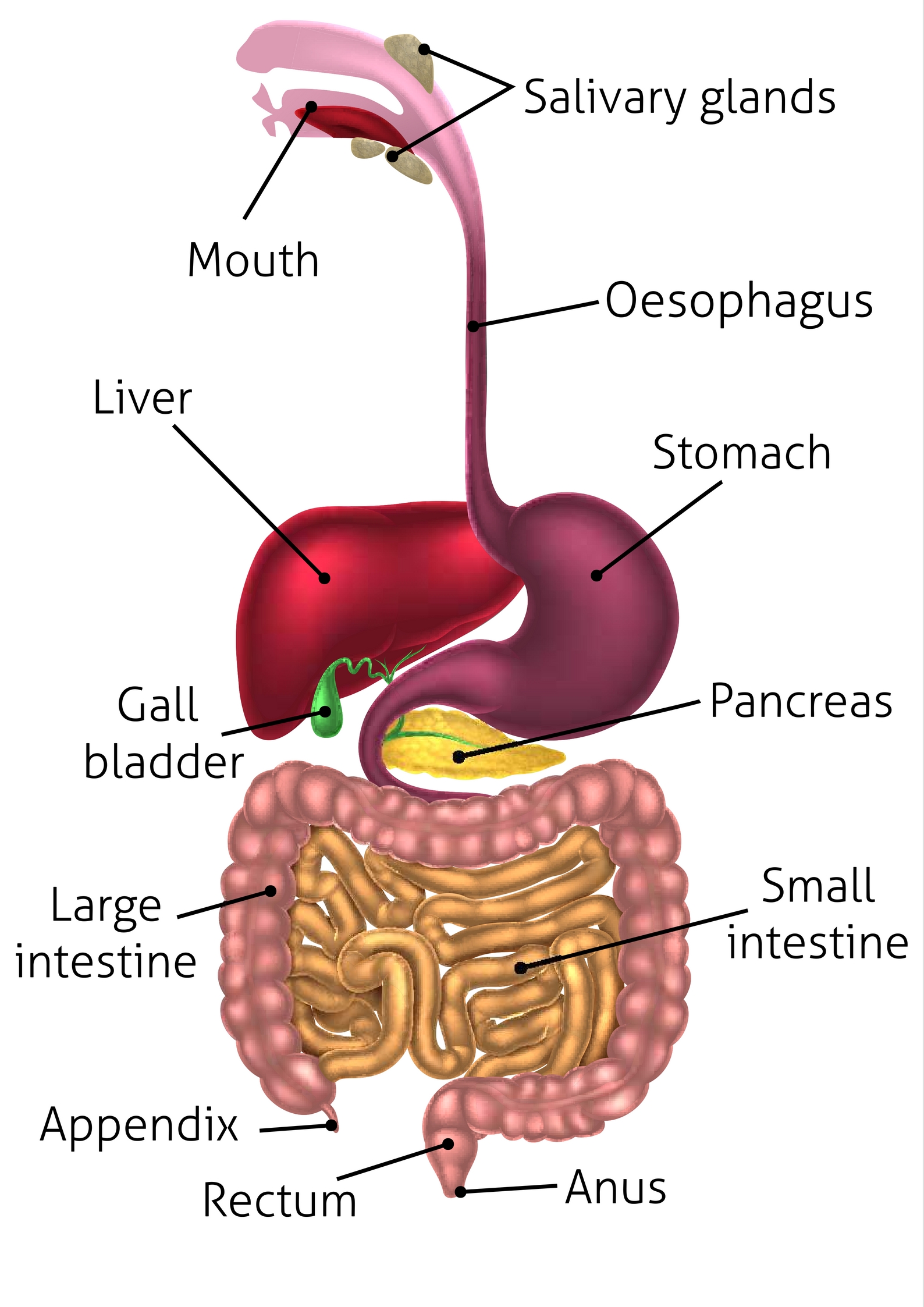
What type of tooth is the wisdom tooth?
molars
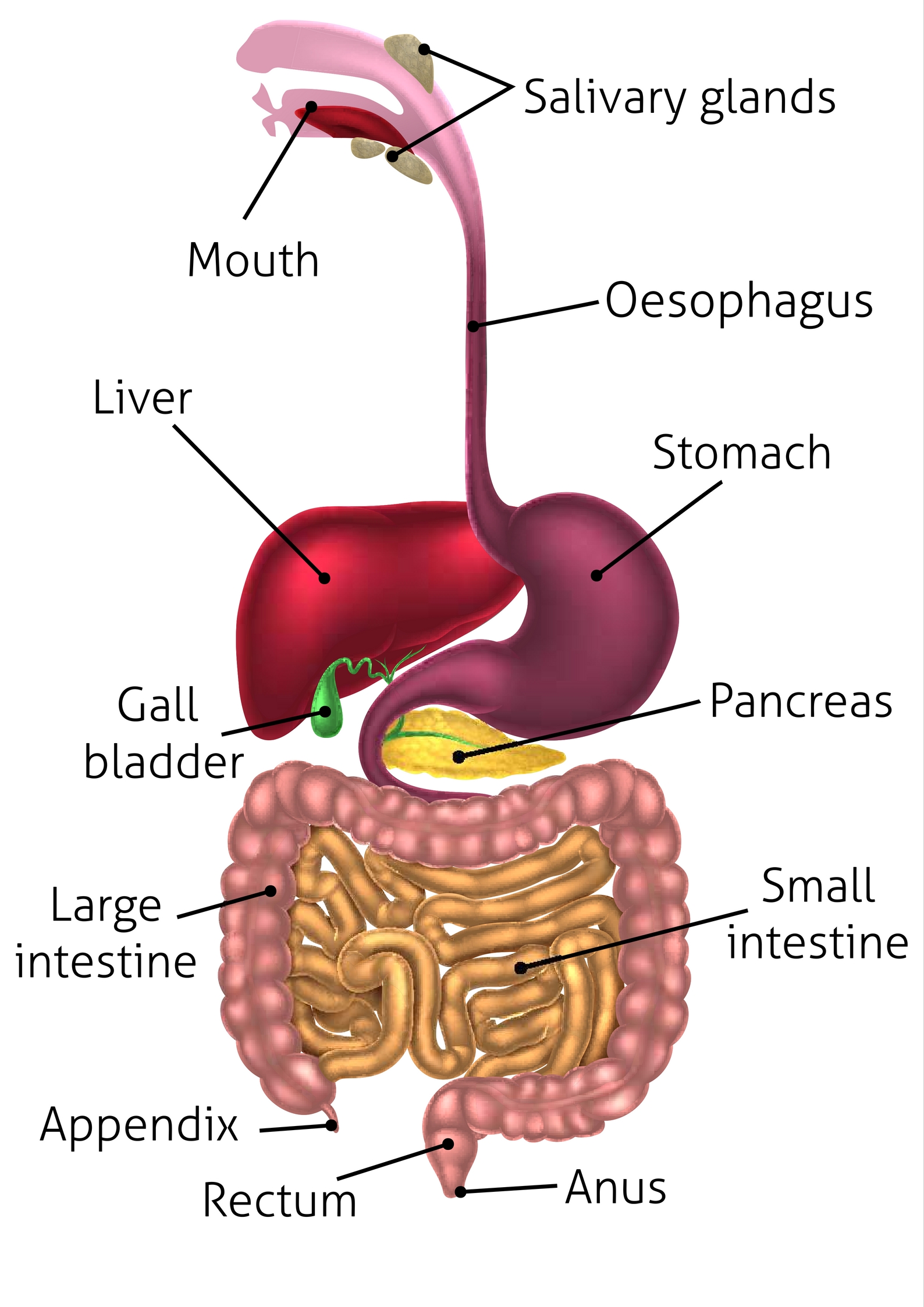
stomach
An organ of the digestive system that adds hydrochloric acid and enzymes and then churns the food
Which organ is the longest?
small intestine
chyme
A mixture of food, enzymes and acid in the stomach
sodium bicarbonate
Produced by a group of glands and is found in baking soda
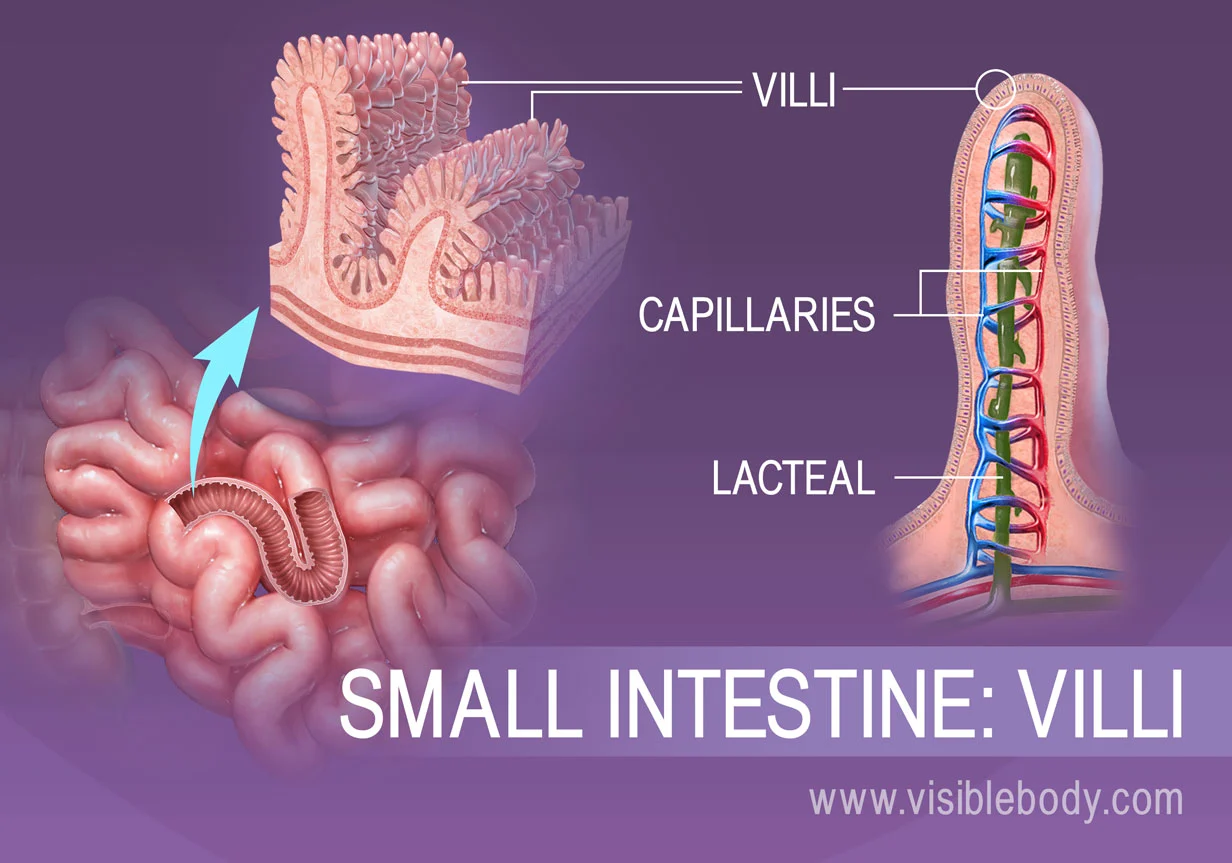
villi
microscopic fingerlike structures that aid in absorbing digested food.
appendicitis
When the large intestine forces some of its contents into the appendix, the weak muscles of the appendix cannot move the solids back into the intestines. As the materials decompose, they produce gases and poisons.
What are some foods we eat that are carbohydrates.
bread, cereal, potatoes, and sweets
proteins
serve as enzymes or building blocks for many tissue and organs in the body.
What are proteins made of?
amino acids
lipids
The fats and oils in foods.vi
vitamins
Made by living organisms and are essential to the normal functioning of the body.
minerals
vital substances that are usually not made of living things. The body uses minerals to build certain materials, such as calcium and phosphorus in bones.
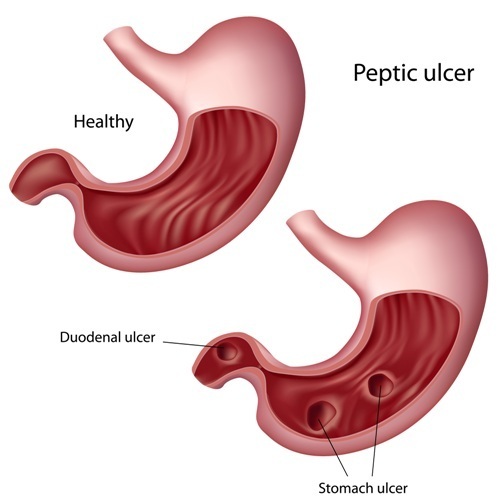
peptic ulcers
Most common type of internal ulcer. It usually occurs in the linings of the esophagus, stomach or part of the small intestine. Most are caused by a bacterial infection in the stomach. But they can also be caused when the valve between the stomach and the small intestine becomes weak and emotional stress. They can be prtreated with antibiotics.
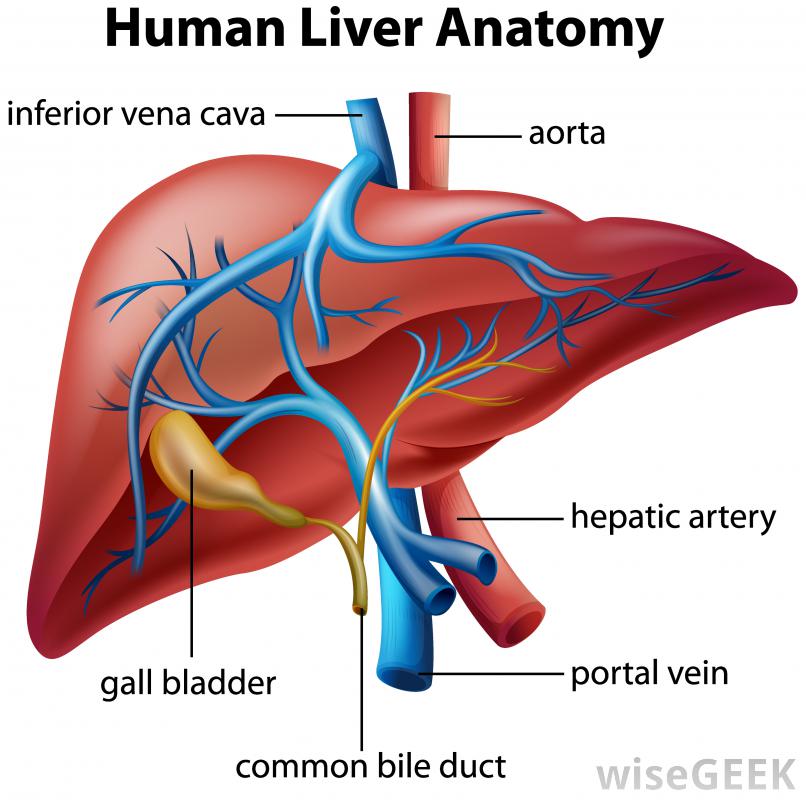
portal vein
Gives a rich supply of blood to the liver.
bile
Breaks up lipids (fats)
calories
a unit of measurement to measure the energy in food
Why do active people need more food than inactive people?
Activity requires energy