STRUCTURAL QUIZ #2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Moment Arm
It is the shortest distance of a force from the point or axis.
Force
It is the action of one body upon another due to direct contact and due to magnetic or gravitational attraction.
Uniform Load
A kind of load which has a series of concentrated loads with uniform magnitude.
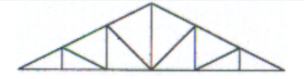
Howe Truss
Identify the type of truss as shown
Scalar
It is a physical quantity that can be described by a single element of a number field such as a real number, or accompanied by units of measurement.
Dynamics
A study applied on a body inducing any motion.
Principle of Transmissibility
It is a principle wherein it states that the external effect of a force on a body acted upon is independent of the point of application of the force but the same for all points along its line of action.
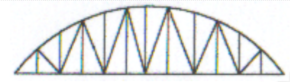
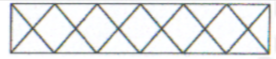
Bowstring
Identify the type of truss as shown
Equilibrium
It is a state in which the resultant of the force system that acts on a body vanishes.
Magnitude
It is the amount of force.
Truss
It is an articulated structure composed of links or bars assumed to be connected by frictionless pins at the joints and arranged so that an area enclosed within the boundaries of the structure is subdivided by the bars into geometric figures which are usually triangles.
Stress
It is the unit strength of any element.
Point Load
A kind of load that is concentratedly imposed at a point on a free body diagram.
Varying Line Load
A kind of load that consists of a series of concentrated loads with varying magnitude.
Vector
A quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Ultimate Strength
The maximum ordinate in the stress-strain diagram is the __________ or tensile strength.
Engineering Mechanics
It is a branch of Engineering that deals with external forces of an assumably rigid bodies.
Direction
It is orientation of the path where the force will be imposed.
Modulus of Elasticity
It is the ratio between the unit stress and unit deformation caused by stress
Stress
It is the unit deformation of a material subjected to an applied load.
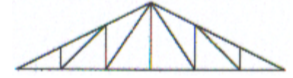
Pratt Truss
Identify the type of truss as shown
Seismograph
It is an instrument at the ground surface which records the electrical effects transmitted to it by a seismometer and thus shows the times and amplitude of earth shocks
Yield Point
It is the point at which the material will have an appreciable elongation or yielding without any increase in load.
Strength of Materials
It is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behavior of solid bodies subjected to various types of loading.
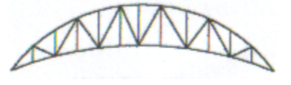
Crescent Truss
Identify the type of truss as shown
Moment
It is the rotation of a force at a point or an axis.
Moment of Inertia
It is a quantity of a body’s tendency to resist angular acceleration.
Strain Gauge
It is the instrument used to measure a minute deformation.
Rupture Strength
It is the strength of the material at rupture which is also known as the breaking strength.
Deformable Body
It is defined as a body on which the distance between two points changes under action of some forces when applied on it.
Axial Stress
It is a stress that develops to resist axial force.
Elasticity
It is a material property wherein it enables deformity upon the force applied and recovers after removing such force.
Malleability
It is a material property wherein it enables it to deform under compressive strength.
Toughness
The ability to absorb energy before rupturing.
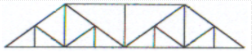
Parker Truss
Identify the type of truss as shown
Elastic Deformation
It is a temporary change in the shape of the body produced by a stress less than the elastic limit of the material.
Rigid Body
It is defined as a body on which the distance between two points never changes whatever be the force applied on it.
Elastic Limit
It is the limit beyond which the material will no longer go back to its original shape when the load is removed
Centroid
It is the center of mass of a geometric object of uniform density.
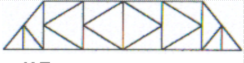
Baltimore Truss
Identify the type of truss as shown
Compression
A type of axial load wherein it is an act of shortening or state of pushing together.
Fatigue
A type of material failure wherein it failed to maintain elastic limit subjected to repeated series of stress.
Normal Stress
It is the stress that occurs when the surface of the body is loaded by an axial force.
Tangential Stress
A force acting in a generally horizontal direction
Strain
It is the change in the size or shape of a body due to the deforming force.
K-Truss
Identify the type of truss as shown
Stress
It is the applied force or system of forces that tends to deform a body.
Permanent Set
It is the inelastic strain in a material
Tensile Stress
It is the stress state leading to expansion.
Tension
A type of axial load wherein it is an act of stretching or state of pulling apart.