HA TOPIC 4: EVALUATING A HEALTH EDUCATION PLAN
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Evaluation
a critical component of the nursing practice decision-making process, the education process, and the nursing process
Steps in Conducting an Evaluation
1. Determining the focus of the evaluation
2. Designing the evaluation
3. Conducting the evaluation
4. Determining methods to analyze and interpret the data collected
5. Reporting results and a summary of the findings from the data collected
6. Using evaluation results
EVALUATION
Process of evaluation involves gathering, summarizing, interpreting and using data after an activity has been completed
ASSESSMENT
Focuses on initially gathering, summarizing, interpreting and using data to decide a direction for action
Evaluation focus includes the 5 basic components:
1. Audience
2. Purpose
3. Questions
4. Scope
5. Resources
Audience
persons or groups for whom evaluation is being conducted
all members of the audience must receive feedback
The nurse educator carrying out the evaluation must first consider the primary audience
Purpose
Answers the questions, “Why is the evaluation being conducted?”
Not synonymous with who or what is being evaluated
Keep it singular. “The purpose is..” not “The purpose are..”
Questions
Directly related to the purpose for conducting the evaluation
Must be specific and measurable
Scope
Determined in part by the purpose for conducting the evaluation and in part by available resources
what is being examined, such as, “How many aspects of education will be evaluated?”, How many individuals or representative groups will be evaluated?”, and “What time frame is to be evaluated?
Resources
Include time, expertise, personnel, materials, equipment and facilities
RSA MODEL (Evaluation Models)
Provides a visual of five basic types of evaluation in relation to one another based on focus, purpose, related questions, scope and resources available
RSA EVALUATION MODEL
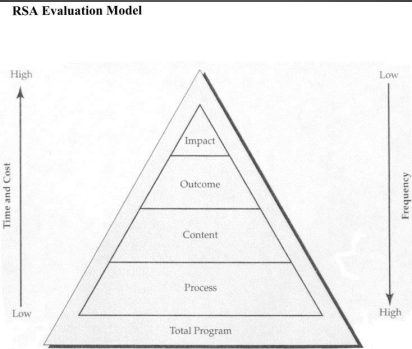
PROCESS (FORMATIVE EVALUATION)
conducted during program development and implementation
is to make adjustment in an educational activity as soon as they are needed, whether those adjustment be in personnel, materials, facilities, learning objectives or even one's own attitude.
CONTENT EVALUATION
purpose of content evaluation is to determine wheather learners have acquired the knowlegde or skills taught during the learning experience.
OUTCOME (SUMMATIVE EVALUATION)
should be completed once your programs are well established and will tell you to what extent the program is achieving its goals
determine the effects or outcomes of teaching effort.
guideing question in outcome eval including the ff:
was teaching appropriate?
did the individual(S) learn?
were behavioral objectives met?
did the patient who learned a skill before discharge use that skill correctly once home?
IMPACT EVALUATION
determine the relative effects of education on the institution or community or to obtain information
help decide obtain information that will help decide whether continuing an educational activity worth its cost.
PROGRAM EVALUATION
can be generically described as "designed and conducted to assist an audience to judge and improve the worth of some object.
Designing an Evaluation
be consistent with the purpose, questions and scope and must be realistic given available resources
Evaluation design includes at least interrelated components: Structure, methods and instruments
Designing Structure
“How rigorous should the evaluation be?”
It should be systematic and carefully planned or structured they are conducted
The structure depends on:
1. The questions to be answered by the evaluation
2. The complexity of the scope of the evaluation
3. The expected use of evaluation results
Evaluation Methods
Answer to the following questions can assists in selecting the most appropriate, feasible methods
Which type of data will be collected?
What data will be collected and from whom?
How, when, and where will data be collected?
Who will collect the data?
1. Sampling Course objectives: (EVALUATION INSTRUMENTS)
course objectives should be tested. The clearly defined behavioral objectives will serve as basis for developing good test.
2. Sampling of course content:
Not all course content can be tested. The teacher must make certain that enough items represents the range of the course content taught.
3. Validity
the degree or extent to which it measures what it intends to measure. What it intends to measure is the criterion for the relevance of the test.
4. Reliability
can be determined through application and statistical computation.
A test is reliable if it yields the same results each it is applied to the same situation or group of students under the same condition.
5. Practicality:
it refers to the development of instruments capable of being administered and scored
6. Usefulness:
Instruments can be use in various purposes not only as basis for student's grades but also student's capabilities
ANALYZING AND INTERPRETING DATA COLLECTED
1. To organize data so that they can provide meaningful information.
2. To provide answers to evaluation questions.
Basic decisions about how data will be analyzed are dictated by:
The nature of the data; can either be quantitative or qualitative
The questions used to focus the evaluation
Quantitative data (STEPS IN ANALYSIS)
1. Organization and summarization using statistical treatment
2. Select the statistical procedure appropriate for the type of data collected that will answer questions posed in planning the evaluation
Qualitative data
1. Summarized into categories of similar comments (Themed)
2. each theme or category is qualitatively describe by directly quoting one or more comments that are typical of that category.
3. These categories may then be quantitatively describe using descriptive statistics
REPORTING EVALUATION RESULTS
1. Be audience focused.
2. Stick to the evaluation purpose.
3. Stick to the data.