RP6 - Use of aseptic techniques to investigate the effect of antimicrobial substances on microbial growth.
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Explain examples of aseptic techniques that could be used (5)
1. Wash hands with soap and disinfect surfaces → kill microbes and prevent contamination
2. Sterilise pipette / spreader / boil agar growth medium → kill microbes and prevent contamination
3. Flame neck of bottle of bacteria → kill microbes and prevent contamination
4. Keep Bunsen burner close → upward current of air draws air-borne microbes away to prevent contamination
5. Lift lid of petri dish slightly / minimise opening → prevent entry of microbes and contamination
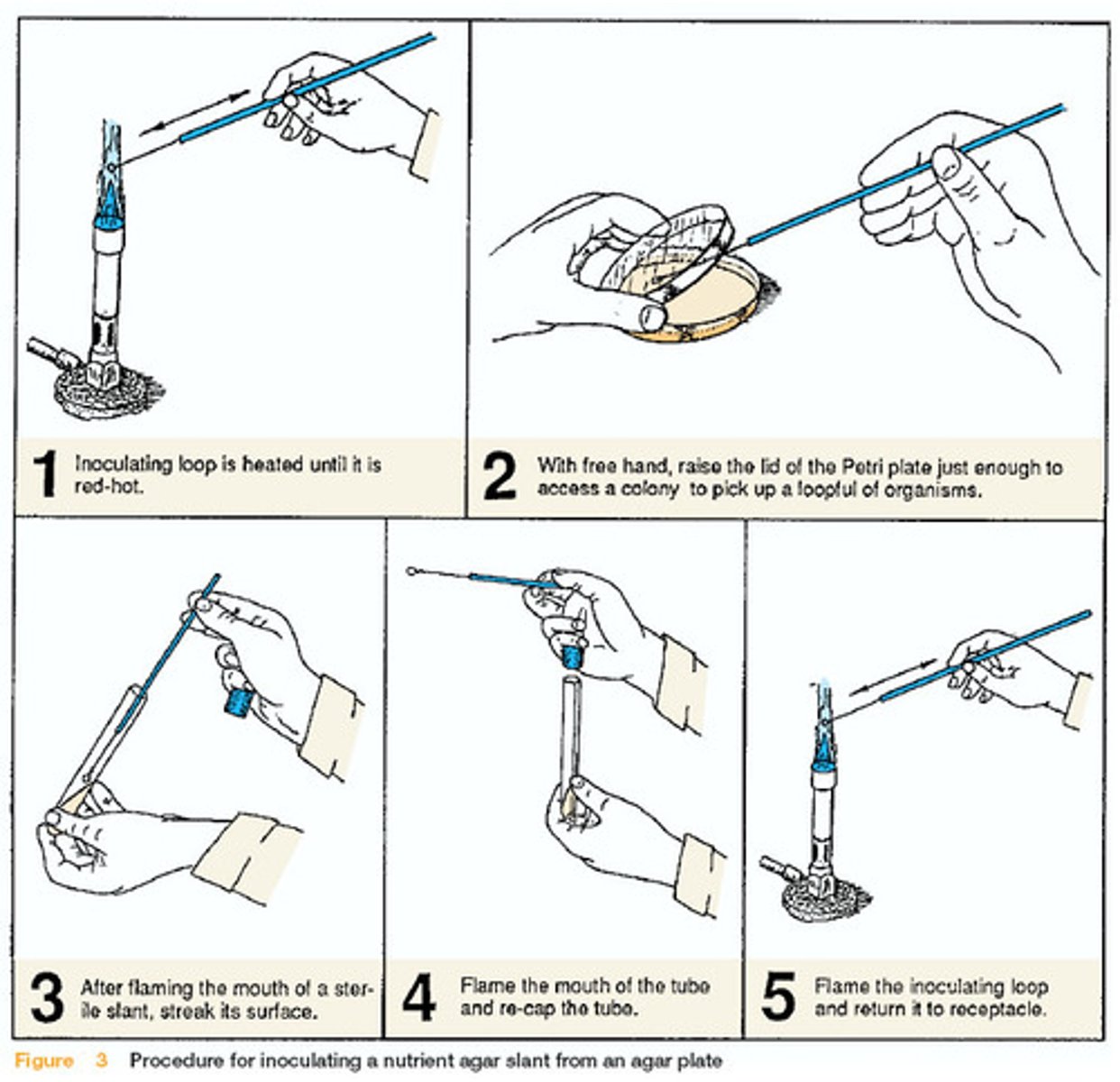
Describe a method to investigate the effect of antimicrobial substances (eg. antibiotics, disinfectants, antiseptics) on microbial growth
1. Prepare area using aseptic techniques
2. Use a sterile pipette to transfer bacteria from broth to agar plate using aseptic techniques
3. Use a sterile spreader to evenly spread bacteria over agar plate
4. Use sterile forceps to place same size discs that have been soaked in different types / concentrations of antimicrobials for same length of time, onto agar plate (at equal distances)
5. Lightly tape lid onto plate (not fully sealed), invert and incubate at 25°C for 48 hours 6. Measure diameter of inhibition zone around each disc and calculate area using πr2
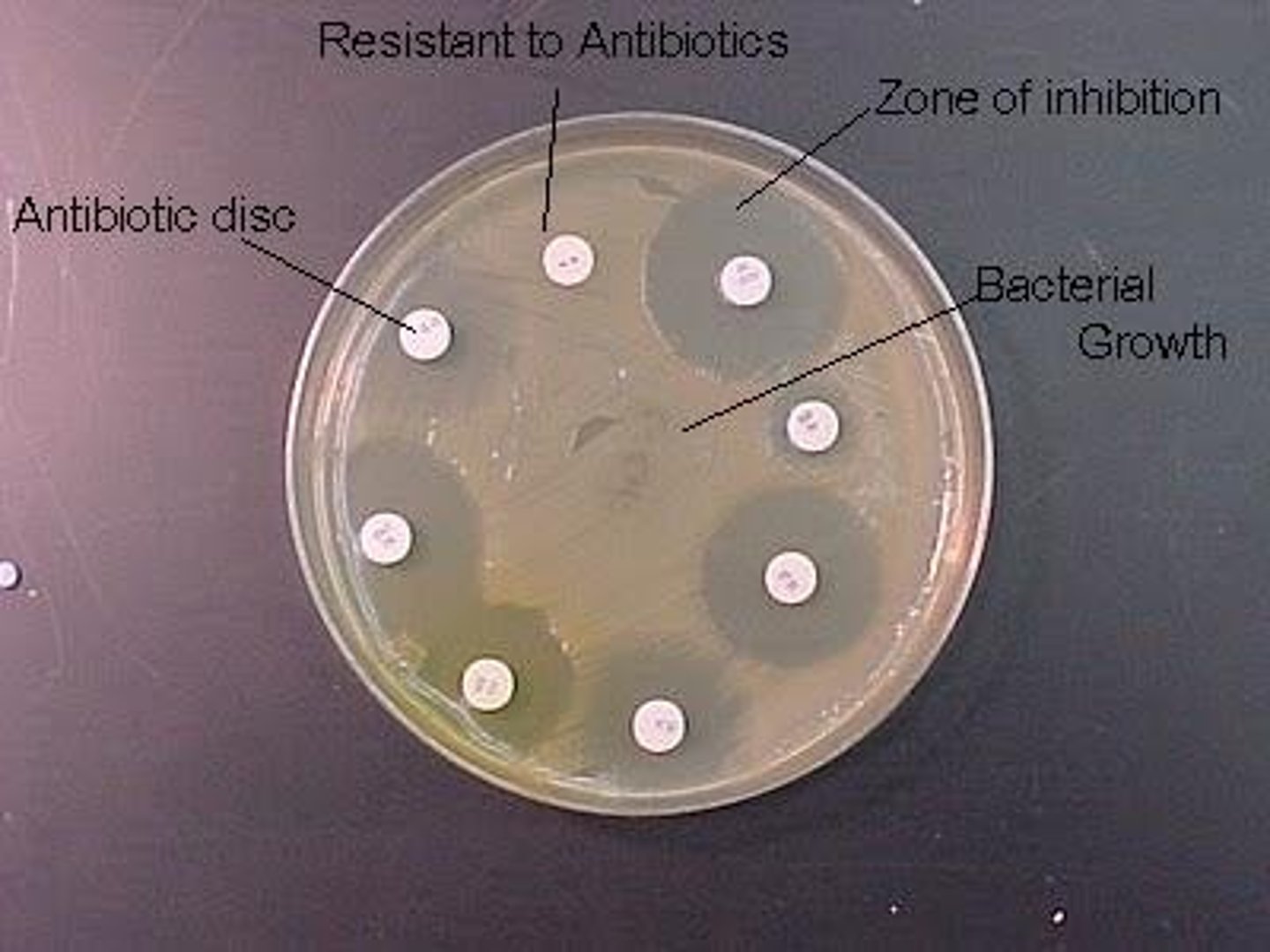
Why is it important to maintain a pure culture of bacteria?
● Bacteria may outcompete bacteria being investigated
● Or could be harmful to humans / pathogenic
Why hold lid with 2 pieces of tape instead of sealing it completely?
● Allows oxygen in preventing growth of anaerobic bacteria ● Which are more likely to be pathogenic / harmful to humans
Why use a paper disc with water / no antimicrobial agent?
● Act as a control
● Ensuring antimicrobial prevented growth, not paper disc
Why incubate upside down?
● Condensation drips onto lid rather than surface of agar

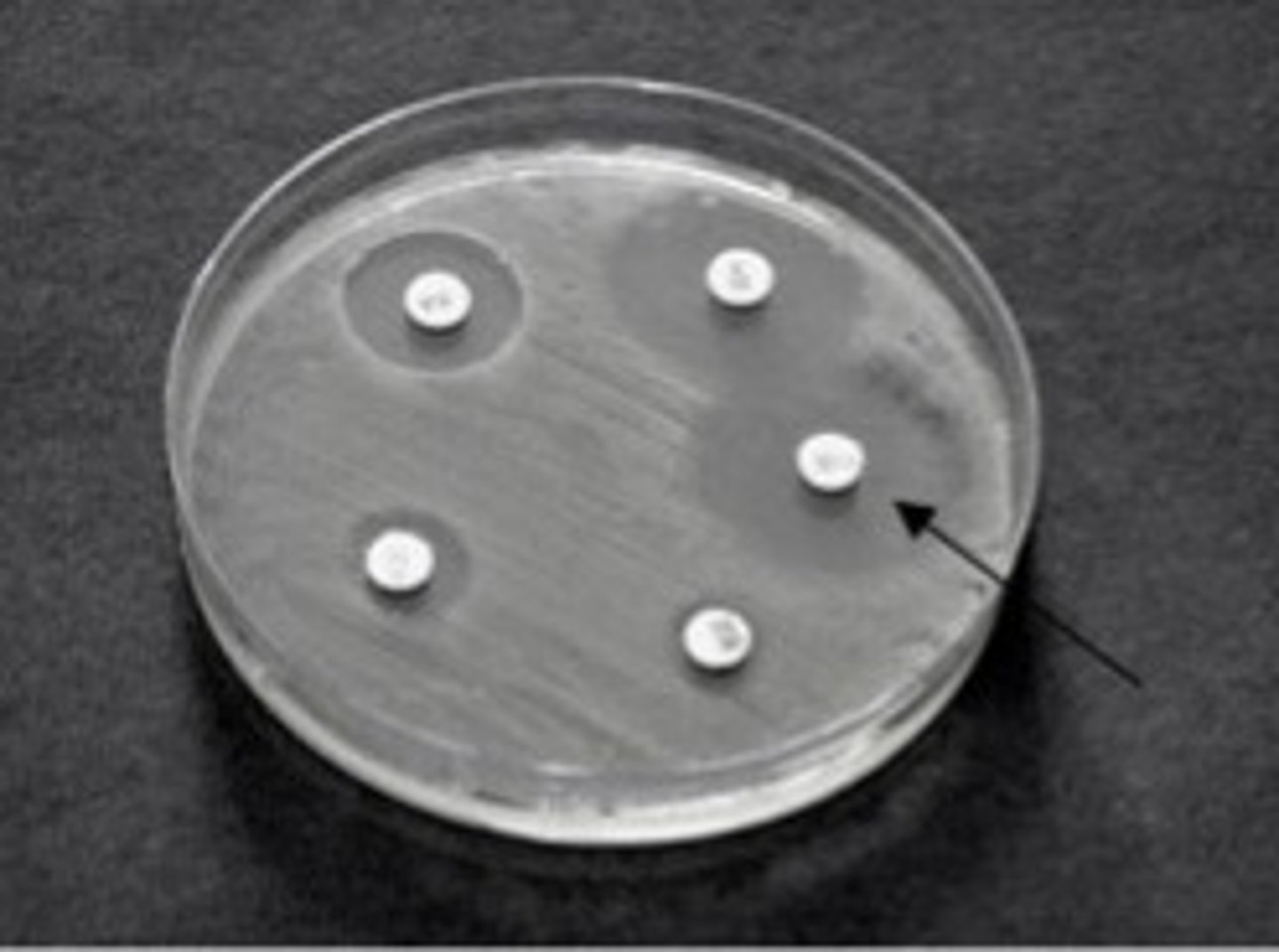
What if inhibition zones are irregular?
● Repeat readings in different positions, calculate a mean
Why not use higher antimicrobial conc.?
● More bacteria killed so clear zones may overlap
Why incubate at 25C or less?
● Below human body temp to prevent growth of pathogens

Describe how data about the effect of antimicrobial substances can be presented as a graph
● Categorical data → bar chart (X axis type of antimicrobial, Y axis area of zone of inhibition / mm3 )
● Continuous data → line graph joined by a line of best fit (X axis concentration of antibiotic / μgmL -1 , Y axis area of zone of inhibition / mm3 )
Explain the presence of clear zones
1. Clear zones → antimicrobial diffuses out of disc into agar, killing / inhibiting growth of bacteria
● the larger the clear zones → the more bacteria killed → more effective antimicrobial
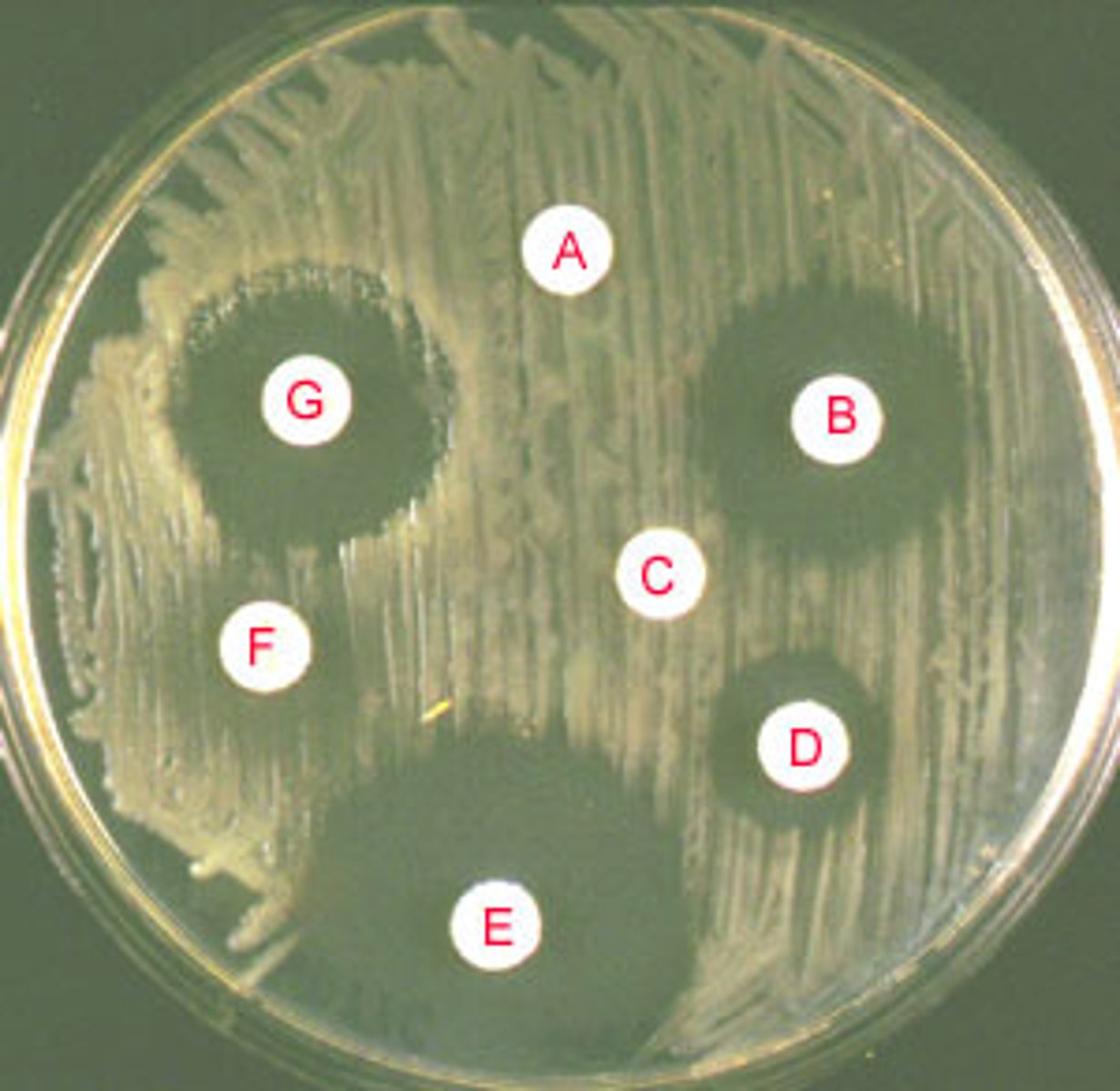
Explain the absence of clear zones
2. No clear zones → if antibiotic used, bacteria may be resistant or antibiotic may not be effective against that specific bacteria