3.2.2.1 THE CIRCULAR FLOW OF INCOME
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What does national income measure?
The flow of new output produced by an economy in a particular time period, such as a year
The total monetary value of all goods and services produced in an economy usually in a year
What is the difference between nominal and real national income?
nominal (includes inflation) - measures the flow of output at the current price level in the economy
real (does not include inflation) - the flow of new output - the actual goods and services that are produced
What is the role of real national income as an indicator of economic performance?
The level of real national income is an indicator of current living standards living within the economy
What is the difference between economic development and economic growth?
Economic growth - a growing economy
Economic development - does this mean that people are better off?
What is the debt to GDP ratio?
100% (£2.6 trillion)
What is the 3 word that all begin with national that equal each other?
National income = national output = national expenditure
What is national income?
Incomes received by the differnt factors of production (labour)
What is national output?
Summing the total of the actual goods and services produced by the economy
What is national expenditure?
How wages and profits end up being spent on the goods and services produced by the economy
What is the income approach?
Sums the factor incomes to the factors of production
What is the output approach?
Adds to the 'value added' by each of the industries in the economy
What is the expenditure approach?
Suns consumption and investment and government expenditure and exports minus imports
What is the equation for this?
AD = C + I + G + (X - M)
What does each letter stand for?
C - consumption - consumers
I - investments - businesses
G - government spending
X - imports
M - exports
What are the 2 types of flows?
real flow (households own factor services which they hire out of firms)
money flow (household receive payments for their services - income - and use this money to buy the outputs of firms - consumption
What are the 4 main factors of the circular flow of income?
income
households
consumption
firms
What does the circular flow of income look like?
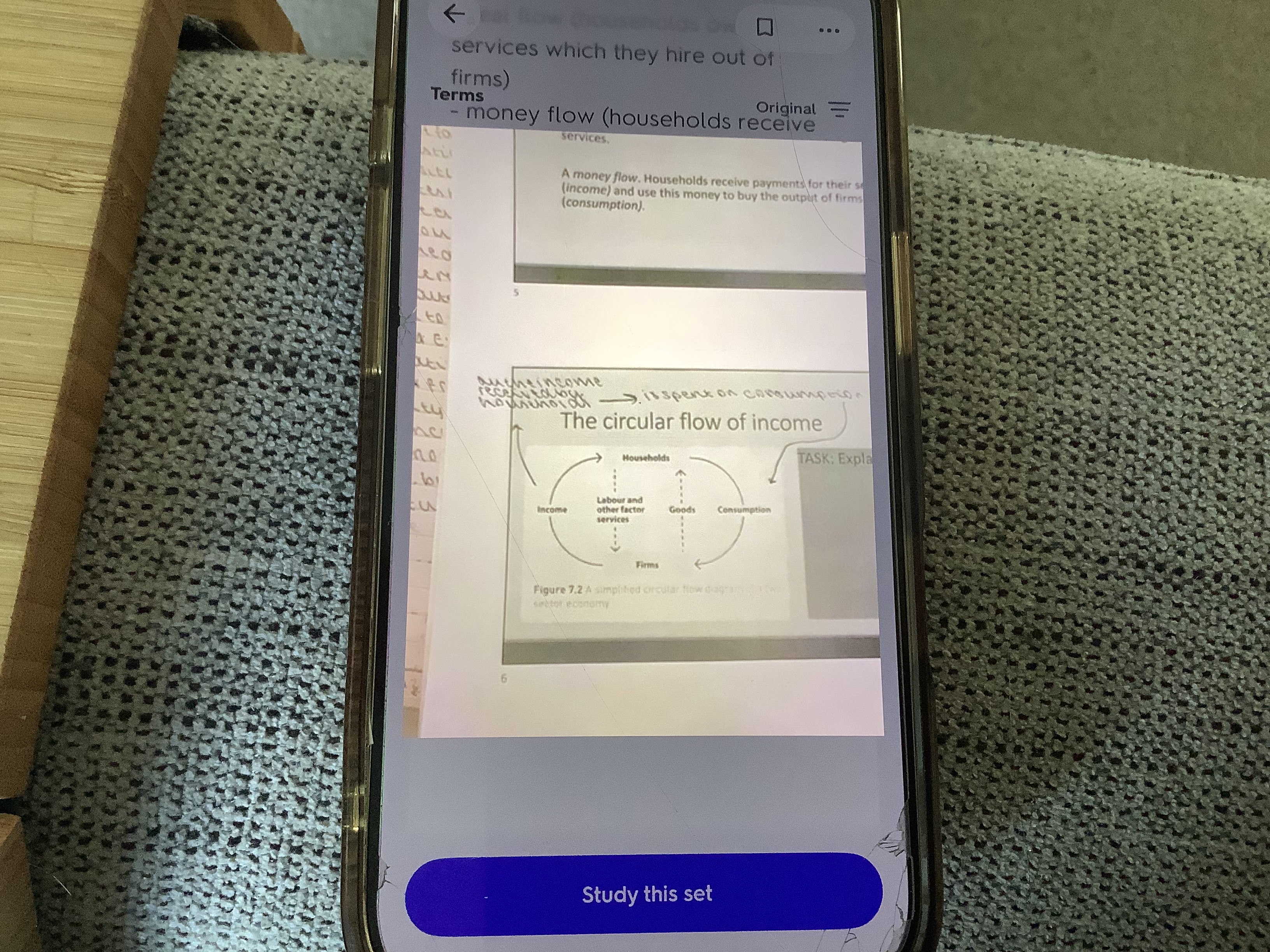
What does a closed economy mean?
An economy with no international trade
An examples of a closed economy?
Iceland
Is the UK a closed or open economy?
Open - the UK exports services
What services does the UK predominantly export?
Finance related services
What is FDI?
Foreign direct investment - when businesses have outlets in different countries, but all the money/profit goes to the parent country
Define saving
Income which is not spent
Define withdrawal
A leakage of spending power out of the circular flow of income into savings - taxation or imports
Define investments
Total planned spending by firms on capital goods produced within the economy
Define injection
Spending entering the circular flow of income as a result of investment, government spending and exports
What is equilibrium national income?
The levels of income at which withdrawals from the circular flow of income equal injections into the flow
Also the level of output at which aggregate demand equals aggregate supply
What equation shows equilibrium?
Planned saving = planned investment
S = I
What does an open economy mean?
An economy open to international trade
What is hoarding?
When consumers keep a fraction of their income and do not spend it
Income that is not spent
Is hoarding a good or bad thing for the economy?
A bad - this does not help the multiplier as it is leaving the circular flow of income and not back into the economy
Why do consumers hoard money?
Consumers have a propensity to either spend or save their money - depending on their confidence
Examples of withdrawals into the circular flow?
put aside for future saving
paid to the government in taxes
spent on foreign goods imported into the country
Examples of infections into the circular flow?
other firms - investment expenditure
the government - expenditure
foreigners - export expenditure
Explain how hoarding affects the equilibrium national income?
Leads to deficient aggregate demand in the economy which means there is too little demand to buy the output the economy is capable of producing
What happens to national income when:
S + T + M = I + G + X
National income is in equilibrium
What happens to national income when:
S+T+M > I+G+X
National income level decreases
What happens to national income:
S+T+M < I+G+X
National income level increases
What does S+T+M = I+G+X stand for?
saving + taxation + imports = investments + government spending + exports
What is another word for withdrawals?
Leakage
What are the 3 leakages/withdrawals?
savings
taxation
imports
What are the 3 injections?
investments
government spending
exports
Which out of the 3 injections, do not contribute to AD?
Imports
Is this statement true or false?
If the sum of all injections is greater than the sums of all withdrawals then national income will rise and the economy should grow
True
Is this statement true or false?
If saving plus government spending equals taxation plus investment then the economy is in equilibrium?
False
Why is this?
It ignores other injections and withdrawals
If exports are £-50bn, does this mean money is flowing in or out of the economy?
Out - so exports would go from 300 to 350 as more money is leaving the economy