Edexcel IGCSE Physics - (Unit 1) Forces & Motion
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
unit for speed
m/s
momentum
how difficult it is to stop a moving object
equation linking moment, force and perpendicular distance
Moment = force x perpendicular distance from pivot
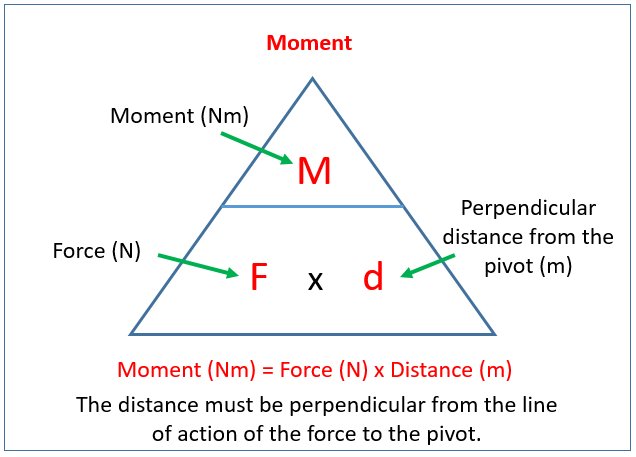
unit for acceleration
m/s²
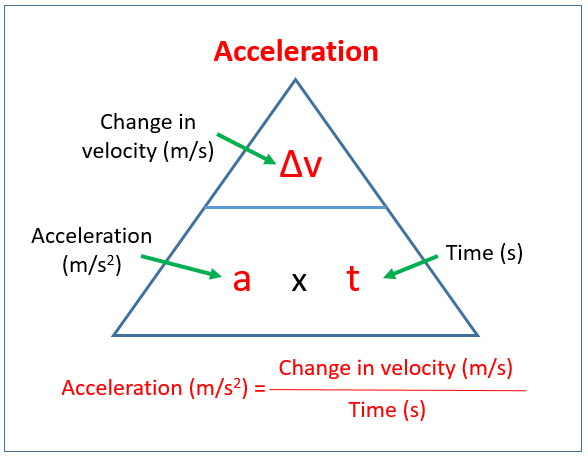
equation linking acceleration, change in velocity and time taken
a = (v-u)/t
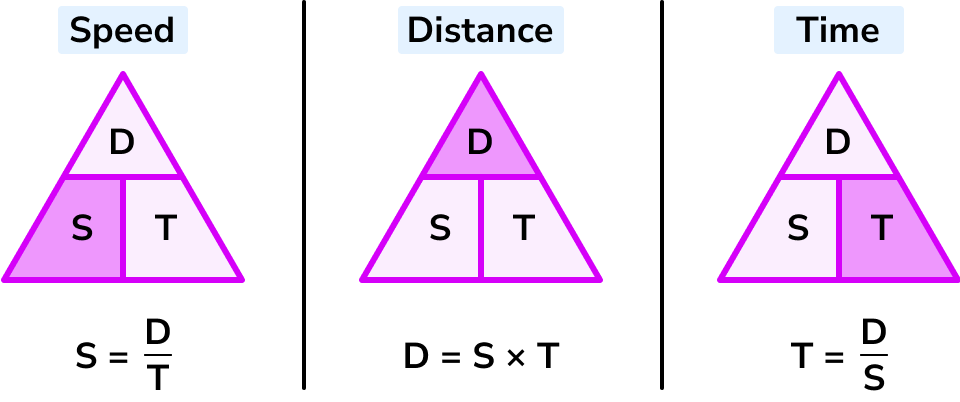
Equation linking average speed, distance travelled and time taken
v=s/t speed = distance/time
Equation linking final velocity, initial velocity, acceleration and displacement (This equation is especially useful when time is not given in the problem.) equation of motion or the third equation of motion.
v² = u² + 2as
Vector quantities have...
magnitude and direction
Scalar quantities have...
magnitude only, no direction
Gradient of velocity-time graph gives...
acceleration
Area under a velocity-time graph gives...
distance travelled
Equation linking force, mass and acceleration
F=ma
Hooke's law:
The force exerted by a spring is directly proportional to its extension, provided the elastic limit is not exceeded.
Formula:
Where:
: Force (N)
: Spring constant (N/m)
: Extension (m)
Limit of proportionality is where
a spring stops obeying Hooke's Law
Equation linking weight, mass and gravitational field strength
W = mg
Stopping distance =
thinking distance + braking distance
Factors affecting vehicle stopping distance:
speed, mass, road condition and reaction time
Thinking distance =
distance travelled before responding to a stimulus
Braking distance =
distance travelled while the brakes are applied
Terminal velocity
velocity when drag and weight forces are balanced
equation linking momentum, mass and velocity
p=mv
momentum = mass x velocity
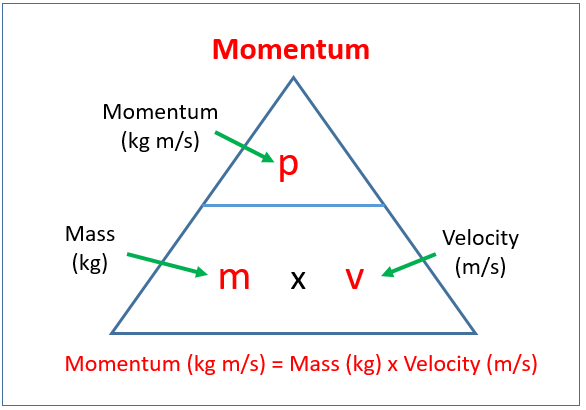
Unit for momentum
kg m/s
Unit for force and weight
N (Newton)
Unit for moment
Nm
Unit for mass
kg
Equation linking force, change in momentum and time
F = (mv - mu)/t Force = change in momentum/time

What is speed?
Speed is how fast you're going and is a scalar quantity. e.g. 30m/s
What is the formula for average speed?
Average Speed = Distance moved/time taken
What is velocity?
Velocity is speed in a certain direction and is a vector quantity. e.g. 30m/s north
What is acceleration?
Acceleration is the rate at which velocity is changing and is a vector quantity.
What is the formula for acceleration?
Acceleration = Change in velocity/time taken
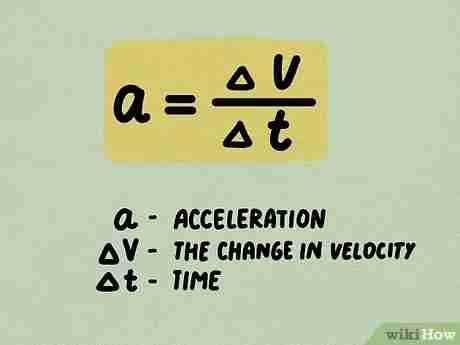
How do you find speed in a distance-time graph?
Gradient = Speed
What is gravity?
The force of attraction between all masses.
What is the difference between weight and mass?
Mass is consistent throughout the galaxy whereas weight changes depending on the strength of gravity.
What is formula for weight?
Weight = mass x gravitational field strength
What are the seven types of force and in which direction do they act? (if applicable)?
- Gravity/Weight, always acting downwards.
- Reaction force, usually acting upwards from a surface.
- Electrostatic force (between two charged objects), the direction depends on the type of charge, whether they repel or attract.
- Thrust
- Drag/air/friction, slowing object down
- Lift
- Tension in a rope/cable
What are the three ways friction occurs?
- Friction between solid surfaces which are gripping, AKA static friction.
- Friction between solid surfaces sliding past each other.
- Resistance/drag from fluids.
How would the motion of a toy car on a ramp be measured?
- Car is placed on the ramp behind a marked line and let go.
- Travels down slope and passes through multiple light gates which record data onto a data logger.
- Distance is measured between gates to find average speed.
What is terminal velocity?
When oppositely acting forces are equal to one another, meaning there is no resultant force and thus no acceleration.
Which factors affect terminal velocity and how?
The area and mass of the falling object affects the speed at which terminal velocity occurs.
How could terminal velocity be measured?
Using sycamore seeds with different wing lengths.
What is Newton's first law of motion?
So long as the forces on an object are balanced, the object will just stay still or if it's already moving, continue at a constant velocity.
What is Newton's second law of motion?
If there is an unbalanced force, the object will accelerate in the direction of the resultant force.
What is Newton's third law of motion?
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
If object A exerts a force on object B, object B exerts the exact opposite force on object A.
What is the formula for force?
Force = mass x acceleration
How would you work out resultant force?
The vectors would be combined.
What are the two factors that effect stopping distances?
- Thinking distance
- Breaking distance
What affects thinking distance?
- How fast you're going
- Whether you're sober or not
What affects braking distance?
- How fast you're going
- Mass of the vehicle
- Quality of brakes
- Quality of road/road conditions
What is the formula for momentum?
Momentum = mass x velocity
What happens to the speed of something after a collision if it gains mass?
The speed will decrease.
Momentum=Mass×Speed
then
New Speed=Original Momentum/New Mass
How are cars design to reduce injuries?
Lessening the force exerted on the passengers by increasing the time it takes for a change in momentum.
How is this achieved?
- Crumple zones crumple on impact.
- Seat belts stretch slightly.
- Air bags slow passengers down.
What is a moment?
A moment is a turning effect of a force.
How is a moment maximised?
One has to exert the largest possible force as far away from the pivot as possible, pushing at right angles.
What is the centre of gravity?
The point through which the weight of a body acts.
How can a centre of gravity of a flat object be found?
Hanging the shape from two different pivots and drawing a line directly perpendicular to the ground. Where the two lines cross is the centre of gravity.
What is the principle of moments?
If the object is balanced then, total anticlockwise moments = total clockwise moments
If the object is unbalanced...
... there will be a resultant moment so the object will turn.
How can Hooke's law be investigated?
With a spring hung from a clamp. Different masses are hung andthe extension is measured.
Where is our solar system?
In the milky way galaxy.
What is a galaxy?
A collection of stars maintained by gravity that rotates.
What is the universe?
A large collection of billions of galaxies.
If an object is travelling in an elipse...
... it is constantly changing direction and thus there must be a force acting on it.
What is the effect of distance between objects on the force of gravity?
The closer two objects are, the stronger the gravitational force between them.
For orbiting objects, a greater distance means a weaker gravitational force, which results in slower orbital speed