07 - Seed to tree
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Two mobile life cycle phases
seed dispersal syndromes
polination syndrome
why do you need seed dispersal
Without seed dispersal adaptations, most seeds are deposited close to mother plant
why is it bad to most seeds are deposited close to mother plant
→ parent-offspring competition for space & resources
→ mating btw. closely related individuals: inbreeding depression
Explosive self dispersal DIY:
Ballistochory
Wind dispersal:
Anemochory
Water dispersal:
Hydrochory
“Internal hitchhiking”:
Endozoochory
“External hitchhiking”:
Exozoochory
Ant dispersal:
Myrmecochory
Gravity+:
Barochory & 2ndary dispersal by animals
Ballistochory
seeds catapolted away
build up pressure slightest force causes to catapolt
Anemochory:
hairs → allows seed to be picked up by wind
parachute → good adaptation to move away (dandilions)
wings (Winged maples)
Hydrochory
water travel
need a seed coat so seed can curvive in salt water
contains airpocket which keeps them floating
eg coconut - good floater, well defense shell, survive long period
Exozoochory
hooks grab onto fur or hair and fall out when you move
Endozoochory
animals eat it and poop it up
eg. berries indicate with colour when seed inside is ripe
their seed coat = strong so it survives the acidiic environemtn of the stomach and teeth
Myrmecochory
tranfered by ants
Myrmecochory relationship
→ Symbiotic relationship: plant → seed dispersal; ant → food
Elaiosomes
(elaios- oil, some- body): food for ants
Fleshy structure attached to seeds
Rich in lipids and proteins

Barochory and small animal dispersal
fall down and animal carry
Big, heavy seeds Starch-rich, oil-rich → great food Survive winter: seed caching! Some caches: forgotten → tree seedling recruitment
Scatter hoarding
puts seeds all over the place
Larder hoarding:
in one place
Comparison of dispersal distances

testa
Contains plant embryo1 , covered with protective seed coat
radicle
Embryo: embryonic shoot, root3
embryonic leaves
cotyledons4
endosperm
Food for embryo
food storage cells inside seed; not part of embryo
how is endosperm developed
developed through Double Fertilization
Double Fertilization
(angiosperms only): parallel to fertilization of egg by pollen (→ embryo), one pollen nucleus (1n) fertilizes ‘central cell’ (2n) inside ovule → endosperm (3n)
do all angios keep double fertilization goingn
no
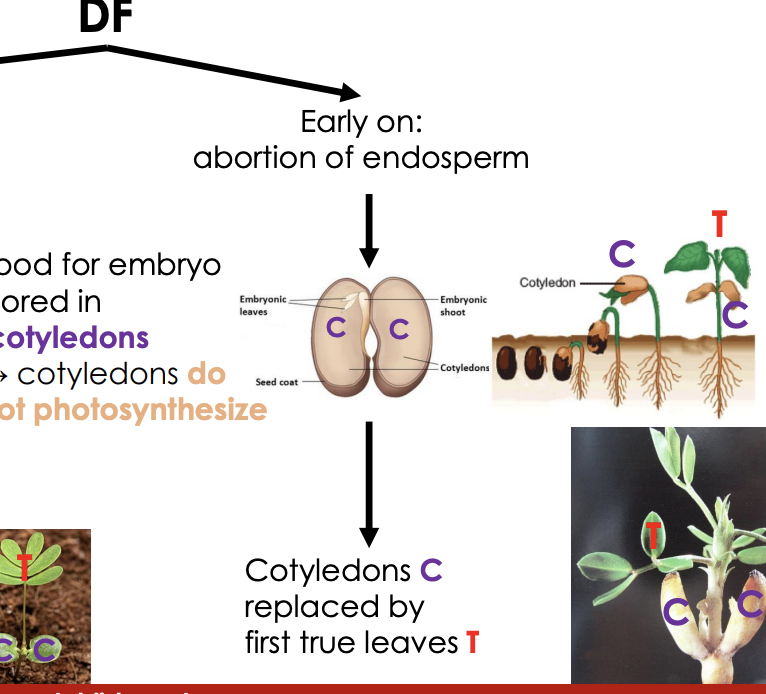
Early on: abortion of endosperm
Food for embryo stored in cotyledons → cotyledons do not photosynthesize
Cotyledons C replaced by first true leaves T
process of df when kept going
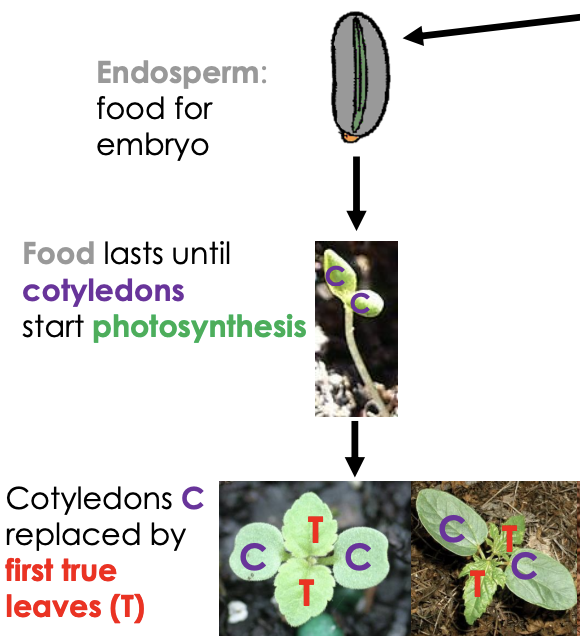
Endosperm: food for embryo
Food lasts until cotyledons start photosynthesis
Cotyledons C replaced by first true leaves (T)
In which of the 7 dispersal mechanisms do elaiosomes play a role?
Myrmecochory
In which seed dispersal mode does the plant need to invest into a seed coat which is resistant to grinding or abrasion or acid
Endozoochory
In which seed dispersal mode do plants need to construct parts which are under elastic pressure, where the power gets released as the seed matures and dries out
Ballistochory
Which seed dispersal mode was the role model for the invention of Velcro?
Exozoochory
Which dispersal mechanism involves seeds which are especially light and non-dense
Anemochory
Which seed dispersal mode relies on hoarding
Barochory
Which seed dispersal mode is more common on high mountains above tree line, on islands and generally in areas without much tree cover?
Anemochory
For which seed dispersal mode are fur and feathers important?
Exozoochory
Which seed dispersal mode is especially important for Ontario’s spring ephemerals in forests?
Myrmecochory
In which seed dispersal mode does the plant indicate to the dispersal agent when seeds are ripe?
Endozoochory
Which seed dispersal mode relies on the forgetfulness of the disperser?
Barochory
When an endozoochorous fruit is eaten by an animal vector, the seed is most likely still viable after the gut passage
tru
When an seed dispersed through barochory is eaten, it is still viable after gut passage.
false
What is the food source for the embryo?
Endosperm
What is the name for the first generation leaves or embryonic leaves?
Cotyledons
What organ develops through double fertilization?
Endosperm
All angiosperms at least initiate the development of the endosperm
true
ploidy levels cotyledons
diploid
ploidy levels - embryo
diploid
ploidy levels - endosperms
triplpoid
Many angiosperms abort the development of the endosperm and the energy needed for the embryo gets absorbed into the cotyledons
True
In angiosperms which store the food for the embryo in the cotyledons, the cotyledons are typically photosynthetic
false
When you are eating popcorn, what are you eating? Choose all appropriate solutions
food for the embryo, embryo, endosperm
When eating a peanut, you are mostly eating the…
Cotyledons
Where in the tree of life was the endosperm invented?
angio