Lecture 16 & 17: Ecdysozoan Nematodes
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
what 2 phylums are in Clade Ecdysozoans?
-Nematoda
-Arthropoda
summary:
Ecdysozoa
“ecdysis”: shedding exoskeleton
-include nematodes (25k named spp); arthropods (1mil+ spp)
summary:
Phylum Nematoda (8)
-most are microscopic
-interstitial dwellers (fresh, marine water, soil, etc)
-decomposers
-parasitic
-non-segmented, cylindrical body (tapered on both ends)
-ecdysis: shed cuticle @ each molt
-complete gut with mouth, anus
-dioecious (having male reproductive organs in one individual and female in another)sexual repro, internal fertilization
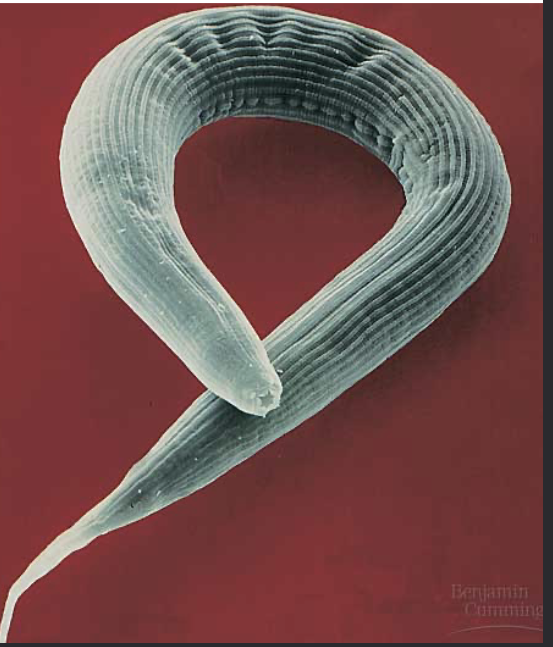
phylum Nematoda (roundworm)
-notice tapered at both ends
definition:
ecdysis
-shed cuticle (exoskeleton)
phylum Nematoda are also known as?
roundworms
phylum Nematoda:
body (5)
-triploblastic
– Body wall lined by thick cuticle, which is secreted by underlying epidermis. This holds high internal pressure.
– Pseudocoelom
– Body with longitudnal muscles only
– No respiratory or circulatory system
phylum Nematoda:
Transport
– No respiratory or circulatory system
– Internal transport via body fluid
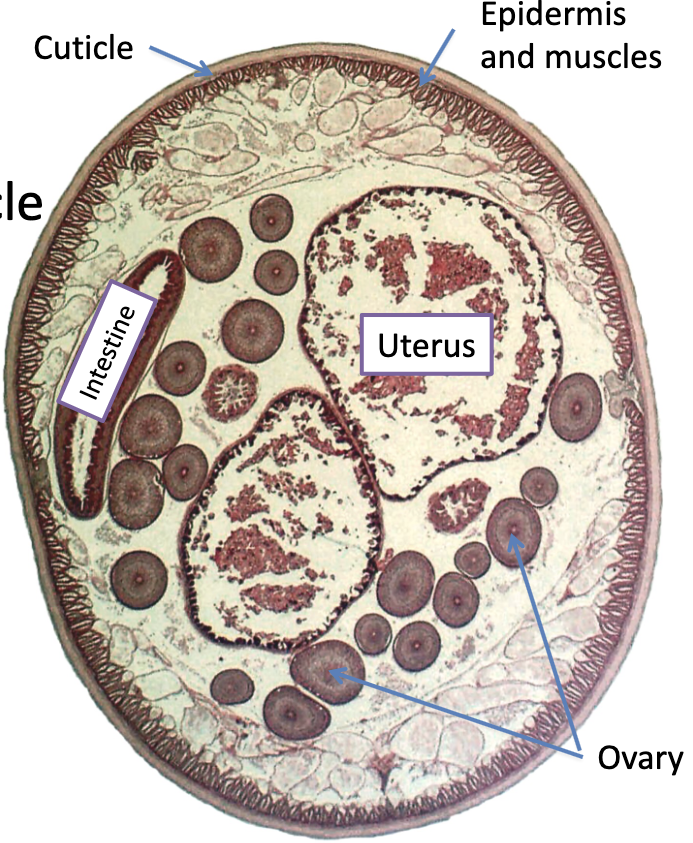
t.s. Ascaris suum
-pig parasite
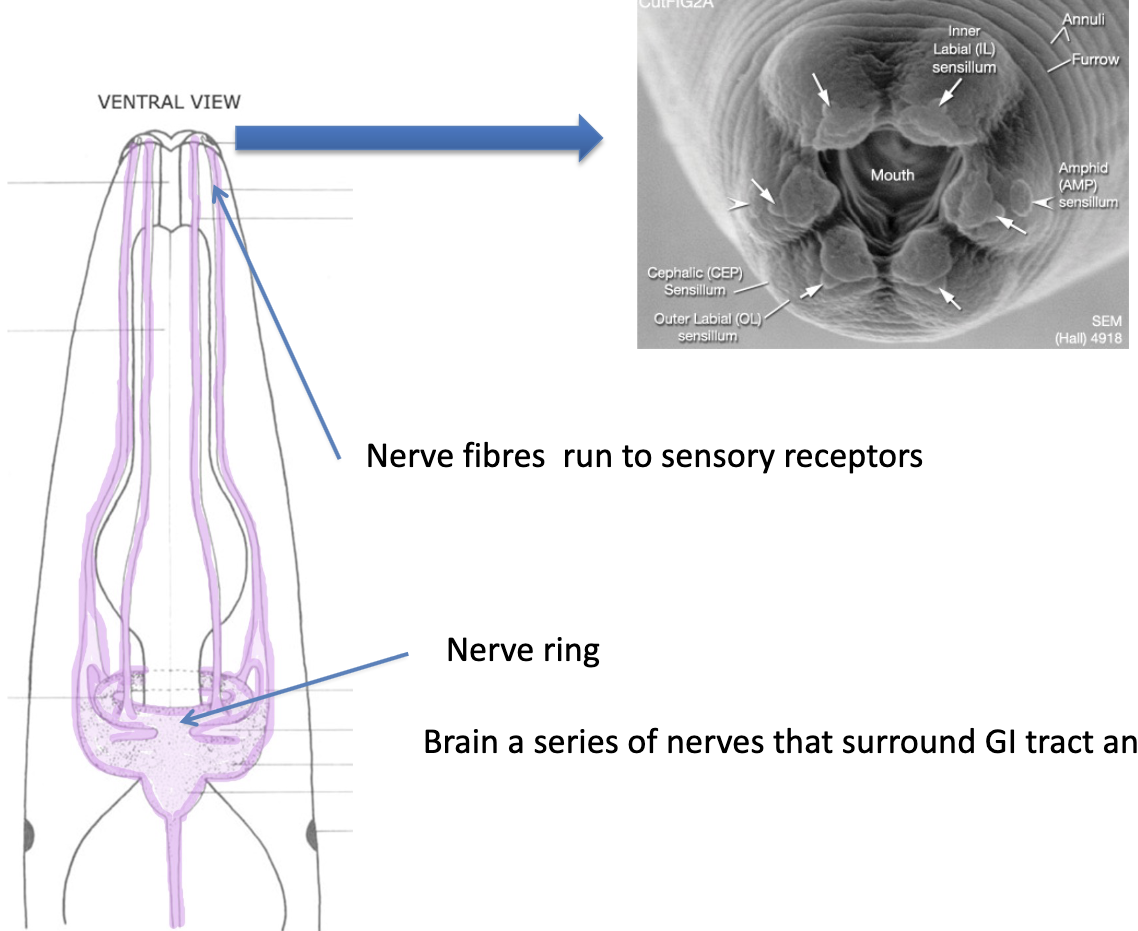
What is important to note about nerve cuticle of nematoda?
-many rings (annuli) but NOT segmented
Nematoda:
brain
-a series of nerves that surround GI tract, anteriorly
Nematoda:
excretory system
-complex
-distinct pore and canals that drain pseudocoelomic cavity
-more osmoregulatory not excretory (remove salts not N)
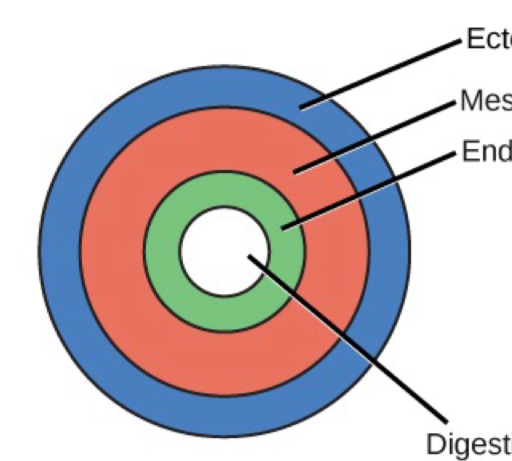
Acoelomate
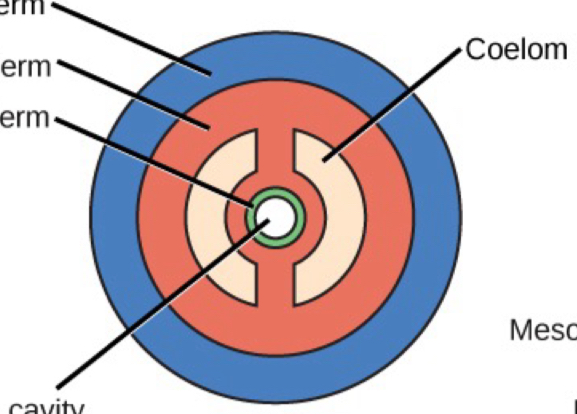
eucoelomate
what groups are acoelomates?
flatworms
what groups are eucoelomates? (5)
-annelids
-mollusks
-arthropods
-echinoderms
-chordates
what groups are pseducoelomates?
-roundworms
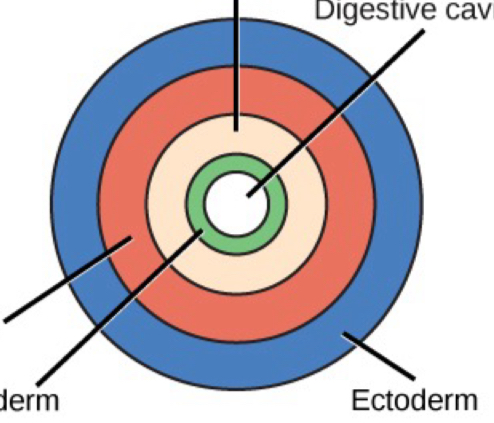
pseudocoelomate
nematodes:
growth (3)
ecdysis
-shed to grow
-molting associated with change in enviro, repro, and/or behavior
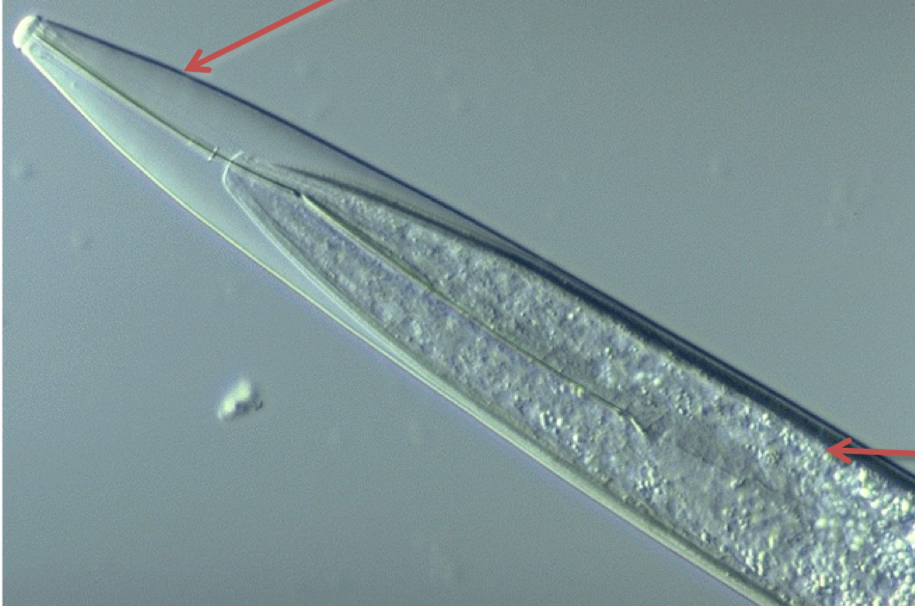
ecdysis
top: old cuticle
inside: new cuticle w worm
nematode:
movement
-muscles attached so to flex body in one plane
-dorsal ventral movement
– Muscles act on exoskeleton
– Serpentine movement
– Move in aquatic, interstitial, or across substrates
Nematodes:
Exoskeleton (3)
– Rigid
– Resilient
– Flexible
nematode:
hydro-skeleton
– High internal P acts to bring body straight
summary:
Caenorhabditis elegans
-model organism
– Free living soil, nematode
– First multi cell organism to have its genome sequenced
- Few cell types
– Short generation time
– 959 somatic cells in adult hermaphrodite
– Ancestry of each cell established
Definition:
Model organism
– Organism chosen by researchers wishing to understand broad biological principles
I.e.. Genetic studies of development, mechanisms involved in aging
summary:
Haemonchus contortus
– Barber’s pole worm red and white stripes)
– Blood feeder
– Major sheep, pathogen, parasite
– Occurs during summer rainfall areas
– Resistant to anthelminthic treatments well entrenched
What is another name for Haemonchus contortus?
Barber’s pole worm
Where do you find Haemonchus contortus?
QLD
Northern NSW
Why is Haemonchus contortus so rampant in South Africa?
Drug resistant strains of parasites
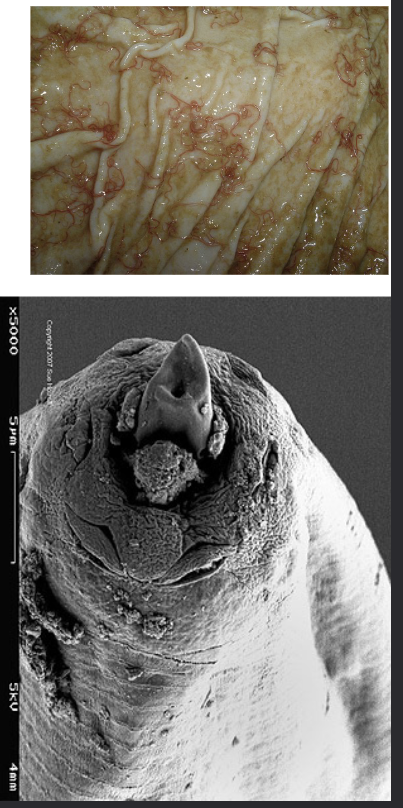
Haemonchus contortus
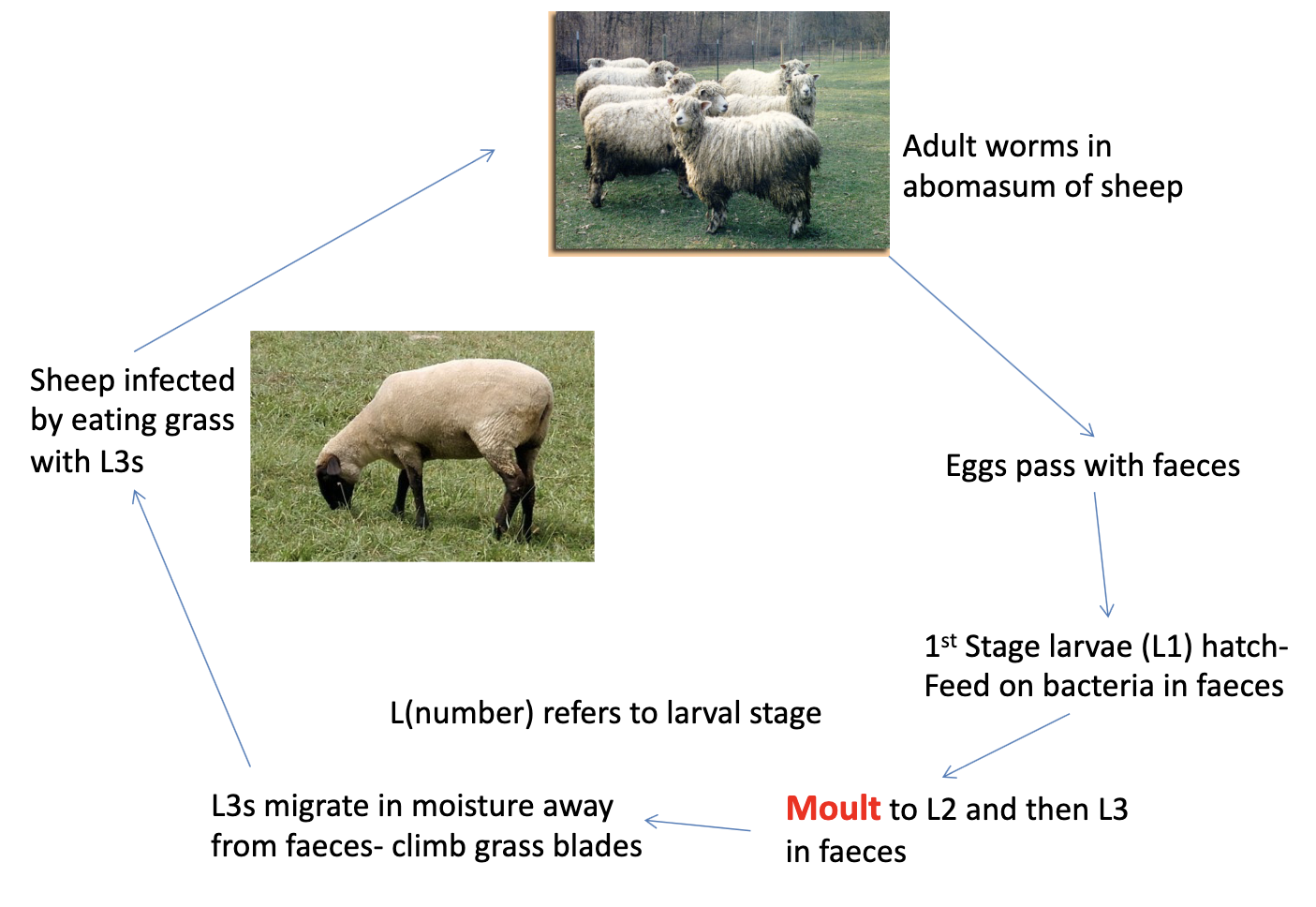
Lifecycle of Haemonchus contortus
Haemonchus contortus:
life cycle
– Adults found in sheep abomasum
-eggs pass through feces
– First larva hatch (L1) feed on bacteria in faeces
– Molt to stage two (L2) then stage three (L3)
– L3s migrate from faeces by climbing grass blades
– Sheep are infected by eating L3 infested grass
hookworms
Human and animal parasite
Name of dog hookworm
Ancylostoma caninum
Name of human hookworm (2)
Necator americanus
Ancylostoma caninum
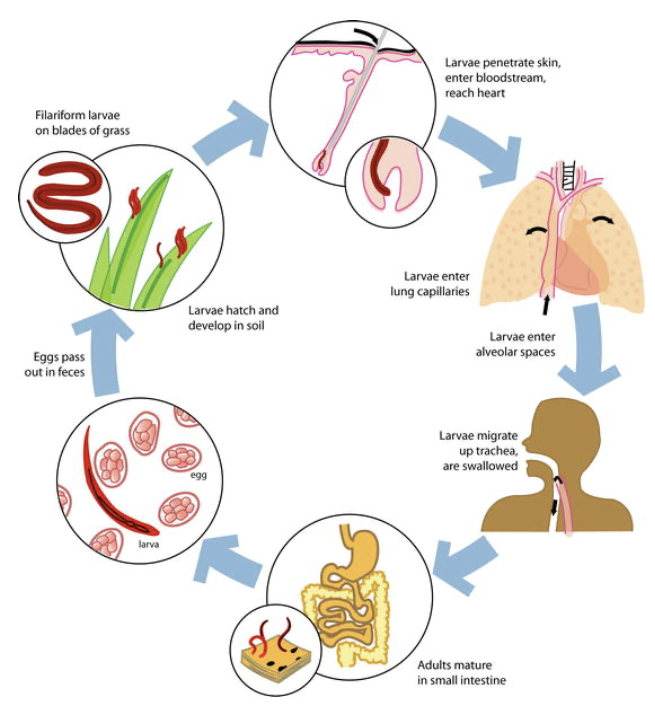
hookworm life cycle
The hookworm will feed in the intestine’s of the host. It will feed on blood and are quite wasteful so if the host has lots of hook worm, it can lead to anaemia. Serious infections of hook worm in children can affect the growth physically and mentally. Hook worm can also cause death in puppies and young animals
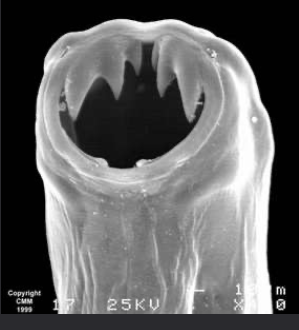
hookworm
ascaris
large intestinal worms (in mammals)
ascarids (2)
-cause disease by occluding intestine and intense migration in host
– Females lay desiccation resistant eggs
name of ascarid found in horses
Parascaris equorum
how long is development of Parascaris equorum?
(horses)
12 weeks
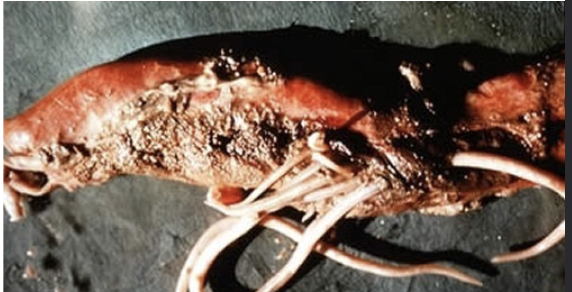
Parascaris equorum
-in small intestine
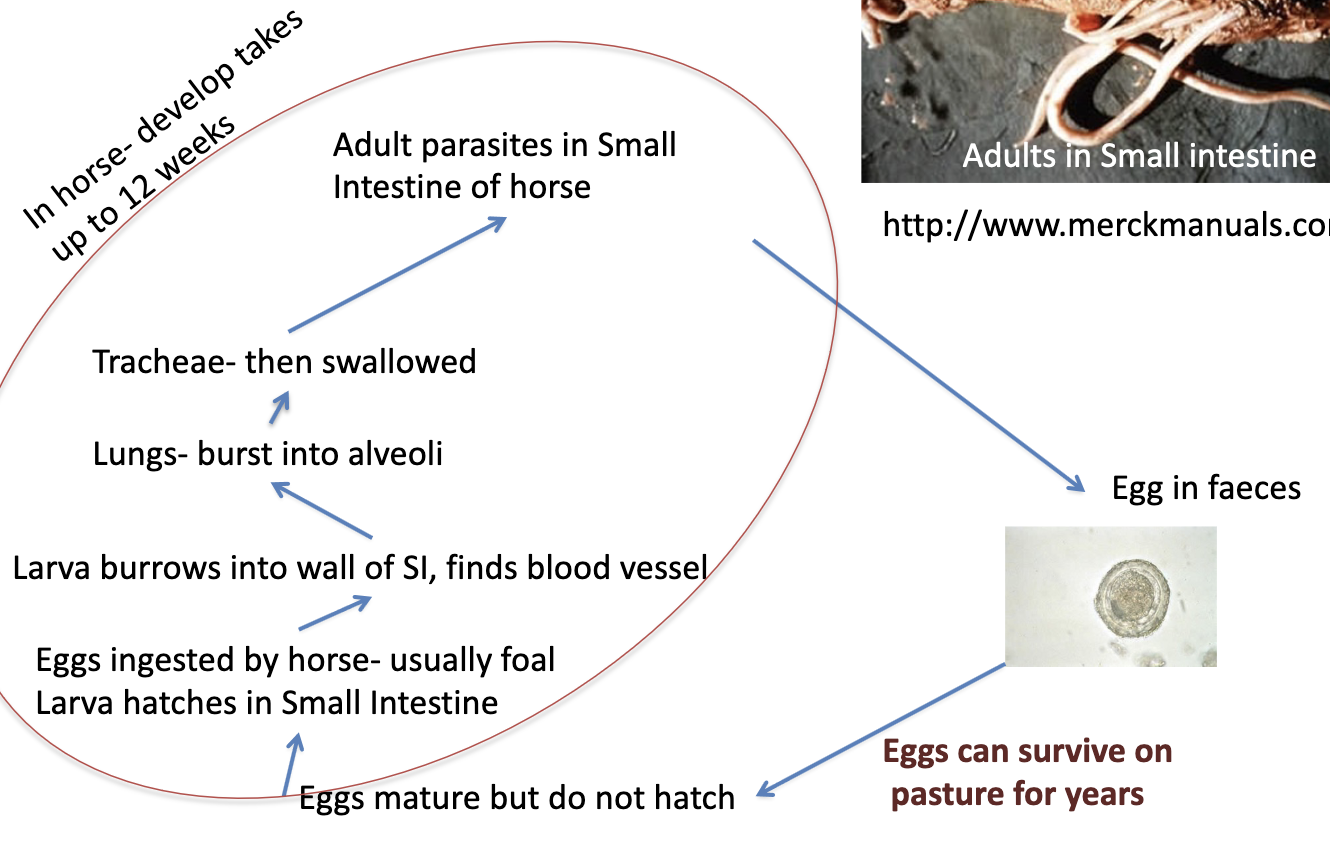
Parascaris equorum lifecycle
the effect of Parascaris on horses (4)
– Lung effects, due to migrating larva; can lead to pneumonia
– Loss of energy
– Colic
– Intestinal perforation or obstruction

Parascaris equorum (in horses)
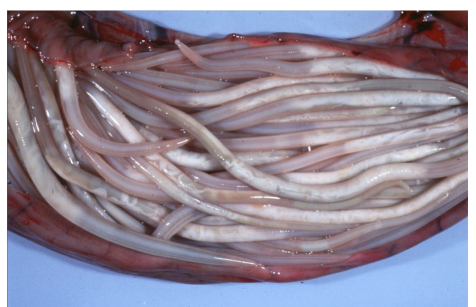
Parascaris equorum (in horses)
Name of dog heartworm
Dirofilaria immitis
Where are the adult heartworms found?
– Right side of heart and pulmonary artery
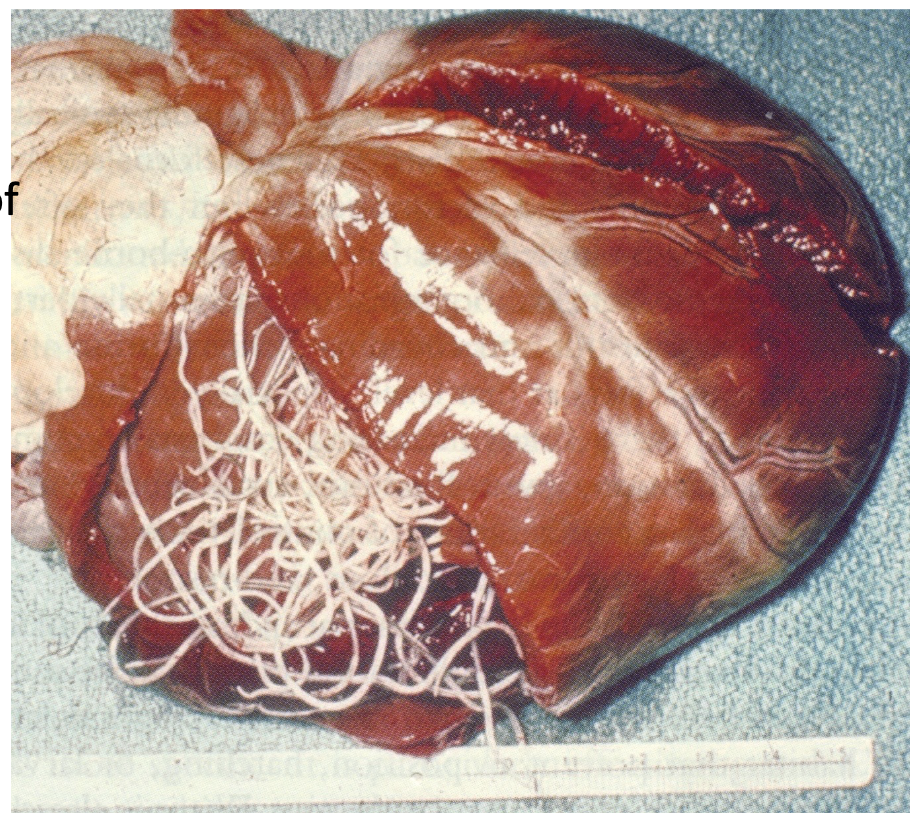
heartworm
Dirofilaria immitis
life cycle of dog heartworm (7)
-adult worms in pulmonary artery produce infective stage (microfilaria)
-L1s still encased in sheath
-microfilaria circulate in blood
-ingested by mosquito
-mosquito vector transmits heartworm with blood meal
-microfilaria develop to L3 (in muscle)
-L3 migrate to salivary gland
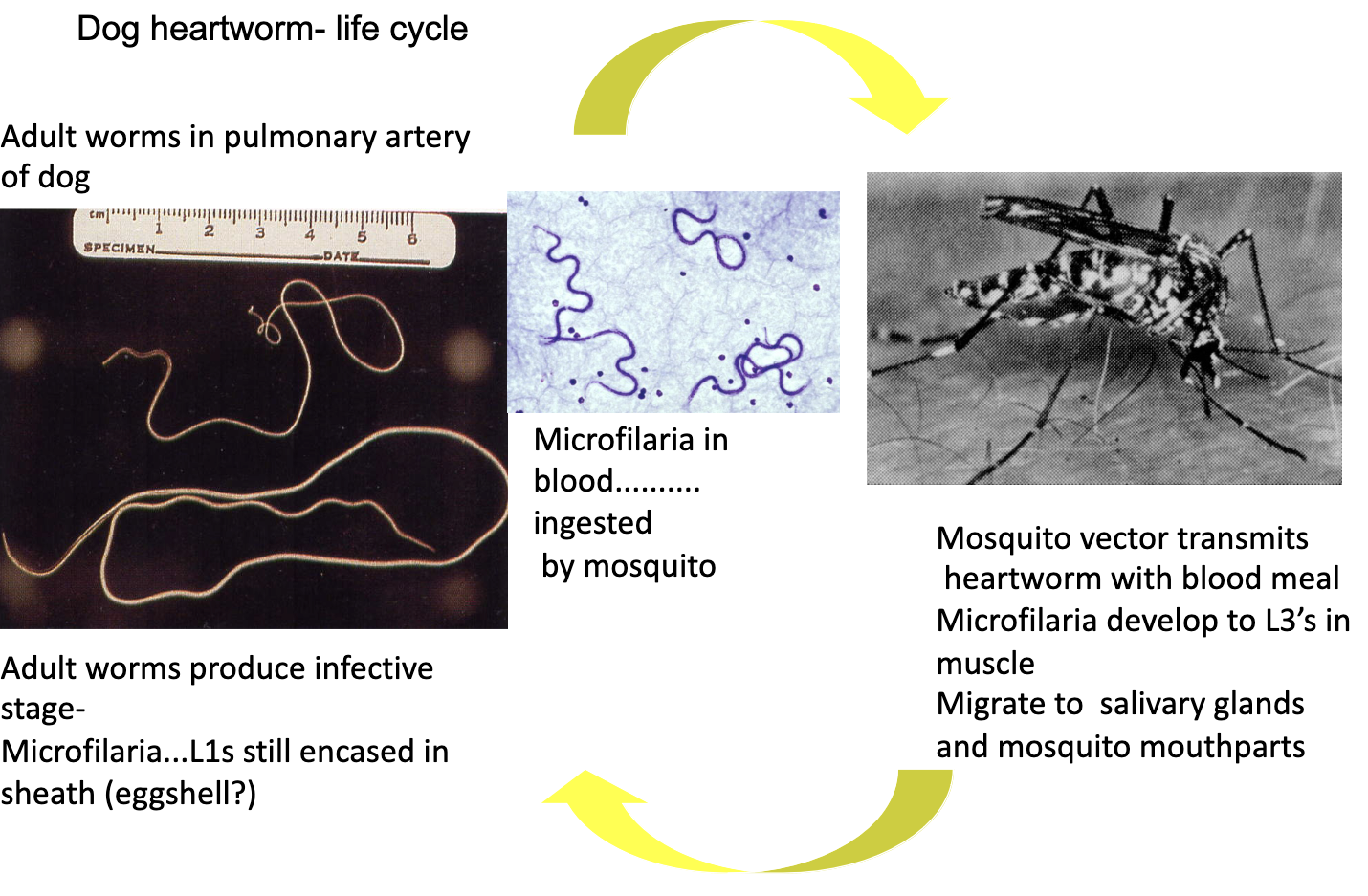
dog heartworm life cycle
Why is dog heartworm becoming more common in Queensland?
It is a vector born disease transmitted by mosquitoes, which are the vector host. It is becoming more common, most likely from the moist conditions.