Physical Feature of India[Introduction and the Himalayan Mountains]
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Which physical feature constitutes one of the ancient landmasses on the Earth’s surface?
Peninsular Plateau
Which 2 physical divisions are the most recent landforms?
The Himalayas and the Northern Plains
What are the major physiographic divisions of India?
The Himalayan Mountains
The Northern Plains
The Peninsular Plateau
The Indian Desserts
The Coastal Plains
The Islands
The Himalayan Mountains[geographically young and structurally fold] are stretch over which borders of India?
Northern
In which direction do Himalayan ranges run?(also mention their extent using rivers)
They run in a west- east direction.[from Indus to Brahmaputra]
Write some common points under the heading: The Himalayan Mountains.
The Himalayas represent loftiest and one of the most rugged mountain barriers of the world.
They form an arc which covers a distance of about 2400km.
Their width varies from 400km in Kashmir to 150km in Arunachal Pradesh.
The altitudinal variations are greater in the eastern half than in the western half.
Himalaya consists of which 3 parallel ranges in its longitudinal extent?(along with their other names)
Himadri or The Great/Inner Himalayas
Himachal or Lesser Himalaya
Shiwaliks
(A number of valleys lie between these ranges.)
What are the key features/characteristics of Himadri?
It is the northernmost range
It is a continuous range loftiest peak with an average height of 6,000 meters.
It contains all prominent Himalayan peaks.
The folds of Himadri are asymmetrical in nature.
The core of this part of Himalayas is composed of granite.
It is perennially snow bound and a number of glaciers descend from this range.

What are the key features/characteristics of Himachal?
It lies in the south of the the Great Himalayas and has the most rugged mountain system.
The ranges are mainly composed of highly compressed and altered rocks.
The altitude varies between 3,700 and 4,500 meters.
Its average width is 50km.
This range consists Pir Panjal range (the longest and most important range), the Dhaula Dhar and the Mahabharat ranges, the famous valley of Kashmir and the Kangra and Kullu Valley in Himachal Pradesh.
This region is well known for its hill stations.

What are the key features/characteristics of Shiwaliks?
It is the outermost range of Himalayas.
They extend over a width of 10-15km and have an altitude varying 900 to 1100 meters.
These ranges are composed of unconsolidated sediments brought down by rivers from the main Himalayan ranges located farther north.
These valleys are covered with thick gravel and alluvium.
The longitudinal valley lying between lesser Himalaya and the Shiwaliks are known as Duns. Dehra Dun, Koti Dun and Patli Dun are some of well-known Duns.

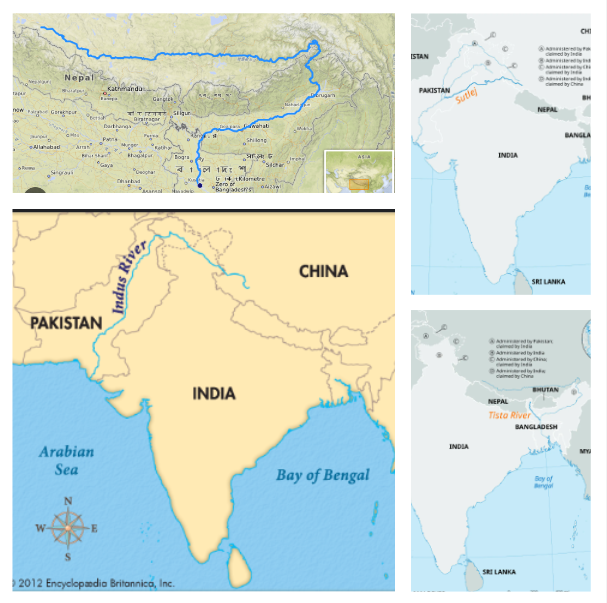
Besides the longitudinal divisions, the Himalayas have been divided on the basis of regions from west to east.[These divisions have been demarcated by river valleys.]
Punjab Himalaya- The part of Himalayas lying between Indus and Satluj. It is also known as Kashmir and Himachal Himalaya from west to east respectively.
The Kumaoan Himalayas- The part of Himalayas lying between Satluj and Kali rivers.
The Nepal Himalayas- Demarcated by Kali and Teesta rivers.
Assam Himalayas- Demarcated by Teesta and Dihang rivers.
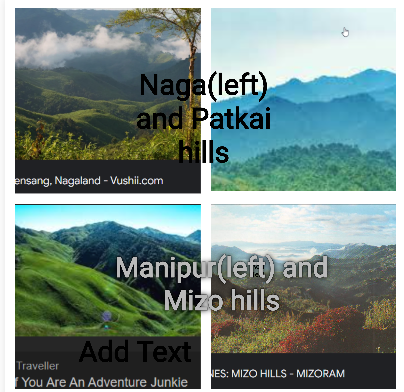
Write a short note on Purvachal.
The Brahmaputra marks the eastern most boundary of the Himalayas.
Beyond the Dihang gorge, the Himalayas bend sharply to the south and spread along the eastern boundary of India. These are known as the Purvachal or the Eastern hills and mountains.
These hills running through the north- eastern states are mostly composed of strong sandstone , which are sedimentary rocks.
Covered with dense forests, they mostly run as parallel ranges and valleys.
The Purvachal comprises the Patkai hills, the Naga hills, the Manipur hills and the Mizo hills.