2. BIO 110 LO2: Chemistry of Life
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
What are the three subatomic particles found within atoms?
Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons.
What are the two main organizational components of an atom?
The Nucleus (central core) and Energy levels (orbitals) (regions surrounding the nucleus).
What are the defining characteristics of a Proton?
A positively charged particle located in the nucleus.
What are the defining characteristics of a Neutron?
A neutral particle located in the nucleus.
What is the Atomic number?
The total number of protons in the nucleus; this determines the type of atom.
What is the atomic mass?
Number of protons and neutrons combined
What is the negatively charged particle in an atom?
An Electron.
How many electrons can the energy level closest to the nucleus contain?
Up to two electrons.
How many electrons can the remaining energy levels contain?
Up to eight electrons.
How does energy relate to the distance of an energy level from the nucleus?
Energy increases with distance from the nucleus.
Define an Element.
A pure substance; made up of only one kind of atom (e.g., oxygen is O2).
Define a Molecule.
A group of atoms bound together to form a larger chemical unit (e.g., H2O).
Define a Compound.
Substances whose molecules have more than one kind of element (e.g., CO2; NaCl).
What does the chemical formula determine?
determines atoms present in a compound
What are the four most abundant elements in living organisms, accounting for 96%?
Oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen.
Why do chemical bonds form?
To make atoms more stable.
What characteristic makes an atom chemically stable and unlikely to form a bond?
Having a full outer shell.
What are the two main types of chemical bonds discussed?
Ionic and covalent.
Describe the formation of an Ionic Bond.
They form between an atom that has 1 or 2 electrons in its outermost level (which donates them) and an atom that needs 1 or 2 electrons to fill its outermost level (which borrows them).
What is an Ion?
An atom or group of atoms with an electrical charge (e.g., positive or negative)
How is a Positive ion formed?
By having lost electrons.
How is a Negative ion formed?
By having gained electrons.
How do ionic bonds ultimately form between ions?
When positive and negative ions attract each other because of electrical attraction.
Define an Electrolyte.
A molecule that dissociates, or breaks apart, in water to form individual ions; an ionic compound (e.g., Na+)
How do Covalent bonds form?
When atoms fill their energy levels by sharing electrons to become stable.
Why are covalent bonds generally not easily broken or dissociated in water?
Because the atoms must stay close to each other in order to share electrons.
What is the function of a Hydrogen Bond?
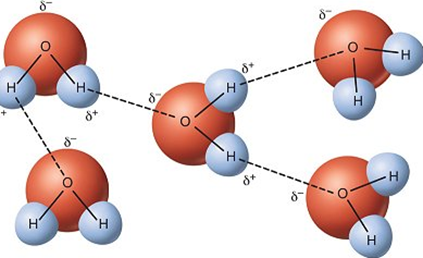
To provide subtle forces that help to keep larger molecules in a certain configuration (e.g., H2O).
Which of the bonds is a weak force holding molecules in folded shapes or in groups?
Hydrogen bonds
What defining characteristics must Organic compounds possess?
They must contain carbon–carbon covalent bonds and/or carbon–hydrogen covalent bonds.
What is the definition of Inorganic compounds?
Compounds that do not contain carbon–carbon covalent bonds and/or carbon–hydrogen covalent bonds.
List three examples of inorganic molecules.
Water, some acids, bases, and salts.
Which molecules usually dissolve in water and dissociate (break apart) to form free ions (electrically charged)
Ionic molecules
When discussing water, what is a Solvent?
A liquid into which solutes are dissolved, that forms aqueous solutions in the body.
Define the chemical reaction Dehydration synthesis.
Water is removed from small molecules so they can be strung together to form a larger molecule.
Define the chemical reaction Hydrolysis.
Water is added to the subunits of a large molecule to break it apart into smaller molecules.
What always accompanies chemical reactions?
Energy transfers.
In pure water, what is the balance of H
(hydrogen ion) and OH– (hydroxide ion)?
Define an Acid.
A substance that shifts the H
Define a Base (also known as an alkaline).
A substance that shifts the H
What is pH (Potential of Hydrogen)?
A mathematical expression/unit of measurement used to express the H
What pH value is considered neutral?
7.
What range of pH values indicates a basic solution?
7.
What range of pH values indicates an acidic solution?
What occurs during Neutralization?
‘Strong’ acids and ‘strong’ bases mix and form salts and water.
What are Buffers, and what is their function related to pH?
They are chemical systems that absorb excess acids or bases and thus maintain a relatively stable pH (homeostasis).
What are the four major groups of organic compounds in the body?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids.
What are the six-carbon subunits of carbohydrates called?
Monosaccharides or single sugars (e.g., glucose).
Give an example of a Disaccharide and the two monosaccharides it is made of.
Sucrose (glucose
fructose), Maltose (glucose
glucose), or Lactose (glucose
galactose).
What is a Polysaccharide?
A complex carbohydrate made up of many monosaccharide units (e.g., glycogen made up of many glucose units).
What is the primary function of carbohydrates in the body?
To provide the body with ENERGY.
What is the difference between fats and oils?
Fats are solid at room temperature, while oils are liquid at room temperature.
What three components make up a Triglyceride?
1 glycerol unit and 3 fatty acids.
What three components make up a Phospholipid?
1 glycerol, 2 fatty acids, and 1 phosphorus-containing group.
In a phospholipid, which part is hydrophilic and which is hydrophobic?
The head of the phosphorous-containing group is hydrophilic while the double tail is hydrophobic.
Why are phospholipids important parts of cell membranes?
They form stable double layers (bilayers) in water.
What is the core structure of Cholesterol?
A steroid structure consisting of 20 carbons bonded together that take the form of 4 fused rings.
What is one function of cholesterol within cell membranes?
It stabilizes the phospholipid tails in cellular membranes.
What type of organic compounds are proteins?
Very large molecules made up of amino acids held together in long, folded chains by peptide bonds.
In addition to carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, what other element do proteins contain?
Nitrogen (N).
What primarily determines a protein's role?
Its complex 3-D shape.
Give an example of a Structural Protein and its role.
Collagen (holds many tissues together) or Keratin (forms tough waterproof fibers in the outer layer of the skin).
Give three examples of Functional Proteins.
Hormones, cell membrane channels and receptors, and enzymes.
What are Enzymes?
Chemical catalysts that help chemical reactions occur.
What factors are required for proper enzyme action?
Optimal temperature and pH.
According to the lock-and-key model, how does an enzyme function?
Each enzyme fits a particular molecule that it acts on, in the same way as only one key fits a lock.
What three components make up a nucleotide unit (the building block of nucleic acids)?
Sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), Phosphate, and Nitrogen bases.
What is the primary role of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)?
Used as the cell’s “master code” for assembling proteins.
What structure does DNA form?
A double helix.
What is the primary role of RNA (ribonucleic acid)?
Used as a temporary “working copy” of a gene (a portion of the DNA code).
By directing the formation of structural and functional proteins, what do nucleic acids ultimately direct?
Overall body structure and function