Systems Lecture 4: Vaporizers and Agents
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
What is a vaporizer?
a delivery device for anesthetic agents that adds a controlled amount of vapor to breathing system FGF
1mL of liquid anesthetic agent can be converted into how much anesthetic vapor?
~200mL
Anesthetic Gases work in what division of the nervous system?
the CNS
Potency of general anesthetics correlate with their...? Indicating the importance of?
solubility in oil; interaction with hydrophobic targets
Anesthetics enhance and suppress which types of signals
enhance inhibitory signals
suppress excitatory signals
Yellow vaporizer is which drug?
Sevoflurane (Ultane)
Purple vaporizer is which drug?
Isoflurane (Forane)
Blue Vaporizer is which drug?
Desflurane (suprane)
How many vaporizers can be used simultaneously?
only one can be used at a time
Myer Overton Rule
Higher lipid solubility = Higher potency
What was morton's vaporizer made of?
sponge soaked in ether
A drug that is slow to induction will be fast or slow during emergence?
slow induction drug = slow emergence
higher lipid solubility = _____ potency
higher potency
MAC stands for
minimum alveolar concentration
What is MAC?
Alveolar concentration that prevents movement in 50% of patients in response to noxious stimuli
Gas with a lower MAC correlates with...
higher potency
What can impact MAC values? (3)
age
temperature
acute intoxication
FGF is determined by... (2)
vaporizer and flowmeter settings
Fi stands for
inspired gas concentration
What 3 things affect Fi?
- FGF
- Breathing circuit volume
- Circuit absorption
FGF + induction/recovery Time
higher FGF, faster induction/recovery time
Circuit Absorption + induction/recovery Time
Lower Circuit Absorption, faster induction/recovery times
Breathing system volume+ induction/recovery Time
Smaller Breathing system, faster induction and recovery time
FA stands for
alveolar gas concentration
What affects FA?
Uptake
Ventilation
Concentration Effect
Second Gas Effect
Fa stands for
arterial gas concentration
What affects Fa?
v/q mismatching
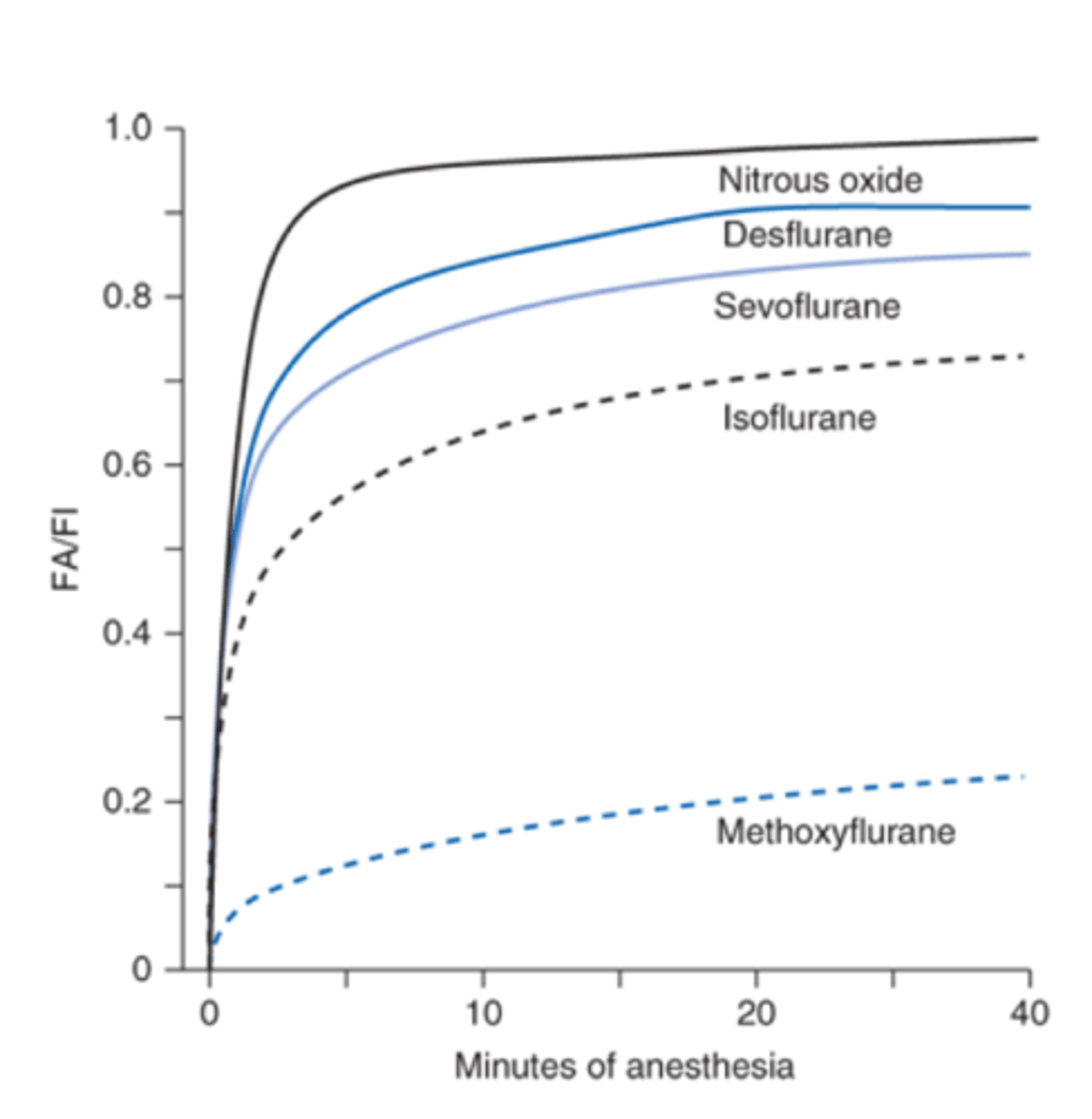
What can FA/Fi represent?
How fast you go to sleep and wake up
What is uptake?
gas molecules taken up from alveoli into pulmonary circulation
Uptake of gas is dependent on (3)
- solubility of gas
- cardiac output
- Alveolar-Venous partial pressure difference
Circulatory uptake and FA
greater circulatory uptake = slower rise in FA
cardiac output and induction speed
lower cardiac output, higher induction speed
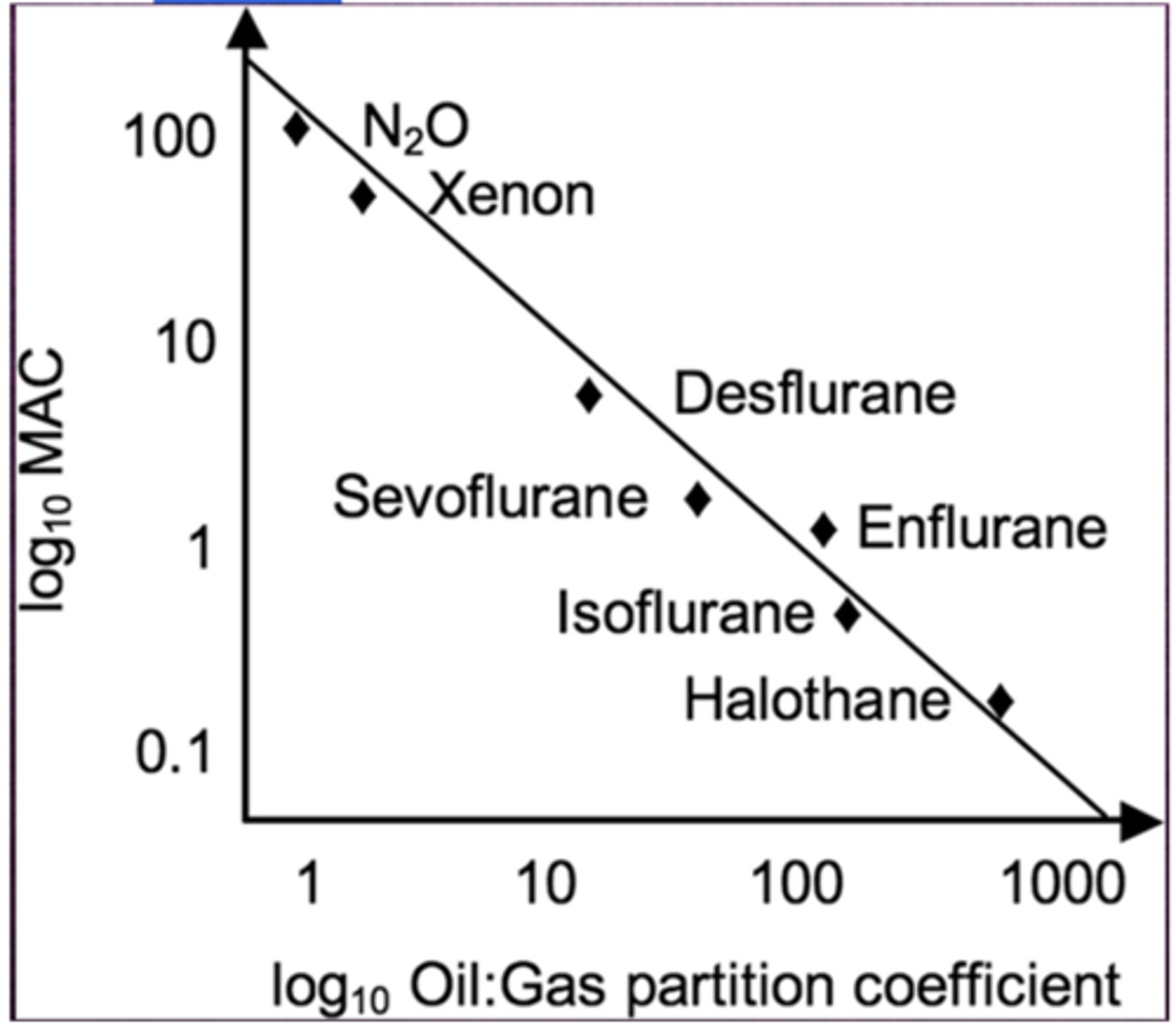
what does the partition coefficient express?
solubility in blood, air, and tissues
Partition coefficient meaning
Ration of concentrations of gas in each of 2 phases at steady state
Blood Gas Partition coefficient of N2O
0.47
N2O's blood gas partition coefficient of .47 indicates
at steady state, 1mL of blood contains .47 as much N2O as does 1mL of alveolar gas
Low Solubility + Flow into Blood
Slower flow into blood, faster increase in alveolar concentration
High Solubility + Flow into blood
higher solubility, alveolar partial pressure rises more slowly, and thus induction prolonged
Gases take the longest time to get into what type of tissue?
fat
Low solubility and speed into the blood
Fastest into and out of the blood
Blood/gas partition coefficient: Desflurane
0.42
Blood/gas partition coefficient: Sevoflurane
0.65
Blood/gas partition coefficient: Isoflurane
1.4
MAC of Desflurane
6%
MAC of Sevo
2%
MAC of iso
1.15%
MAC of N2O
105%
Higher solubility and alveolar partial pressure
Alveolar partial pressure rises more slowly
High Cardiac Output and Anesthetic Uptake
as cardiac output increases, anesthetic uptake increases, rise in alveolar pressure will be slow and induction is delayed
Lower Cardiac Output and Anesthetic Uptake
as cardiac output decreases, anesthetic uptake decreases -> rise in alveolar pressure will be faster and so will induction
High blood flow and FA/Fi ratio
High blood flow through lungs, more blood removing anesthetic, lower FA/Fi ratio
Transfer of anesthetic blood to tissues is dependent on which (3) factors
- tissue solubility
- tissue blood flow
- difference in partial pressure between arterial blood and tissue itself
Which types of organs are the first to take up a significant amount of anesthetic?
vessel rich organs
Vessel rich organ examples
Brain, heart, kidney, liver, endocrine
Which types of organs are next in uptake? Why?
Muscles; not as well perfused
What is next in rate of uptake? why?
fat; very soluble
What is slowest in rate of uptake?
vessel poor (ligaments, bones, teeth, hair, cartilage), insignificant uptake
What 3 things affect uptake?
Solubility of gas, cardiac output, alveolar-venous partial pressure difference
The greater the anesthesia uptake, the _____ the rise in FA and the _____ induction
slower; slower
Do you increase or decrease ventilation in order to speed up induction? why?
increase; constantly replacing anesthetic taken up by the bloodstream, better maintaining the alveolar concentration
increasing ventilation to speed up ventilation is much more profound in...
soluble agents
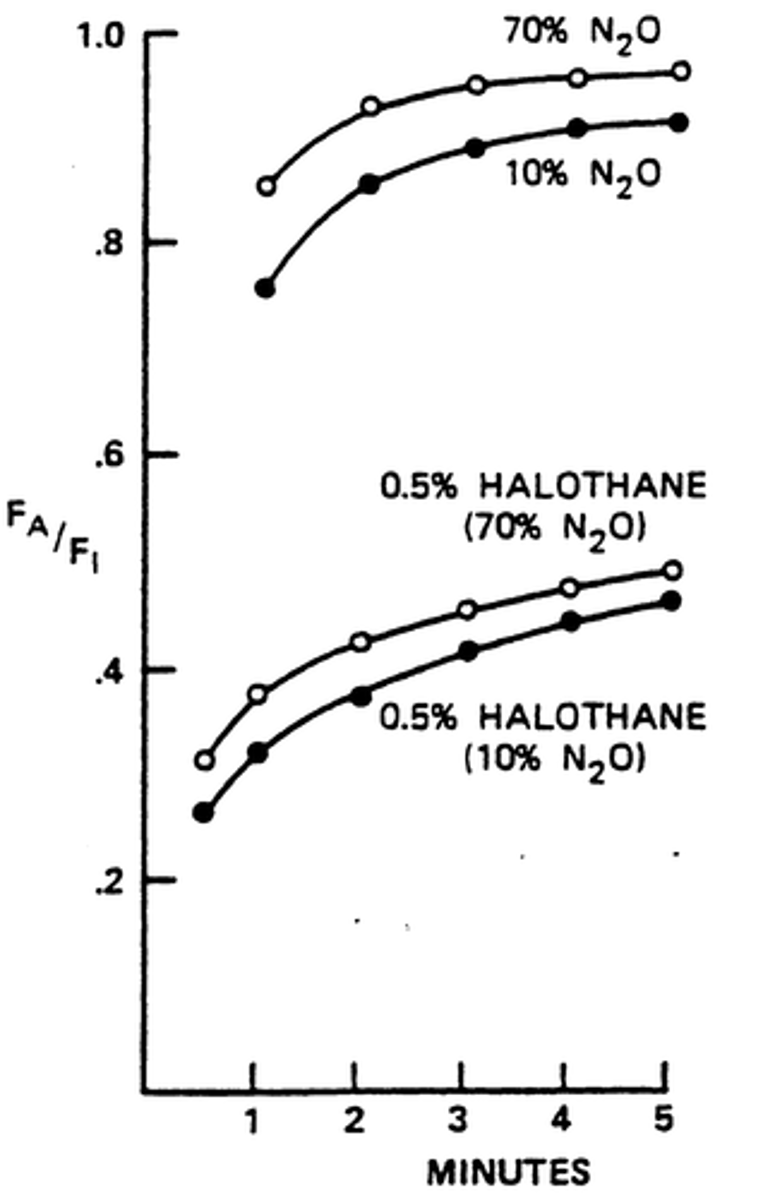
Concentration Effect
Increasing concentration of gas increases rate of rise and alveolar concentration itself
Second Gas Effect
large volume uptake of one gas increases the concentration of the second gas
What is boiling point?
temp where liquids vapor pressure is equal to barometric pressure
Lower Barometric Pressure = ______ BP
lower boiling point
What is vapor pressure?
partial pressure of agent in vapor phase
Temperature and Its Relationship to vapor pressure
as temperature increases, so does vapor pressure
vapor pressure of isoflurane
238 torr
vapor pressure of desflurane
669 torr
vapor pressure of sevoflurane
157 torr
Mac of Halothane
0.75
Mac of Isoflurane
Fractional concentration of agent at outlet of vaporizer formula
(QV x PA) / ((PB - PA) x QT)

Specific Heat
heat (calories) required to raise temp of 1 gram of agent by 1 degree celsius
Specific heat determines what in reference to vaporizers?
the material that the vaporizer is made out of
What materials are vaporizers typically made out of?
copper, bronze bc of high thermal conductivity
What is thermal conductivity?
measure of speed at which heat flows through a substance
Heat of vapor
amount of heat (calories) required to convert 1 gram of liquid agent into a vapor
As you begin to heat up liquid agent into a vapor, what will happen to the remaining liquid?
temperature of remaining liquid will drop, lowering vapor pressure
What color is Halothane
red
What color is enflurane
orange
What kind of filling error would result in higher concentration delivered?
putting an agent with higher vapor pressure into a vaporizer intended for a lower vapor pressure
What kind of filling error would result in a lower concentration delivered?
putting an agent with a lower vapor pressure into vaporizer intended for higher vapor pressure
What is variable bypass?
As concentration is increased, more of the gas flow is diverted into vaporizing chamber. This gas then re-meets with FGF downstream
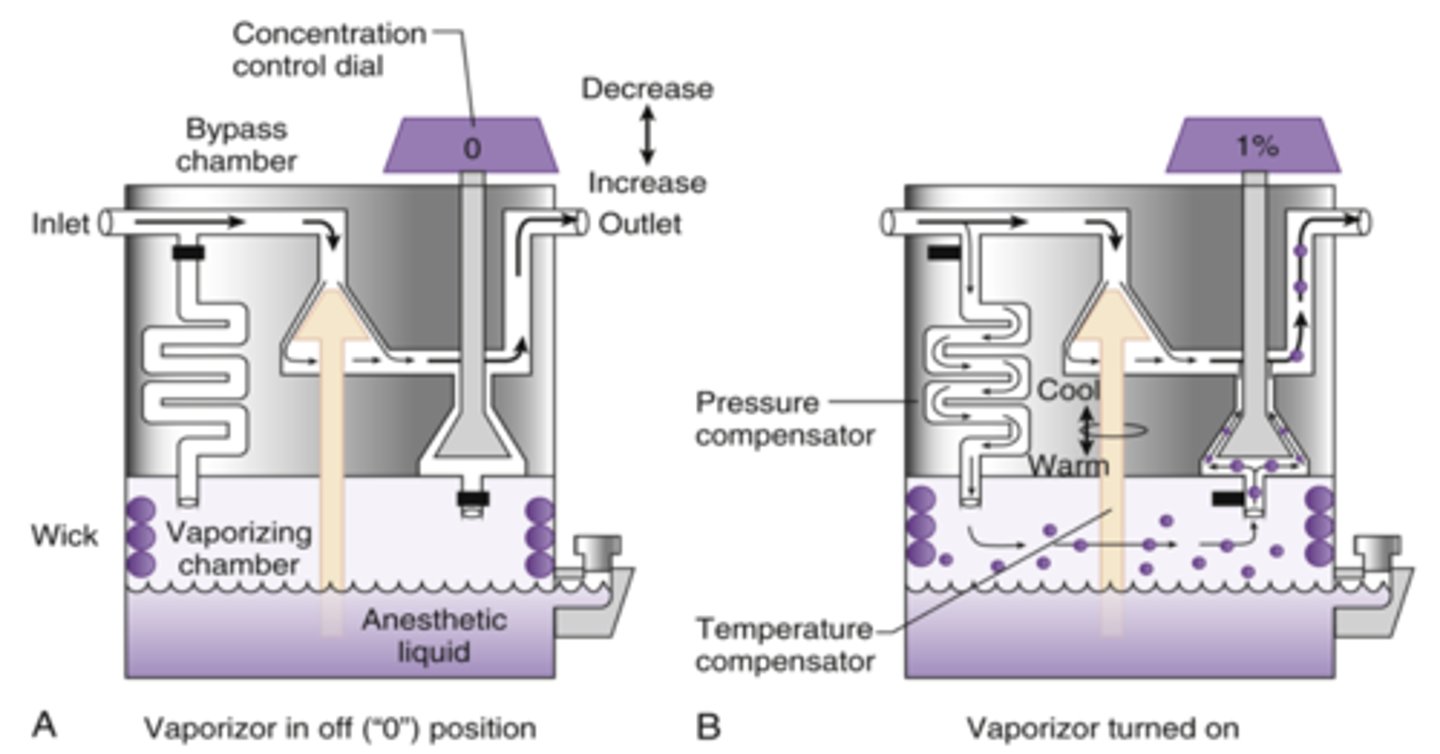
What is the splitting ratio?
ratio of bypass gas to gas going through vaporizing chamber
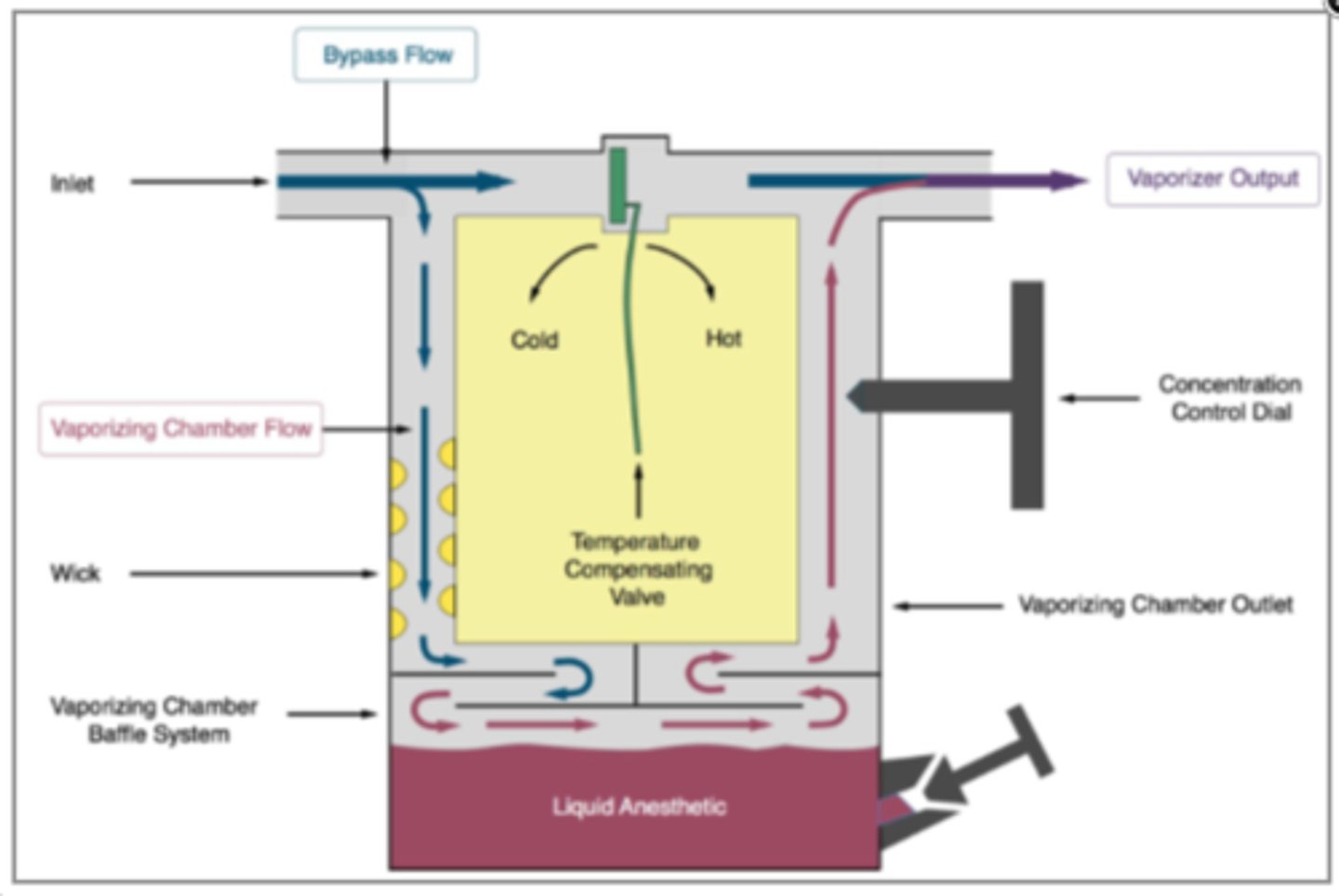
Why do vaporizers have to do Temperature Compensation?
◦As liquid is vaporized, energy in form of heat is lost
◦As temp of liquid decreases, so does its vapor pressure
◦Must maintain a constant vapor output during times of fluctuation in liquid anesthetic temp
Mechanical thermocompensation
◦Alters splitting ratio - increase or decrease flow of carrier gas that is directed to vaporizing chamber
Mechanical thermocompensation: If temperature decreases: what happens to flow of gas?
◦If temp decreases, more gas is allowed to pass thru vaporizing chamber
Mechanical thermocompensation: If temperature increases, what happens to flow of gas?
◦If temp increases, restricts more gas to pass thru vaporizing chamber
How many flow streams in the Tec-4 vaporizer?
2
How many wicks line the outlet in a ten-4 vaporizer? why?
2; to keep gas in contact with liquid agent
Tec-6 Vaporizers always contains
DES
Desflurane Vaporizer: Unique qualities
- plugs in
- will turn off if tilted past 10 degrees
- maintains agent vapor and fresh gas at same pressure when mixed
Which vaporizers can you fill in the middle of case?
You CAN refill DES
You CANNOT refill Sevo/Iso
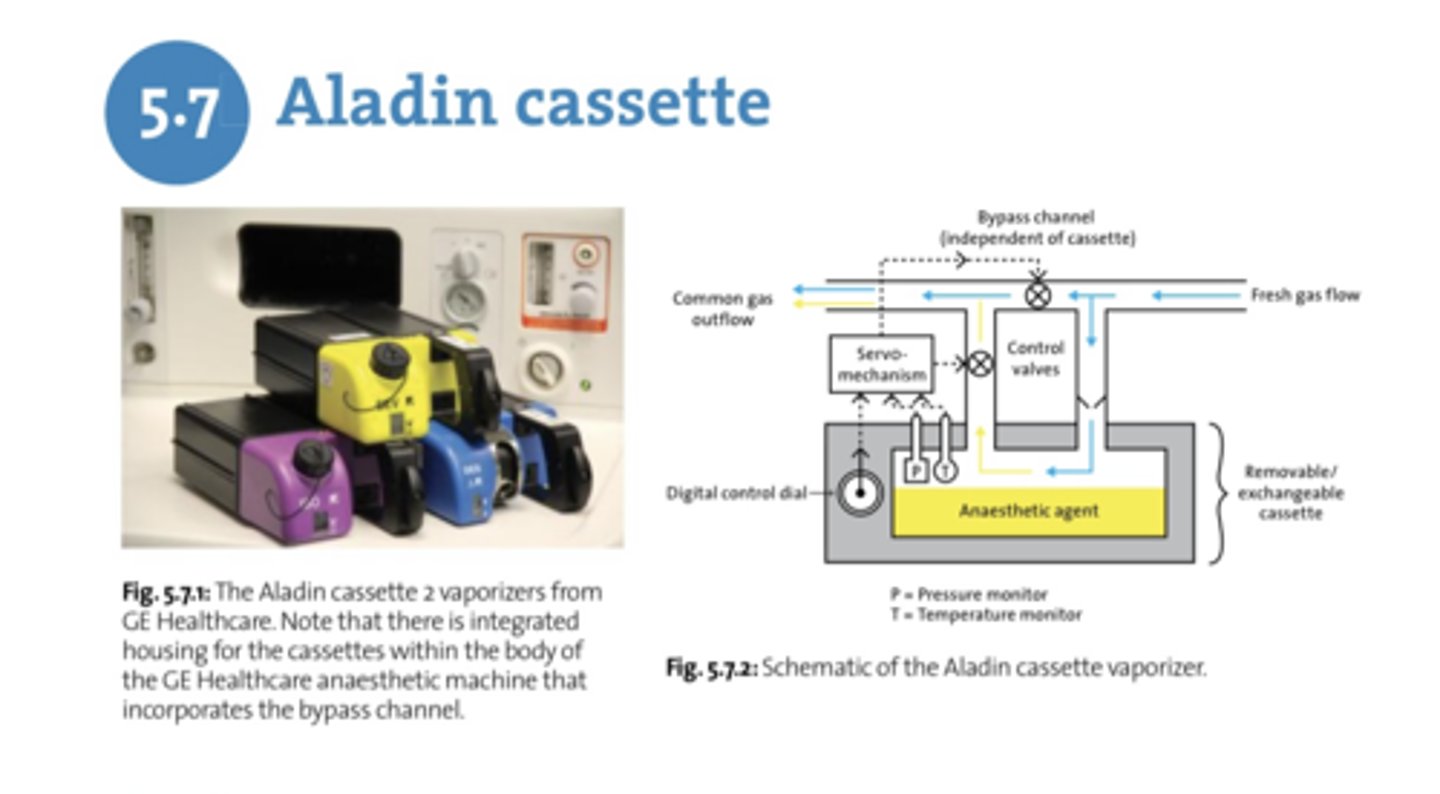
What is unique about the aladin cassette?
can be flipped upside down, sideways, etc. without any problems
Why does an aladin cassette have no problem with tilting or gas escaping during handling?
No bypass flow channels
How many cassettes does the machine accept at a time?
1
What helps adjust the amount of FGF into the vaporizer in an aladin cassette?
Flow restricter valve
Best practice when filling cassette vaporizers
Push both inlet and outlet valves at the same time to depressurize before filling to the line
What allows gas to flow into the cassette vaporizer?
Pins in the back