yay more bio review (its 2 am.)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
First division of meiosis
Chromosome number is cut in half because matching chromosomes separate
Prophase I events
Chromosomes pair up and swap DNA pieces called crossing over
Cause of nondisjunction
Homologous chromosomes fail to separate in anaphase I
Meiosis only process
Homologous chromosomes move to opposite sides of the cell
Meiosis in male animals
Four gametes are made each with the same number of chromosomes
Always passed in sexual reproduction
A haploid set of chromosomes from the mother
Chromatid relationship
Chiasmata form between non sister chromatids
Shared feature of meiosis and mitosis
Chromatids separate in both processes
Tetrad chromosome count
If a tetrad has 48 chromosomes then diploid number is 24
Meiosis II unique event
Sister chromatids move to opposite poles
Independent assortment meaning
Homologous chromosome pairs line up randomly in metaphase I which creates variation
Meiosis vs mitosis summary
Meiosis makes four unique haploid cells for reproduction with crossing over and random assortment / mitosis makes two identical diploid cells for growth and repair
Importance of meiosis in evolution
Creates variation so some traits help survival and can be selected
Process not in stroma
Reduction of NADP does not happen in the stroma
ATP role in photosynthesis
ATP moves energy from light reactions to Calvin cycle
Chlorophyll location
Found in the thylakoid membrane
Light dependent reaction result
ATP and oxygen are made
ATP production in PSII
Light excites electrons / electrons move through ETC / water replaces electrons / protons build up / ATP synthase makes ATP
Light reactions support Calvin cycle
ATP gives energy and NADPH gives electrons to make sugar
Mitochondria and chloroplast similarities
Both have double membranes and folded inner membranes
Mitochondria vs chloroplast function
Mitochondria break down food to make ATP / chloroplasts use light to make glucose
Photolysis
Water is split to replace electrons and oxygen is released
Light as limiting factor
Low light means fewer excited electrons so less ATP and NADPH
Temperature as limiting factor
Low temperature slows enzymes / high temperature denatures enzymes
Round green seed prediction
About 101 round green seeds are expected
DNA methylation reset reason
Allows early development genes to turn on
Recombinant guinea pig genotypes
rrDd and Rrdd are recombinant types
Linked gene gametes
All four gamete types are produced equally
Morgan fly experiment conclusion
Red eye allele is dominant
Cause of continuous variation
Traits controlled by many genes
Blood group parent genotypes
Parents are IAi and IBi
Allele definition
Different forms of a gene with small base changes
Wolf recombinant phenotypes
Black coat with brown eyes and black coat with yellow green eyes
Inheritance test method
Chi squared test compares expected and observed results
Observed vs expected fly ratios
More rare combinations appeared than expected
Mesocosm advantage
Allows controlled study in near natural conditions
Sweet pea F1 genotype
CcRr
9 to 7 ratio explanation
Complementary genes both needed for purple color
Cross outcome prediction
CcRr and ccRr offspring are expected
Twin methylation differences
Caused by different environments and experiences
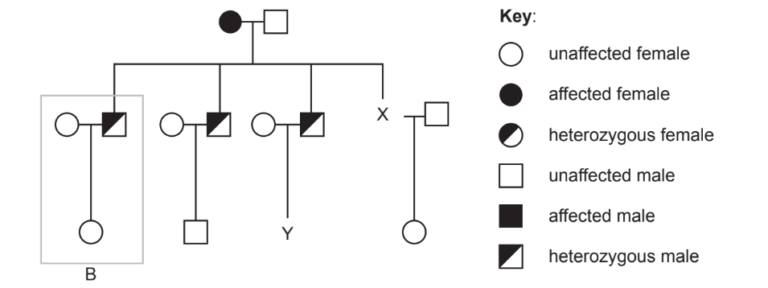
Thrombophilia probability based on pedigree chart
There is a fifty percent chance
Not sex linked evidence
Males can carry the allele
Polyploid speciation evidence
Polyploid plants can breed with each other
Hardy Weinberg assumption
Population must be large
Dog domestication type
Artificial selection by humans
Wolf mating isolation
Behavioral isolation even though offspring are possible
Peppered moth change cause
Less pollution helped light moths survive
Quill similarity reason
Same environment caused similar traits
Natural selection result
Some traits become less common
Bat and insect wings
Analogous structures with same function
Closest elephant relative
Mammoth
Elephant evolution type
Divergent evolution
Finch beak development
Different diets favored different beak shapes
Hybridization barriers
Prezygotic and postzygotic barriers prevent fertile offspring
Virus envelope origin
Membrane comes from host cell
Virus cell origin evidence
Shared enzymes and genetic material suggest common origin
Lytic vs lysogenic difference
Lysogenic inserts viral DNA into host DNA
Virus structure X
Capsid
Virus structure feature
Has genetic material and a protein coat
Disease from animals
Zoonosis
Why viruses are not living
They cannot metabolize or reproduce alone
Lysogenic reproduction
Viral DNA joins host DNA and copies with it
Viral vector use
Virus inserts new gene into host DNA
Virus and cell similarity
Both contain genetic material