(Unit 2) Early childhood & Middle Childhood
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
At what age is BMI the lowest than any other time in life?
5-6 years old
What age is considered “early childhood”?
2-6 years old
Each year of early childhood children can be expected to grow…?
•3 inches
•4 ½ pounds per year
By age 6 children should be…?
•3 ½ feet tall
•40-50 pounds
•Lean not chubby
When is the best time to prevent childhood obesity?
Early childhood
As family income decreases, what can be expected to increase?
Malnutrition and obesity
At age 2, the brain weighs what percentage of an adult brain?
75%
At age 6, the brain weighs what percentage of an adult brain?
90%
Define myelination
The process by which axons become coded with myelin, a fatty substance that speeds the transmission of nerve impulses from neuron to neuron.
As prefrontal cortex develops, _____ also develops
Social understanding
As the prefrontal cortex matures…
•Sleep becomes more regular
•Emotions become more nuanced and responsive
•Temper tantrums subside
•Uncontrollable laughter and tears are less common
Which half of the brain is responsible for logical reasoning, detailed analysis, and basics of language?
The left half
Which half of the brain is responsible for emotional and creative impulses, art, music, and poetry?
The right half
Define corpus callosum
A long, thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain and allows communication between them.
Define impulse control
The ability to postpone or deny the immediate response to an idea or behavior.
Define perseveration
To stay stuck, or persevere, in one thought or action for a long time. The ability to be flexible, switching from one task to another is beyond most young children.
What 2 impulses do neurons have?
On/Off or Activate/Inhibit
What does lack of impulse control signify in adulthood?
Personality disorder
Some stress on the brain aids in _____?
Cognition
How does the brain protect itself from too much stress?
By shutting down
What does excessive stress on a maltreated child cause?
Permanently damaged brain pathways
What is harder to master, gross motor or fine motor skills?
Fine motor skills
What is a direct cause of asthma?
Pollution
Define Injury control/ Harm reduction
Practices that are aimed at anticipating, controlling, and preventing dangerous activities; these practices reflect the beliefs that accidents are not random and that injuries can be made less harmful if proper controls are in place.
Define primary prevention
Actions that change overall background conditions to prevent some unwanted event or circumstance, such as injury, disease, or abuse.
Define secondary prevention
Actions that avert harm in a high risk situation, such as stopping a car before it hits a pedestrian
Define tertiary prevention
Actions, such as immediate and effective medical treatment, that are taken after an adverse event (such as illness or injury) and that are aimed at reducing harm or preventing disability.
Define child maltreatment
Intentional harm to or avoidable endangerment of anyone under 18 years of age.
Define child abuse
Deliberate action that is harmful to a child’s physical, emotional, or sexual well-being.
Define child neglect
Failure to meet a child’s basic physical, educational, or emotional needs.
What is the most common and most frequently fatal form of child maltreatment?
Neglect
Define executive function
The cognitive ability to organize and prioritize the many thoughts that arise from the various parts of the brain, allowing the person to anticipate, strategize, and plan behavior
What are the 3 foundations of executive function?
•Memory
•Inhibition
•Flexibility
Define preoperational intelligence
Piaget’s term for cognitive development between the ages of about 2 and 6; it includes language and imagination, but logical, operational thinking is not yet possible at this stage.
Define symbolic thought
A major accomplishment of preoperational intelligence; it allows a child to understand words can refer to things not seen and that an item, such as a flag, can represent something else (a country)
Define animism
The belief that natural objects and phenomena are alive, moving around, and having sensations and abilities that are humanlike.
Define centration
The tendency to focus on one aspect of a situation, excluding all others
What is “focus on appearance“?
A characteristic of preoperational thought in which a young child ignores all attributes that are not visible.
What is “static reasoning”?
A characteristic of preoperational thought in which a young child thinks that nothing changes. Whatever is now has always been and always will be.
Define irreversibility
A characteristic of preoperational thought in which a young child thinks that nothing can be undone. A thing cannot be restored to the way it was before a change occurred.
What is “conservation logic”?
The principle that the amount of a substance remains the same, even when its appearance changes.
Define egocentrism
Piaget’s term for children’s tendency to think about the world entirely from their own personal perspective.
What gradually disappears and becomes more logical?
Preoperational thought (magical & symbolic, not logical & realistic)
Define scaffolding
Temporary support that is tailored to a learners needs and abilities and aimed at helping the learner master the next task in a given learning process.
What is overimitation?
When a person imitates an action that is not a relevant part of the behavior to be learned.
When is overimitation common?
2-6 years old
What is private speech?
The internal dialogue that occurs when people talk to themselves (either silently or out loud).
What is social mediation?
Human interaction that expands and advances understanding, often through words that one person uses to explain something to another.
What is ZPD?
A term for skills that a person can exercise only with assistance, not yet independently.
Zone of Proximal Development
Define theory-theory
The idea that children attempt to explain everything they see and hear by constructing theories.
Match the parenting style with its tendencies: Neglectful
•Uninvolved or absent
•Provides little nurturance or guidance
•Indifferent to a child’s social, emotional, and behavioral needs
Match the parenting style with its tendencies: Authoritarian
•Parent-driven
•Sets strict rules and punishments
•One way communication, with little consideration of child’s social, emotional, and behavioral needs
Match the parenting style with its tendencies: Authoritative
•Solves problems together with their child
•Sets clear rules and expectations
•Open communication and natural consequences
Match the parenting style with its tendencies: Permissive
•Child-driven
•Rarely gives or enforces rules
•Overindulgences child to avoid conflict
Bullying aggression is a sign of _____?
Poor emotional regulation
Define scaffolding
Temporary support that is tailored to a learners needs and abilities and aimed at helping the learner master the next task in a given learning process.
What are the 4 general principles of developmental psychopathology?
•Abnormality is normal
•Disability changes year by year
•Life may get better or worse (plasticity and compensation are widespread)
•Diagnosis and treatment reflect the social context
Define comorbid
Refers to the presence of two or more unrelated disease conditions at the same time in the same person.
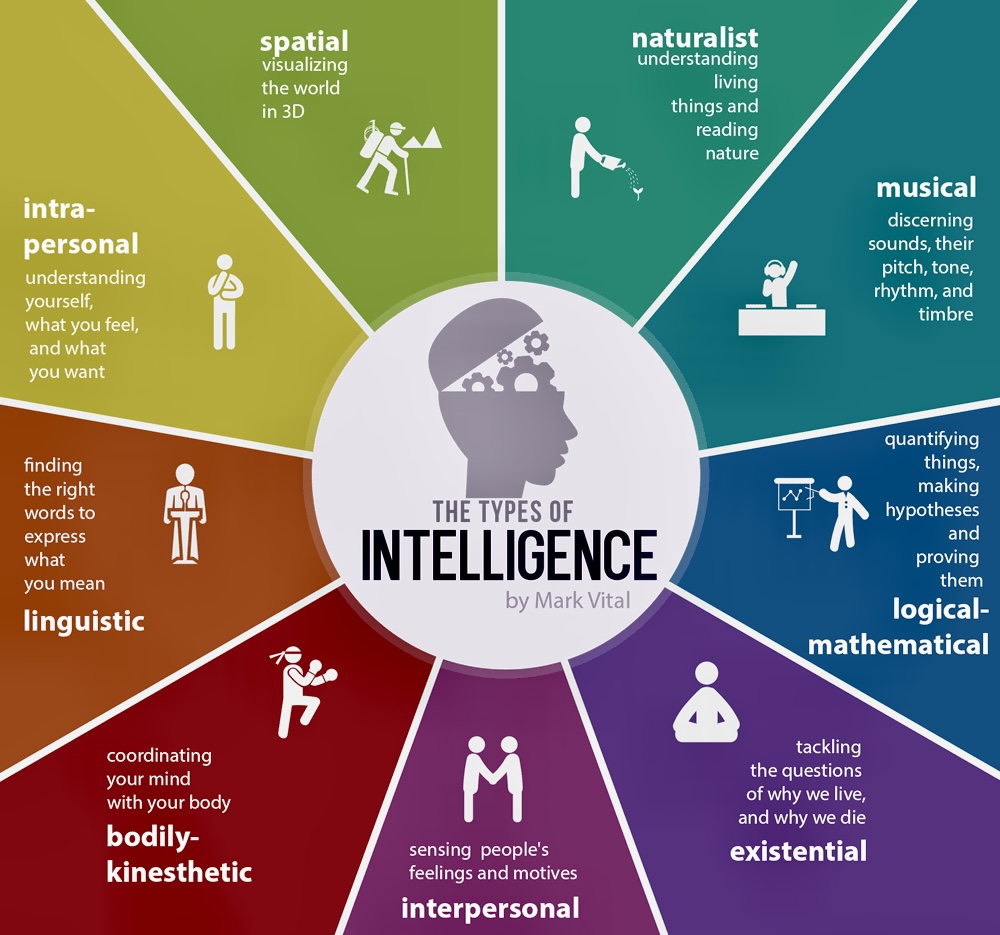
The 9 types of intelligence
•Naturalist
•Intra-personal
•Musical
•Spatial
•Linguistic
•Bodily kinesthetic
•Interpersonal
•Existential
•Logical-mathematical
Important takeaways of intelligence
Brain development depends on experiences
Dendrites form and myelination changes throughout life
Children with disorders often have unusual brain patterns, and training may change those patterns
Concrete operational thought
The ability to reason logically about direct experiences and perceptions