ORAL HISTOLOGY EXAM 3
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
200 Terms
submucosa
in which layer are MINOR SALIVARY GLANDs
major salivary glands
produce 90% of saliva volume
wetting, lubricating, digestive, mineralization, protective
functions of saliva
parotid
produces majority of saliva when eating
parotid
produces saliva with SIgA
submandibular
produce majority of daily saliva volume
serous
what kind of saliva do parotids produce
serous and mucous
what kind of saliva do submandibulars produce
mucous
what kind of saliva do sublingual glands primarily produce
intercalated ducts
Small ducts that connect the secretory areas of a gland to the striated ducts
serous (dark in color)
what kind of cell is this?
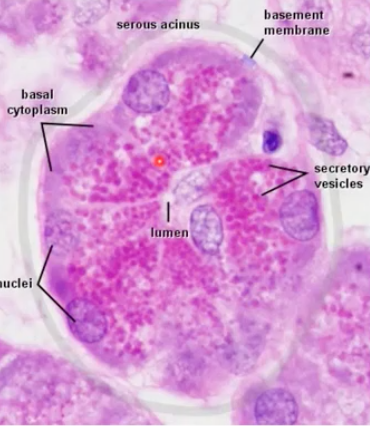
serous cells
secrete alpha-amylase to digest dietary starch
mucous cell (light in color and polarized)
what kind of cell is this?
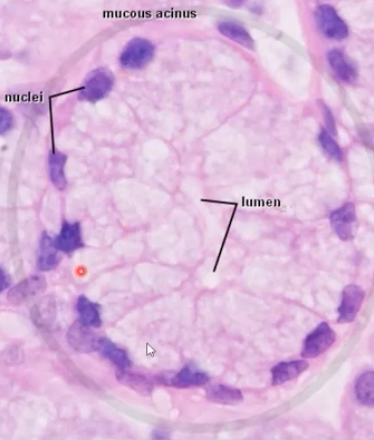
myoepithelial cells
assist in the expulsion of secretory products from serous cells
myoepithelial cells
what kind of cell is this
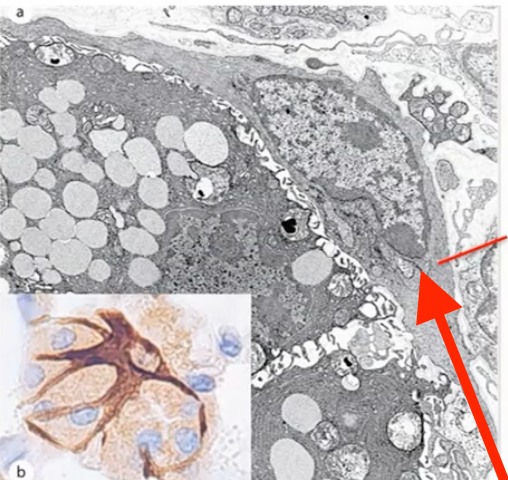
serous cell
where can myoepithelial cells be found?
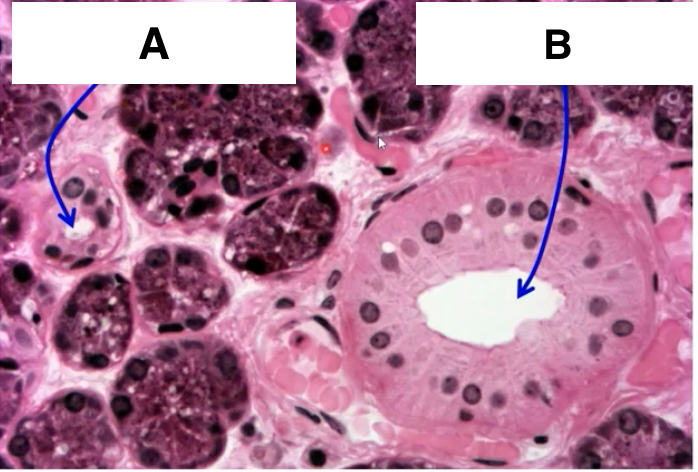
intercalated duct
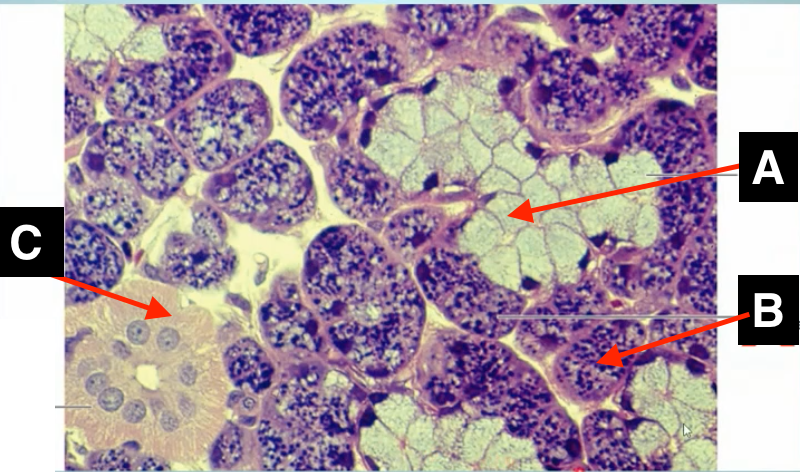
idenify A
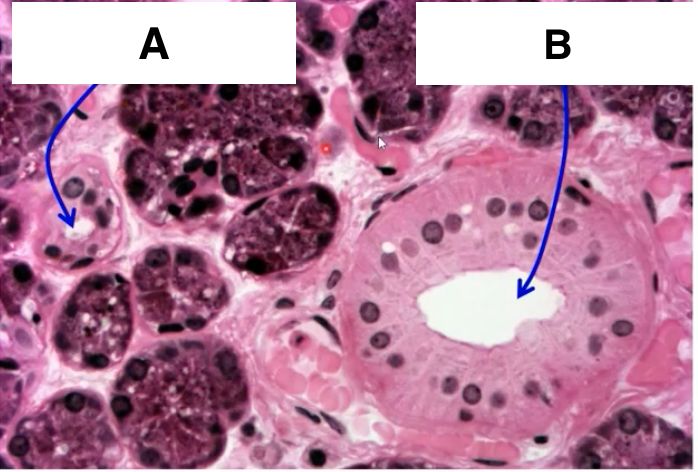
striated duct
identify B
intercalated duct
act as stem cells for serous and mucous glands
intralobular ducts
small ducts within the lobules of glands that include INTERCALATED and STRIATED ducts.
interlobular
ducts located between the lobules of glands, such as EXCRETORY ducts
intercalated duct cells
synthesize and secrete lysozyme and lactoferrin
striated duct cells
plays role is assembly and transcytosis of SIgA
striated duct cell (polarized nucleus)
what kind of cell is this
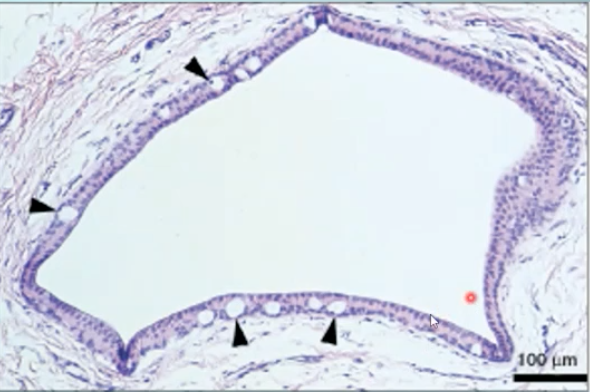
excretory duct
what structure is shown here?
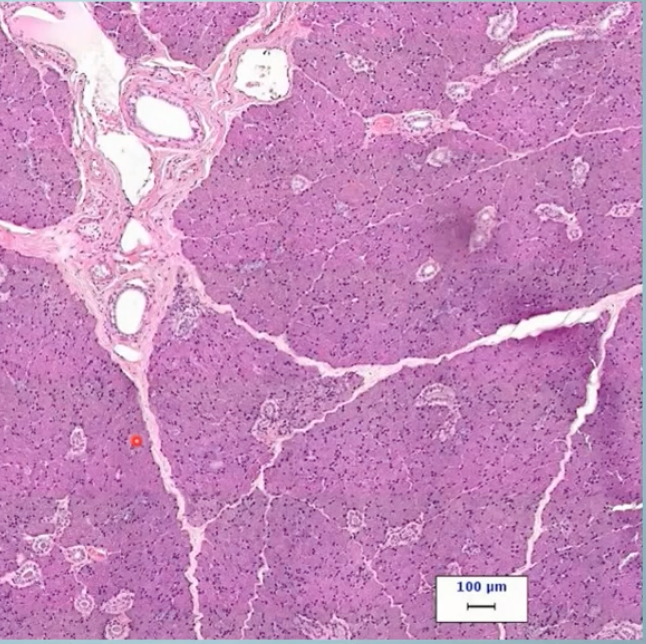
parotid
what gland is this?
parotid gland
produces the highest amount of amylase
parotid
what gland is this?
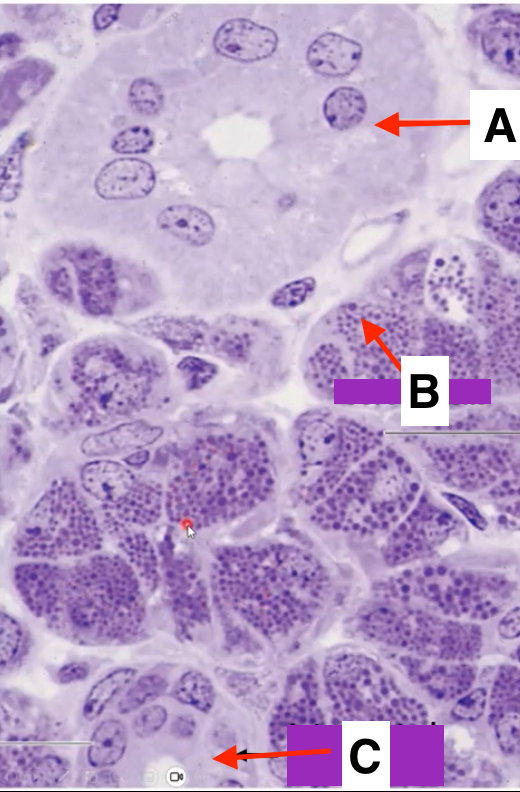
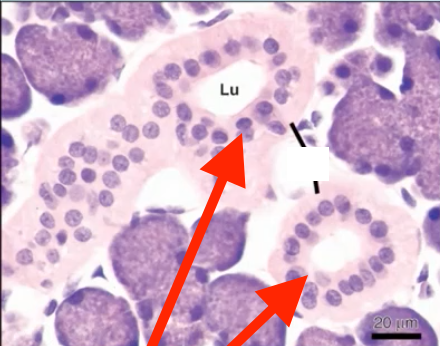
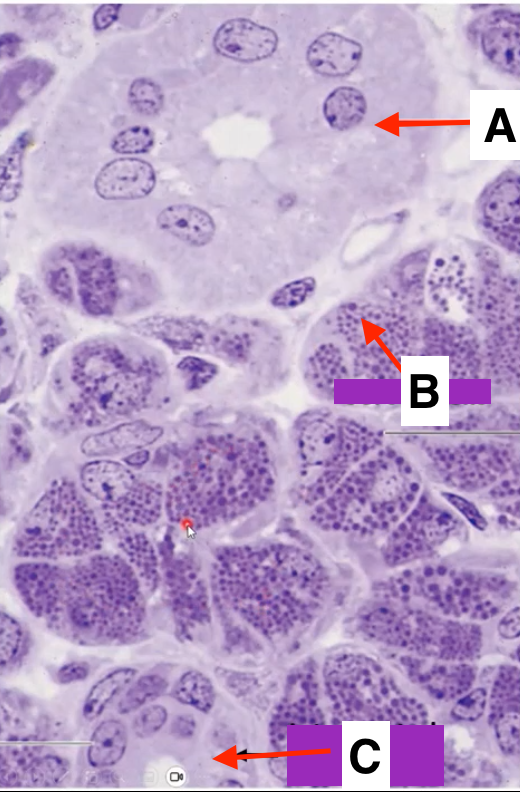
striated duct
identify A
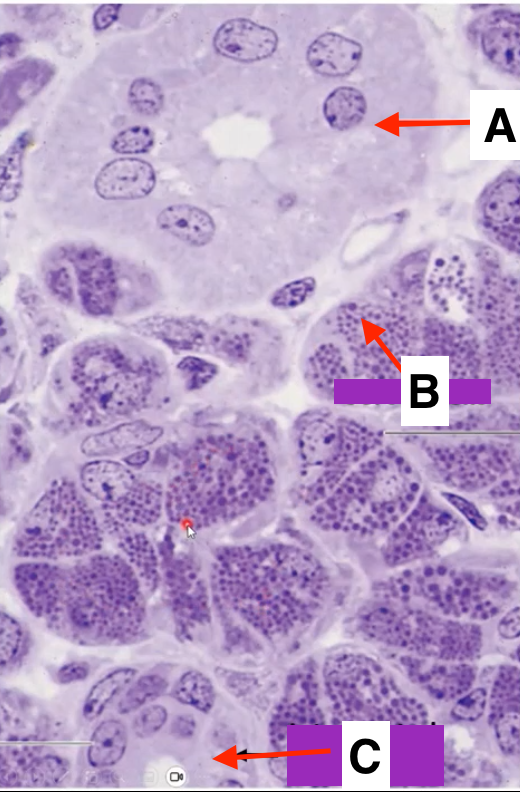
serous cell
Identify B
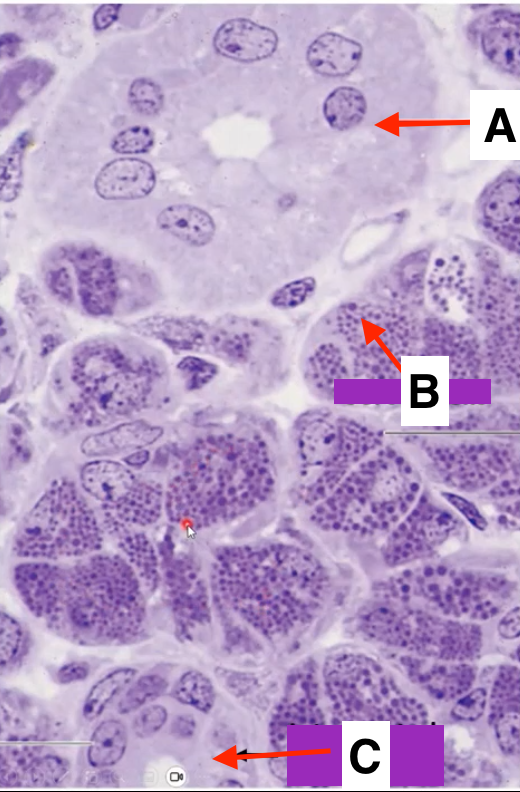
intercalated duct
identify C
submandibular
what gland is this?
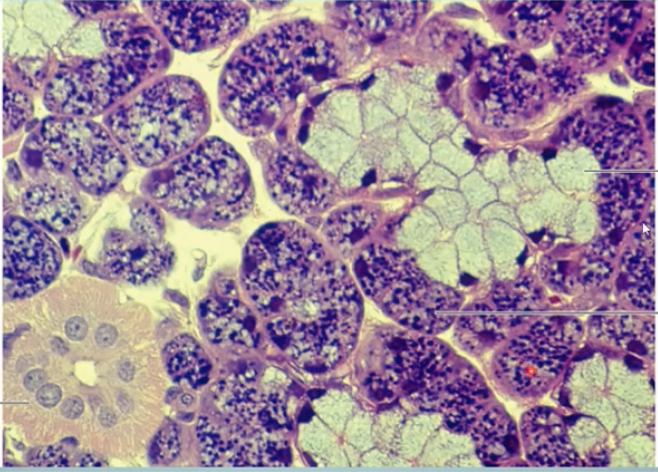
serous cell
secrete lysozyme to kill bacteria
parotid
produces mostly ACTIVE/STIMULATED saliva
submandibular and sublingual
produces mostly RESTING saliva
mucous cell
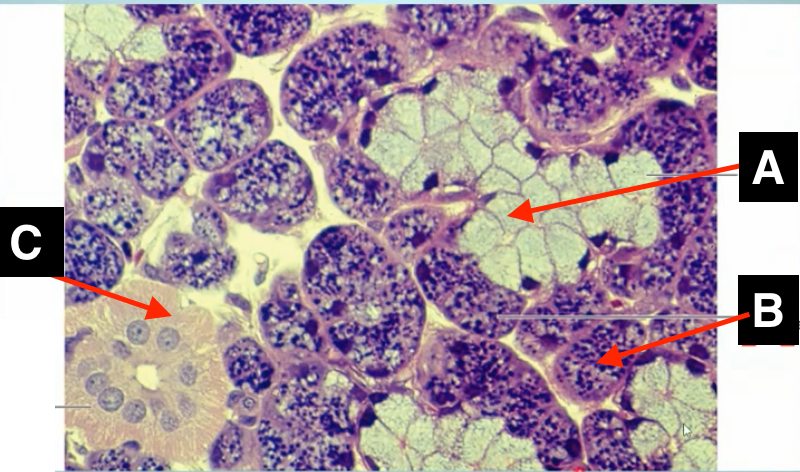
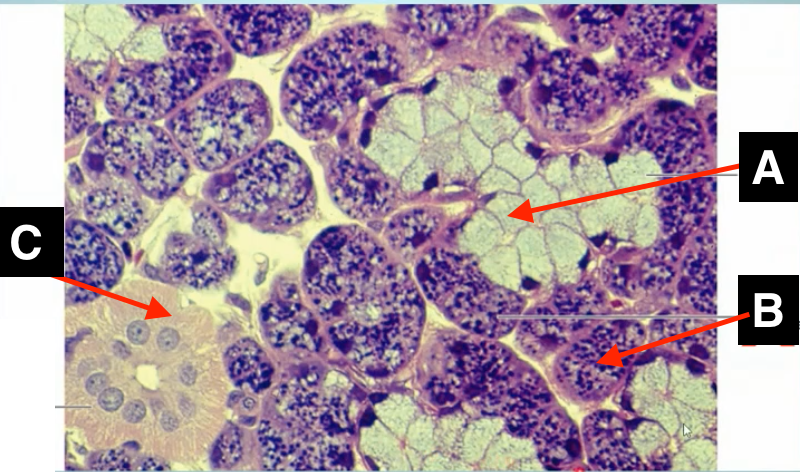
identify A
serous cell
identify B
striated duct
identify C
sublingual
what kind of gland is this
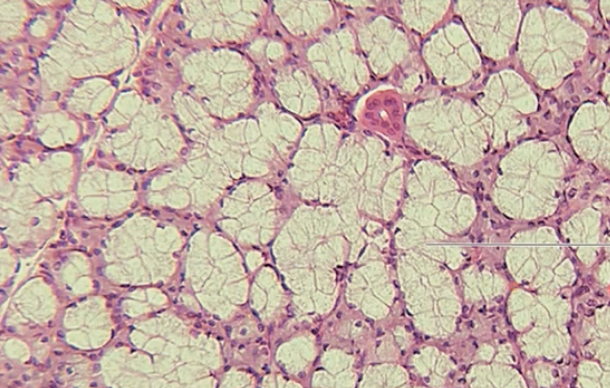
sublingual
what gland is this?
palate and posterior tongue
where are MUCOUS minor salivary glands found?
buccal mucous, labial mucosa, and anterior tongue
where are MIXED minor salivary gland found
minor salivary glands
produces MAJORITY of MUCOUS secretion
glands of von ebner
SEROUS glands in posterior and lateral regions of the tongue
glands of von ebner
glands associated with papillae, assist with TASTE
webers glands
MUCOUS glands associated with glands of von Ebner, assist with SWALLOWING
mesenchyme
what regulates what the gland will look like
epithelium
what regulates what the gland will produce
Eda
stimulates salivary gland BUD formation
FGF
stimulates salivary gland CORD GROWTH
sonic hedgehog
stimulates salivary gland BRANCHING
FGF/EGF
stimulates secretion of collagen and LOBULE formation
Eda
what signaling molecule defect is associated with Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
collagen III and fibronectin
important for CLEFT formation
collagen IV, and proteoglycans
important for BRANCHING
minor salivary glands
continuous with surrounding tissue
major salivary glands
within mesenchyme capsule
proteins, water, electrolytes
components of saliva secreted by salivary glands
taste, chewing, smell, and conditioned reflexes
what stimulates saliva production
CN VII and CN IX
afferent pathway for taste signals to the brain
CN VII (facial)
efferent (stimulates salivation) innervation of sublingual and submandibular glands
CN IX (glossopharyngeal)
efferent (stimulates salivation) innervation of PAROTID gland
inferior salivatory nucleus (ISN)
nucleus in brainstem that provides parasympathetic efferent fibers to the PAROTID and von Ebner gland via the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX).
superior salivatory nucleus (SSN)
nucleus in brainstem that provides parasympathetic efferent fibers to the SUBMANDIBULAR and SUBLINGUAL glands via the facial nerve (CN VII).
inferior salivatory nucleus
stimulates SEROUS saliva production in parotid and von ebner glands
unstimulated/resting
saliva that confers the most protection
stimulated/active
saliva that is rich in digestive enzymes
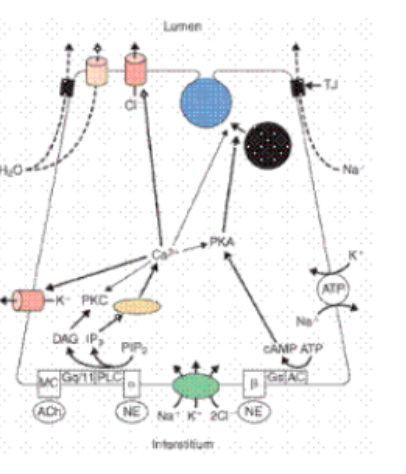
acetylcholine
PARASYMPATHIC, only affects FLUID secretion
norepinephrine
SYMPATHETIC, stimulates release of PROTEINS
Na/K ATPase
creates Na gradient that allows for influx of Na in acinar and ductal cells
NaK2Cl co transporter
drives acinar Cl- ions into cytoplasm
acetylcholine binding M3R
causes release of Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum in acinar cells to stimulate FLUID secretion
Ca 2+
opens Cl- and K+ channels, causes H2O secretion into lumen
cAMP (activated by norepinephrine)
activates protein kinase A (PKA) leading to protein secretion
aldosterone
influences the ductal epithelial cells to REABSORB Na into blood, making the final saliva HYPOTONIC
night (during sleep)
when is salivary flow the LOWEST
water
what is the main component of saliva
salivary pellicle
a thin layer formed by the adsorption of proteins onto the tooth surface, critical for oral health
histatins
salivary component that functions in WOUND CLOSURE
sjogrens syndrome
an autoimmune disorder that affects saliva production, leading to dry mouth and other symptoms
up to 1 liter
how much salvia is poduced per day
lubrication, mineral homeostasis, determines microbial colonizers, protect from acid
function of salivary pellicle
sjogrens, lupus, GvHD, irradiation, medication
causes of reduced salivary flow
ectoderm
origin of PAROTID epithelial cells
endoderm
orgin of SUBMANDIBULAR and SUBLINGUAL gland epithelial cells
NCCs
origin of extracellular matrix of major salivary glands
intercalated duct
lactoferrin is an antibacterial added too saliva, where in saliva is it added?
protein digestion
which of the following is NOT a function of saliva
buffering
lubrication
anti-microbial
protein digestion
norepinephrine binding beta receptor
what sets up the conditions for PROTEIN secretion by exocytosis
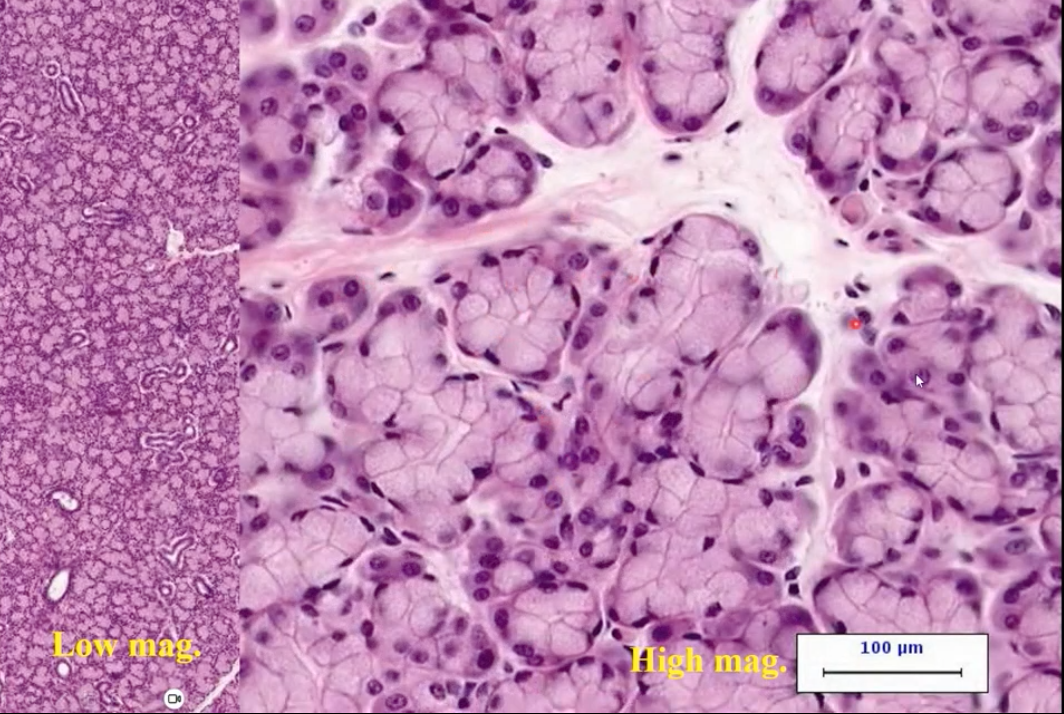
submandibular glands
gland primarily responsible for salivary flow during unstimulated conditions
collagen III and fibronectin
connective tissue critical to the process of these CLEFTs forming
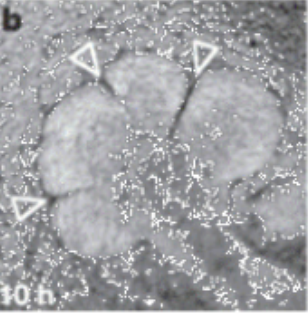
von-Ebners
only on minor gland is fully serous, which one?
sublingual
which gland looks most similar to the gland in this section
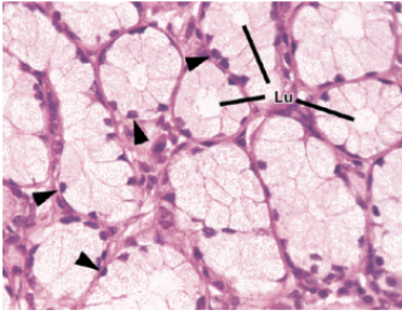
bud formation
which developmental stage is Eda a critical signaling molecule?
foliate papillae
which lingual papillae is NOT present on the DORSAL surface of the tongue
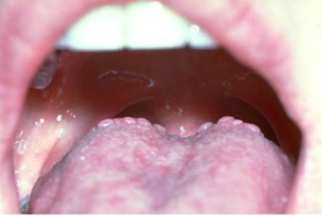
circumvallate papillae
identify the structure in this image
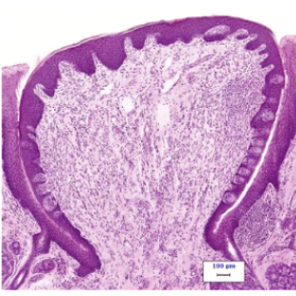
fungiform papillae
what structure is highlighted by the red arrow
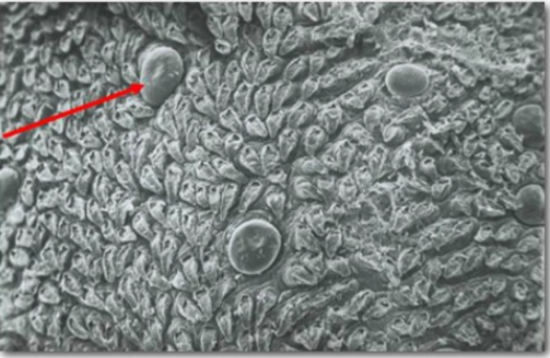
Type II in both fungiform and circumvallate papillae
which taste cell type has the G-protein coupled receptors responsible for transducing BITTER taste perception
sweet and umami taste receptors (T1Rs)
which G protein coupled receptors operate as hetero dimers and have long N terminal with VENUS FLYTRAP domains
loss of taste, numbness, fungiform atrophy, more sensitive to bitter
what can happen if the lingual nerve is damage during the extraction of a third molar