Reaction Kinetics
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is meant by rate of reaction?
The change in concentration of reactants or products over time
How does concentration affect rate of reactoin?
Increasing the concentration increasing the number of molecules per unit volume leading to greater collisions and hence greater succesful ones
Rate of reaction is increases
What is linked by the rate constant?
Rate of reaction and the concentrations of the reactants raised to their orders in the rate equation
How do you work out rate constant?
Rearrange the rate equation to make k the subject
Substitute units into the equation
Cancel the common units to find k
Work out the unit of the rate constant in the following equation Rate=[A][B]²
K= Rate/[A][B]²
k= s^-1/mol3dm-9
k= dm9 mol^-3s^-1
How is the order of reaction used in the rate equation? What is meant by overall order?
The order with respect to a reactant is the power to which the concentration of that reactant is raised to in the rate equation
Overall order = sum of the orders of each reactant in an equation
How does order with respect to a reactant affect rate?
Zero order: If rate is [A]^0 then the rate of reaction is unaffected by changing the concentration of A
First order: If rate is [A]^1 then rate of reaction increases at the same rate as concentration increases
Second order: If rate is [A]² then rate will increase by the square of the factor the concentration increases by
What is the rate equation?
In terms of A and B
Rate= k[A]^m[B]^n
m and n represent the orders
K is the constant
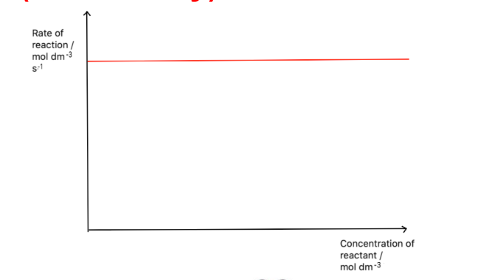
Draw a rate-concentration graph for a zero order reactant
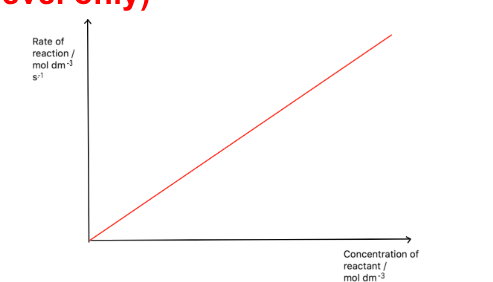
Draw a rate-concentration graph for a first order reactant
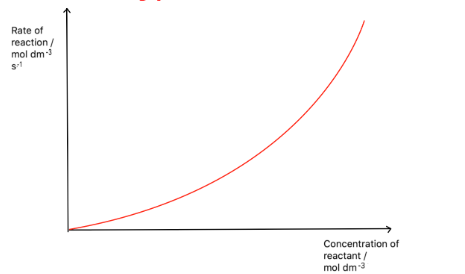
Draw a rate-concentration graph for a second order reactant
What is meant by half-life of a reaction?
The average time taken for the concentration of the reactant to decrease by half, t1/2
Define the term ‘Order of reaction’
The power to which the concentration is raised to in the rate equation
How do you calculate the rate constant, k from half life, t1/2, for a first order reaction?
k=In2/t(1/2)
This equation applies to first order reactants only
The half life of a first order reactant is independent of concentration
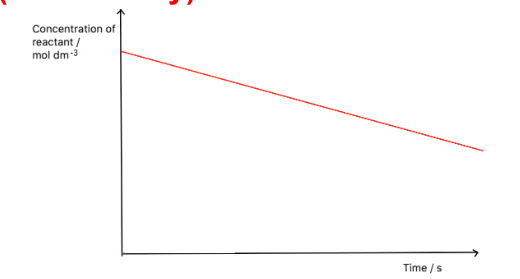
Draw a concentration-time graph for a zero order reactant
Draw a concentration-time graph for a first order reactant
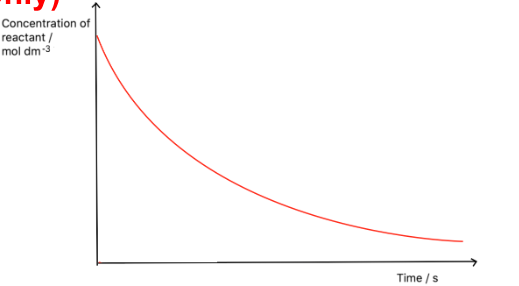
How do you calculate half life from a first order concentration -time graph?
Using the graph, find the time taken for the concentration to halve
Then find the time taken for it to half again
Calculate the average of the two
How do you calculate the rate from a first order concentration-time graph?
Draw a tangent at the time you want the rate of reaction
The gradient of this tangent will equal the rate of reaction
How do you calculate k from a first order rate-concetnration graph?
Calculate the gradient of the line of best fit
The gradient will equal the rate constant, k
What is the rate determining step?
The slowest step of a reaction
Only species that take part in this step affect the rate
What is the relation between the rate determining step and the rate equation?
The species present in the rate equation are those that take part in the rate determining step
For any reactant in the rate equation, the order attached to it tells you how many molecules of it are involved in the rate determining step
Suggest a step-by-step reaction mechanism for the reaction
CO + NO2 ——> CO2 + NO
Rate equation: rate=k[NO2]²
Step 1: 2NO2 ——> NO + NO3 (slow)
Step 2: NO3 + CO ——> NO2 + CO2
How can the order of reactant be predicted using a reaction mechanism?
Identify the rate-determining step
Observe how many molecules of each reactant react in the rds
E.g. if two molecules of reactant A react in the rate determining step, the reaction is second order with respect to A
How can rate of reaction be measured?
Initial rates method- i.e. the iodine clock reaction
A continuous monitoring method- i.e. measuring the volume of gas released in a reaction over time
Describe the initial rates method
Measure the initial rate of a reaction for several different sets of initial concentrations and see how rate varies
What is activation energy?
The minimum amount of energy required for a particular reaction to occur
What is boltzman distrbution?
A curve that shows the relative energies of molecules
Area under graph=total number of molecules
How does the rate constant, k vary with increasing temperature?
When temperature increases so does the number of successful collisions therefore k will increase
What is catalysis?
The increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to the addition of a catalyst
What is a homogenous catalyst?
A catalyst that is in the same state as the reactants
What is a heterogeneous catalyst?
A catalyst that is in the different state as the reactants
Why do catalysts increase the rate of reaction?
A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a reaction by causing the reaction to have a different mechanism
What are enzymes?
Biological catalysts that increase the rate of biochemical reactions
What catalyst is used in the Haber process? Describe the role of it
A heterogeneous iron catalyst
The iron also has KOH added to it to make it more efficient
Nitrogen and hydrogen are adsorbed onto the catalyst surface, breaking the bonds in the nitrogen and hydrogen molecules
New bonds form between the iron and individual nitrogen and hydrogen atoms
Nitrogen then bonds to hydrogen to form ammonia which desorbs from the catalyst
What are the stages in heterogeneous catalysis?
Diffusion
Adsorption
Reaction
Detaching
Diffusion
How does a catalytic converter reduce harmful emissions from car exhaust?
2CO2 + 2NO ——> 2CO2 + H2
Heterogeneous catalyst
Metals like platinum, palladium and rhodium are used
How do oxides of nitrogen catalyse the oxidation of sulfur dioxide?
Homogeneous catalyst, NO2
Nitrogen dioxide reacts with SO2 before being regenerated:
SO2 + NO2 ——> SO3 + NO
NO + 1/2O2 ——> NO2
How do iron ions act as a catalyst in the I-/S2O8²
Homoegeneous iron catalyst
S2O8²- + 2I- ——> 2SO4²- + I2
Iron ions react with reactants to form intermediates (this is a much more successful pathway as two negatively charge reactants do no have to collide)