L3: Carbohydrates
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:40 PM on 9/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
1
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
Major source of energy from our diet.
2
New cards
C, H, and O
CARBOHYDRATES Composed of the elements: ____________
3
New cards
saccharides
CARBOHYDRATES is also known as ___________
4
New cards
sugar
saccharides means ____________
5
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
Produced by photosynthesis in plants.
6
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
Are oxidized in living cells (respiration) to produce CO2, H20, and energy.
7
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
“Hydrate of carbon”.
8
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
Derived from the formula Cn(H2O)m
9
New cards
Glucose
C6H12O6 or C6(H2O)6
10
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
Provides energy.
11
New cards
**Glycogen**
**provides short term energy reserves.**
12
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
Supply carbon for synthesis of other biochemical substances.
13
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
Part of the structure of DNA and RNA
14
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
Linked to lipids – in cell membrane.
15
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
Linked to proteins – in biological recognition processes
16
New cards
**CARBOHYDRATES**
Regulation of blood sugar.
17
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
Spare the use of protein for energy
18
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
Breakdown of fatty acids and preventing ketosis.
19
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
Provide flavor and sweetness.
20
New cards
CARBOHYDRATES
Source of dietary fibers
21
New cards
Superimposable Mirror Images
coincide at all points when images are laid upon each other
22
New cards
Nonsuperimposable Mirror Image
not all points coincide when images are laid upon each other.
23
New cards
Chiral Center
Atom in a molecule that has four different tetrahedrally bonded to it.
24
New cards
TRUE
Mirror images are NOT superimposable
\
T/F
\
T/F
25
New cards
Isomers
compounds possessing identical molecular formulas but different structures
26
New cards
Geometric
Isomers differ in their spatial arrangement about a double bond
27
New cards
Optical
Isomers differ in the arrangement of atoms in 3D space which create mirror images of each other
28
New cards
Structural Isomers
same molecular formula but differ from each other by having different structures.
29
New cards
Stereoisomerism
same molecular formula and same structure but differ in configuration.
30
New cards
Stereoisomerism
differ in arrangement of their atoms in space.
31
New cards
Stereoisomerism
presence of chiral centers allows for the formation of stereoisomers.
32
New cards
D and L, Optical, Epimerism, α and β anomerism.
Types of Stereoisomerism Associated with Glucoses:
33
New cards
Enantiomers
molecules are nonsuperimposable mirror images of each other.
34
New cards
Diastereomers
molecules are not mirror images of each other.
35
New cards
Optical Isomerism
optical activity is the capacity of a substance to rotate the plane polarized light passing through it.
36
New cards
Dextrorotatory(d) or (+)
Optical Isomerism
\
Clockwise direction
\
Clockwise direction
37
New cards
Levorotatory(l) or (-)
Optical Isomerism
\
Counterclockwise direction
\
Counterclockwise direction
38
New cards
chiral compounds
______________ rotate polarized light clockwise or counterclockwise through a certain angle.
39
New cards
Epimerism
if two monosaccharide differ from each other in their configuration around a single specific carbon (other than anomeric) atom
40
New cards
Anomerism
isomers obtained from the change of position of hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon e.g. α and β glucose are 2 anomers.
41
New cards
**Anomerism**
Also α and β fructose are 2 anomers
42
New cards
Mutarotation
the change in the specific optical rotation by the interconversion of α and β forms of D glucose to an equilibrium mixture.
43
New cards
Monosaccharide
simplest carbohydrates
44
New cards
Disaccharides
2 monosaccharides
45
New cards
Oligosaccharides
2-10 monosaccharides
46
New cards
Polysaccharides
many monosaccharides
47
New cards
3-6
MONOSACCHARIDE typically consists of __________ carbon atoms
48
New cards
MONOSACCHARIDE
A carbonyl group (aldehyde or ketone)
49
New cards
MONOSACCHARIDE
Several hydroxyl groups.
50
New cards
MONOSACCHARIDE
Colorless, crystalline solids.
51
New cards
Aldose
Monosaccharides with an aldehyde group.
52
New cards
Triose
With many hydroxyl (–OH) groups: ________________ = 3 C atoms
53
New cards
Tetrose
With many hydroxyl (–OH) groups: __________ = 4 C atoms
54
New cards
Pentose
With many hydroxyl (–OH) groups: _____________ = 5 C atoms
55
New cards
Hexose
With many hydroxyl (–OH) groups: _____________ = 6 C atoms
56
New cards
Ketose
Monosaccharides with a ketone group.
57
New cards
D-glucose
Found in fruits, corn syrup, and honey.
58
New cards
D-glucose
An aldohexose with the formula = C6H12O6
59
New cards
D-glucose
Known as blood sugar in the body
60
New cards
D-glucose
The monosaccharide in polymers of starch, cellulose, and glycogen.
61
New cards
70-90
In the body, glucose has a normal blood level of ________ mg/dL/
62
New cards
Glucose Tolerance Test
measures blood glucose for several hours after ingesting glucose.
63
New cards
D-fructose
Is a ketohexose = C6H12O6
64
New cards
D-fructose
The sweetest carbohydrate
65
New cards
D-fructose
Found in fruit juices and honey.
66
New cards
D-fructose
Converts to glucose in the body.
67
New cards
D-galactose
An aldohexose = C6H12O6
68
New cards
D-galactose
Not found free in nature.
69
New cards
D-galactose
Obtained from lactose, a disaccharide.
70
New cards
D-galactose
A similar structure to glucose except for the –OH on C4.
71
New cards
Fischer Projection
Straight chain structural formula
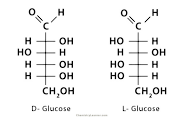
72
New cards
Haworth Projection
Cyclic formula or ring structure.
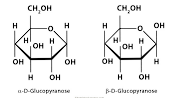
73
New cards
X-ray Diffraction Analysis
Boat and chair form
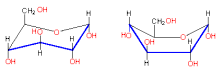
74
New cards
Hermann Emil Fischer (German)
Fischer Projection - Developed by __________________________
75
New cards
Fischer Projection
Used to represent carbohydrates.
76
New cards
Fischer Projection
Places the most oxidized group at the top
77
New cards
Fischer Projection
Shows chiral carbons as the intersection of vertical and horizontal lines
78
New cards
Walter Norman Haworth (British).
Haworth Projection - Developed by ___________________
79
New cards
Haworth Projection
Two-dimensional structural annotation that specifies the three-dimensional structure of a cyclic form of monosaccharide.
80
New cards
Cyclic Structures
The prevalent form of monosaccharides with 5 or 6 carbon atoms
81
New cards
Cyclic Structures
Formed when the hydroxyl group on C5 reacts with the aldehyde or ketone group.
82
New cards
DISACCHARIDES
Glycosides formed by the condensation of 2 simple sugars.
83
New cards
non-reducing
If the glycosidic linkage involves the carbonyl groups of both sugars (sugars) the resulting disaccharide is _________
84
New cards
reducing
If the glycosidic linkage involves the carbonyl group of only one of the 2 sugars (as in maltose and lactose) the resulting disaccharide is _____________.
85
New cards
Maltose
Known as “malt sugar”
86
New cards
Maltose
Composed of 2 D-glucose molecules.
87
New cards
Maltose
Obtained from the hydrolysis of starch.
88
New cards
Maltose
Linked by an α-1,4-glycosidic bond formed from the α –OH on C1 of the first glucose and –OH on C4 of the second glucose.
89
New cards
Maltose
Used in cereals, candies, and brewing
90
New cards
Maltose
Found in both the α- and β- forms
91
New cards
Lactose
A disaccharide of β-D-galactose and α- or β-D-glucose
92
New cards
Lactose
Contains a β-1,4-glycosidic bond
93
New cards
Lactose
Found in milk and milk products
94
New cards
Sucrose
“Table sugar”.
95
New cards
Sucrose
Obtained from sugarcane and sugar beets
96
New cards
Sucrose
Consists of α-D-glucose and β-D-fructose.
97
New cards
Sucrose
Has an α, β-1,2-glycosidic bond.
98
New cards
Fructose
sweetest
99
New cards
Fructose
even sweeter than sucrose
100
New cards
Honey
D-fructose and D-glucose