AP Biology Unit 1 review
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
polarity
having poles (property) or being polar
hydrogen bonding
a strong type of attraction that forms between a hydrogen atom and a lone pair of electrons on another electronegative atom
cohesion
water-water interactions
adhesion
water-other materials interactions
surface tension
object floats on water
evaporative cooling
process where air temperature is lowered as water evaporates
heat capacity
able to hold a lot of heat
dehydration synthesis
adds water to the product
hydrolysis
removes water from the product
complex carbohydrates
polysaccharide - like proteins and fats
sugar phosphate backbone
nucleotide monomer connected by covalent bonds and forms sugar
anti parallel
runs in opposite directions
What happens when a blood vessel is damaged?
platelets near injury release chemicals to attract more platelets
macromolecules
carbs, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids
high specific heat
stable temperature in cells
high heat of vaporization
sweating cools the body
function? - cohesion and adhesion
water moves up through plant roots (capillary action)
cellulose is
a carbohydrate
what is glucose?
C6H12O6
difference between ribose and deoxyribose
ribose: has an -OH group linked to 2’ carbon
deoxyribose: doesn’t have
in a single molecule of water, two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen atom by
polar covalent bonds
which effects can occur because of the high surface tension of water?
a raft spider can walk across the surface of a small pond
which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize
hydrogen bonds
You have two beakers. One contains pure water, the other contains pure methanol (wood alcohol). The covalent bonds of methanol molecules are nonpolar, so there are hydrogen bonds among methanol molecules. You pour crystals of table salt (NaCl) into each beaker. Predict what will happen
NaCl crystals will dissolve readily in water but will not dissolve in methanol.
Water molecules can form hydrogen bonds with
oxygen gas (O2) molecules
Which of the functional groups below acts most like an acid in water?
carboxyl
why are hydrocarbons insoluble in water
majority of their bonds are nonpolar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen linkages
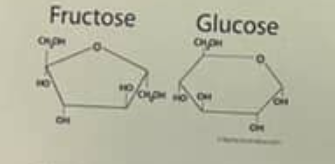
the figure above shows the structure of glucose and fructose. those two molecules differ in the
arrangement of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms
the complexity and variety of organic molecules is due to
chemical versatility of carbon atoms
which functional groups shown above is (are) present in all amino acids
B and C
which of these classes of biological molecules does NOT include polymers
lipids
how many molecules of water are used to completely hydrolyze a polymer that is 11 monomers long
10
which of the following best summarizes the relationship between dehydration reactions and hydrolysis
dehydration reactions assemble polymers, hydrolysis reactions break polymers apart
the molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. what would be the molecular formula for a molecule made by linking three glucose molecules together by dehydration reactions?
C18H32O16
What does the term insoluble fiber refer to on food packages?
cellulose
a glycosidic linkage is analogous to which of the following in proteins?
a peptide bond
how do phospholipids interact with water molecules
the polar heads interact with water; the nonpolar tails do not

the molecule illustrated in the above figure
saturated fatty acid
what component of amino acid structure varies among different amino acids?
the components of the r group
which is the strongest evidence that protein structure and function are correlated?
denatured (unfolded) proteins do not function normally
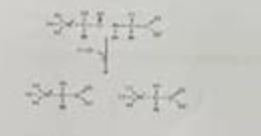
the chemical reaction illustrated in the above figure
hydrolysis reaction
you disrupt all hydrogen bonds in a protein. what level of structure will be preserved?
primary structure
all of the following contain amino acids EXCEPT
cholesterol
nucleic acids are polymers made up of which of the following monomers?
nucleotides
one of the primary functions of RNA molecules is to
function inthe synthesis of proteins
which of the following descriptions best fits the class of molecules known as nucleotides?
a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a sugar
if a DNA sample were composed of 10% thymine, what would be the percentage of guanine?
40
if one strand of dna molecule has the sequence of bases 5’ATTGCA3’, the other complementary strand would have the sequence
5’TGCAAT3’
basedon your knowledge of the polarity of water molecules, the solute molecule depicted here is most likely
positively charged
question 30 in your packet :]
transpiration rates will fall to zero as nonpolar compounds do not have the properities necessary for adhesion and cohesion
why is carbon so important in biology?
it can from a variety of carbon skeletons and host functional groups
which molecule shown above contains a functional group that cells use to transfer energy between organic molecules (question 21)
D
a typical bag of fertilizer contains high levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium but trace amounts of magnesium and calcium. which of the following best matches the fertilizer component with the molecule which it will be incorporated by organisms in the area?
nitrogen will be incorporated into nucleic acids
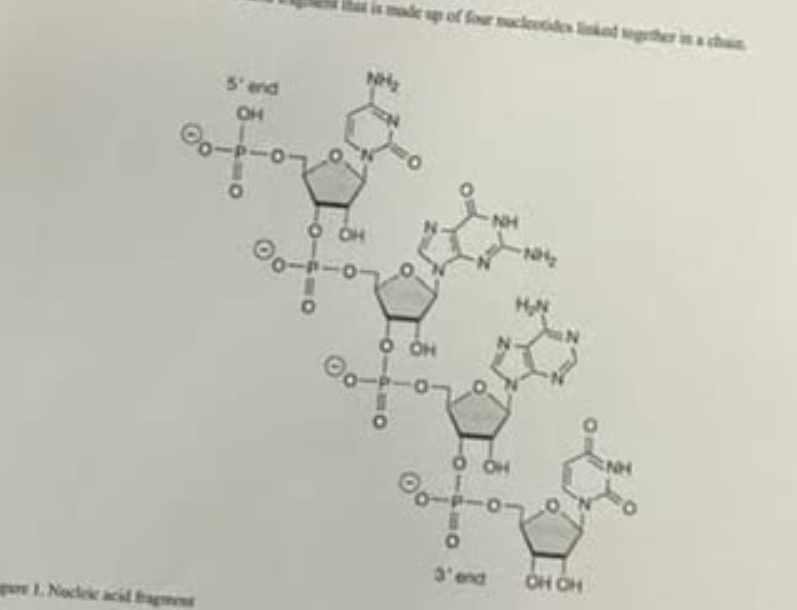
which of the following characteristics of figure 1 best shows that the fragment is RNA not DNA?
the identity of each nitrogenous base
a chemical binds to a protein composed of a single polypeptide chain and prevents the formation of an alpha helix that is typical formed in the absence of the chemica. which of the following ebst describes the effect the chemical has on the structure of the protein?
the secondary structure held together by hydrogen bonds is affected
based on the molecular structure shown in the figure, which molecule is likely to be solid at room temperature?
palmitic acid, because the absence of carbon-carbon double bonds allows the molecules to pack closely together
which best describes the hydrolysis of carbohydrates?
the addition of a water molecule breaks a covalent bond between sugar monomers