Piaget's cognitive development
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Theoretical features
• Genetic epistemology: the development of knowledge
• Theoretical roots in biology and philosophy
• Emphasis on adaption
• Synthesis of nature and nurture - constructivism
Theoretical features
Knowledge is abstracted from our experience
Children progress through discrete stages in an invariant order
Children’s logical thought is qualitatively different in different stages
Mechanisms
Principle of Adaptation:
Assimilation: incorporating new objects into an already existing scheme
Accommodation: modifying or re-organising mental structures in response to a new object/event
Equilibration: A pattern of self-regulation achieving balance between existing schema and modifying them to deal with new information from the environment
Principles of organsiation: The method of integrating the schema and putting them together to achieve aims
Stages of development
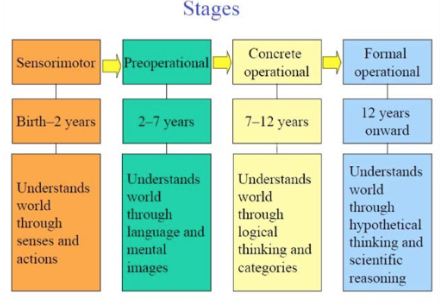
Sensorimotor Stage (0-2 years)
Description: Infants learn about the world through their senses and actions.
Key Developmental Milestones:
Object Permanence: Understanding that objects continue to exist even when they cannot be seen, heard, or touched.
Coordination of Reactions: Beginning to show intentional actions and combine schema (mental structures).
Preoperational Stage (2 to 7 years)
Description: Children begin to use language and think symbolically, but their thinking is still intuitive and egocentric.
Key Developmental Milestones:
Symbolic Play: Using objects to represent other objects, which shows the beginning of abstract thinking.
Egocentrism: Difficulty in seeing things from perspectives other than their own.
Animism: Belief that inanimate objects have feelings and intentions.
Concrete Operational Stage (7 to 11 years)
Description: Children's thinking becomes more logical and organized, but still very concrete. They can perform operations on concrete objects and events.
Key Developmental Milestones:
Conservation: Understanding that quantity remains the same even when its shape changes.
Classification: Ability to group objects based on common features.
Seriation: Ability to arrange objects in an order according to size, shape, or any other characteristic.
Formal Operational Stage (12 years and up)
Description: Adolescents develop the ability to think about abstract concepts. Logical thought, deductive reasoning, and systematic planning emerge.
Key Developmental Milestones:
Abstract Thought: Ability to think about hypothetical situations and abstract concepts.
Hypothetical-Deductive Reasoning: Ability to develop hypotheses and systematically deduce which is the best path to follow in solving a problem.
Problem-Solving: Enhanced ability to think about multiple variables and outcomes simultaneously.
Limitations
Infants and young children are more cognitively competent than Piaget recognised
Margaret Donaldson: tasks (and the language used in the tasks) need to make human sense
Object permanence in young infants
(Baillargeon & DeVos, 1991)
Contextually meaningful tests of visual
perspective-taking (e.g., Hughes)