Patho: Genetic Tooth Disorders (ch. 6c)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What are the inherited tooth disorders?
1) Amelogenesis Imperfecta
2) Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
3) Dentin Dysplasia
Amelogenesis Imperfecta is a group of __ different inherited conditions affecting enamel.
14
What is the inheritance and clinical onset of Amelogenesis Imperfecta?
-inheritance: varies = dominant/recessive/X-linked dominant
-clinical onset: 6 months → when teeth erupt (both dentitions)
What are the oral features of Amelogenesis Imperfecta?
-affects primary and permanent dentitions = all teeth
-on XR → normal dentin/normal pulp/abnormal enamel
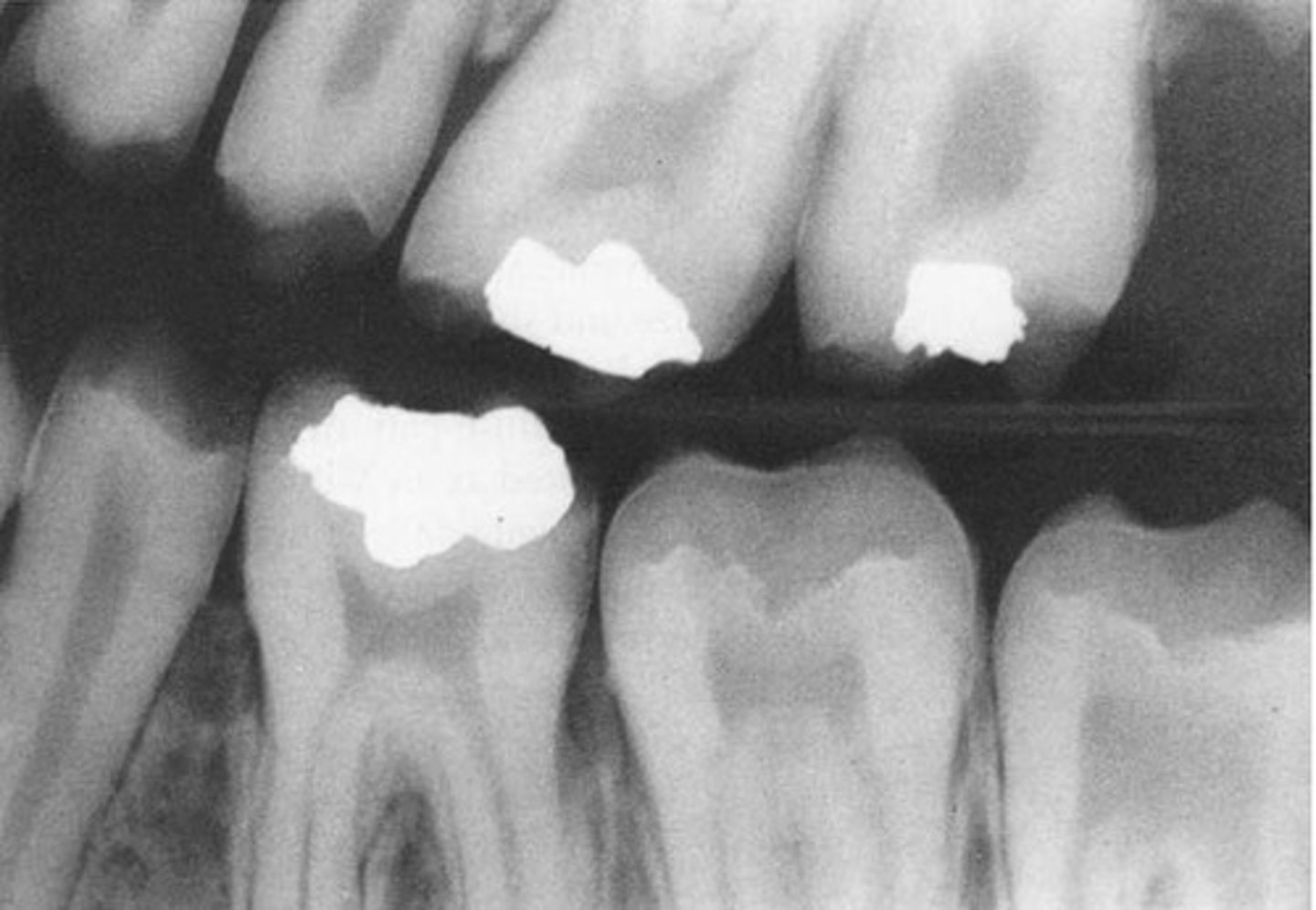
What are the treatment modifications for Amelogenesis Imperfecta?
genetic testing for specific genes:
1) AMELX (amelogenin)
2) ENAM (enamelin)
3) MMP-20
4) KLK4
5) DLX3
6) AMBN (ameloblastin)
What are the 3 different types of AI?
1) Hypoplastic AI
2) Hypocalcified AI
3) Hypomaturation AI
What are the clinical features of hypoplastic AI?
-decreased enamel matrix = thin
-normal mineralization
-harder than dentin
-more radiopaque than dentin
-pitted, smooth, or rough
-localized or generalized
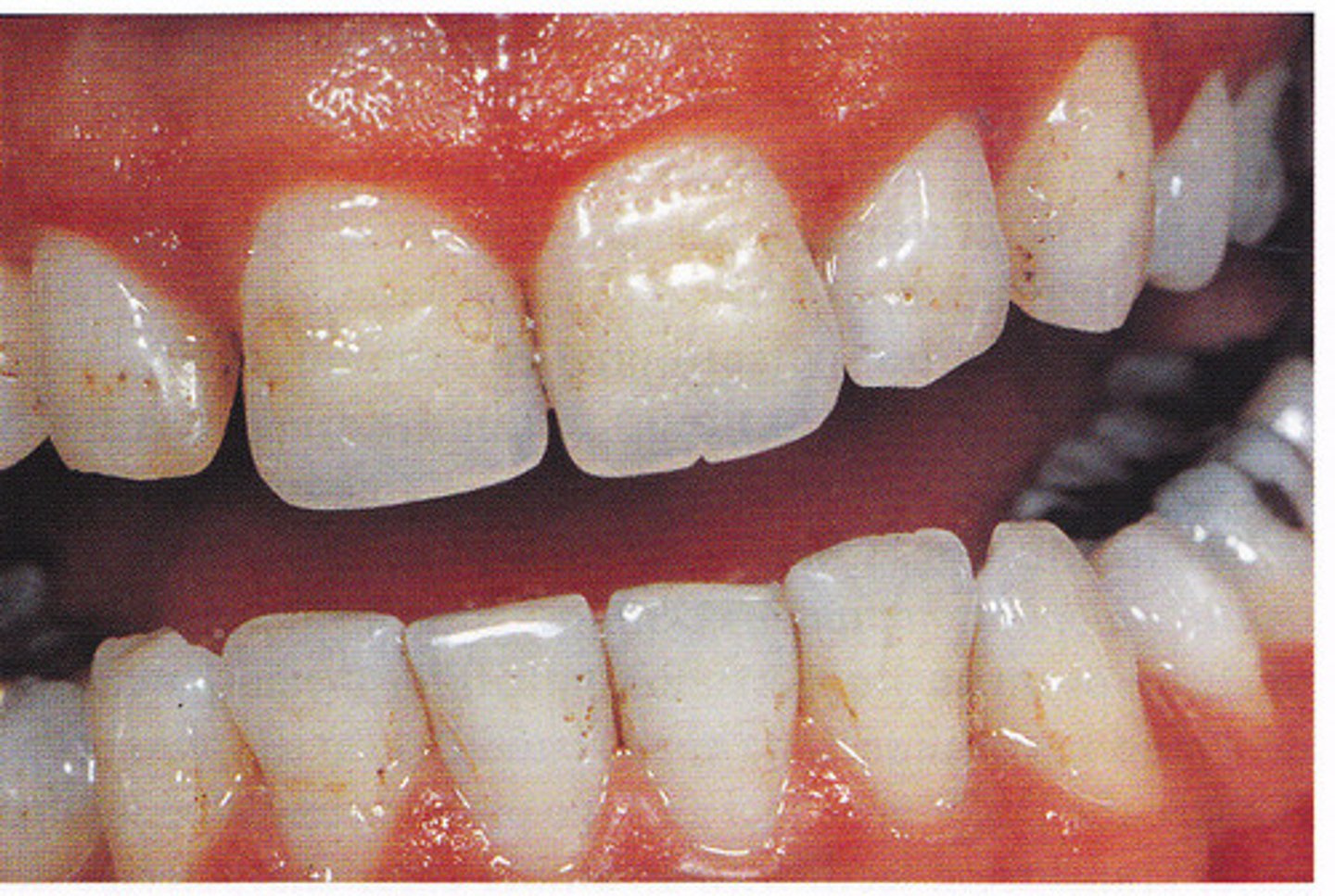
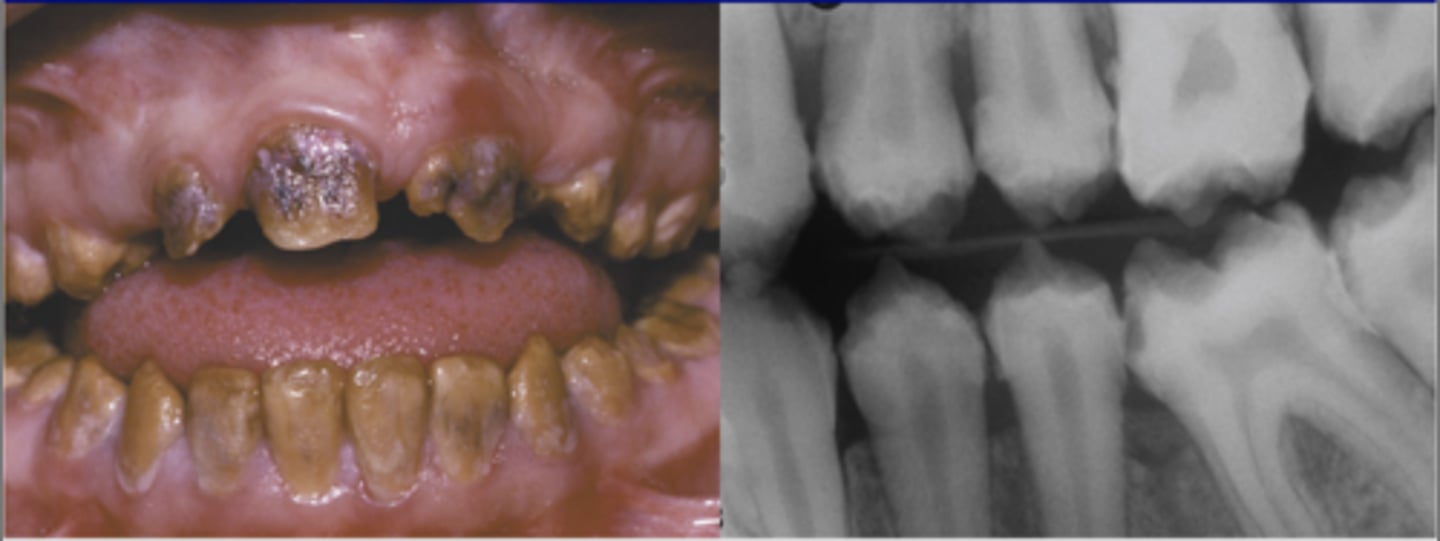
What are the clinical features of hypocalcified AI?
-normal amount of enamel
-decreased mineralization
-very soft; rapidly lost
-radiodensity like dentin
-yellow-brown/orange color → turns black (decay)
-normal shape at eruption → wears down quickly
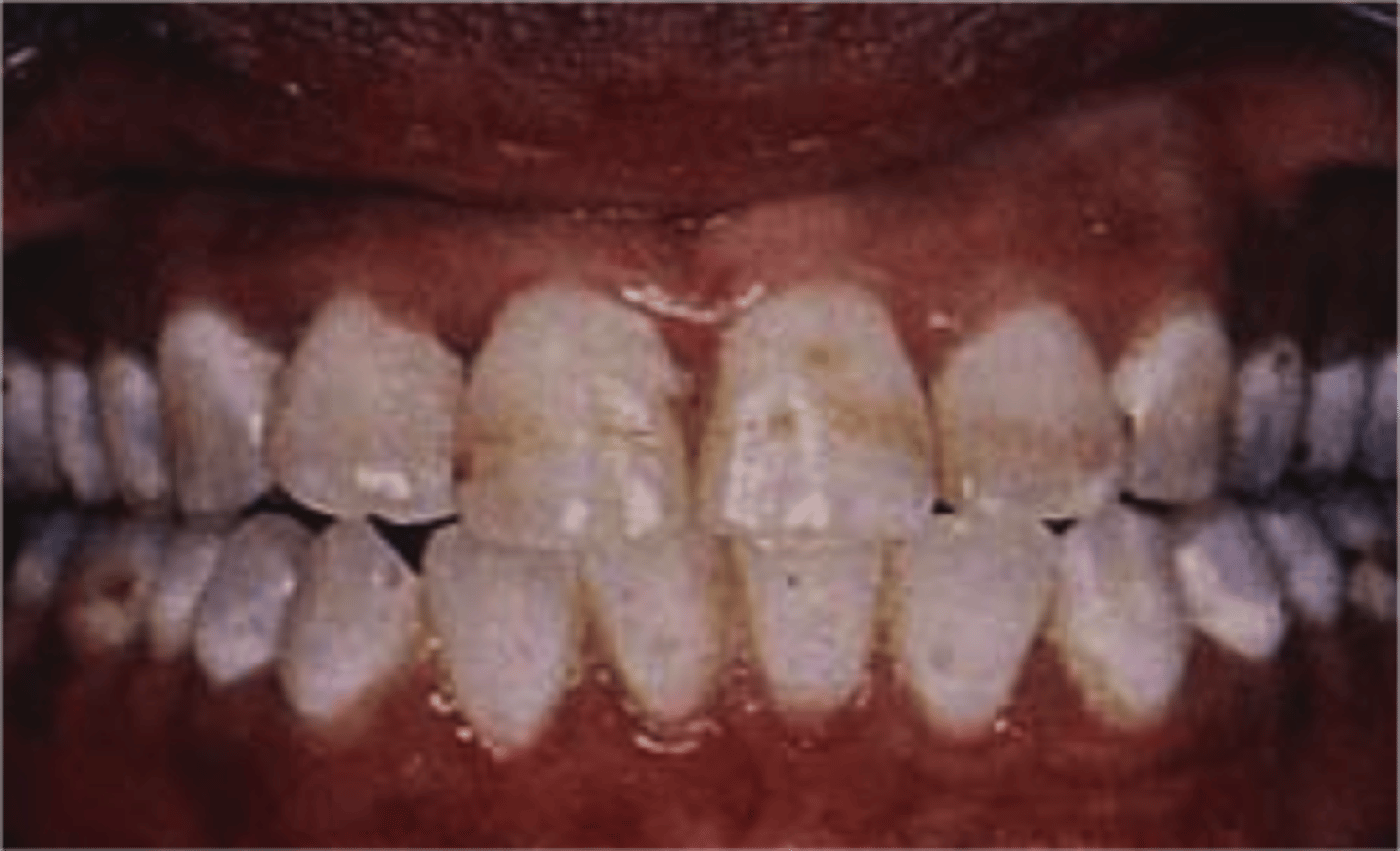
What are the clinical features of hypomaturation AI?
-normal amount of enamel
-decreased mineralization → abnormal crystallization (enamel rods don't form)
-harder than dentin
-radiodensity like dentin
-mottled - white/brown/yellow → "snow-capped" (white cusp tips)
-normal shape at eruption → enamel chips off of dentin
What is Dentinogenesis Imperfecta?
odontoblasts lay down defective dentin then regenerate
-3 types → I, II, III
What is the inheritance and clinical onset of Dentinogenesis Imperfecta?
-inheritance: autosomal dominant
-clinical onset: 6 months → when teeth erupt (both dentitions; primary more severely affected than permanent)
What are the clinical features of Dentinogenesis Imperfecta?
-Type I is associated with Osteogenesis Imperfecta (systemic collagen defect; abnormal bone)
**collagen defect = multiple bone fractures, blue sclera
-all teeth usually lost by age 30
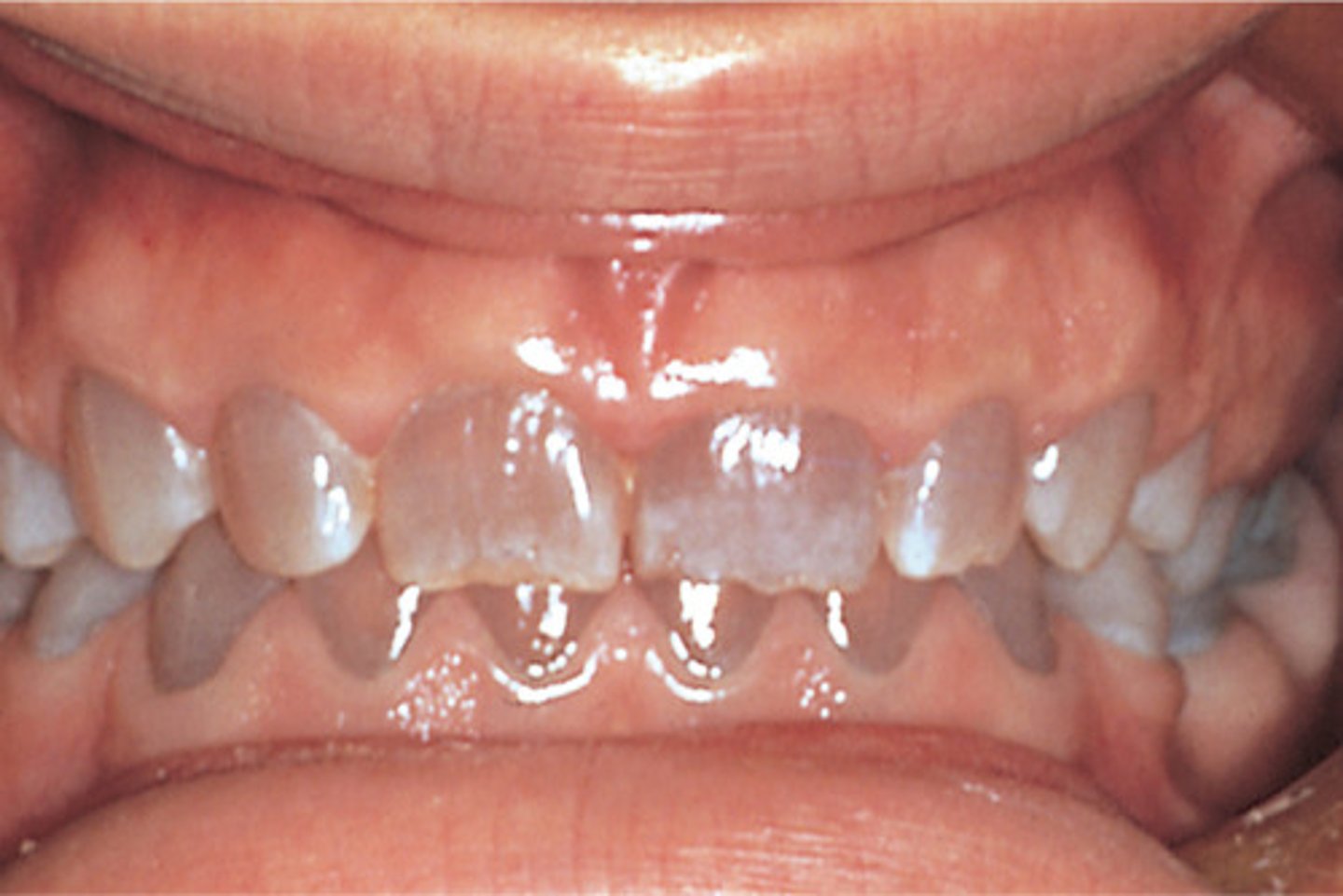
What are the oral features of Dentinogenesis Imperfecta?
-bulbous crowns
-bluish/translucent color of teeth
-enamel breaks off defective dentin = brown surface
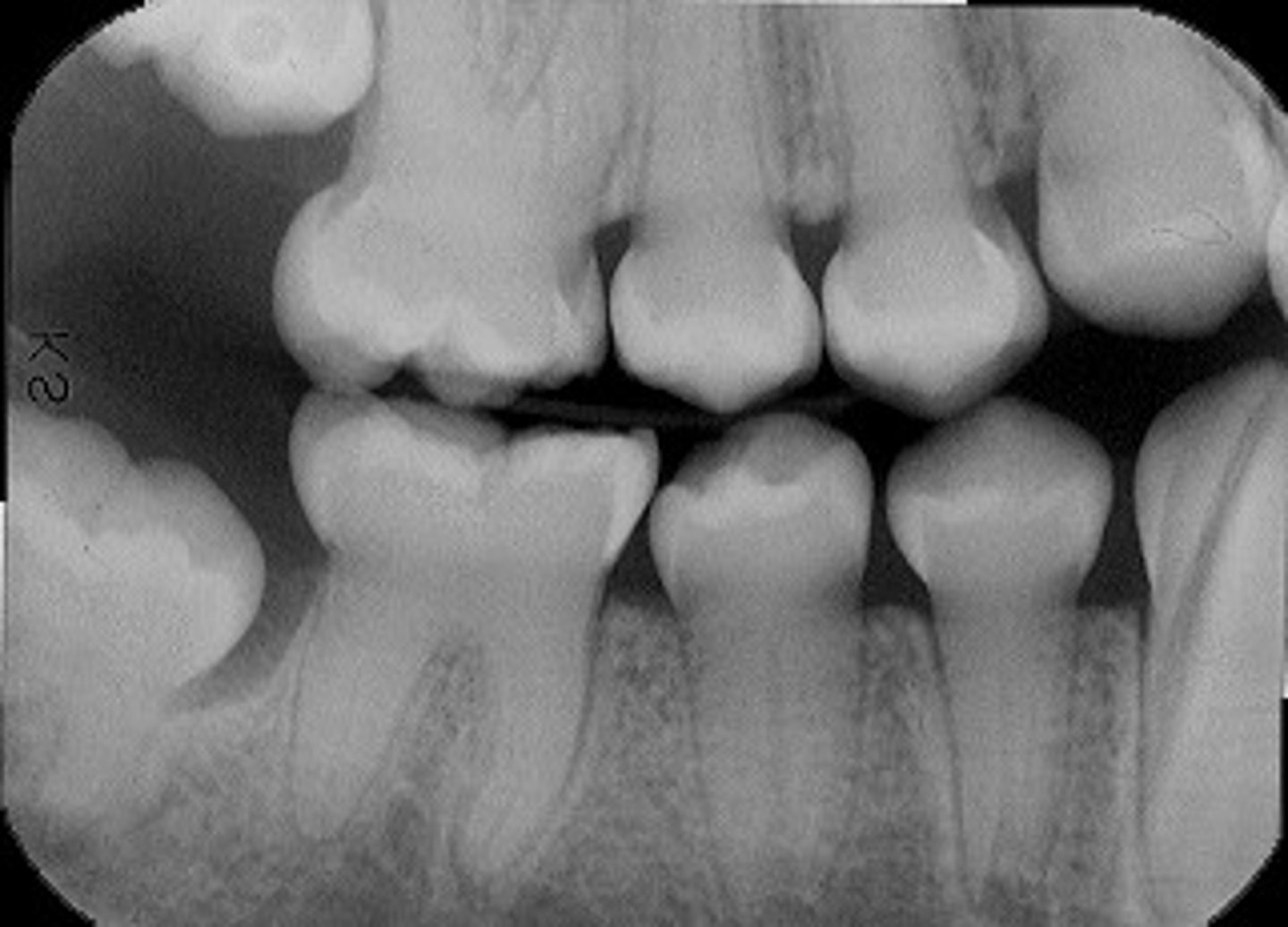
-on XR → no pulp/short roots/periapical radiolucencies
What is the inheritance and clinical onset of Dentin Dysplasia?
-inheritance: autosomal dominant
-clinical onset: 6 months → when teeth erupt (both dentitions)
What are the types of Dentin Dysplasia?
-Type I: Radicular Dysplasia
-Type II: Coronal Dysplasia
**Type I is more common than Type II
What are the treatment modifications of dentin dysplasia?
-meticulous oral hygiene = decreased pulp exposure
-RCT easier in Type II than Type I
Describe the oral features of Type I Dentin Dysplasia (Radicular Dysplasia):
-roots
-crown color
-crown shape
-pulp
-Roots → very short roots = "rootless"
-Crown color → normal
-Crown shape → normal
-Pulp → obliterated + large pulp stones
**MULTIPLE periapical radiolucencies
Describe the oral features of Type II Dentin Dysplasia (Coronal Dysplasia) in PRIMARY DENTITIONS:
-roots
-crown color
-crown shape
-pulp
-Roots → thin & tapered
-Crown color → amber translucency
-Crown shape → bulbous
-Pulp → obliterated
Describe the oral features of Type II Dentin Dysplasia (Coronal Dysplasia) in PERMANENT DENTITIONS:
-roots
-crown color
-crown shape
-pulp
-Roots → normal
-Crown color → normal
-Crown shape → normal
-Pulp → "thistle shape" +/- pulp stones