1.2.3 software development
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
analysis stage
stakeholders state what they require from the finished product
this information is used to clearly define the problem and the system requirements
requirements may be defined by
analysing strengths and weaknesses with current way this problem is being solved
considering types of data involved including inputs, outputs, stored data and amount of data
design stage
the different aspects of the new system are designed, such as
inputs: volume, methods, frequency
outputs: volume, methods, frequency
security features: level required, access levels
hardware set-up: compatibility
user interface: menus, accessibility, navigation
development stage
the design from the previous stage is used to split the project into individual, self-contained modules, which are allocated to teams for programming
testing stage
alpha testing
carried out in-house by the software development teams within the company
bugs are pinpointed and fixed
beta testing
carried out by end-users after alpha testing has been completed
feedback from users is used to inform the next stage of development
white box testing
a form of testing carried out by software development teams in which the test plan is based on the internal structure of the program
all of the possible routes through the program are tested
black box testing
a form of testing where the software is tested without the testers being aware of the internal structure of the software and can be carried out both within the company and by end-users
the test plan traces through inputs and outputs within the software.
implementation stage
once the testing stage has been used to make the appropriate changes to the software, it is installed onto the users’ systems
evaluation stage
after the implementation stage, the effectiveness of the software is evaluated against the system requirements defined at the analysis stage to evaluate its suitability in solving the problem
different criteria are considered, including robustness, reliability, portability and maintainability
maintenance stage
any errors or improvements that could be made to the software are flagged up by the end-users.
programmers will regularly send out software updates to fix any bugs, security issues or make any needed improvements
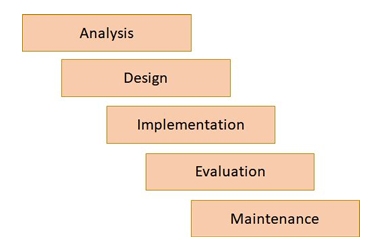
waterfall lifecycle
based on a series of stages which are completed in sequence, from start to finish
if a change needs to be made within a project being developed using the waterfall model, programmers must revisit all levels between the current stage and the stage at which a change needs to be made
this makes the model inflexible and so unsuitable to projects with changing requirements
this also means that users have little input as they are only involved at the very beginning and end of the waterfall lifecycle, during the analysis and evaluation stage
agile methodologies
collection of methodologies
focused on the idea that requirements will change during development
build on a series of iterations known as sprints
short period where a team has focused goals
easier to make improvements or changes to the software
the problem can be broken down into sections which are developed in parallel
extreme programming
framework
aims to produce high quality code
simplicity
communication
feedback
agile framework that encourages small regular iterative software releases
spiral model
risk driven development methodology
4 parts
determine objectives
identify and resolve risks
development and test
plan next iteration
develops porotypes with different requirements
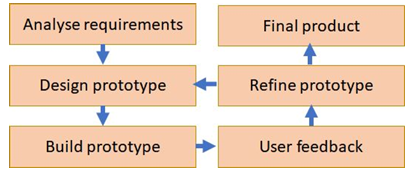
rapid application development
producing successive prototypes of software until a final version is produced
increasingly refined prototypes are made
get feedback
new requirements - new prototype
ADV waterfall
Straightforward to manage
clearly documented
DIS waterfall
Lack of flexibility
No risk analysis
Limited user involvement
ADV agile
Produces high quality code
Flexible to changing requirements
Regular user input
DIS agile
Poor documentation
Requires consistent interaction between user and programmer
ADV Extreme Programming
Produces high quality code
Constant user involvement means high usability
DIS extreme programming
High cost of two people working on one project
Teamwork is essential
End-user may not be able to be present
ADV spiral
Thorough risk-analysis and mitigation
Caters to changing user needs
Produces prototypes throughout
DIS spiral
Expensive to hire risk assessors
Small to medium projects with unclear initial requirements requiring excellent usability.
Lack of focus on code efficiency
High costs due to constant prototyping
ADV Rapid Application Development
Caters to changing user requirements
Highly usable finished product
Focus on core features, reducing development time
DIS Rapid Application Development
Poorer quality documentation
Fast pace may reduce code quality
waterfall lifecycle TELOS
the analysis stage includes a feasibility study in which designers evaluate the feasibility of the project using ‘TELOS’:
Technical: is the project possible considering the technology available and accessible
Economic: can the project be financed in the short-term and the long-term
Legal: can the project be solved within the law
Operational: can the project be successfully implemented and maintained
Scheduling: can the project be completed given the time available
writing and following algorithms
an algorithm is a set of instructions used to solve a problem
they are core to computer science and can be used to tackle a wide range of problems.
regardless of the problem, all good algorithms have certain key qualities
Inputs must be clearly defined - what is valid and what is invalid?
Must always produce a valid output for any defined input
Must be able to deal with invalid inputs Must always reach a stopping condition
Must be well-documented for reference
Must be well-commented so modifications can easily be m
uses of waterfall
static, low-risk projects which need little user input, such as a piece of general-purpose software
uses of agile
small to medium projects with unclear initial requirements
uses of extreme programming
small to medium projects with unclear initial requirements requiring excellent usability
uses of spiral
large, risk-intensive projects with a high budget
uses of rapid application development
small to medium, low-budget projects with short time-frames