Rad 350: Electromagnetism
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Magnetism
The ability of a material to attract iron, cobalt, or nickel
exists whenever electric charges move relative to other objects or relative to a frame of reference
When a charged particle is in motion, a magnetic force field perpendicular to the motion will be created
classification of magnets: natural
earth, iodestone
classification of magnets: artificial permanent magnets
horseshoe magnet, bar magnet, magnetic compass
classification of magnets: electromagnets
temporary magnets produced by means of an electric current
Magnetic states of matter: Non-magnetic
unaffected by a magnetic field
Magnetic states of matter: Diamagnetic
weakly repelled from both poles
Magnetic states of matter: Paramagnetic:
weakly attracted to both poles
Magnetic states of matter: Ferromagnetic:
can be strongly magnetized
FERROMAGNETIC MATERIALS
Iron, nickel, or alloys containing either or both of these elements
When a magnet is brought near to ferromagnetic materials the atoms in the material become lined up (temporarily magnetized) and a magnetic force is produced
ELECTRON SPIN
The nature of magnetic materials is such that the orbital electrons of their atoms spin in predominately one direction
rotation creates a magnetic field
SPIN MAGNETIC MOMENT
A magnetic field is established when electrons spin on their axes
MAGNETIC DOMAIN
When these small magnetic dipoles form groups of similarly aligned atoms
Alignment of the dipoles= acts like a magnet
DIPOLES
Groups of atoms with their net magnetic field moving in the same direction
DOMAINS
An accumulation of dipoles where all are aligned in the same direction
How do you create a magnet
When magnetic materials are placed in a strong magnetic field, the domains align with the external field
NON-MAGNETIC:
Atoms are not magnetic, and no domains are formed, cannot be magnetized
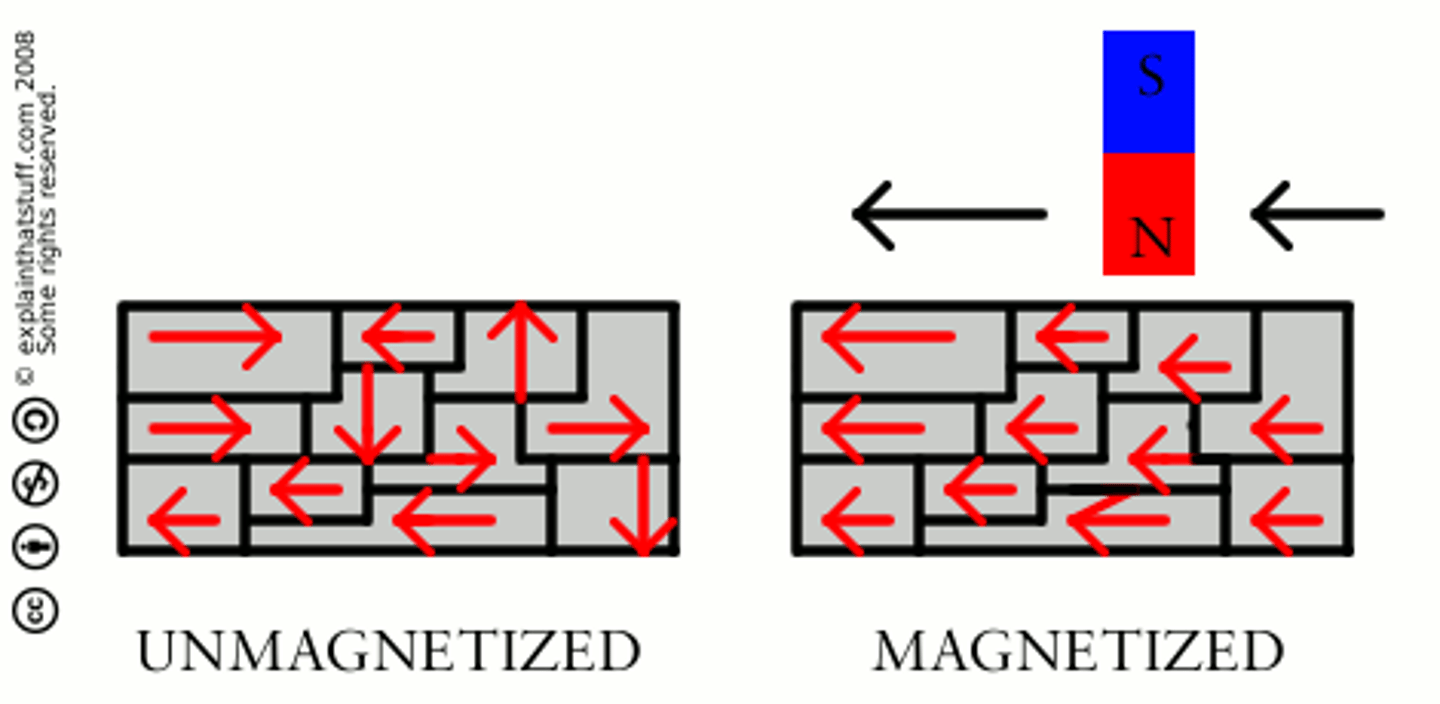
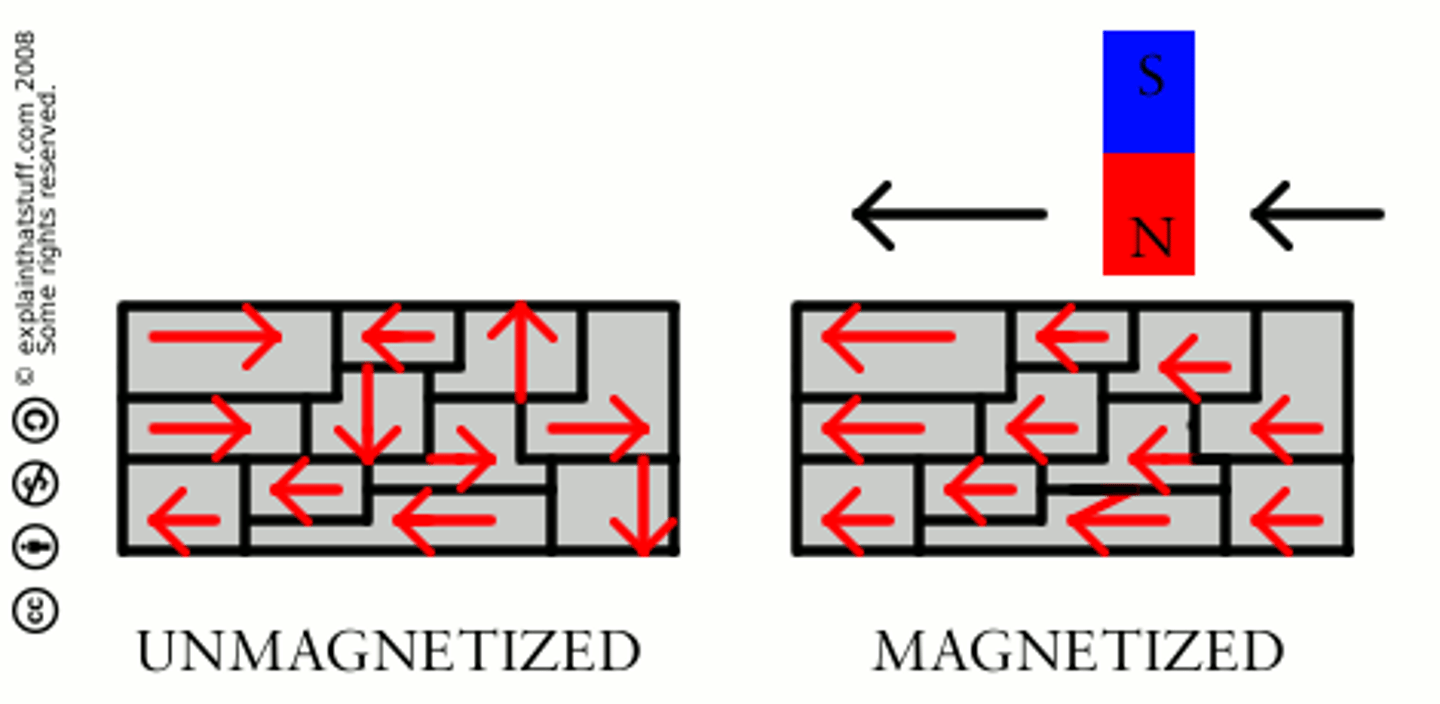
NON-MAGNETIZED MATERIAL:
Domains are in a state of random disorder, but can be aligned to become a magnet
MAGNETIZED MATERIAL:
The domains are aligned in orderly fashion, where poles are facing the same direction
MAGNETIC FIELDS (flux lines)
¨Lines of force flowing through the magnet and to the outside of the magnetic material, forming a three dimensional field
The strength of the magnetic field is measured in the SI unit
tesla (T)
LAWS OF MAGNETISM
Every magnet has two poles (North and South)
Like magnetic poles repel, unlike poles attract
Magnetic field lines are closed loops
A changing magnetic field can produce a current
A changing electric field can produce a magnetic field
MAGNETIC INDUCTION
¨The process by which a material becomes magnetized by the temporary orientation of the dipoles
ELECTROMAGNETISM
A form of energy resulting from electric and magnetic disturbances is space
Any charged motion induces a magnetic field
ELECTROMAGNET
A current carrying coil of wire (solenoid) wrapped around an iron core, which intensifies the induced magnetic field
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
Moving a conductor (such as a copper wire) through a magnetic field induces an electric current in that conductor
Faraday's Law
Varying magnetic field intensity induces an electric current
INCREASING THE VOLTAGE: HOW?
Fashioning the conductor into a coil and passing it through a magnetic field
¤Increase the number of coils
Increase the strength of the magnetic field
Increase the speed which the conductor is passed through the magnetic field
Factors for faraday's law
The strength of the magnetic field
The speed of the motion between lines of force and the conductor
The angle of the conductor to the magnetic field
The number of turns in the conducting coil
FLEMING HAND RULES: RIGHT HAND THUMB RULE
If the right hand is used to grasp a wire, the thumb is in the direction of current flow, the fingers indicate direction of magnetic field lines
FLEMING HAND RULES: RIGHT-HAND GENERATOR RULE
If the thumb points in the direction the conductor is moving and the index finger points in the direction of magnetic lines of force field, the middle finger will indicate the direction of conventional current
FLEMING HAND RULES: LEFT HAND MOTOR RULE
States that if the index finger points in the direction of the magnetic lines of force field and the middle finger points in the direction of the conventional current, the thumb will indicate the direction the conductor will move
Electric motor:
an electric current produces a mechanical motion
Generator or Dynamo:
converts the mechanical energy of the motion to electrical energy
transformers:
changes the intensity of alternating voltage and current