Genetics - Chapter 8
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Like traditional vaccines, DNA vaccines stimulate the immune system to recognize pathogens, such as viruses.
True
In the early 20th century, scientists believed that protein, not DNA, carried the genetic information.
True
Griffith's experiments on pneumonia were the first to show that traits could be passed from one bacterium to another via the transforming factor.
True
DNA was confirmed to be the carrier of genetic information by the experiments of two groups: Avery, MacCleod, and McCarty, and Hershey and Chase.
True
Hydrogen bonds are defined as a pair of electrons shared between two atoms.
False
Nucleotides are the building blocks of proteins.
False
Watson and Crick used data from other scientists as they modeled their three dimensional structure of DNA.
True
DNA is a single stranded molecule, with equal numbers of purines and pyrimidines.
False
A recent U.S. Supreme Court decision invalidated the premise that companies can patent human genes.
True
RNA and DNA have identical structures and functions.
False
Following semiconservative DNA replication, the newly copied DNA molecule is composed of two new DNA strands.
False
DNA replication occurs when the cell is preparing for cell division.
True
Understanding the organization of chromosomes in the nucleus is important for understanding gene expression, DNA replication, and homologous pairing during meiosis.
True
Because telomerase is present in most cancer cells − but not normal cells − inhibiting telomerase may be an effective way to treat cancer.
True
After DNA replication, sister chromatids attach at their telomeres.
False
nuclein
extracted and purified from the nucleus of a cell which contains DNA
transformation
how genetic information is passed between cells by DNA molecules
transforming factor
historic term now known to be DNA
Genetic traits can be transferred between bacterial strains by DNA.
True
DNA, and not proteins, carries genetic information.
True
ribonucleic acid (RNA)
a single stranded nucleic acid where thymine is replaced by uracil
nitrogen-containing base
can be either a purine (adenine and guanine) or pyrimidine (thymine, cytosine, and uracil)
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
double stranded helix that carries genetic information
Nucleotide
building block of DNA and RNA - a base, a sugar and a phosphate group
Hydrogen bond
weak bond between hydrogen and another atom
DNA is made up of four types of nucleotides with the following bases: adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine.
False
Nucleotides are linked together to form chains of polynucleotides - these have different chemical groups at each end, meaning that strands are organized in opposite (antiparallel) direction.
True
S represents
deoxyribose
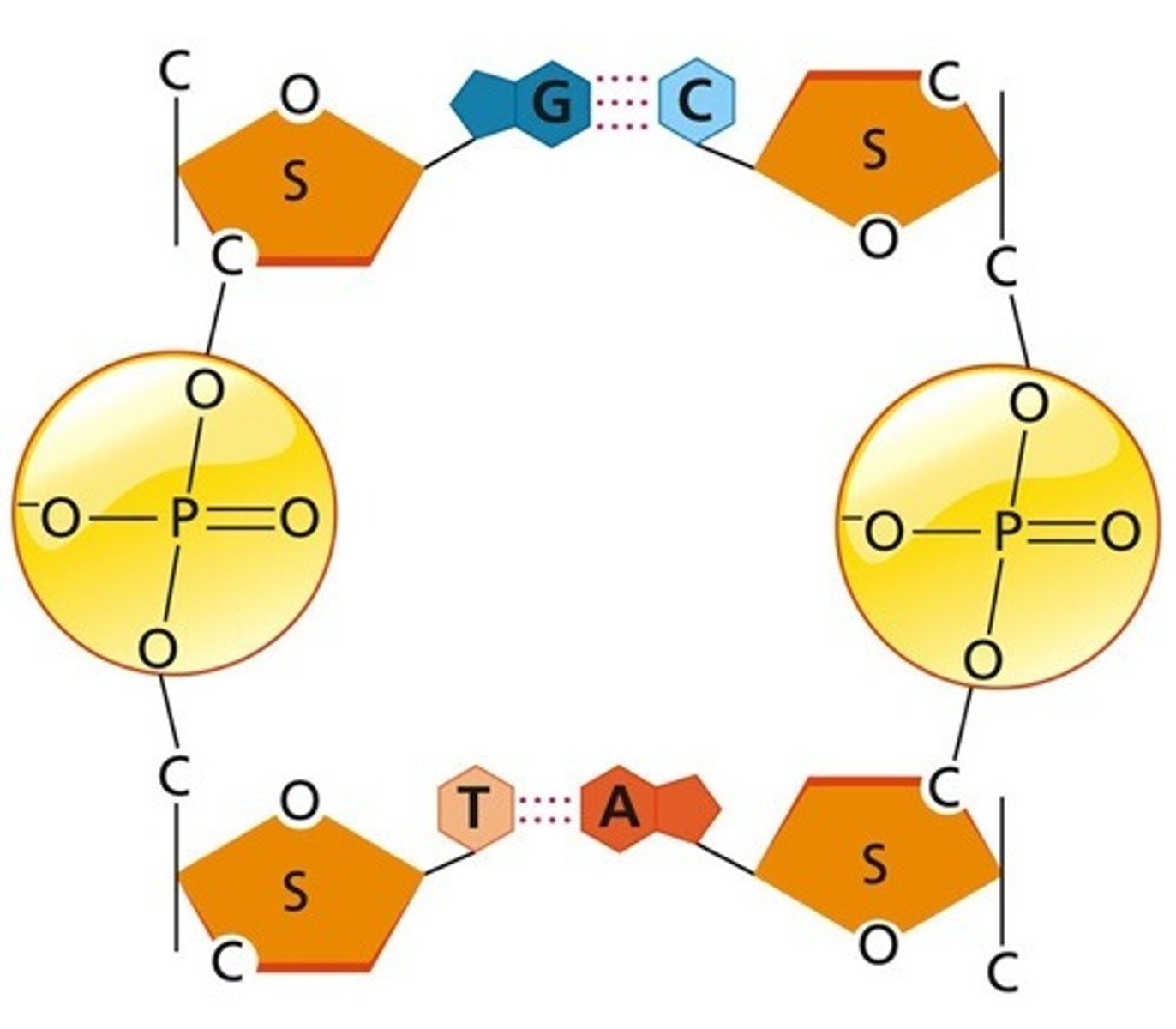
The straight lines between the S and the PO4 molecule represent
covalent bonds
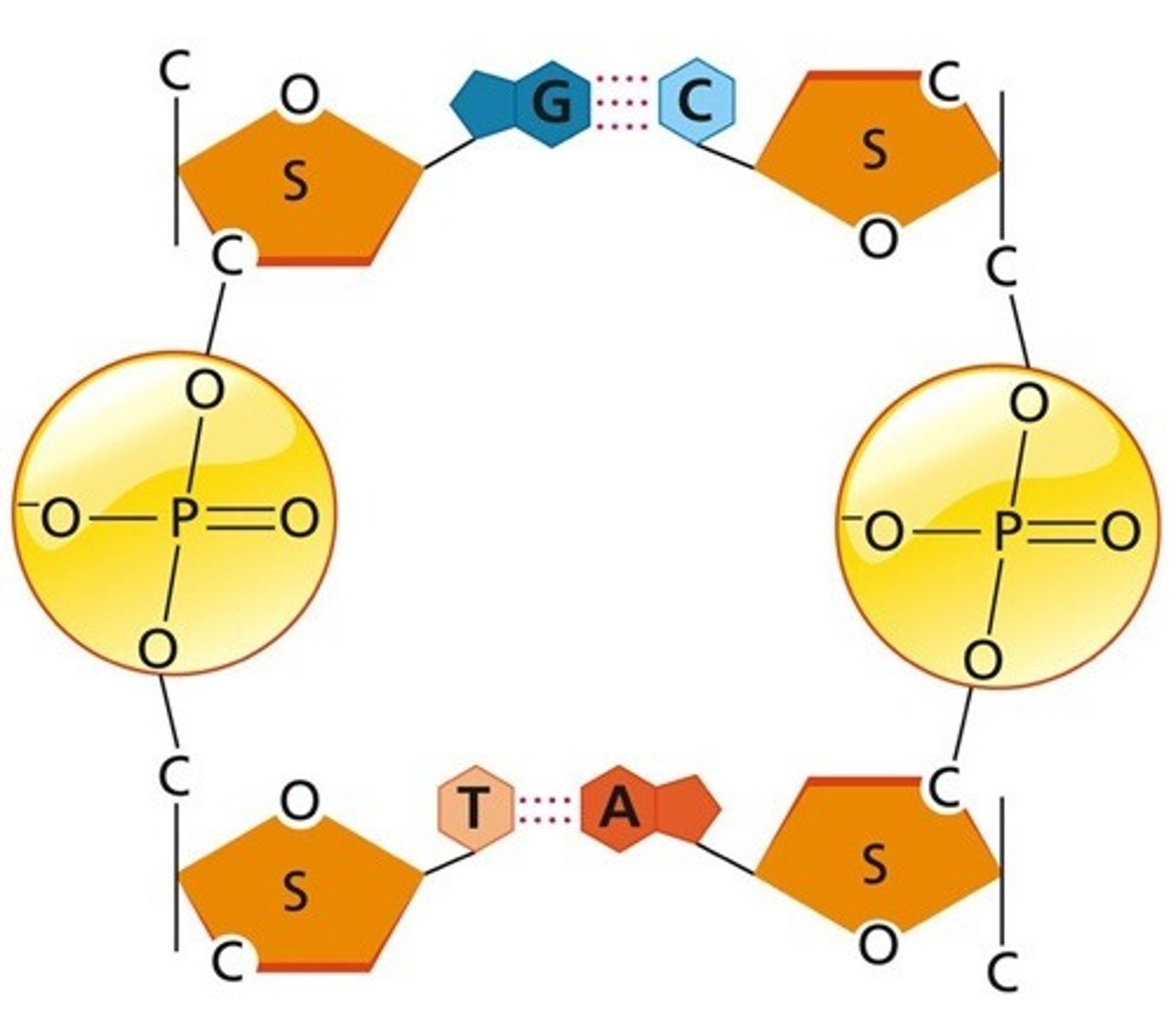
T and A represent
bases
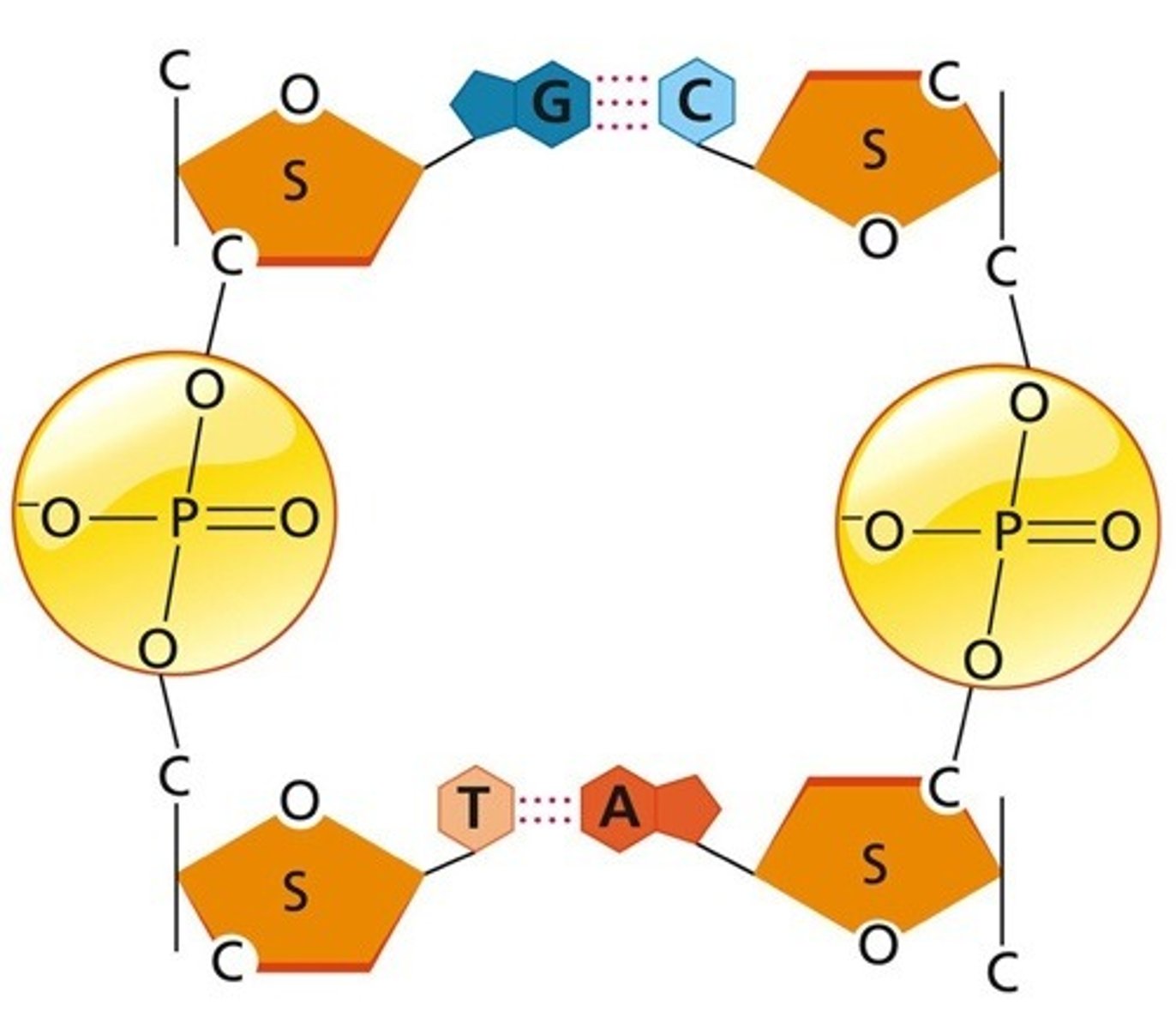
The dotted lines between A and T, and C and G, represent
Hydrogen bonds
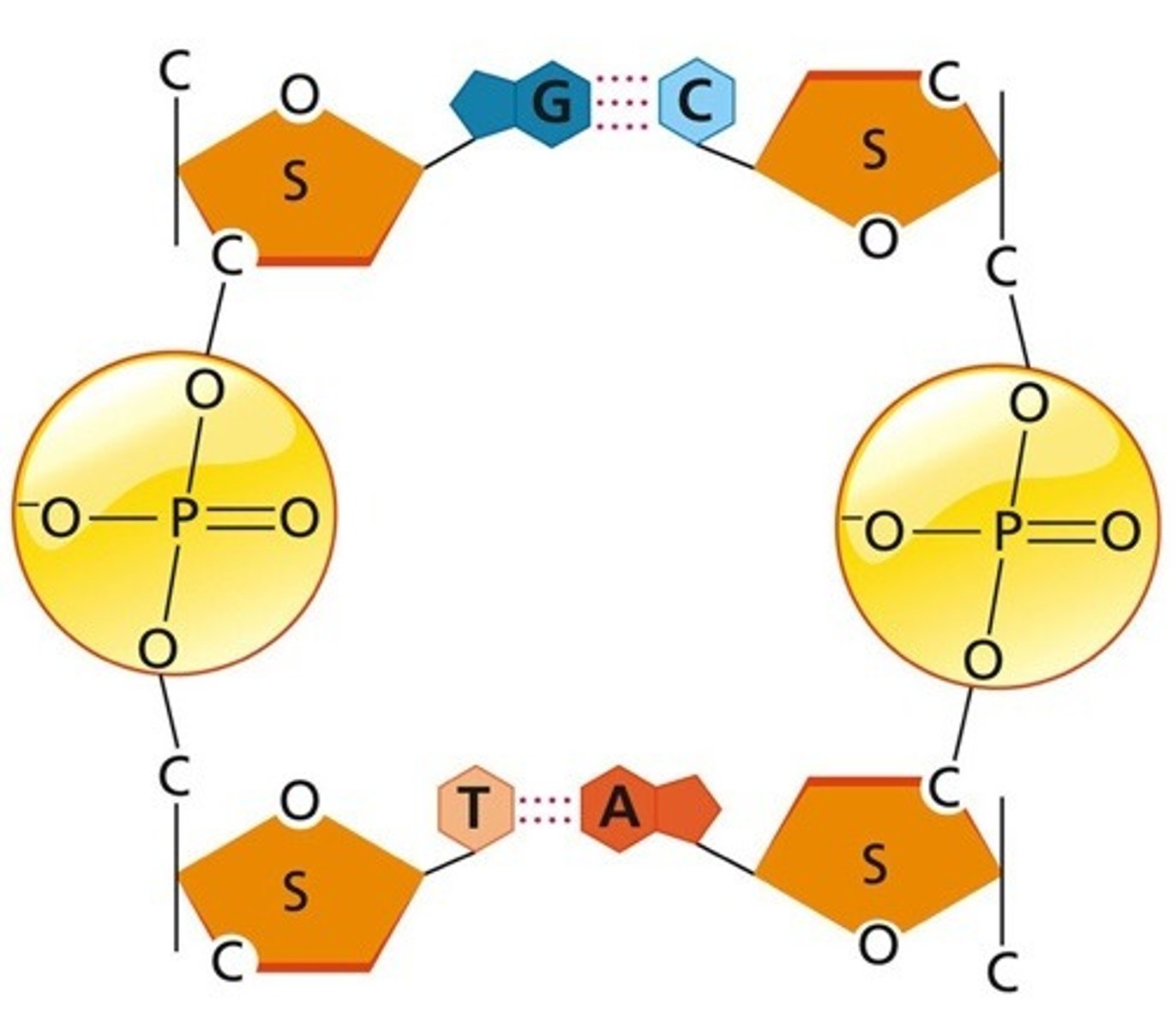
Why is the sugar molecule in one DNA strand pointing up and the sugar on the opposite strand pointing down?
because the strands run in antiparellel direction
The bases of the polynucleotide chain of DNA form the rungs of this ladder-like molecule.
True
A always pairs with G and C always pairs with T.
False
DNA is one form of nucleic acid, RNA is another. RNA is found only in the cytoplasm.
False
In RNA the base uracil takes the place of thymine, so A pairs with U.
True
RNA participates in the synthesis of proteins, but not in the regulation of gene expression.
False
semiconservative replication
one old strand is conserved in each new molecule and one new strand is synthesized
okazaki fragments
short DNA sequences added to a template strand whose direction is 3' to 5'
DNA polymerase
DNA polymerase
DNA replication
Step 1: the double helix starts to be unwound at sites along the chromosome called "origins of replication" and the hydrogen bonds are broken
Step 2: DNA polymerase reads the nucleotide sequence of a template strand that links nucleotides together along the 5' to 3' direction of the template
Step 3: DNA polymerase also reviews the newly synthesized sequence as it moves along the template, removing any incorrect base pairs and inserting correct ones
Step 4: A newly synthesized strand is made continuously only on one template strand since nucleotides can only be added at a 3' end. the newly synthesized strand on the other template is made in short stretches involving Okazaki fragments
Step 5: Once a number of short stranded segments are assembled, DNA ligase passes over them to seal/glue them into a continuous form
Step 6: Proteins now wind the template and the newly formed strands together to form a closed DNA double helices
A double stranded DNA molecule combined with proteins - visible as thread-like structures in nuclei.
chromatin
In order to fit the long polynucleotide double helix of DNA into the nucleus it must be tightly compacted. To do this, DNA is wrapped around these proteins.
histones
These bead-like structures of DNA and histones are known as _______
nucleosomes
telomere
found at the end of each chromosome and made up of repeated short sequences of DNA
centromere
found at the constricted region of a pair of chromosomes where sister chromatids attach
telomerase
an enzyme that makes extra repeats of short DNA segments so that these end regions are constant from one cell division to the next
The DNA in the SARS DNA vaccine encodes a(n) ________ protein.
a. immune
b. viral
c. human
d. bacterial
e. mouse
b. viral
The experiments of Friedrich Miescher succeeded in ________.
a. showing that mice can be infected with pneumonia
b. proving that only protein had the complexity to be the genetic material
c. proving that DNA was the genetic material
d. isolating the first bacterial virus
e. isolating the first cellular organelle
e. isolating the first cellular organelle
Griffith's experiments identified the process of ________ by the ________ in bacteria, which allowed non-virulent R strain Streptococcus pneumonia cells to acquire infectious traits from heat-killed S strain cells.
a. viral infection; transforming factor
b. transformation; nuclein
c. transformation; transforming factor
d. infection; bacteriophage
e. transformation; protein
c. transformation; transforming factor
Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty revealed that DNA was the genetic material by showing ________; Hershey and Chase reached the same conclusion by showing that ________.
a. DNA is the transforming factor in bacteria; only bacteriophage DNA enters bacteria during infection
b. DNA is the transforming factor in viruses; DNA carries genetic information in bacteria
c. proteins control the synthesis of gene products; bacteriophage proteins enter bacteria
d. DNA is the transforming factor in bacteria; radioactivity kills bacteriophages
e. nuclein contains DNA; mice are vulnerable to Streptococcus pneumonia infection
a. DNA is the transforming factor in bacteria; only bacteriophage DNA enters bacteria during infection
DNA is a polynucleotide composed of ________.
a. adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil
b. adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine
c. pyrimidines only
d. hydrogen bonds linking nucleotide building blocks
e. purines only
b. adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine
Strong chemical bonds are known as ________, while weak chemical interactions are known as ________.
a. element interactions; simple bonds
b. covalent bonds; hydrogen bonds
c. hydrogen bonds; covalent bonds
d. nucleotide bonds; atomic bonds
e. covalent bonds; natural bonds
b. covalent bonds; hydrogen bonds
According to Rosalind Franklin's X-ray diffraction data, DNA has ________.
a. nitrogen bases on the outside, and phosphate groups on the inside, of the double helix
b. an equal amount of cytosine and guanine
c. one polynucleotide strand
d. an equal amount of adenine and thymine
e. a helical structure with a constant diameter
e. a helical structure with a constant diameter
The complementary base pairing in the double stranded DNA structure explains how ________.
a. DNA is copied before each cell division
b. the diameter of the helix is kept constant
c. sister chromatids separate
d. genetic information is carried in the phosphate groups
e. covalent bonds hold the polynucleotide strands together
a. DNA is copied before each cell division
Biotechnology companies argued unsuccessfully that human genes should be patentable because ________.
a. human genes are not found in nature
b. by isolating human genes from the body, they are creating something not found in nature
c. they invented the human genes
d. disease causing genes are not found in nature
e. diagnostic tests based on human genes are patentable
b. by isolating human genes from the body, they are creating something not found in nature
The structure of RNA differs from that of DNA in that it has a ________ sugar and ________ instead of thymine.
a. ribose; guanine
b. ribose; adenine
c. deoxyribose; cytosine
d. ribose; uracil
e. deoxyribose; uracil
d. ribose; uracil
Semiconservative DNA replication is possible because the two polynucleotide strands ________.
a. are held together by hydrogen bonds
b. have identical sequences
c. are complementary
d. are composed of Okazaki fragments
e. are copied at different times during the cell cycle
c. are complementary
During DNA replication, ________ synthesizes one continuous polynucleotide from one DNA strand and a series of shorter fragments from the other, while ________ joins the short fragments together.
a. RNA polymerase; DNA ligase
b. DNA polymerase; DNA ligase
c. DNA polymerase; unwinding enzymes
d. DNA ligase; DNA polymerase
e. a sister chromatid; a centromere
b. DNA polymerase; DNA ligase
Chromatin is composed of ________.
a. DNA and RNA
b. DNA and nucleotides
c. DNA and proteins
d. chromatids and centromeres
e. centromeres and kinetochores
c. DNA and proteins
What is the function of centromeres?
a. Centromeres delineate chromosome territories in the nucleus.
b. Spindle fibers attach to centromeres during cell division.
c. The centromeres shorten with each cell division.
d. Centromeres prevent the shortening of telomeres.
e. DNA polymerase begins DNA replication at the centromeres.
b. Spindle fibers attach to centromeres during cell division.
Telomerase is active only in ________ and functions to ________.
a. centromeres; attach spindle fibers to kinetochores
b. dividing cells; replicate DNA
c. eggs, sperm, and most cancer cells; maintain telomere length
d. chromosome territories; maintain telomere length
e. nucleosomes; compact chromosomes
c. eggs, sperm, and most cancer cells; maintain telomere length
The basic building block of DNA and RNA is a(n) ____.
a. sugar-phosphate backbone
b. ribose sugar
c. nitrogenous base
d. amino acid
e. nucleotide
e. nucleotide
In the Watson-Crick model of DNA structure, the polynucleotide chains ____.
a. are oriented in the same direction
b. form covalent bonds between uracil and adenine
c. are of unequal length
d. are oriented in opposite directions
e. are arranged with the bases forming the backbone of the helix
d. are oriented in opposite directions
DNA vaccines ____.
a. have been created but are ineffective
b. use RNA to assist in the transformation process
c. show promise in animal studies and are now in clinical trials
d. sometimes infect the subject with the disease it's attempting to fight
e. have been approved by the government to fight several diseases
c. show promise in animal studies and are now in clinical trials
After contracting SARS, about ____ percent of the infected died.
a. 50
b. 10
c. 25
d. 75
e. 100
b. 10
The search for a(n) ____ treatment led to the discovery that DNA carries genetic information.
a. influenza
b. SARS
c. pneumonia
d. AIDS
e. tuberculosis
c. pneumonia
The sugar in RNA nucleotides is ____.
a. sucrose
b. dextrose
c. ribose
d. glucose
e. deoxyribose
c. ribose
DNA polymerase catalyzes the synthesis of ____.
a. proteins
b. histones
c. DNA
d. ribose
e. nucleosomes
c. DNA
Telomeres are short DNA sequences ____.
a. that signal transcription to begin
b. repeated along the backbone of a DNA molecule
c. located at each end of a chromosome
d. located in the middle of a chromosome
e. that code for genetic traits
c. located at each end of a chromosome
Histones are the ____.
a. initiators of DNA replication
b. major class of proteins in chromatin
c. cause of SARS
d. molecules that prevent strong hydrogen bonding
e. genes that encode for deoxyribose
b. major class of proteins in chromatin
Bacteriophages are viruses that ____.
a. interfere with DNA replication in the cytoplasm of cells
b. infect and copy themselves inside bacterial cells
c. produce histones
d. catalyze bacterial reproduction
e. attach to bacterial cells and extract bacterial DNA
b. infect and copy themselves inside bacterial cells
In the early 1950s, James Watson and Francis Crick ____.
a. were awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine or Physiology
b. began to work out the structure of DNA by organizing the information about DNA that was already available
c. isolated two strains of S. pneumoniae and used them to further research the structure of DNA
d. produced X-ray diffraction photographs from highly purified DNA samples
e. combined all of their previous research in order to explain the structure of DNA
b. began to work out the structure of DNA by organizing the information about DNA that was already available
Once the strands of DNA are separated, the enzyme DNA polymerase ____ and links nucleotides together.
a. reads the nucleotide sequence of the template strand
b. transforms the template strand to either 3' or 5'
c. transforms adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine
d. unwraps the DNA from the nucleosomes
e. folds the bases back on themselves
a. reads the nucleotide sequence of the template strand
Friedrich Miescher, after he began to study the chemical composition of the nucleus, was one of the first to ____.
a. isolate DNA and propose its structure
b. discover that the nucleus contained DNA but no proteins
c. isolate and purify a cellular organelle
d. discover that human and mice chromosome chemistry differs greatly
e. propose the nuclear structure of the H5N1 virus
c. isolate and purify a cellular organelle
The chemical formula for glucose, C6H12O6, represents ____ atom(s) and ____ molecule(s).
a. 3; 6
b. 12; 12
c. 24; 1
d. 3; 3
e. 1; 24
c. 24; 1
Purines and pyrimidines are two classes of organic bases found in ____.
a. phosphates
b. fats
c. sugars
d. nucleic acids
e. carbohydrates
d. nucleic acids
SARS symptoms include ____.
a. eye pain, loss of vision, and headaches
b. heart arrhythmia, kidney failure, and calcium depletion
c. liver cirrhosis and difficulty swallowing
d. brittle bones and rash
e. high fever, headaches, and respiratory problems
e. high fever, headaches, and respiratory problems
Adenine and guanine are nitrogen-containing bases found in nucleic acids.
True
The H5N1 influenza killed more than 50% of those infected.
True
In the early twentieth century, most scientists believed that only nucleic acids were complex enough to carry genetic information.
False
Rosalind Franklin did not share a part of the 1962 Nobel Prize for Medicine or Physiology because she had died four years earlier.
True
The process of transferring genetic information between bacterial cells is accomplished with a transformation factor called DNA.
True
_______ is spread by droplets produced when an infected person sneezes or coughs.
SARS
The sugar found in DNA is a(n) _____
deoxyribose
In many organisms, ______ functions to transfer genetic information from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
RNA
A(n) _______ is made up of a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base.
nucleotide
Cytosine, uracil, and thymine are single-ringed nitrogen-containing organic bases called _____
pyrimidines
The name of the enzyme that replicates DNA is ______
DNA polymerase
Sugars and phosphates are held together in a DNA molecule by a(n) _______ bond.
covalent
The type of chemical bond that holds together adenine and thymine in the middle of a DNA molecule is a(n) ________ bond.
Hydrogen
The woman scientist who made a major contribution to the discovery of the structure of DNA was _______
Rosalind Franklin