Economic models - Chapter 2 - ECON100
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Economic models
The Production possibility frontier
Comparative advantage
The circular flow diagram
The Production possibility frontier
A diagram that shows the combinations of two goods that are possible for a society to produce at full employment
Shows all combinations of two goods that an economy can possibly produce given its resources and technology
Needs to be feasible and efficient
The points on the line (PPF) are feasible and efficient
The points below the line are inefficient
The points above the line are not feasible
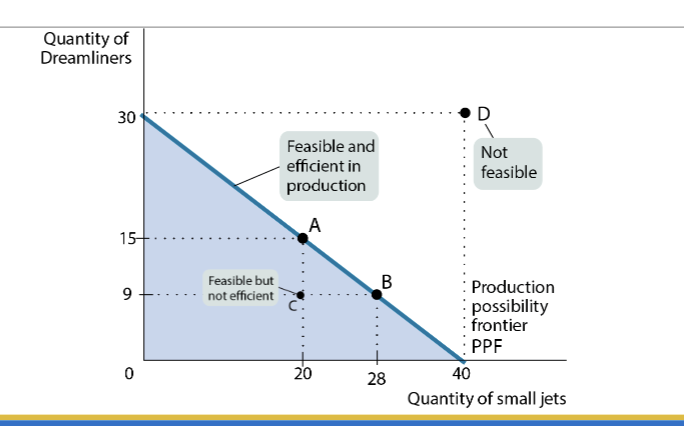
Efficiency
An economy is efficient when there are no missed opportunities
It is inefficient in production, if it can produce more of some goos without reducing others
Opportunity cost
What must be given up in order to get an extra good
Opportunity cost of A = change in quantity of B/change in quantity of A
Comparative advantage
It makes sense to produce things you are especially good at producing and buy everything else from others
A country has comparative advantage in producing a good or service if its opportunity cost of producing a good or service is lover than for other countries
An individual has comparative advantage in producing a good or service if his or her opportunity cost of producing a good or service is lower than for other people
Having less opportunity cost means you are ___ at production
Better
Whoever has less opportunity cost has the comparative advantage.
Comparative advantage and gains from trade
Since each country has a different opportunity cost, it makes sense to specialize and trade
Through specialization and trade, both countries produce more and consume more than if they were self-sufficient
Just because a country is efficient at producing both goods on a PPF, does not mean they are better off without trade
Barter
Exchanging goods and services for other goods or services without using money.
Circular flow diagram
Trade takes the form of barter when people directly exchange goods or services that they have for other goods and services that they want
Represents the transactions in an economy by flows around a circle
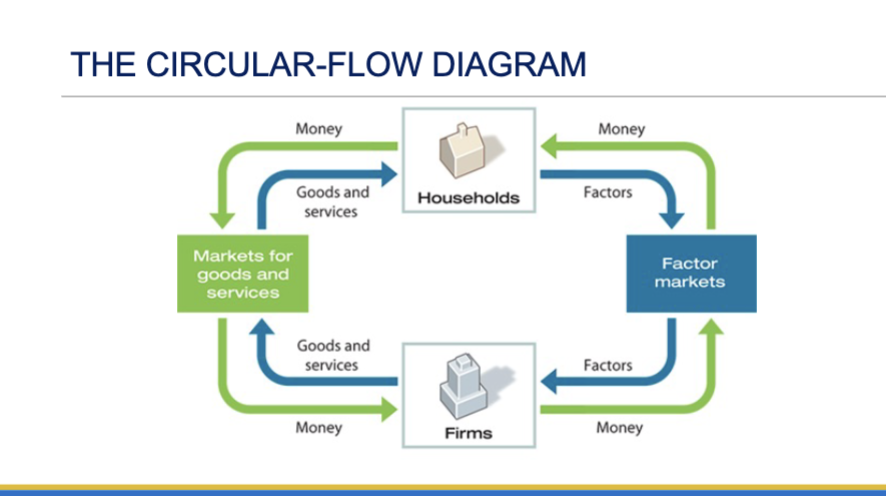
Household (circular flow diagram)
A person or group of people that share their income
Firm (circular flow diagram)
An organization that produces goods and services for sale
Factor Markets (circular flow diagram)
Where firms buy the resources they need to produce goods and services (land, labor, physical capital, human capital)
Income distribution (circular flow diagram)
The way in which total income is divided among the owners of various factors of production
Positive economics
Branch of economic analysis that describes the way economics actually works
Normative economics
Makes prescriptions about the way the economy should work
example: If COVID-19 didn’t happen, what would have happened to the economy now?
Forecast
Simple prediction of the future