MedChem Lecture 1
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
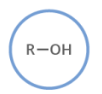
name this structure.
alcohol
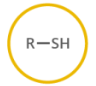
name this structure.
thiol
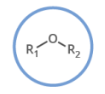
name this structure.
ether
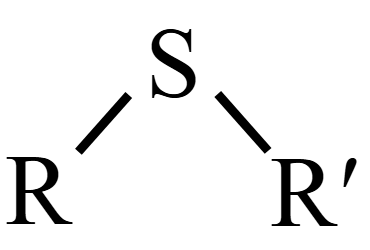
name this structure.
thioether
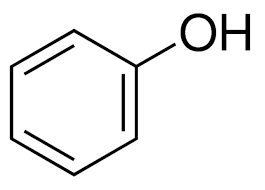
name this structure.
phenol
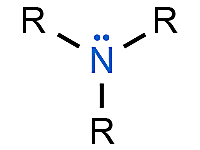
name this structure.
amine
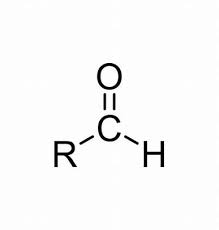
name this structure.
aldehyhde
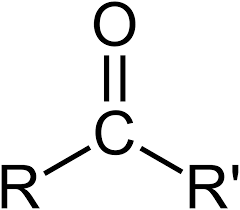
name this structure.
ketone
what bond does an alcohol group form? what is the significance?
h-bond → increases water solubility
what happens when an alcohol group is oxidized?
becomes a ketone.w
what metabolic transformations can an alcohol group allow for?
oxidation (loss of electrons to gain energy) and conjugation (linkage)
are thiols larger or smaller than alcohols?
thiols are larger because sulfur is larger than oxygen
what bonds do thiols form? what significant properties result from this?
van der waals bonds → no increase in water solubility, but better for hydrophobic interactions
what metabolic transformations would thiol allow for?
nucleophilic transformations → thiols donate their electrons to create bonds
are thiols commonly found in drugs? why or why not?
no → easier to oxidize, which allows for easy formation of covalent bonds between the drug and itself or a targer. high levels of toxicity when off target.
what is the role of Mesna?
Mesna can be used ot decrease toxicity of electrophilic drug metabolites by competeting with cystines in the body for bonds with the metabolites.
are ethers stable?
yes, except for when strained
what amino acids are alcohols found in?
serine and threonine
what amino acids are thiols found in?
cystine
what amino acids are ethers found in?
none.d
do ethers particpate in h0bond formation?
not directly. they don’t form h-bonds but can particpate as an acceptor.
are thioethers more hydrophobic or hydrophilic than ethers?
more hydrophobic → can not form hydrogen bonds
what are the primary interactions of thioethers?
van der waals
can thioethers be oxidized?
yes, metabolicly. they form sulfoxides.
what amino acids are thioethers found in?
methionine
what amino acids are phenols found in?
tyrosine
are phenols hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
hydrophobic → can form H-bonds using OH groupwha
what interactions do phenols participate in?
h-bonds and van der waals
are phenols more or less water soluble that alcohols? why?
more water soluable → they are more acidic, and therefore easier to ionize.c
can phenols be oxidized?
yes, make quinone electrophiles.
what amino acids have amines?
lysine
do histidine and arginine have amine groups? why or why not?
no → they have differing reactivities than amine groups
what forms can amines take and what are the associated propeties?
neutral and positive forms. neutral forms are hydrophobic and can cross the cell membrane, positve forms are water soluable. neutral form can also serve as a nucleophile
what is a shared property of aldehydes and ketones?
they are both H bond acceptors with high electrophilic tendencies
what is the most likely reaction to occur between a aldehyde/ketone group and an amine group
the nucleophilic amine is likely to attack the electrophilic ketone/aldehyde to form a bond.
are aldehydes common in drugs?
no. they have high instability and reactivity.a
are ketones common in drugs?
they can be used, but often have to be sterically-hindered to reduce reactivity.