Chemistry of life
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is electronegativity?
The ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itsself.
What happens to atoms with high electronegativity?
They can attract electrons and become negative ions, or if they are part of a molecule they can have a partial negative charge.
What happens to atoms with low electronegativity?
They can release electrons and become positive ions
What happens in a nonpolar covalent bond?
The electrons are shared equally
What happens in a polar covalent bond?
The electrons are shared unequally
What happens in an ionic bond?
The electrons are transferred
What does the electronegativity difference need to be to form polar bonds?
Greater than 0.4
What is the difference between an ionic bond and a covalent bond?
In an ionic bond, one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another. In a covalent bond, one or more pairs of electrons are shared between atoms.
Describe the general characteristics of bonds between non-metal atoms and bonds between metal and non-metal atoms
Bonds between non-metal atoms are generally covalent in nature while bonds between a metal atom and a non-metal atoms are generally ionic in nature
What are London dispersion forces?
London dispersion forces are intermolecular forces that occur between all atoms and molecules due to the random motion of electrons. They are the weakest of all intermolecular forces.
What happens to the boiling point in dispersion forces?
The boiling point increases with an increase in the strength of dispersion forces
Does the shape of the molecule have an impact on the strength of dispersion forces?
Yes, molecules that can pack have a greater strength of dispersion forces and hence a higher melting point
What are dipole dipole forces?
They are the attractive forces that occur between polar molecules. They are stronger than dispersion forces.
What are dipole induced-dipole forces?
They are attractions between one molecule with a permanent dipole, and one nonpolar molecules
What is the relative strength of the dipole forces?
Dipole dipole forces are stronger than induced-dipole dipole forces, which are stronger than induced-dipole induced-dipole forces
Describe the hydrogen bond
Hydrogen bond is an intermolecular attractive force in which are hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded to a small, highly electron negative atom is attracted to a lone pair of electrons on an atom in a neighbouring molecule. Hydrogen bonds are very strong compared to other dipole dipole interactions, but still much weaker than a covalent bond. Hydrogen bonding only occurs when hydrogen is covalently bonded to one of three elements which are fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen.
Describe an ionic bond
And ionic bond is when oppositely charged particles, attract each other and holds the ions together in an ionic compound
Show the intermolecular forces on a diagram
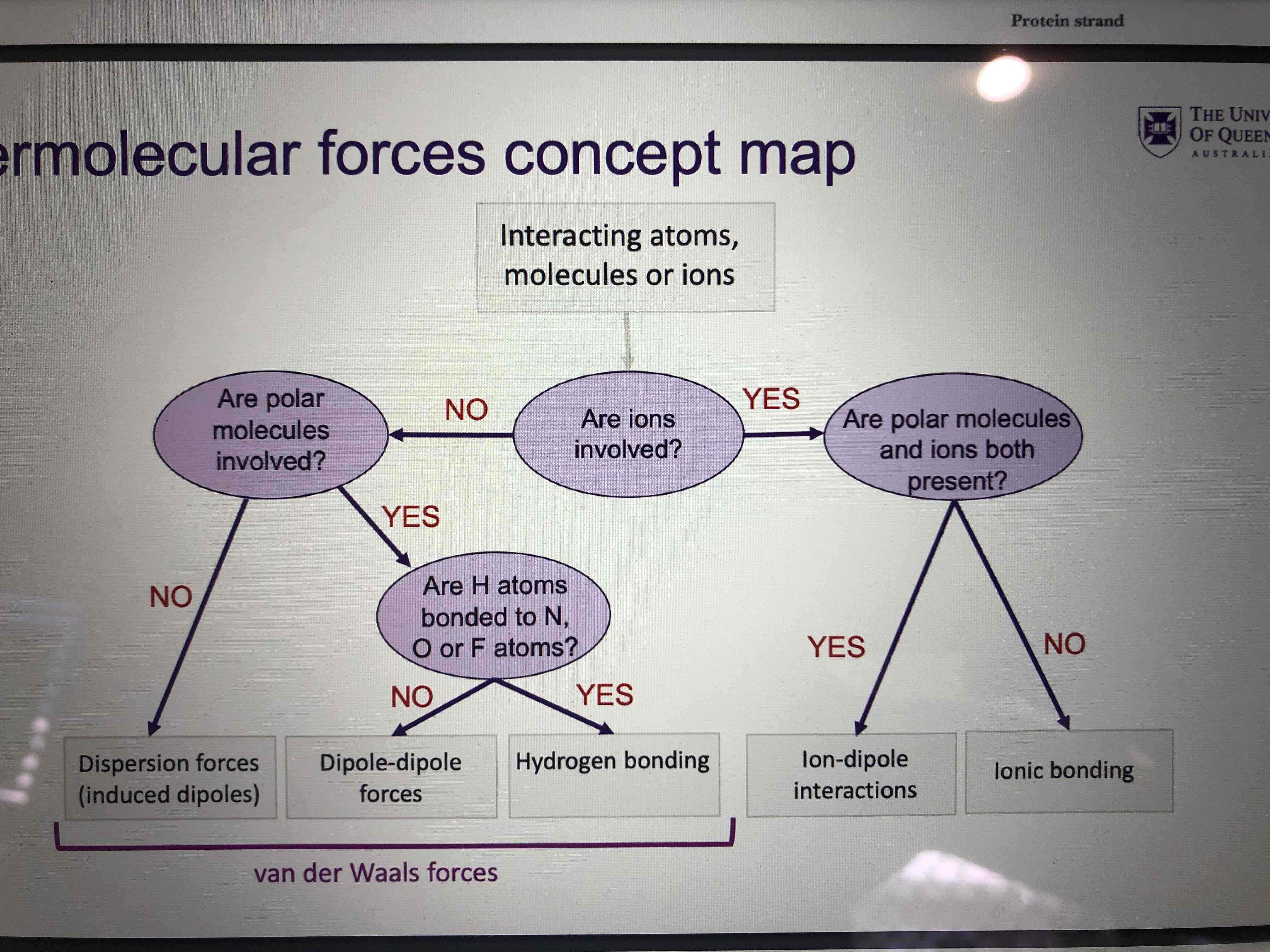
Describe a salt bridge
This occurs within a protein strand when oppositely charged ions from ionic bonds. These are commonly referred to as salt bridges.