B3.2 Animal+Plant Transport
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
blood vessels
arteries
veins
capillaries
arteries , vein , capillaries - exchange of blood
arteries: away
Veins: to
Capillaries: site of exchange
adaptations of capliiaries
short diameter - one cell thick , allow passage of one single RBC at a time
capillary wall - single layer of cell - minimize diffusion distance
surrounded by basement membrane- permeable
Capilaries structure may vary depend on location and function
continous : connected with endothelial cells - limit permeability of large molecules
fenestrated : pores . in tissue specialised for absorption eg. kidney
sinusoidal : imcomplete basemnet membrane - open spaces between cells , permeable to large molecues . eg. liver
arteries&veins
arteries:
narrow lumen : high pressure blood
thick muscle fibre : prevent rupture
thick elastic fibre : pulse.
elastc fibre allwos arteries to stretch - presure exerted on the artieral walls - elastic recoil - pushes blood forward. Contraction of artieries = One pulse
vein
thick lumen : maintain low pressure blood
valve : prevent backflow
thin layer of muscles and elastic fibres , srrounded by skeletal muscle.
skeletal muscle contract, squeeze vein , opens valve - blood move forward. Relaxes, valve close - blood trapped in vein
measurement of heart rate
radial pulse in wrisk
carotid pulse in neck
conorary occultion
artherosclerosis is the hardening and narrowing of artieries due to cholesterol
arteromos develop in the arteries - reduce diameter of lumen
higher pressure exerted on the walls - leading to damage
repaired by inelastic fibrious tissue - reduce elasticity
damaged area forms plaque - plaque ruptures - trigger blood clotting, forming thrombus - restrict blood flow, dislodged - block entire smaller artieriole
consequence
myocardial infaraction ( heart attack)
myocardial tissue requires oxygen and nutrients via conorary artieries to function
conorary artery blocked - result into heart attack
Treatment
bypass surgery
vascular bundle
xylem & phloem
water+ minerals
carbon compounds - sucrose+amino acid+ hormones
xylem
facilitate the movement of water
tube make up of strong dead cells , hollow - unimpeded flow of water
water movement : passive , one direction( roots to leaves)
pits : water transfer between cells
strengthened with lignin in spirals -- withstand low pressure without collapsing
leaves - draw and label and function
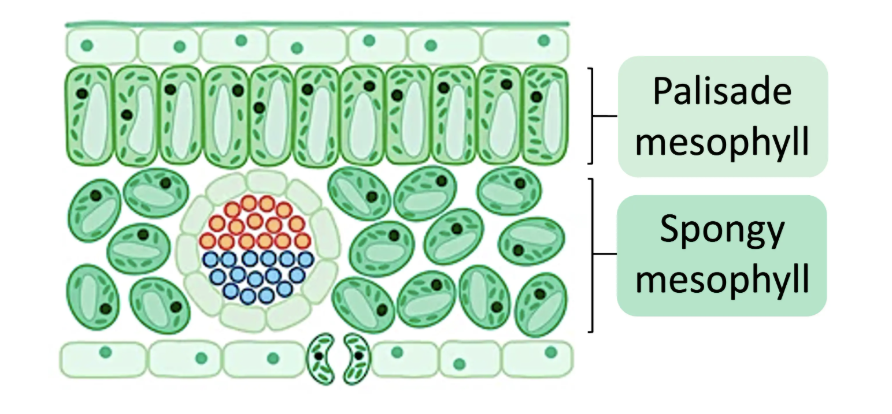
photosynthesis, light absorption , gas exchange
waxy cuticle - hydrophobic, prevent water loss
upper epidermis
palisade mesophyill - chloroplast - photosynthesis
spongy mesophyll - lots of air spaces - gas exchange
vascular bundle
lower epidermis
stoma + guard cells - open channel for gas
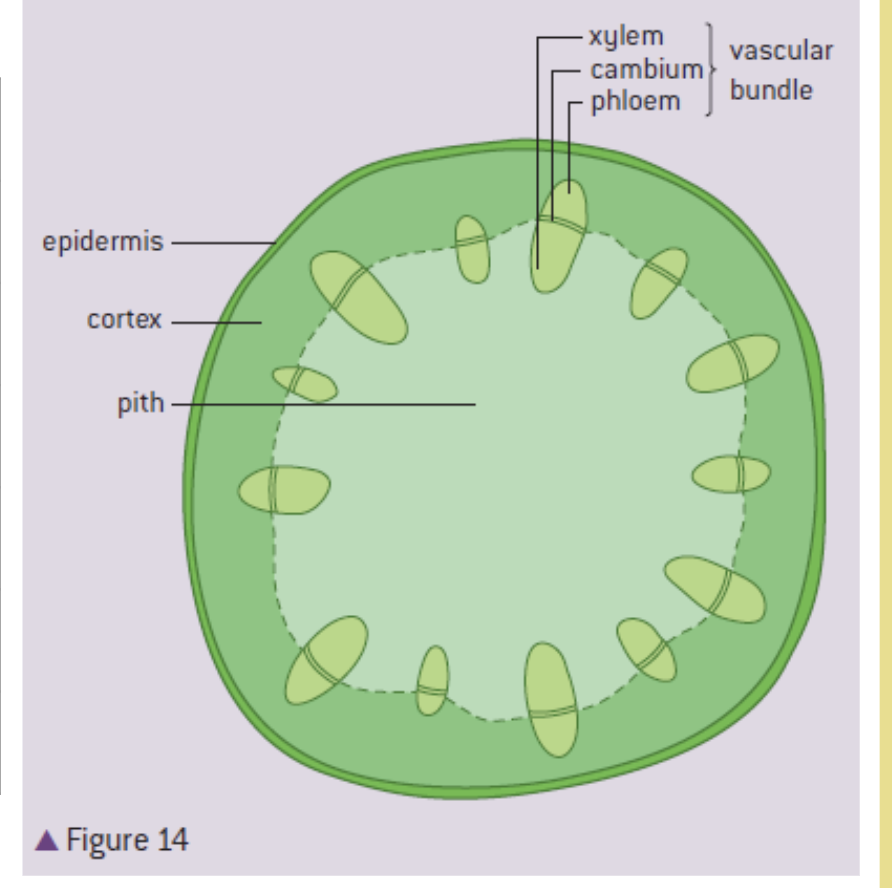
stem - draw and label and function
support, elevate leaves for seed dispersal and photosynthesis
xylem - transport of water from roots - leaves
cambium - production of xylem&phloem tissue
phloem - transport of sugar from source to sink
epidermis - protection and waterproof
cortex - support and photosynthesis
pith - packing tissue ( bulking out the stem)
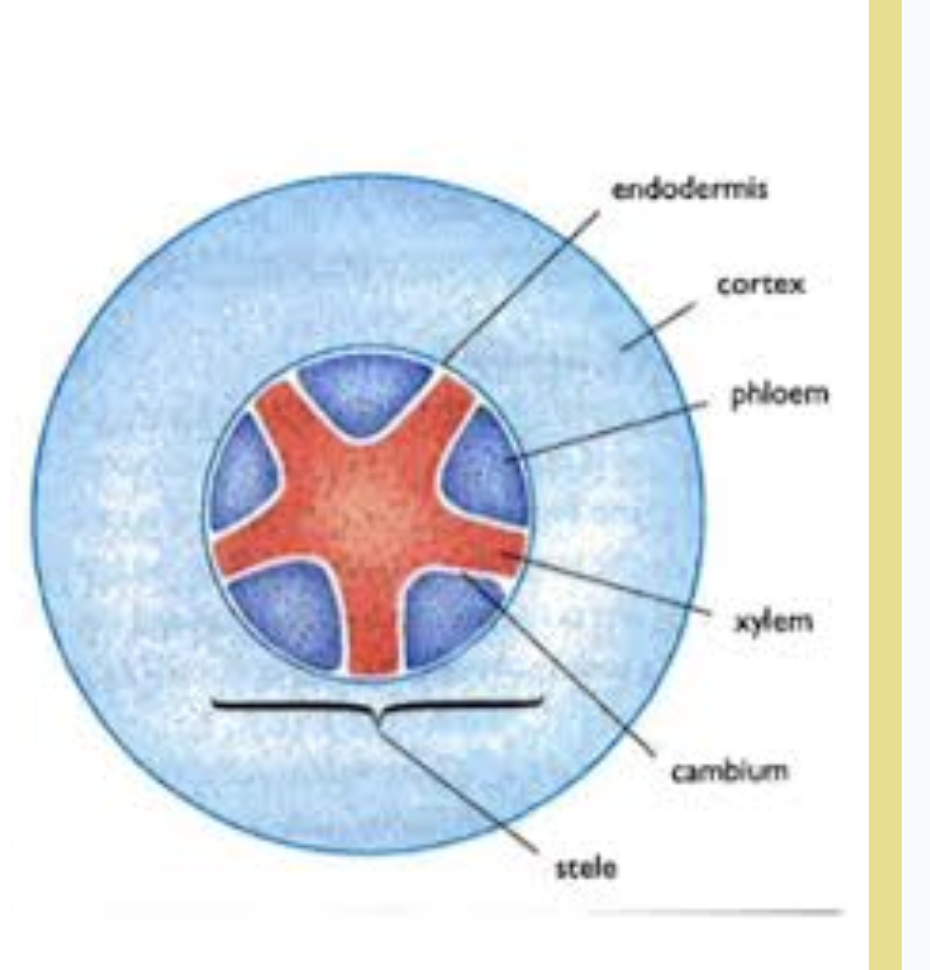
root - draw label and function
(xylem - cambium - phloem - endodermis - cortex - epidermis)
epidermis: has root hair to increase water and mineral absorption
cortex: cells loosely packed - enable movement of water
endodermis: layers of cell water pass through reach xylem
Transpiration
water vapour lost via stomata
facilitates
temperature regulation
absorption of water and minerals from soil
loss of water by transpiration from cell walls in leaf cells
causes water to be drawn out of xylem vessels and through cell walls by capillary action, generating tension (negative pressure potentials).
It is this tension that draws water up in the xylem.
Cohesion ensures a continuous column of water
measure rate of transpiration
potometer