AQA GCSE Chemistry (Atomic structure and the periodic table)
4.5(2)Studied by 5 people
Card Sorting
1/65
Last updated 7:01 PM on 11/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
What is an element?
A substance that contains only one type of atom.
2
New cards
What is a compound?
2 or more elements chemically bonded together.
3
New cards
What is a mixture?
2 or more elements or compounds which are not chemically bonded together.
4
New cards
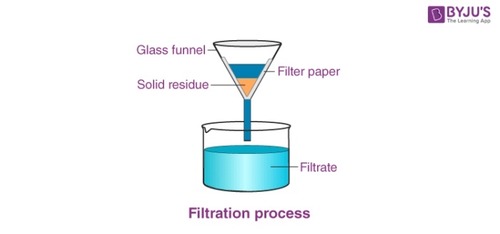
What is filtration?
Separate insoluble solids from a liquid
5
New cards
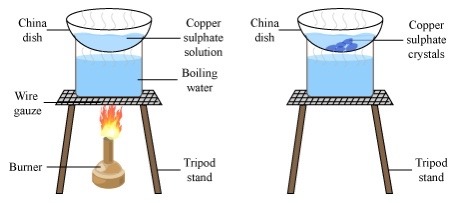
What is crystallisation?
Separation of a soluble solid from a liquid
6
New cards
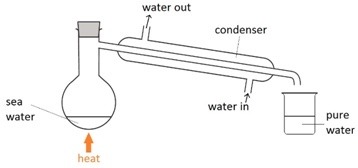
What is simple distillation?
Used to separate a liquid from a solid when we want to keep the liquid.
7
New cards
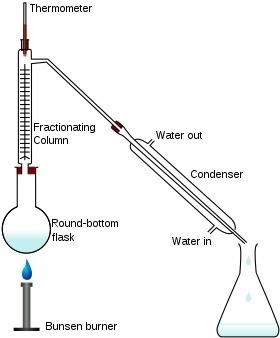
What is fractional distillation?
Used to separate liquids with different boiling points.
8
New cards
What is a molecule?
Any elements chemically combined, even if they are the same element.
9
New cards
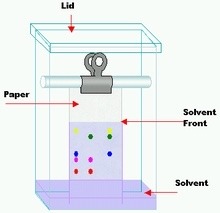
What is chromotography?
A method used to separate a mixture of dyes
10
New cards
What is a solvent?
A liquid that will dissolve a solute.
11
New cards
What is a solute?
A substance that is dissolved.
12
New cards
What is the stationary phase in chromatography?
The paper
13
New cards
What is the mobile phase is chromatography?
The solvent
14
New cards
What will a pure chemical produce in chromatography?
A single spot
15
New cards
What will chemicals in a mixture produce during chromatography?
Separate spots (depending on solvent used)
16
New cards
Why do we draw to starting line in pencil for chromatography?
If we drew the line in pen, the pen ink would move up the paper with the solvent.
17
New cards
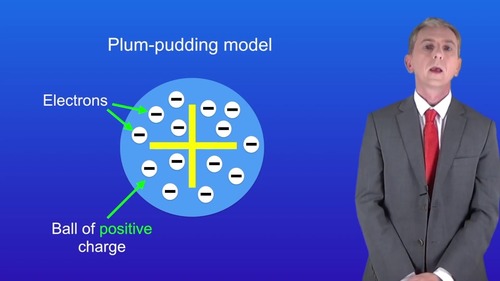
What did the plum pudding model suggest?
That an atom is a ball of positive charge, with negative electrons imbedded in it.
18
New cards
Who came up with the plum pudding model?
JJ Thomson
19
New cards
Explain the Alpha Scattering Experiment:
Step 1?
Step 1?
The scientist took a piece of gold foil
20
New cards
Why was gold used in the alpha scattering experiment?
Gold can be hammered out into very thin foil (a few atoms thick)
21
New cards
Explain the Alpha Scattering Experiment:
Step 2?
Step 2?
Scientists fired tiny alpha particles at the gold
22
New cards
What is the charge of the alpha particles?
Positive
23
New cards
What happed to most of the alpha particles?
They passed through the gold foil without changing direction.
24
New cards
What happened to some of the alpha particles?
Some alpha particles where deflected.
25
New cards
What happened to very few alpha particles?
They reflected back
26
New cards
What did most alpha particles going through the foil tell scientists?
That atoms are mostly empty space, so the plum pudding model had to be wrong.
27
New cards
What did some alpha particles being deflected tell scientists?
The centre of the atom must have a positive charge. Alpha particles that came close where repelled.
28
New cards
What did the alpha particles being reflected tell scientists?
The centre of the atom must contain a great deal of mass.
29
New cards
Who designed the Alpha Scattering Experiment?
Ernest Rutherford
30
New cards
What did Niels Bohr propose?
Electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances. The idea of energy levels/shells
31
New cards
What did scientists find after Bohr's proposition?
The nucleus contained small positively charged particles, which they named protons.
32
New cards
What did James Chadwick discover?
The nucleus also contained neutral particles called neutrons.
33
New cards
Why do atoms have no overall charge?
Because the number of protons and electrons are equal, so they cancel out, leaving neutrons.
34
New cards
What is the average radius of an atom?
0.1nm (1x10^-10 m)
35
New cards
What is the radius of the nucleus?
1/10000 of the atom
36
New cards
What is the relative charge of protons, neutrons and electrons?
Proton: +1
Neutrons: 0
Electrons: -1
Neutrons: 0
Electrons: -1
37
New cards
What is the relative mass of protons, neutrons and electrons?
Proton: 1
Neutron: 1
Electrons: Very small
Neutron: 1
Electrons: Very small
38
New cards
What does the relative mass number tell?
The number of protons and neutrons together.
39
New cards
What does the atomic number tell?
The number of electrons and protons.
40
New cards
What is an isotope?
Atoms of an element with different numbers of neutrons.
41
New cards
What is an ion?
A charged atom
42
New cards
How is relative atomic mass calculated with isotopes?
The relative atomic mass is the average of the mass number of the different isotopes. It is waited for the abundance of each isotope.
43
New cards
Relative atomic mass of isotopes formula:
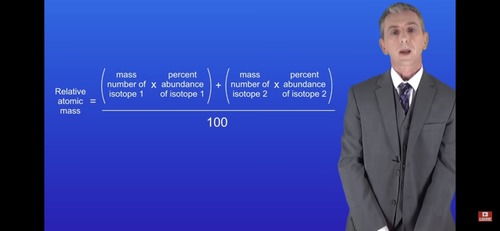
44
New cards
What is the maximum amount of electrons each energy level can hold from 1-4?
1st: 2
2nd: 8
3rd: 8
4th: 18
2nd: 8
3rd: 8
4th: 18
45
New cards
How did Newlands arrange the elements?
In order of atomic weight
46
New cards
What were the issues with arranging elements in order of atomic weights?
Sometimes elements were grouped together when they had totally different properties.
47
New cards
What did Mendeleev do differently to Newland?
• He switched the order of specific elements so that they fitted the pattern.
• He left gaps in the periodic table for elements that hadn't yet been discovered.
• He left gaps in the periodic table for elements that hadn't yet been discovered.
48
New cards
How are elements arranged in the modern periodic table?
In order of atomic number (amount of protons)
49
New cards
What was the problem with ordering elements by atomic weight (by Mendeleev)?
Elements can appear in the wrong order due to isotopes.
50
New cards
What is the name of elements in group 0?
Noble gases
51
New cards
Why are noble gases unreactive?
All noble gases have a full outer energy level.
52
New cards
How does the boiling point change in group 0?
It increases as the relative atomic masses increase (going down the group)
53
New cards
Do metals lose or gain electrons?
They lose electrons (becoming positive ions)
54
New cards
What are elements in group 1 called?
Alkali metals
55
New cards
How do group 1 metals react with oxygen?
Rapidly
More rapidly as you move don group 1
More rapidly as you move don group 1
56
New cards
How do group 1 metals react with chlorine?
Rapidly. They form metal chloride
57
New cards
In group one, metals get ______ reactive as you move down the group.
More
58
New cards
Why are metals more reactive as you go down group 1?
The outer electrons are further away from the nucleus making them less attracted and easier to lose l.
59
New cards
What are elements in group 7 called?
Halogens
60
New cards
What type of compound do group 7 elements form with other non-metals?
Covalent compounds
61
New cards
What type of compound do group 7 elements form with metal atoms.
Ionic compound
62
New cards
Elements in group 7 get ______ reactive as you move down the group.
Less
63
New cards
Why do elements become less reactive as you move down group 1
• There is a greater distance from the nucleus as you move down meaning less attraction.
• Internal electrons shield the nucleus, reducing attraction.
• Internal electrons shield the nucleus, reducing attraction.
64
New cards
Explain the displacement reactions of halogens.
A more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive halogen from an aqueous solution of its salt.
65
New cards
What are the properties of alkali metals?
• Soft metals (can be cut with a knife).
• Relatively low melting points.
• Low density.
• React rapidly with water, oxygen and chlorine.
• Form positive ions.
• Relatively low melting points.
• Low density.
• React rapidly with water, oxygen and chlorine.
• Form positive ions.
66
New cards
What are the properties of transition elements?
• Hard and strong (e.g. iron)
• High melting points
• Much less reactive than group 1 metals.
• Can form ions with different charges.
• Form coloured compounds.
• Can be used as catalysts.
• High melting points
• Much less reactive than group 1 metals.
• Can form ions with different charges.
• Form coloured compounds.
• Can be used as catalysts.