L40 Plant Disease, Pests and Food Production
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Biotic factors
Living organisms causing crop yield losses.
Crop losses
Estimated at 40% of yields globally.
Economic impact
Over $200 billion lost annually due to pathogens.
Acute Oak Decline
Bacterial disease spread by beetle larvae.
Plant Pathogens
Includes bacteria, viruses, fungi, and similar organisms.
Bacterial diseases
Responsible for over 5% annual crop losses.
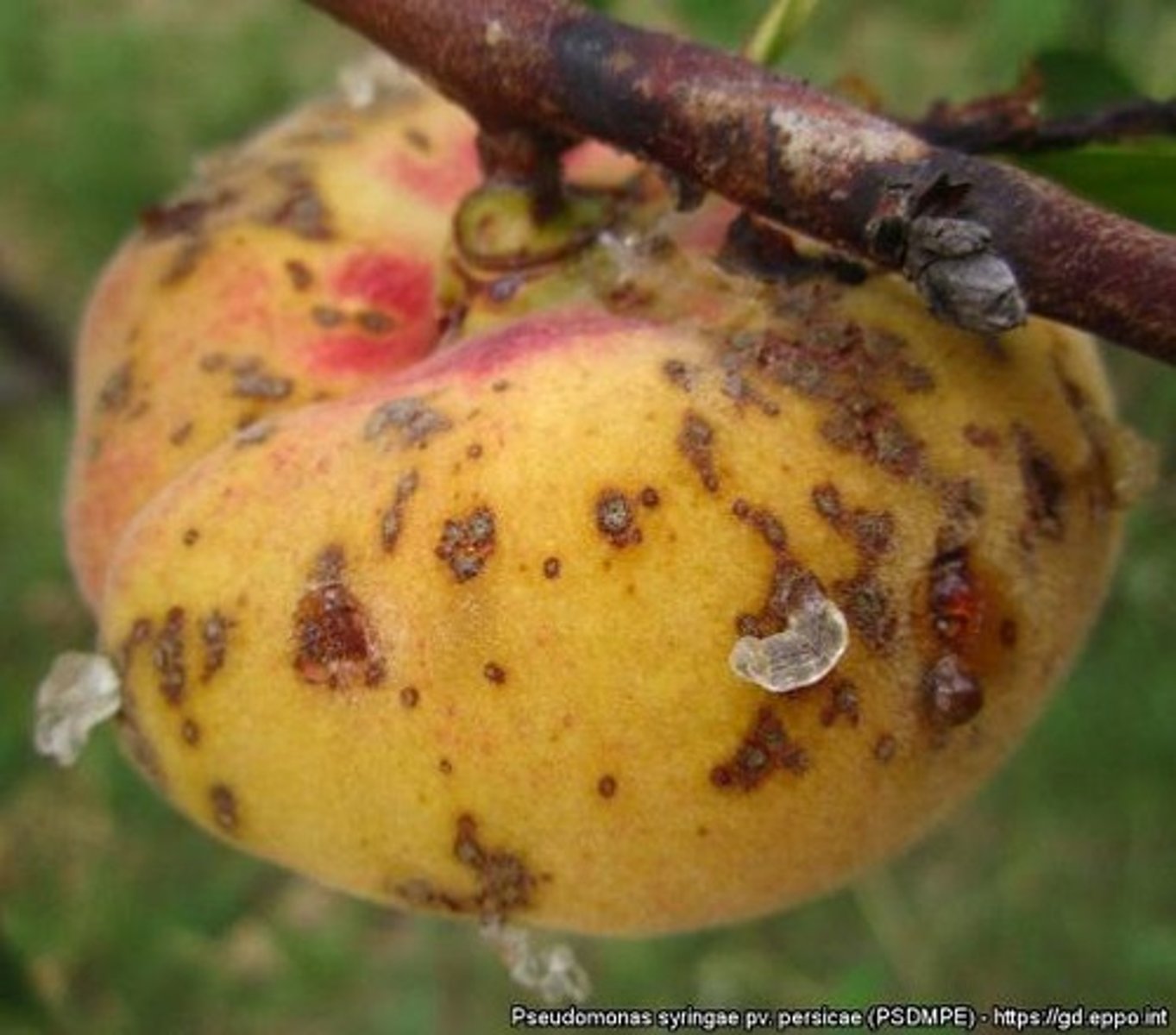
Pseudomonas syringae
Widespread bacterial pathogen affecting various crops.
Bacterial speck
Disease affecting tomatoes, caused by P. syringae.

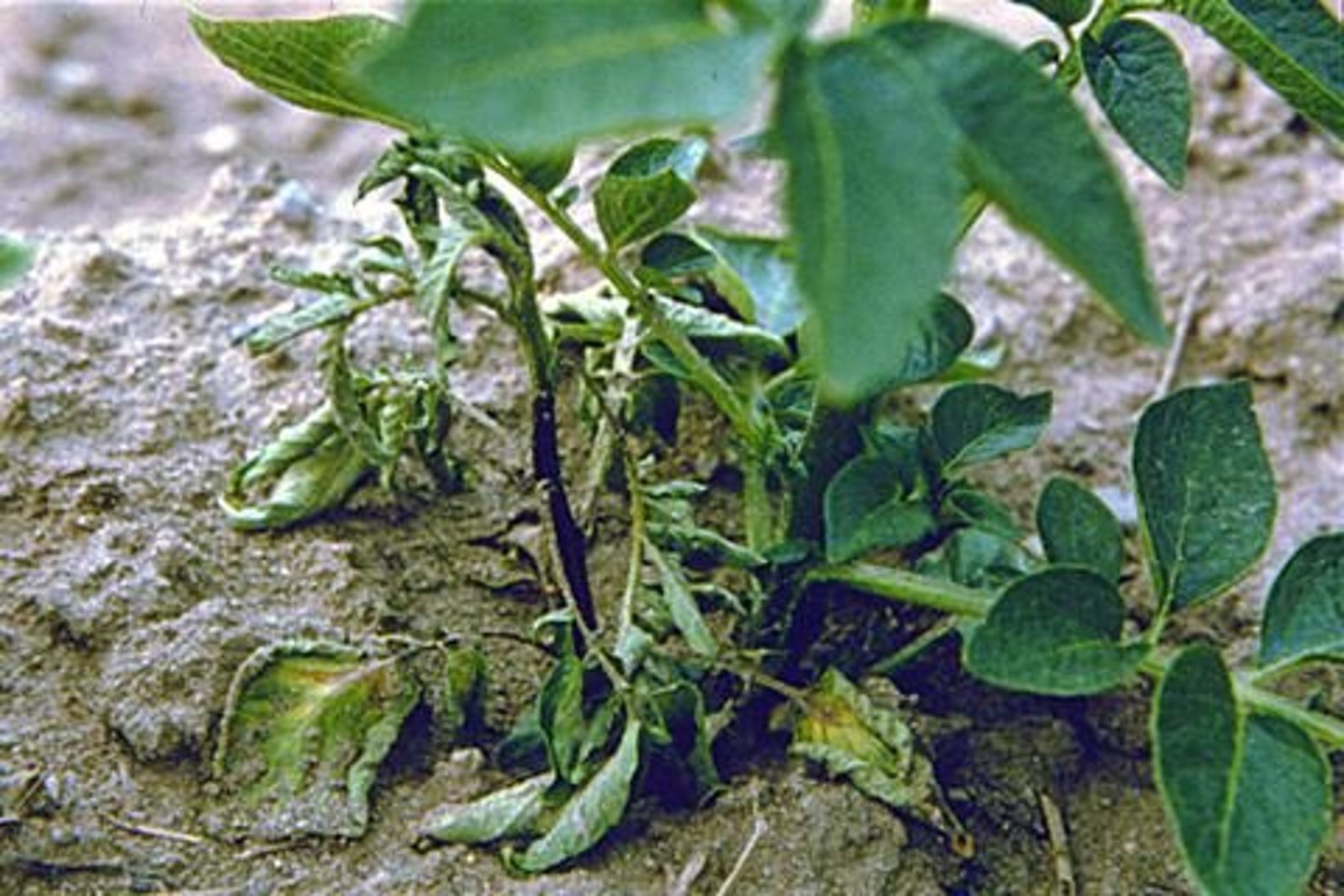
Blackleg disease
Caused by Pectobacterium spp in potatoes.

Soft rots
Potato spoilage in storage due to Pectobacterium.
Virus diseases
Major economic losses, especially in Africa and Asia.
Viral transmission
Spread by vectors like aphids and nematodes.
Cassava mosaic virus
Significant yield losses in African cassava crops.
Phytophthora infestans
Causes Late Potato Blight, linked to Irish Famine.
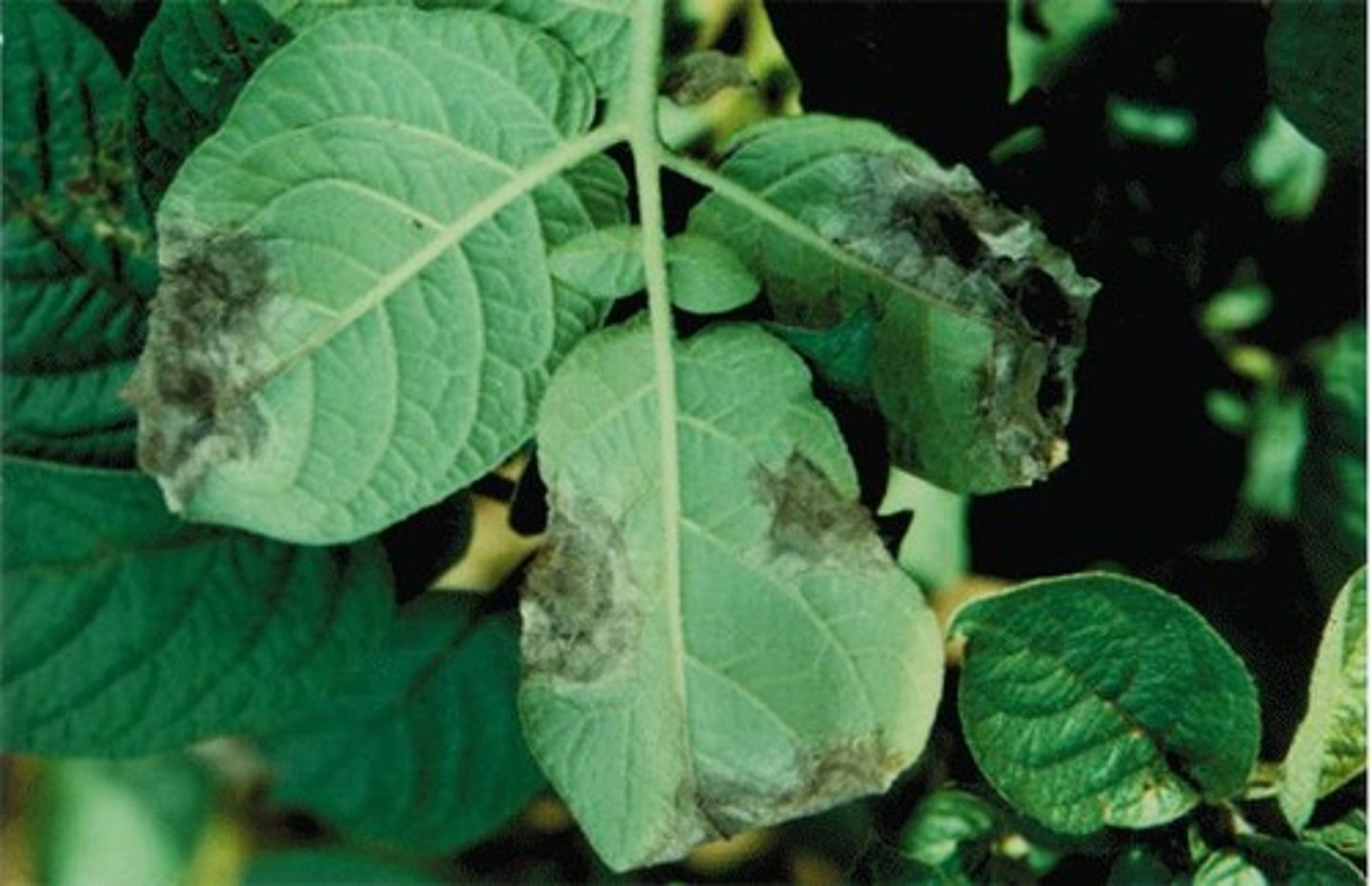

Irish Potato Famine
Resulted in 1 million deaths in the 1840s.
Fungicide costs
Annual losses reach $3 billion worldwide.
Necrotrophic pathogens
Grow in dead tissue, secrete degrading enzymes.
Biotrophic pathogens
Require living tissue for growth and nutrient extraction.
Halo blight
Disease affecting French beans, caused by bacteria.
Bacterial blight
Affects soybeans, causing significant crop damage.
Kiwifruit epidemic
P. syringae caused $2 billion losses in New Zealand.
Defense Mechanisms
Strategies plants use to protect against pathogens.
Preformed Structural Barriers
Physical defenses present before pathogen attack.
Innate Immunity
Inherited defense mechanism against pathogens in plants.
Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs)
Molecules recognized by plant immune systems.
Basal Immunity
Initial immune response using surface proteins.
Gene-For-Gene Hypothesis
Resistance requires matching genes in host and pathogen.
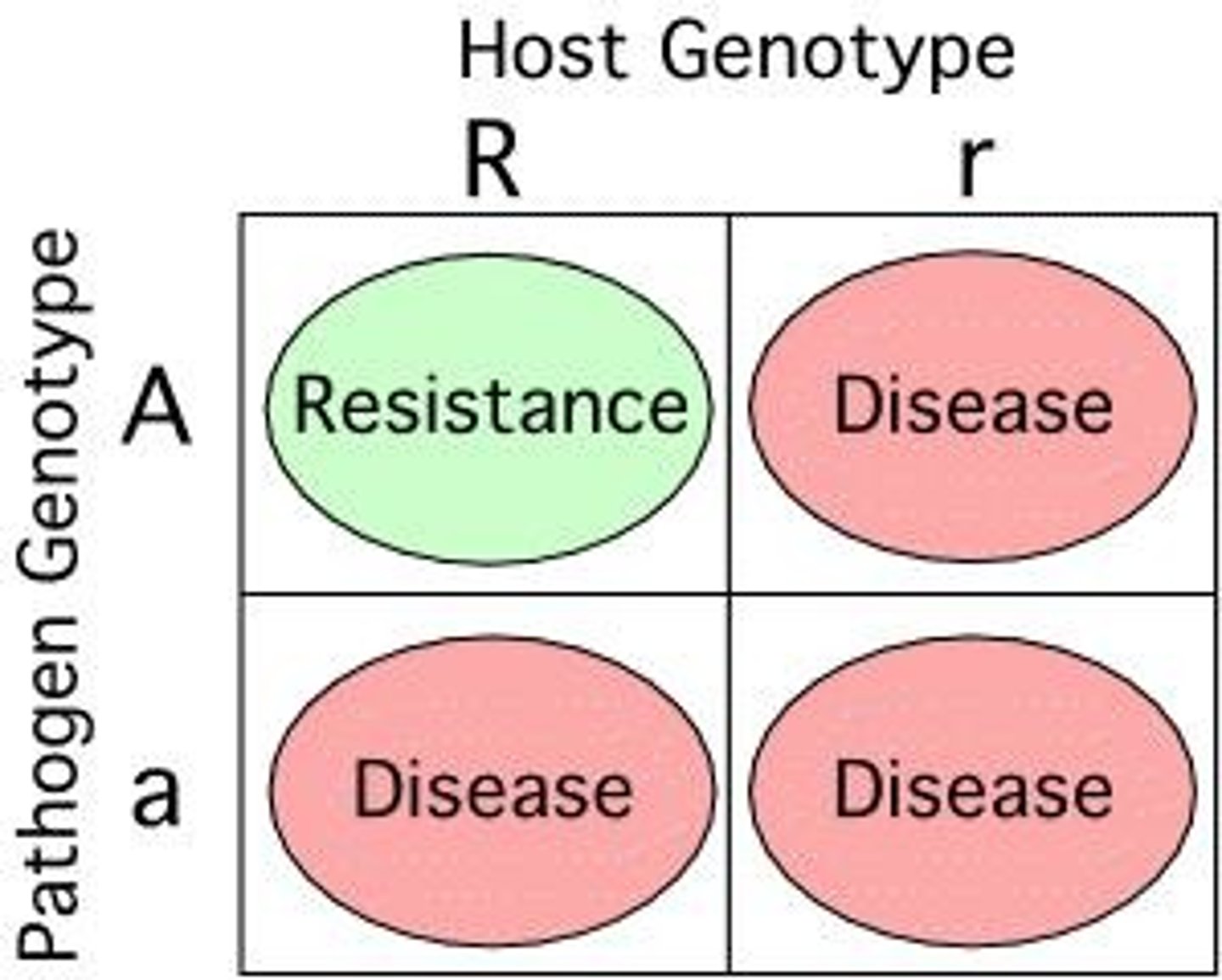
Resistance Genes (R-genes)
Genes in plants that confer resistance to pathogens.
Avirulence Genes
Pathogen genes essential for successful invasion.
PAMP-triggered Immunity (PTI)
Defense response activated by recognizing PAMPs.
Effectors
Pathogen proteins that manipulate host defenses.
Flagellin
PAMP from bacterial flagella, triggers immune response.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
PAMP from bacterial outer membrane, recognized by plants.
Elongation Factor Tu (EF-Tu)
Bacterial protein recognized by plant immune systems.
Ergosterol
Fungal PAMP, component of fungal cell membranes.
Chitin
Structural polysaccharide in fungal cell walls, recognized by plants.
β-glucans
Fungal cell wall components triggering immune responses.
CBEL
Oomycete PAMP, cellulose binding elicitor lectin.
Pep-13
Oomycete PAMP, triggers plant immune response.
Virulent Pathogen
Pathogen capable of causing disease in susceptible hosts.
Avirulent Pathogen
Pathogen that cannot cause disease in resistant hosts.
Pseudomonas syringae
Bacterial pathogen used in plant resistance studies.
Rx Gene
Resistance gene in potatoes against Potato Virus X.
Tobacco Resistance
Tobacco's ability to resist Pseudomonas syringae infection.
Resistance genes
Genes that recognize pathogen effectors in plants.
Type III secretion system (T3SS)
System delivering effectors into host cells.
Effectors
Molecules that suppress plant defense responses.
Avirulence genes
Genes encoding effector molecules in pathogens.
Resistance (R) genes
Plant genes triggering defense against pathogens.
Programmed Cell Death
Localized response to pathogen infection in plants.
Systemic Acquired Resistance (SAR)
Broad-spectrum resistance activated by local infection.
Salicylic acid (SA)
Signaling molecule in Systemic Acquired Resistance.
Pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins
Proteins with anti-pathogen properties synthesized during defense.
Chitinases
Enzymes targeting insect and fungal cell walls.
β1-3 glucanases
Enzymes targeting bacterial and fungal cell walls.
Genetic drift
Pathogen evolution leading to loss of resistance.
Boom or Bust
Cycle of resistance success followed by failure.
P. infestans
Pathogen causing late blight in potatoes.
Rpi-vnt1.1
Promising R gene from Solanum venturii.
Transgenic lines
Plants genetically modified for enhanced resistance.
Simplot Innate Potatoes
Potatoes engineered for multiple disease resistances.
Non-conventional resistance
Resistance strategies not based on R-genes.
Papaya Ringspot Virus
Virus causing significant agricultural losses in Hawaii.
Constitutive expression
Continuous expression of a gene under all conditions.
Field trials
Tests conducted in natural conditions to evaluate resistance.
Cultivated varieties
Domesticated plant species bred for specific traits.
Emergence of new races
Development of new pathogen strains evading existing resistance.