Transcription and Translation Processes in Cells
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
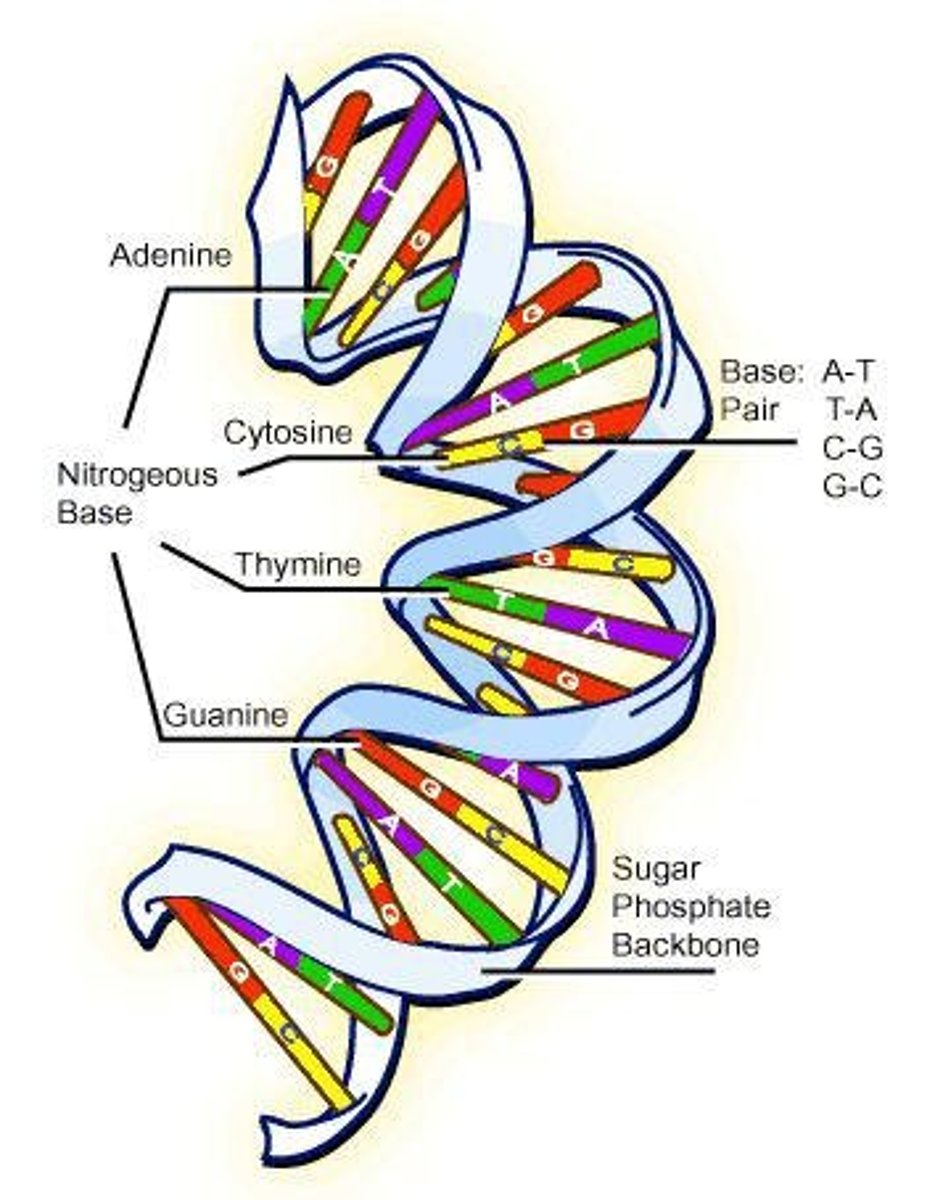
Genome
Total genetic information of an organism.
Gene Expression
Process where a gene produces a product.
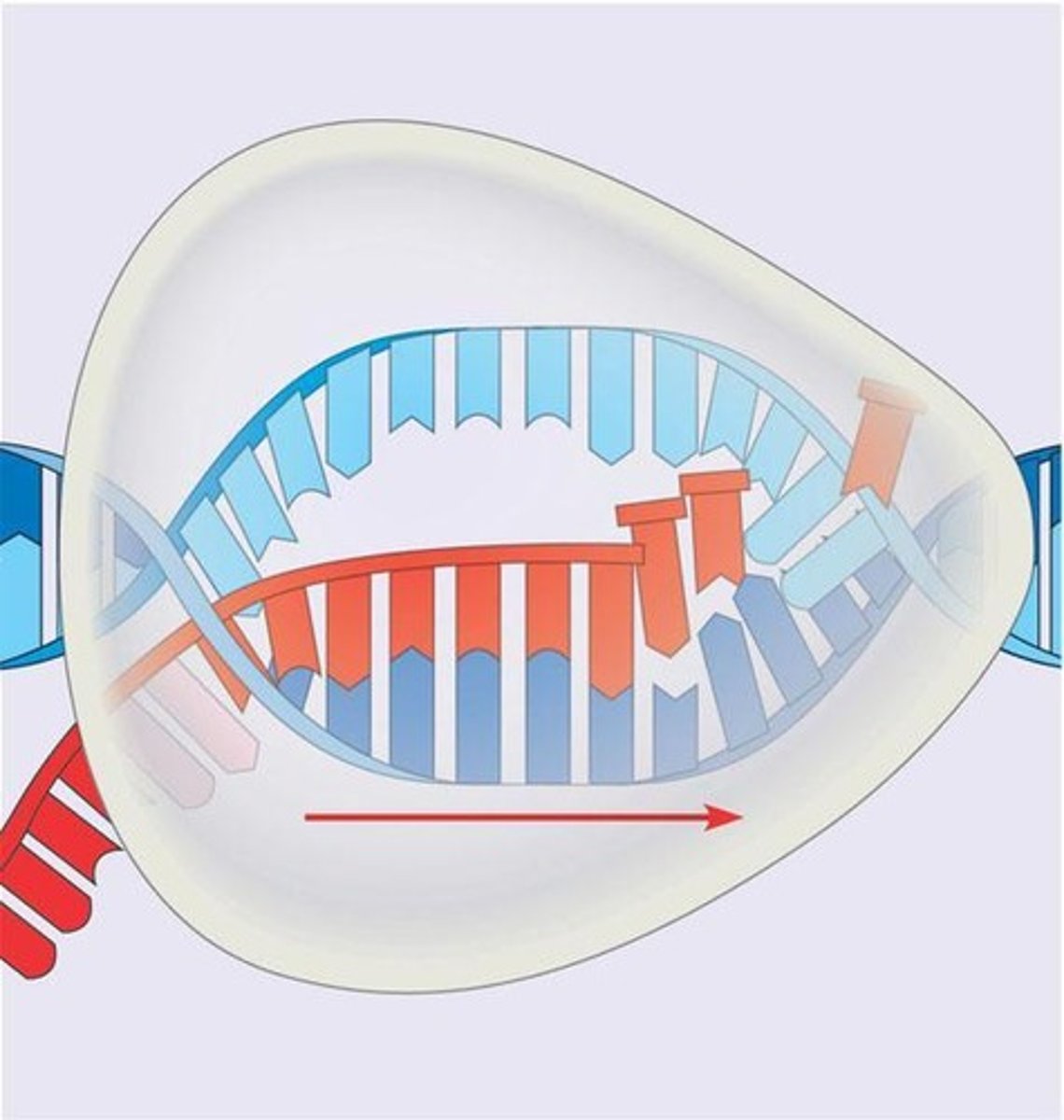
Transcription
Synthesis of RNA from DNA template.
Translation
Synthesis of polypeptide from mRNA.
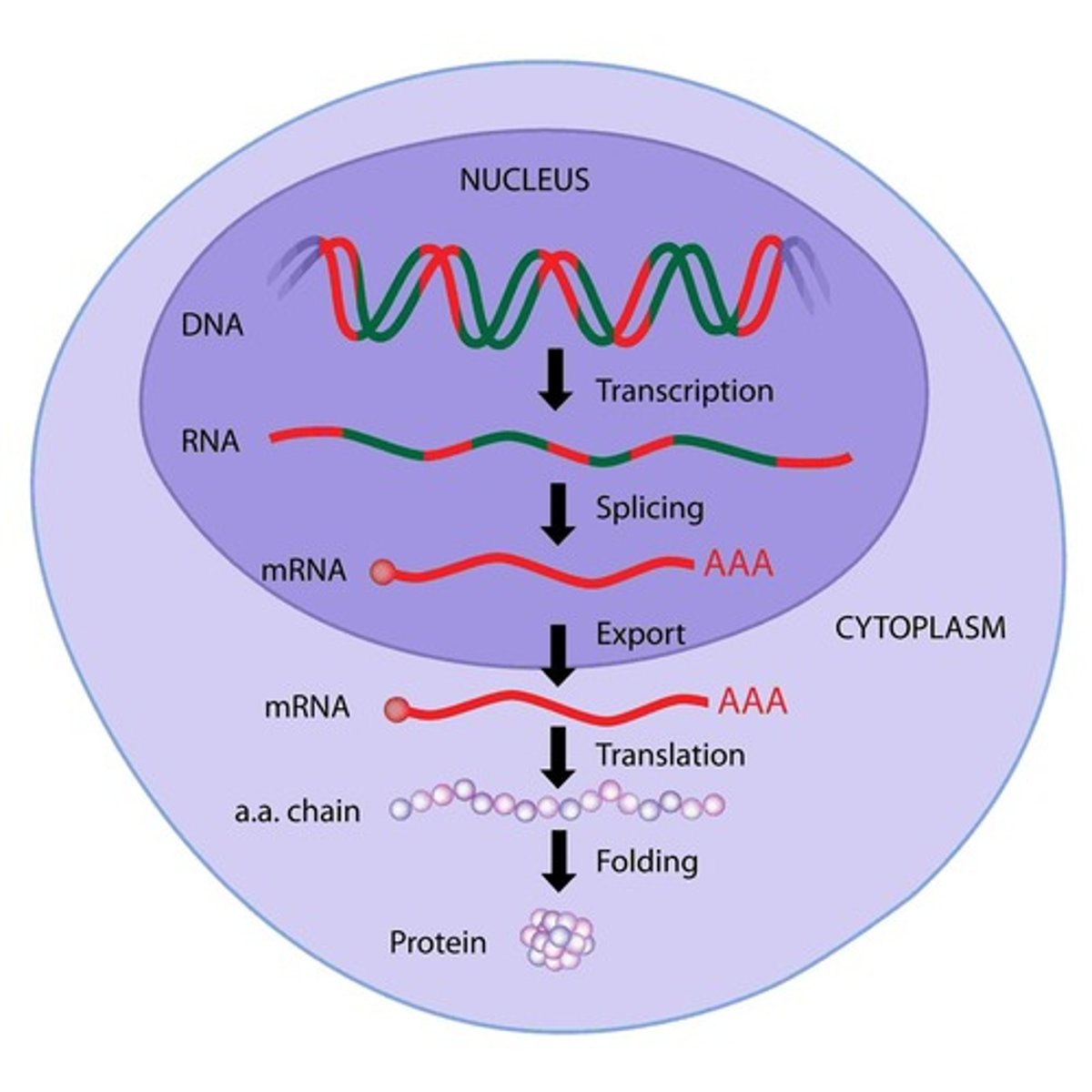
Folding
Formation of a 3D functional protein structure.
Genotype
Genetic constitution of an organism.
Phenotype
Observable traits resulting from gene expression.
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins.
Polypeptide
Chain of amino acids forming proteins.
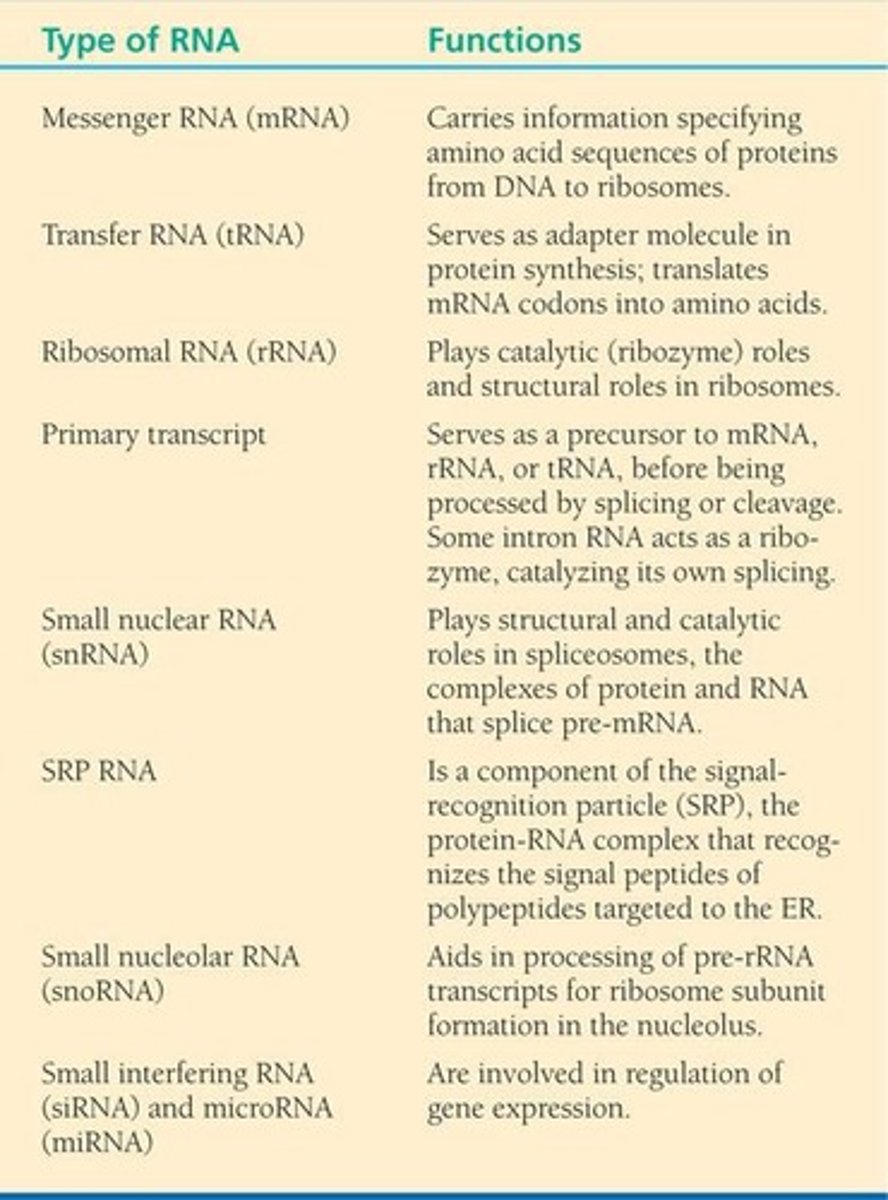
RNA
Single-stranded nucleic acid for protein synthesis.
mRNA
Messenger RNA carrying genetic information.
RNA Polymerase
Enzyme catalyzing RNA synthesis from DNA.
Promoter Sequence
Region marking the start of a gene.
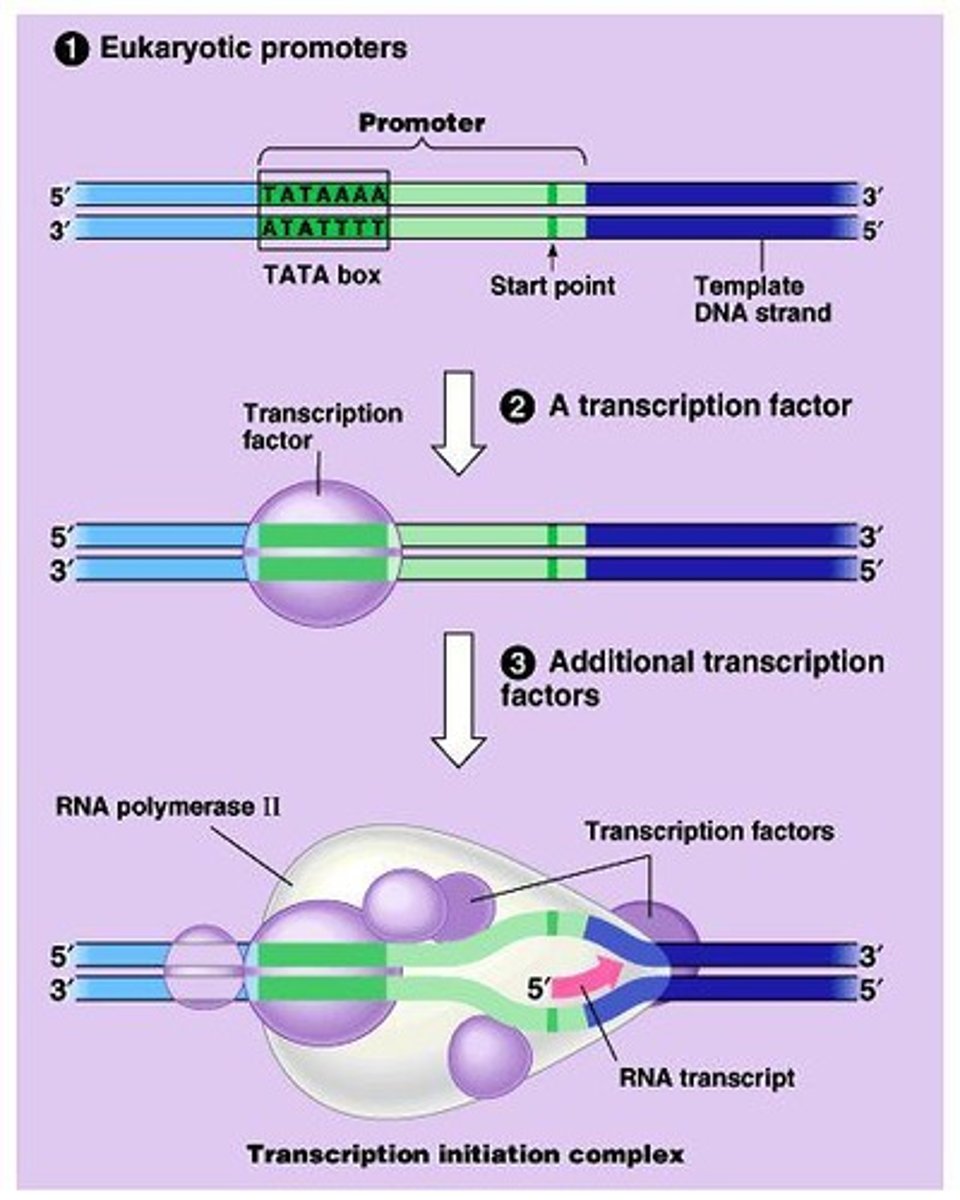
Transcription Factors
Proteins that initiate transcription by binding to DNA.
Non-coding Sequences
DNA regions that do not code for proteins.
Variable Number Tandem Repeats
Repeated DNA sequences used in DNA profiling.
Silencer Sequences
DNA elements that inhibit gene expression.
Enhancer Sequences
DNA elements that promote gene expression.
Centromere
Regions where sister chromatids attach.
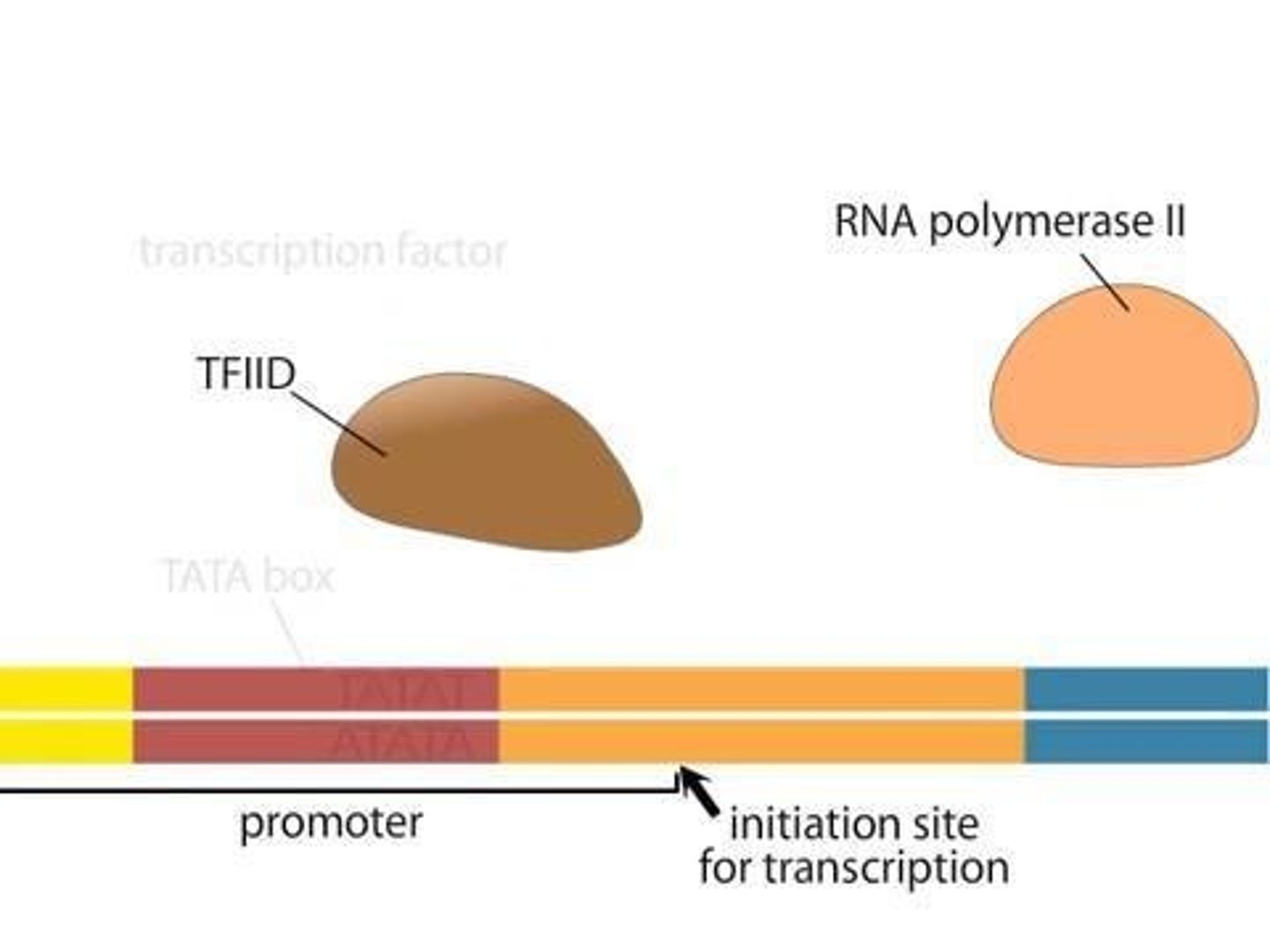
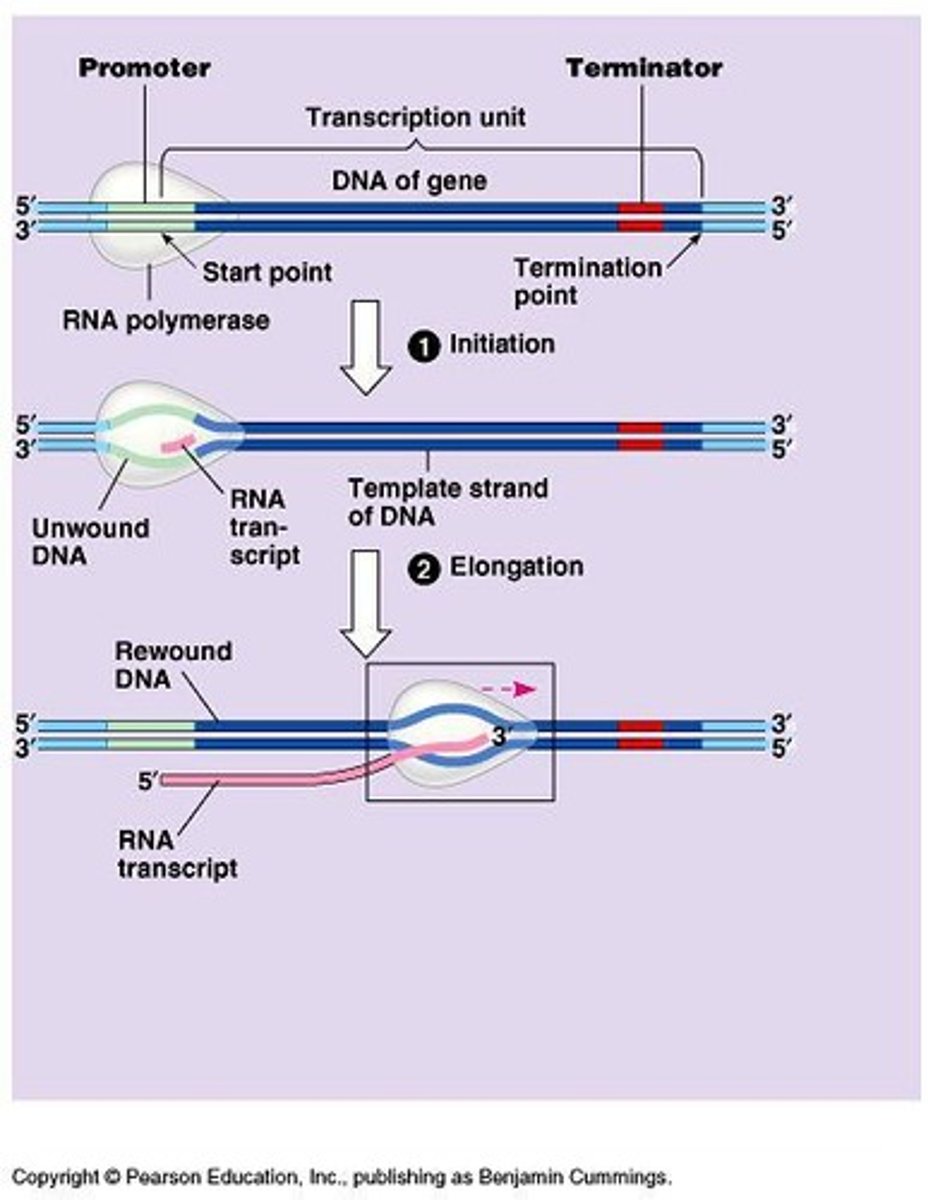
Initiation
First stage of transcription; RNA polymerase binds.
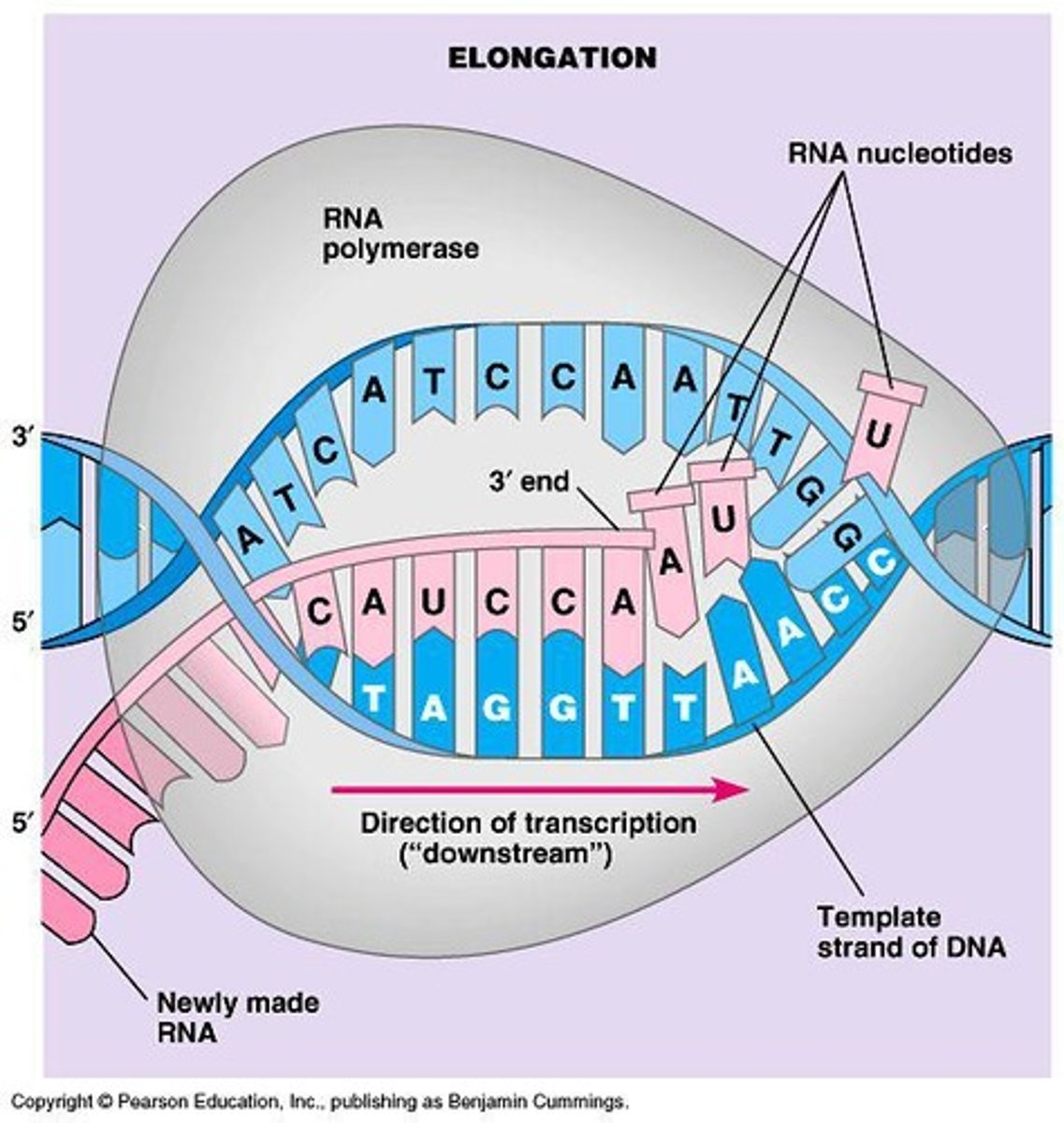
Elongation
RNA polymerase extends RNA transcript.
Termination
Final stage of transcription; RNA transcript released.
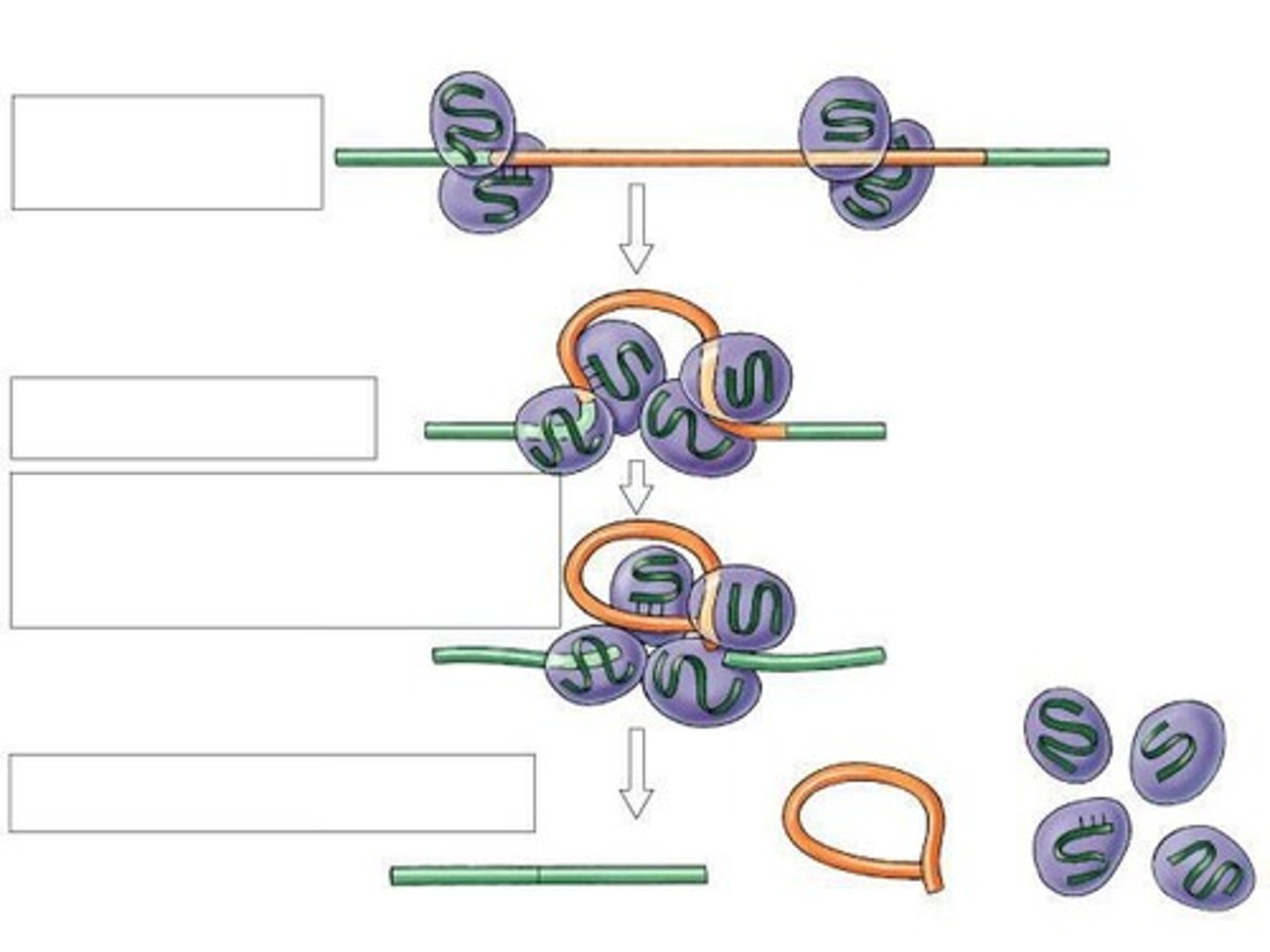
RNA Splicing
Modification of RNA before it leaves the nucleus.
Ribosomes
Cellular structures where translation occurs.
RNA polymerase II
Enzyme that synthesizes RNA from DNA template.
Eukaryotic promoters
DNA sequences that initiate transcription.
TATA box
Common promoter sequence in eukaryotes.
Pre-mRNA
Initial RNA transcript before processing.
Template strand
DNA strand used for RNA synthesis.
Non-template strand
DNA strand with same sequence as RNA.
Transcription initiation complex
Assembly of RNA polymerase and transcription factors.
Antisense strand
Template strand for RNA synthesis, complementary to RNA.
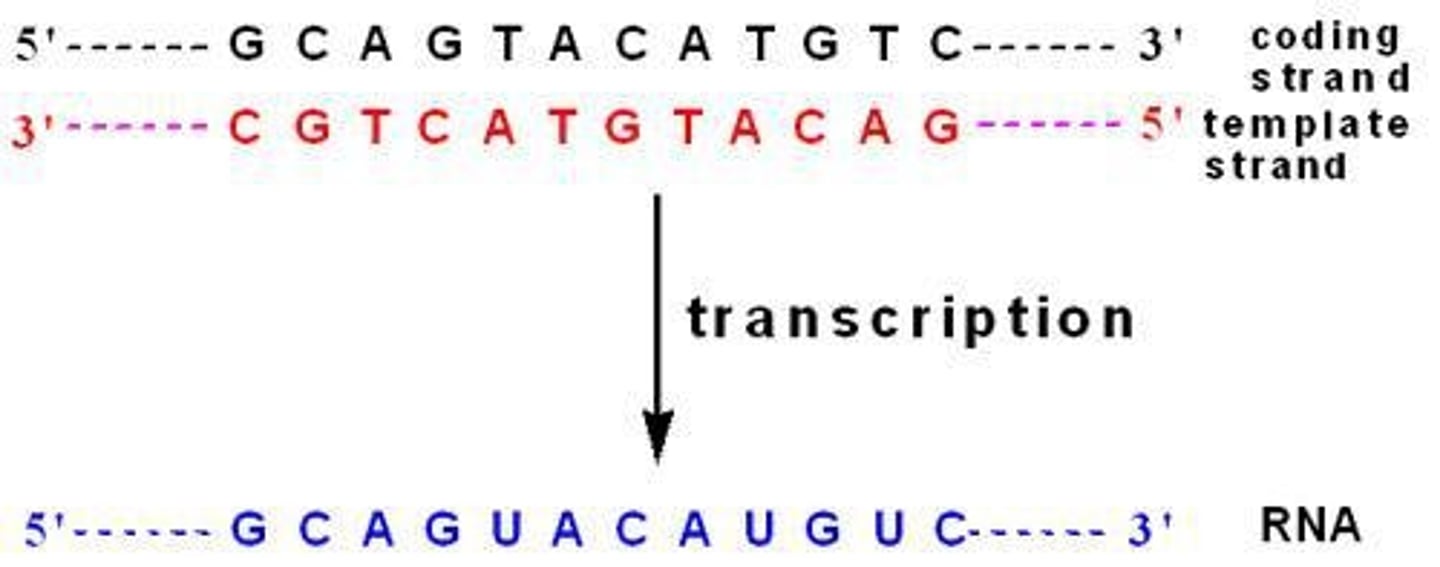
Sense strand
Non-template strand with same sequence as RNA.
Base-pairing rules
Guidelines for pairing nucleotides in RNA synthesis.
Transcription unit
Segment of DNA transcribed into RNA.
RNA nucleotides
Building blocks of RNA, including A, U, C, G.
Direction of transcription
RNA synthesis occurs from 5' to 3' end.
Complementary base pairing
A-U and C-G pairing in RNA synthesis.
Tri-phosphates
Energy source added during RNA synthesis.
Ribosome
Cellular machinery that translates mRNA into proteins.
Transcription terminator
DNA sequence signaling the end of transcription.
Unwinding
Separation of DNA strands for RNA pairing.
Hydrogen bonds
Weak interactions between RNA and DNA bases.
Nucleoside triphosphates
Energy sources for RNA synthesis reactions.
Phosphate hydrolysis
Releases energy for RNA nucleotide addition.
3' end addition
Nucleotides are added to RNA's 3' end.
5' to 3' direction
Direction of RNA synthesis during transcription.
Terminator sequence
Signals the end of transcription in DNA.
RNA separation
Complete detachment of RNA from DNA strand.
Introns
Non-coding sequences excised from RNA transcripts.
Exons
Coding sequences that remain in mature mRNA.
Spliceosome
Complex that facilitates RNA splicing.
snRNPs
Small nuclear RNA-protein complexes involved in splicing.
Alternative splicing
Process allowing multiple proteins from one gene.
5' guanine cap
Protective modification added to RNA's 5' end.
Poly A tail
String of adenines added to RNA's 3' end.
Nuclear envelope
Barrier separating transcription and translation in eukaryotes.
Mature mRNA
Processed RNA ready for translation into protein.
5' GTP cap
Modified guanine nucleotide added to mRNA's 5' end.
3' poly-A tail
Chain of adenine nucleotides added to mRNA's 3' end.
RNA processing
Modifications made to pre-mRNA before translation.
splicing
Removal of introns from pre-mRNA to form mRNA.
domains
Distinct functional regions within a protein.
polyadenylation signal
Sequence indicating addition of poly-A tail.
stop codon
Signal for termination of protein synthesis.
start codon
Initiates translation process in mRNA.
3' UTR
Untranslated region following the stop codon.
5' UTR
Untranslated region before the start codon.
adenine nucleotides
Nucleotides added to the 3' end of mRNA.
guanine triphosphate
Nucleotide added to the 5' end of mRNA.
eukaryotic genomes
Genomes with introns and complex regulatory sequences.
non-protein-coding DNA
DNA sequences that do not code for proteins.
tRNA
Transfers amino acids to ribosomes during translation.
Codon
Three-base sequence coding for amino acids.
STOP Codons
Signals termination of protein synthesis.
Anticodon
tRNA sequence matching mRNA codon.
64 Codons
Total possible codons from four bases.
Universal Genetic Code
Same codons specify amino acids across organisms.
RNA Types
Includes mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA.
3' Terminal Site
Location for amino acid attachment on tRNA.
Enzymes in tRNA
Pair tRNA with corresponding amino acids.
Nucleus to Cytoplasm
Pathway for mRNA after transcription.
Nonoverlapping Codons
Codons do not share bases in translation.
Polypeptide Synthesis
Occurs on ribosomes using mRNA template.
Amino-acyl tRNA Synthetase
Enzyme that attaches tRNA to amino acids.
ATP
Energy molecule used in tRNA activation.
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA, component of ribosomal subunits.
P site
Ribosomal site holding tRNA attached to polypeptide.
A site
Ribosomal site for incoming aminoacyl tRNA.
E site
Ribosomal site where discharged tRNA exits.
GTP
Energy source for translation processes.
Peptide Bond
Covalent bond linking amino acids in polypeptide.
Translocation
Movement of tRNA and mRNA during elongation.
Initiator tRNA
tRNA carrying methionine, starts translation process.
Translation Initiation Complex
Assembly of ribosomal subunits and mRNA for translation.
Polypeptide Chain
Sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
RNA transcript
Initial RNA product before splicing, known as pre-mRNA.
Exon
Coding regions of RNA that remain in mRNA.
Intron
Non-coding regions of RNA removed during processing.
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
Enzyme that attaches amino acids to tRNA.