Microbiology and Immunology Exam 4 Lecture 7 [Adenoviruses & Papillomaviruses]
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Adenoviruses Characteristics
Many serotypes (>50) 1-7 are most common
Virion stucture:
- Non-enveloped
- Icosahedral capside containing dsDNA linear genome
Projecting fiber protein that interacts with the cellular protein Coxsackie Adenovirus receptor (CAR), then the capsid proteins interact with cell surface integrin for internalization
Genome encodes 30-40 genes
Replication in the nucleus using Viral DDDP
Transcription using cellular machinery in nucleus
Adenoviruses: Disease
Infection mainly of epithelial cell on mucous membranes
The target site depends upon virus type which is primarily determined by specificity of virus fiber protein
Clinical syndromes of Adenoviruses
Dependent on virus type
- upper respiratory illness (most common)
- Epidermic Keratoconjunctivitis
- Pharyngoconjunctival fever
- Diarrhea (more common in infants)
- Hemorrhagic cystitis
- Meningitis/Encephalitis (rare)
- Myocarditis (rare)
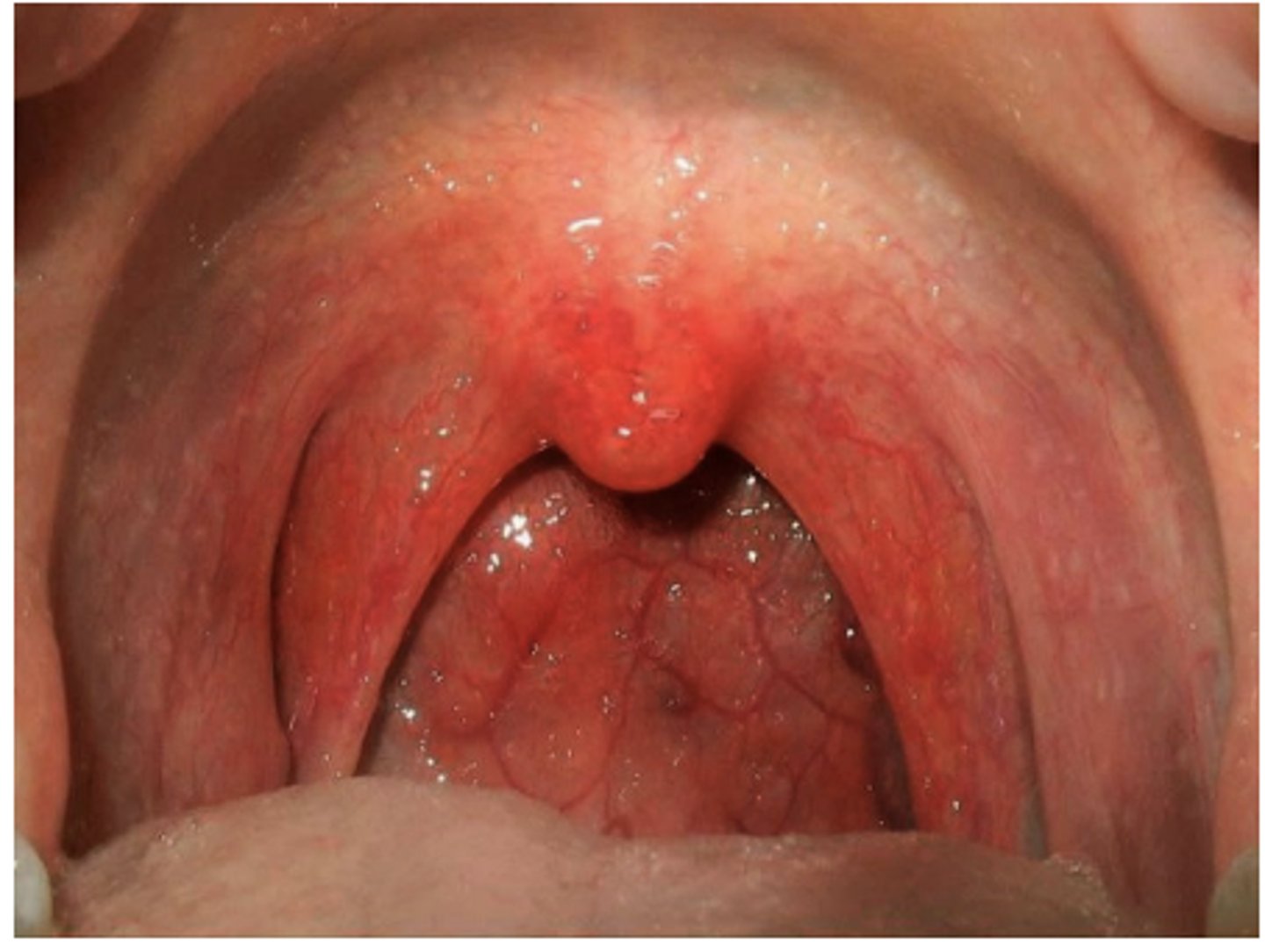
Common Respiratory infection caused by Adenoviruses: Pharyngitis
Type of Adenovirus
- 1-7
Symptoms
- Redness
- Blistering
Duration:
-3-5 days or longer
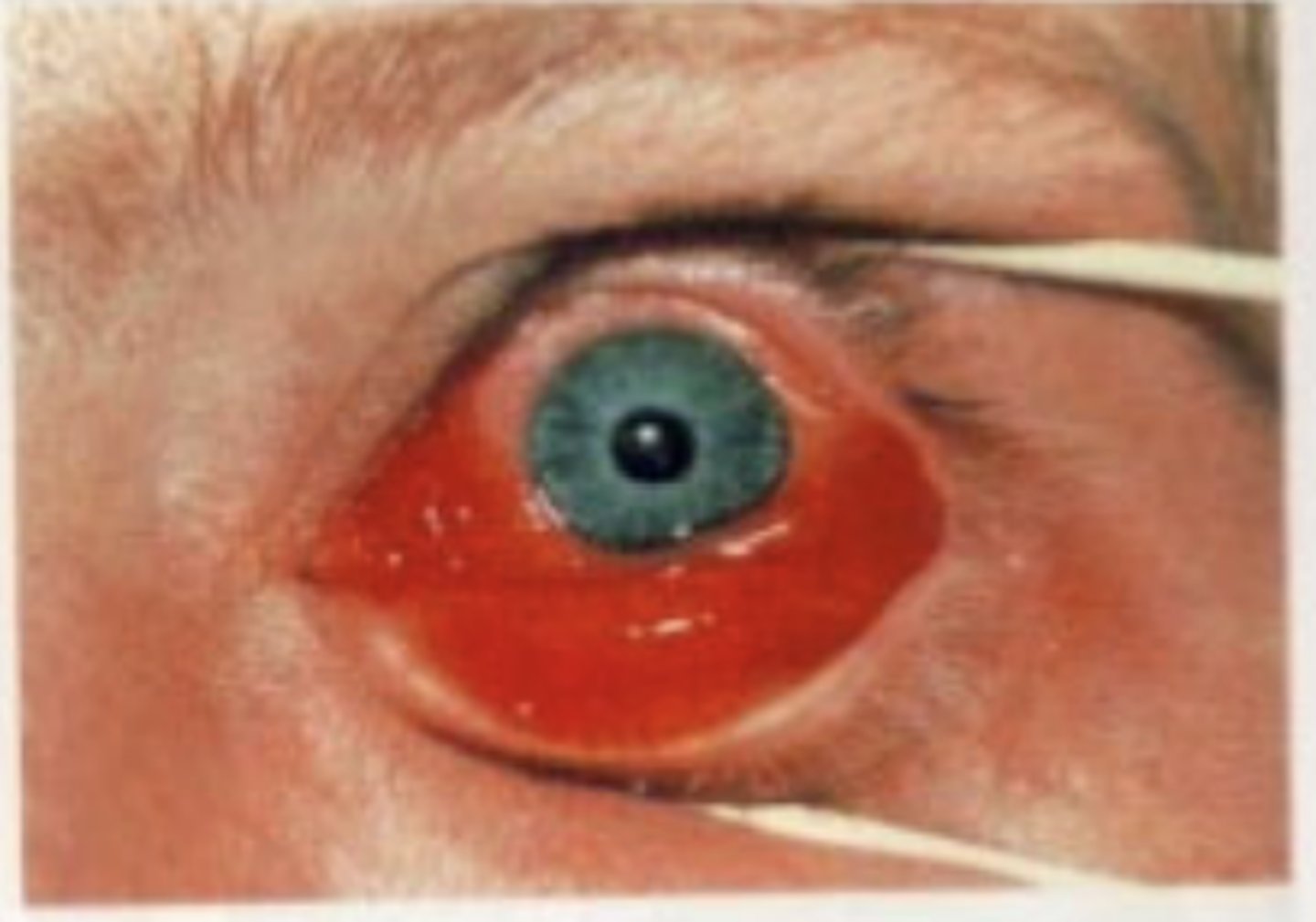
Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis
Type of adenovirus
- 3 and 7
Symptoms
Accompanied by pharynconjunctival fever
Adenovirusues are common cause of Gastroenteritis in
childhood
Types:
- 40,41
Adenoviruses can also cause Hemorrhagic cystitis: Symptoms
Bladder inflammation
bleeding from bladder wall
Hospitalization not uncommon
Types:
- 11 and 21
Treatment and prevention of Adenoviruses
Antiviral:
- None
Immunization:
- Available for military recruits for some serotypes (4 and 7)
Prevention:
- Thorough hand washing helps prevent transmission through fecal-oral route
Papillomaviruses are another virus that infects
Epithelial cells
- cutaneous and mucosal
Mucosal types of papillomaviruses often but not always __________ transmitted
sexually
Cutaneous types of papillomaviruses are trasmitted by
contact
papillomaviruses infection is persistant. Normal clearing after
year or more but can be longer
Infection of papillomaviruses cause ____ and other usually benign proliferations and lesions
warts
Several types of papillomaviruses are associated with and cause ______
cancer
Human Papillomaviruses (HPV) has over ____ types identified
200
HPV risk group: LOW
1,2,3,4
Disease:
Common skin warts
Plantar warts
Benign Oral lesions
HPV risk group: INTERMEDIATE
6, 11
Disease:
Anogenital Warts
Benign Oral lesions
Papillomatosis
HPV risk group: HIGH
16,18,33,39,45
Disease:
Cervical cancer
Vaginal cancer
Other Anogenital cancers
Oral cancers
Clinical manifestations cutaneous warts
Various morphological types
Caused by many HPV serotyeps, usually low-risk types
Long incubation (months)
Difficult to eliminate (cryotherapy, surgery, acid) and can recur
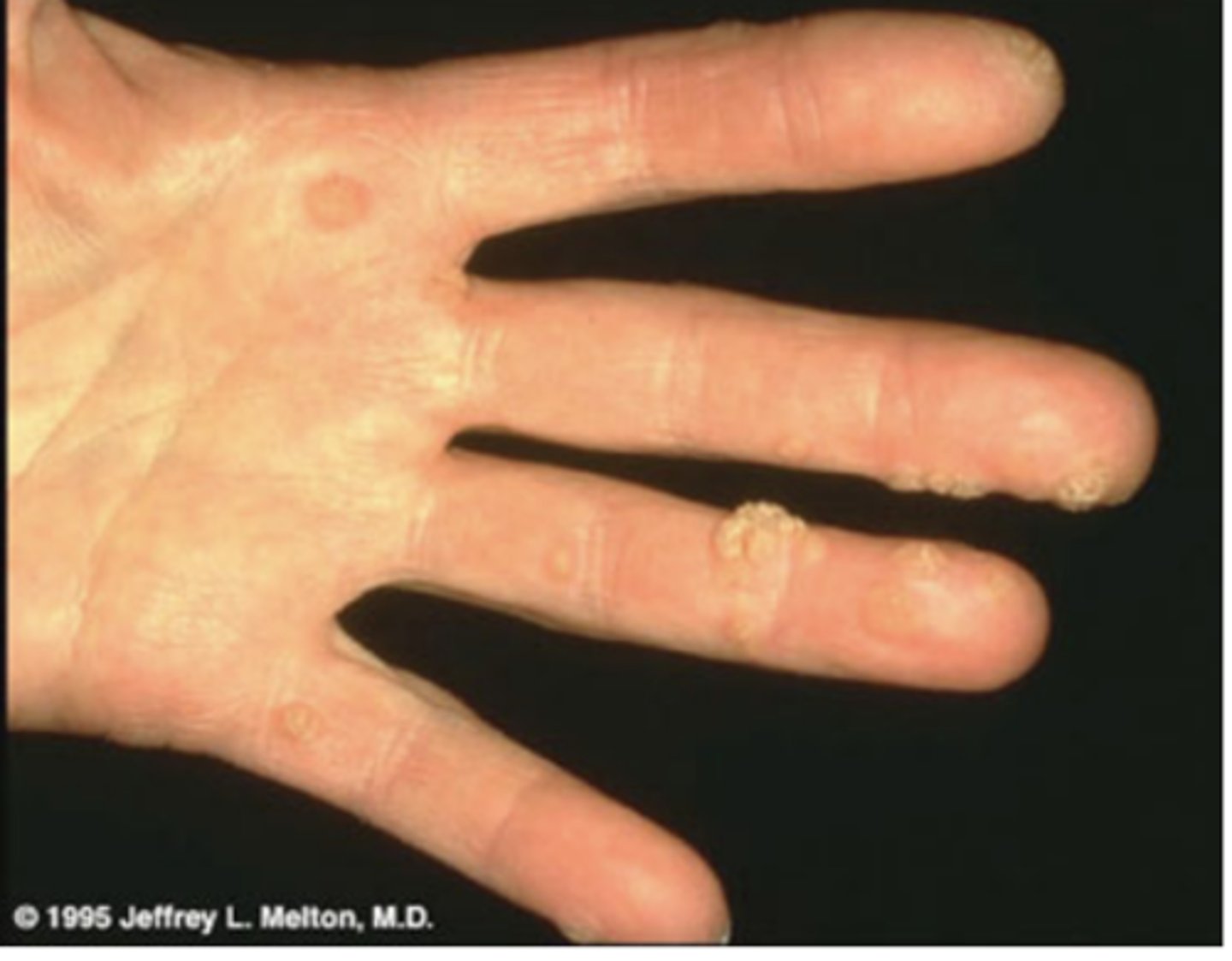
HPV oral Lesions
Depends of HPV type
- Verruca vulgaris
- Condylomas
- Squamous cell papillomas
- Squamous cell carcinoma
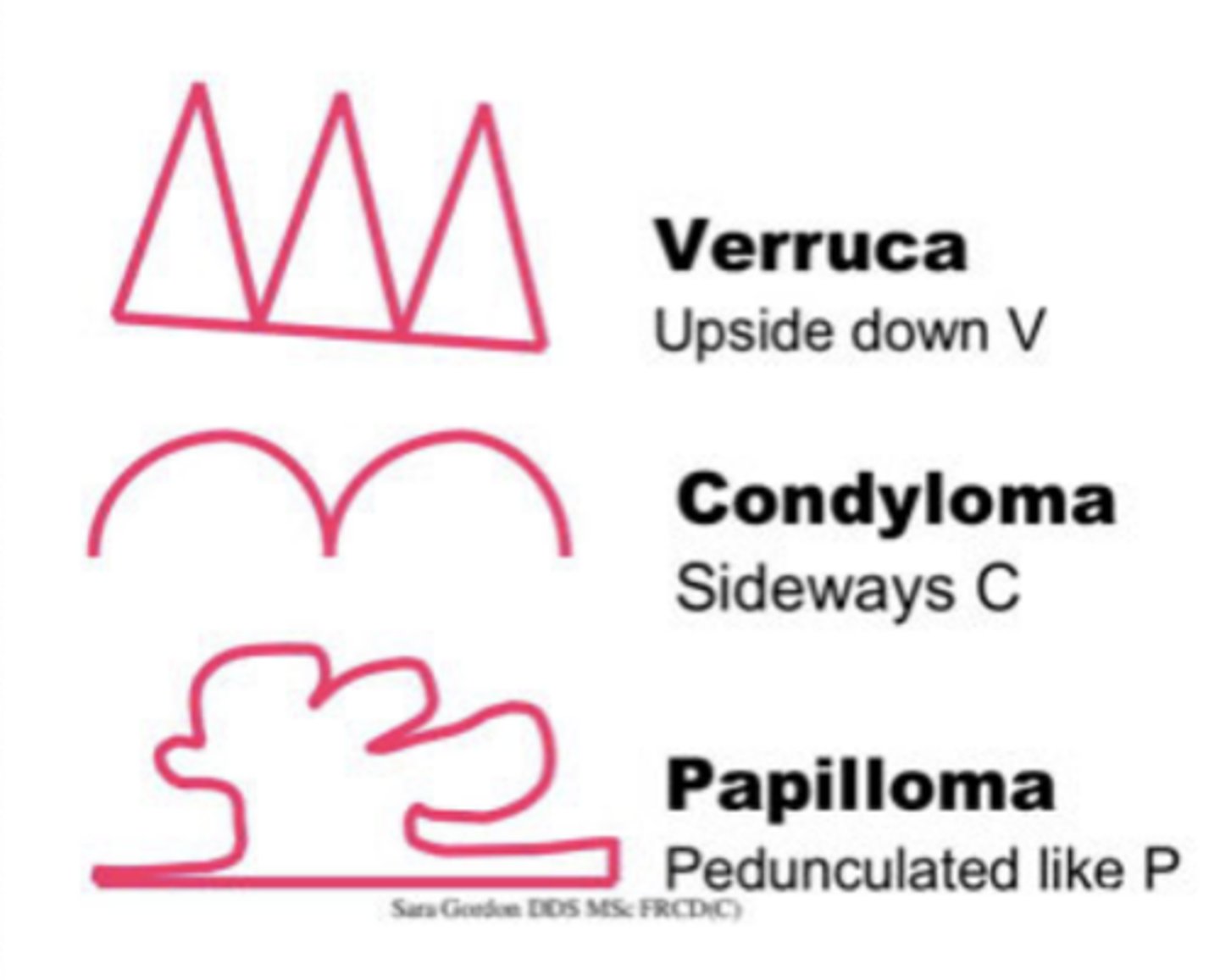
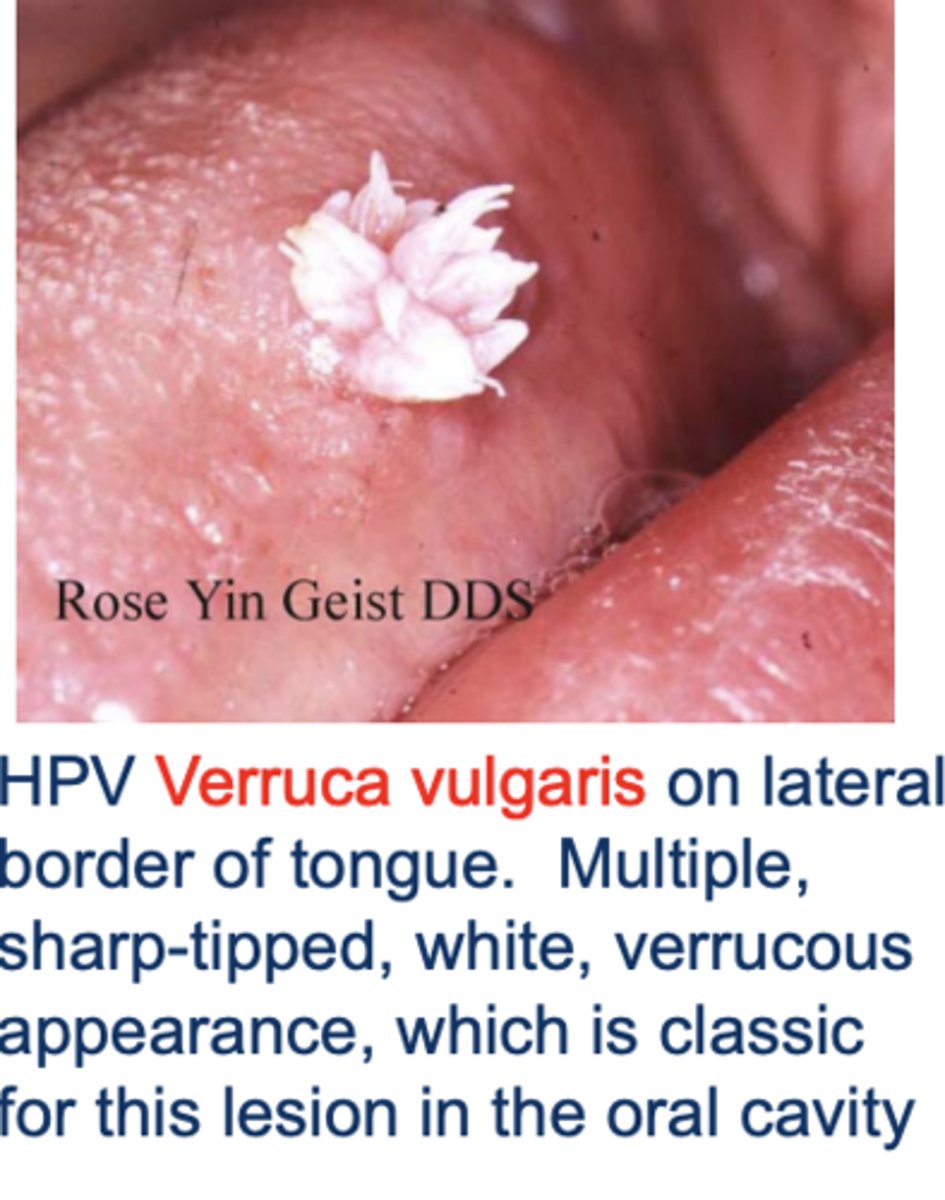
HPV Oral Lesions: Verruca vulgaris
HPV-2 and -4 are common cause
Benign
Treated with excision and or cryotherapy
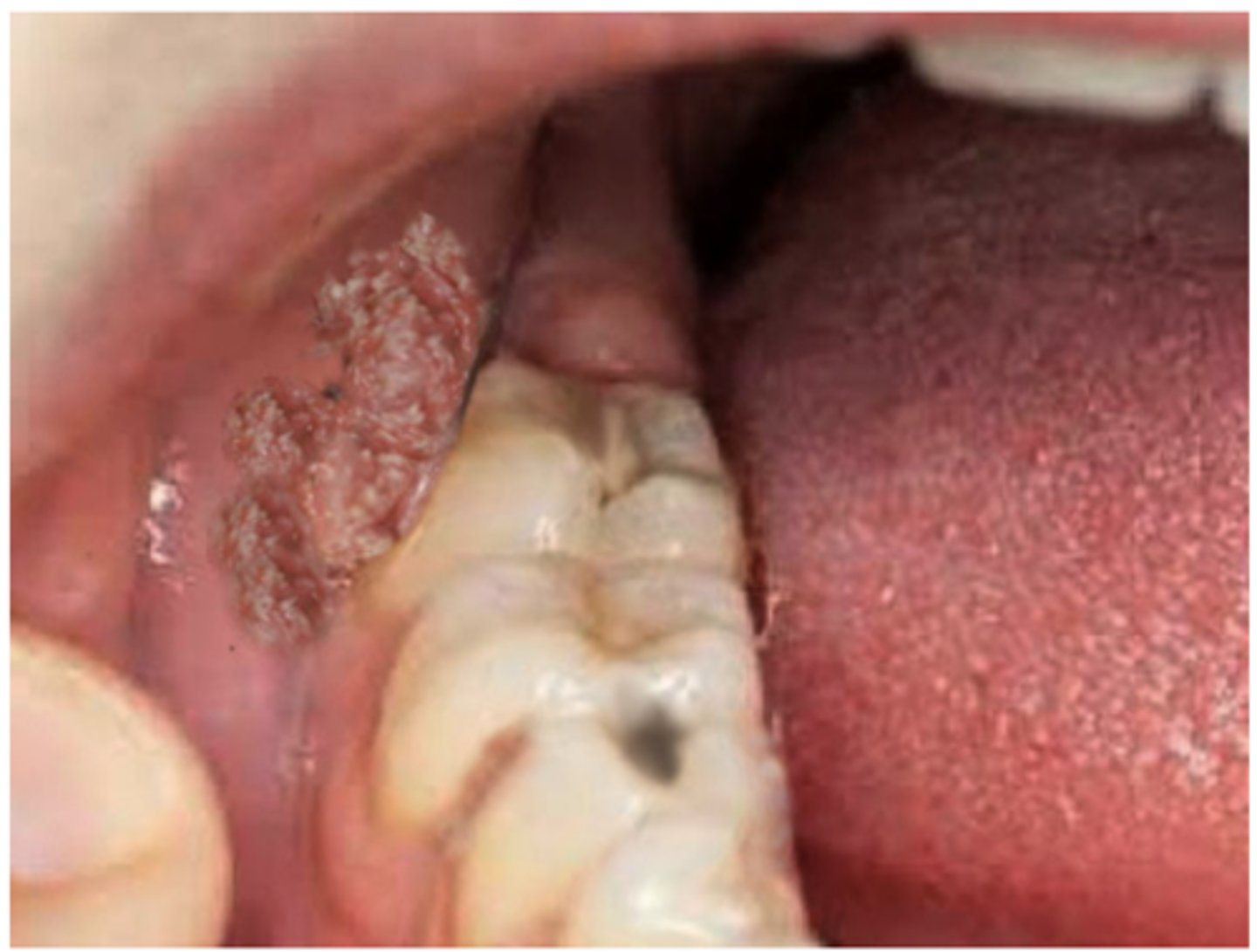
HPV Oral Lesions: Condyloma
Commonly HPV-6 and -11
Usually benign
Treated with excision, cryotherapy, trichloroacetic acid, Imiquimod
Usually sexually transmitted
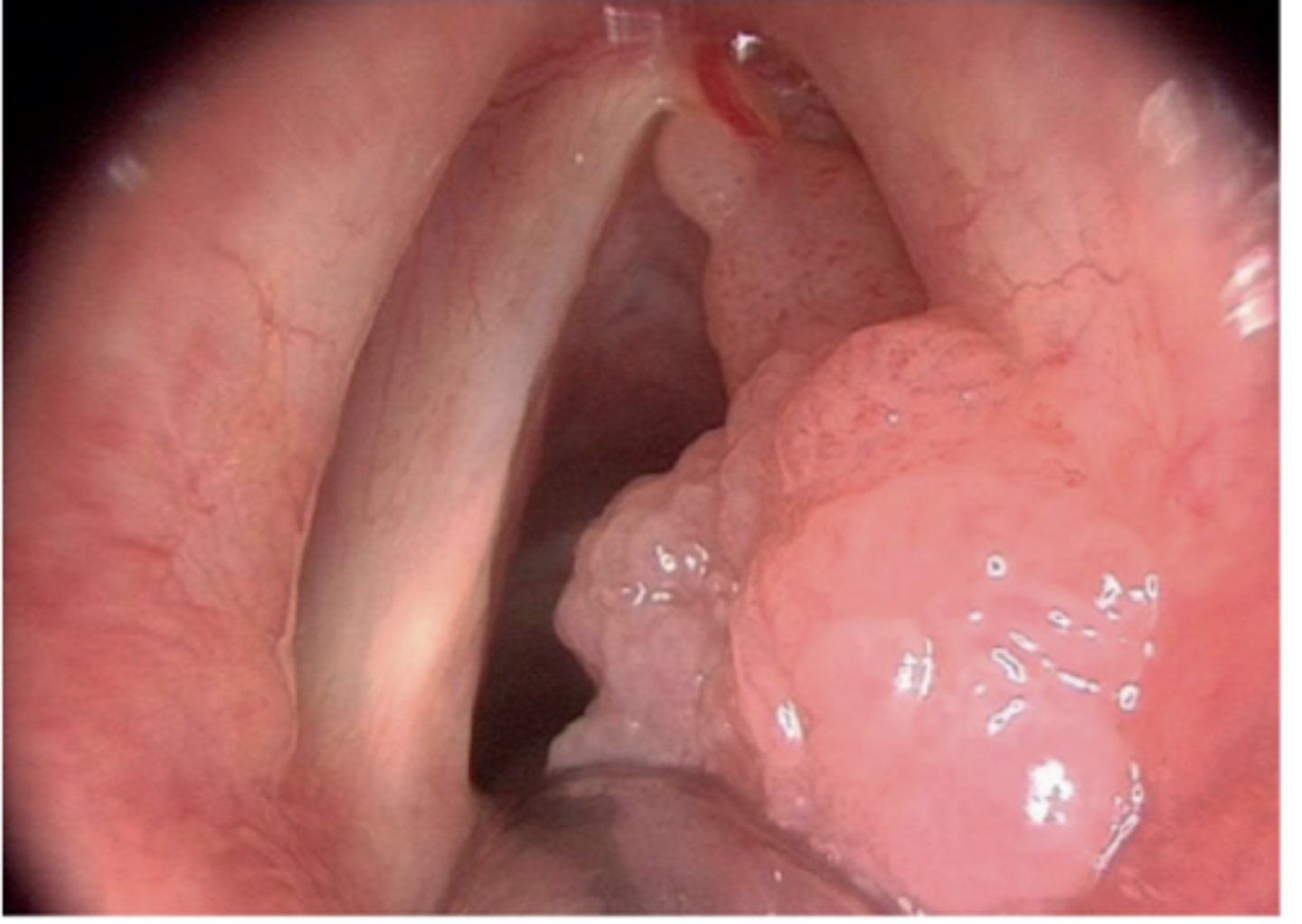
HPV Oral Lesions: Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis (RRP)
Caused by HPV 6 and 11
Usually caused by transmission from mother to baby during birth
Larynx, vocal cords, other areas of respiratory tract
Recurrent, requires constant surgical removal
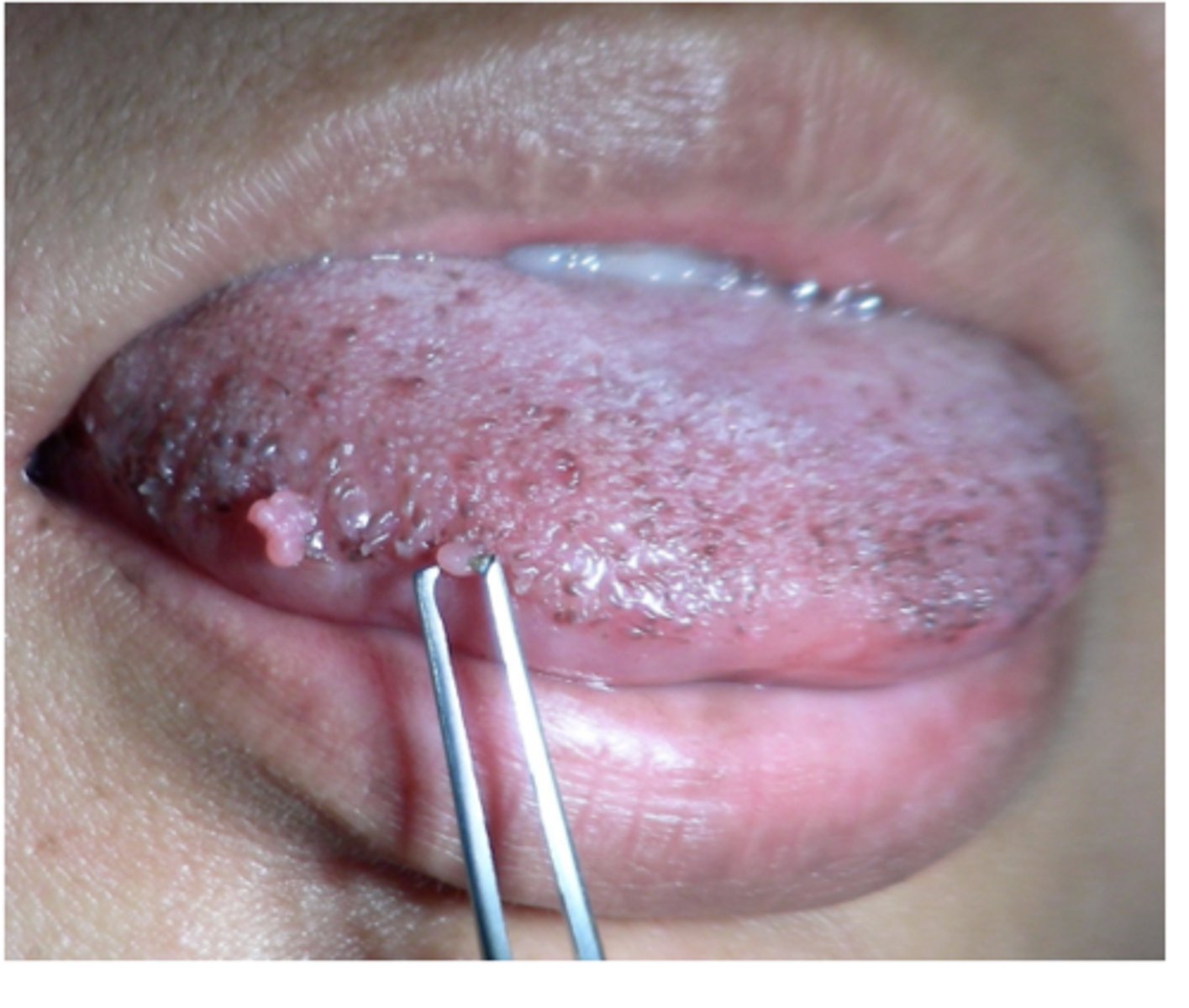
HPV Oral Lesions: Oral papillomas
Commonly HPV-6 and -11
benign HPV lesions are removed surgically or by cryotherapy
May recur
HPV Oral Lesions: HPV associated head and neck cancer
In som cases oral HPV infection can lead (after many years) to HPV-OSCC (HPV positive Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma)
Associated with the high risk serotypes (mainly HPV-16, sometimes 18)
More common in men than women
HPV related cancers
Cervical cancer is still the second most common cancer for women in the world. greater than 90% of cervical vulvar and anal cancers caused by HPV
Men at greater risk for HPV associated head and neck cancers
75% of the sexually active population have or had
anogenital HPV at some time point with 40% with high risk HPV
At any time point ____ of women are infected
1/4
Papillomavirus Viron Characteristics
Icosahedral shape
Non-enveloped
*L1: major capsid protein
L2: Minor capsid protein
Circular double strained viral DNA genome inside capsid
HPV infects basal cells of epidermis through
tear or wound
- Receptor is probably an integrin
- Maintenance of genome at low level in basal cells. No infectious virions produced in the lower basal layer
NOTE:
- Gets into cell and has to go to nucleus
After the tear or wound heals, the basal cells differentiate into squamous cells as they move up in layers of the skin.
What does the HPV virus due during this
Starts replicating more as the cells are pushed out into the suprabasal layer and they don't start producing infectious virions until they get to the surface
- released either as individual virions or in what are called squames
NOTE:
So the squamous cells are the cells on the surface and that is where the HPV is the most virulent so when those cells are shed the virulent HPV goes with and can infect others (or animals)
HPV infection and viral gene expression dive aberrant cell proliferation (JUST A PICTURE NOT A QUESTION)
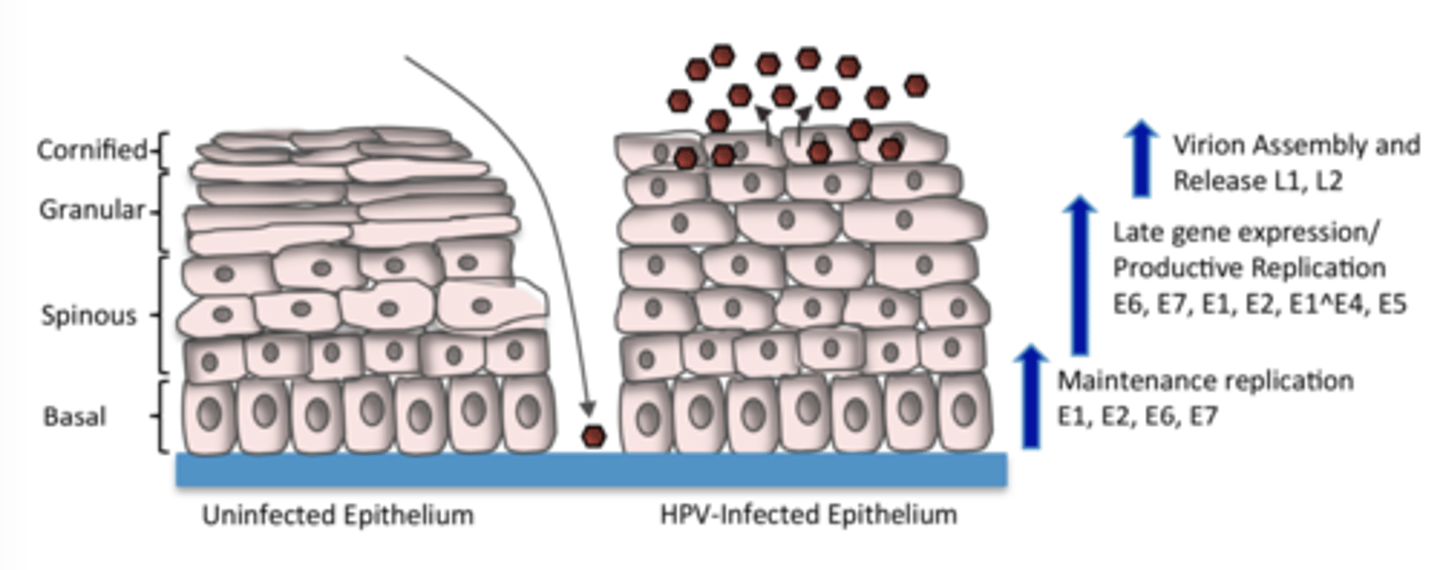
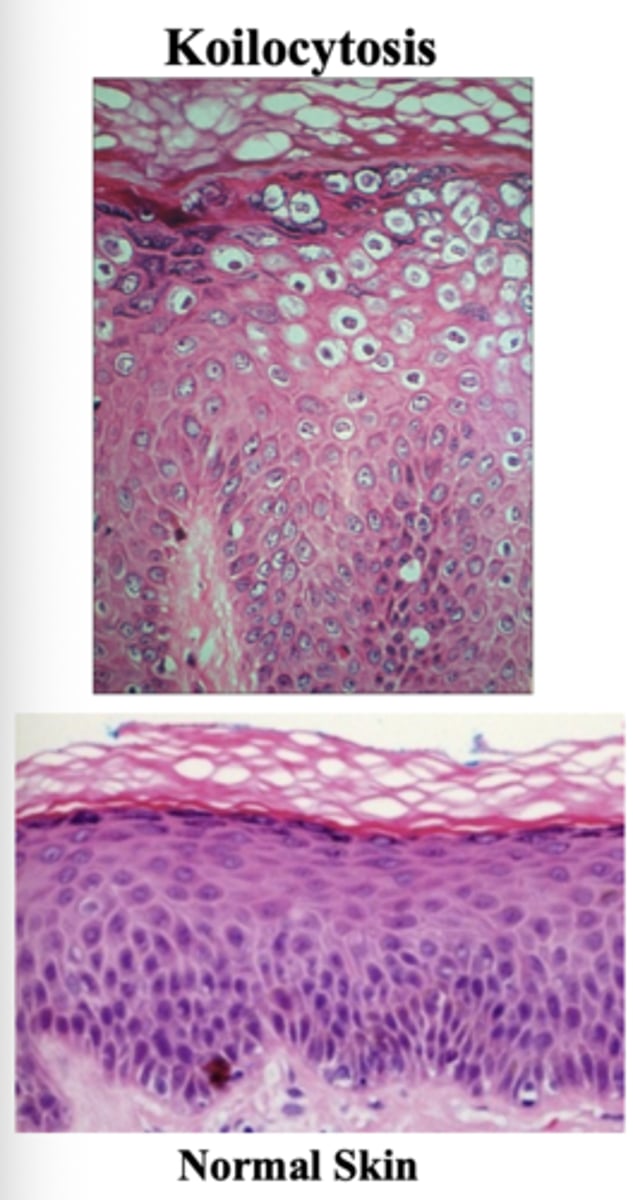
An HPV infection results in aberrant proliferation and the development of __________ in outer layers of skin or mucosal surface
koilocytes
Koiloytosis describes the presend of koilocytes in a specimen:
- Nuclear enlargement
- Irregulatiry of the nuclear membrane contour
- Darker than normal staining nucleus
- Clear area around the nucleus
- Sloughed or scraped off koilocytes can be used for identification of low grade HPV lesion by pap smear
How does HPV cause aberant cell proliferation
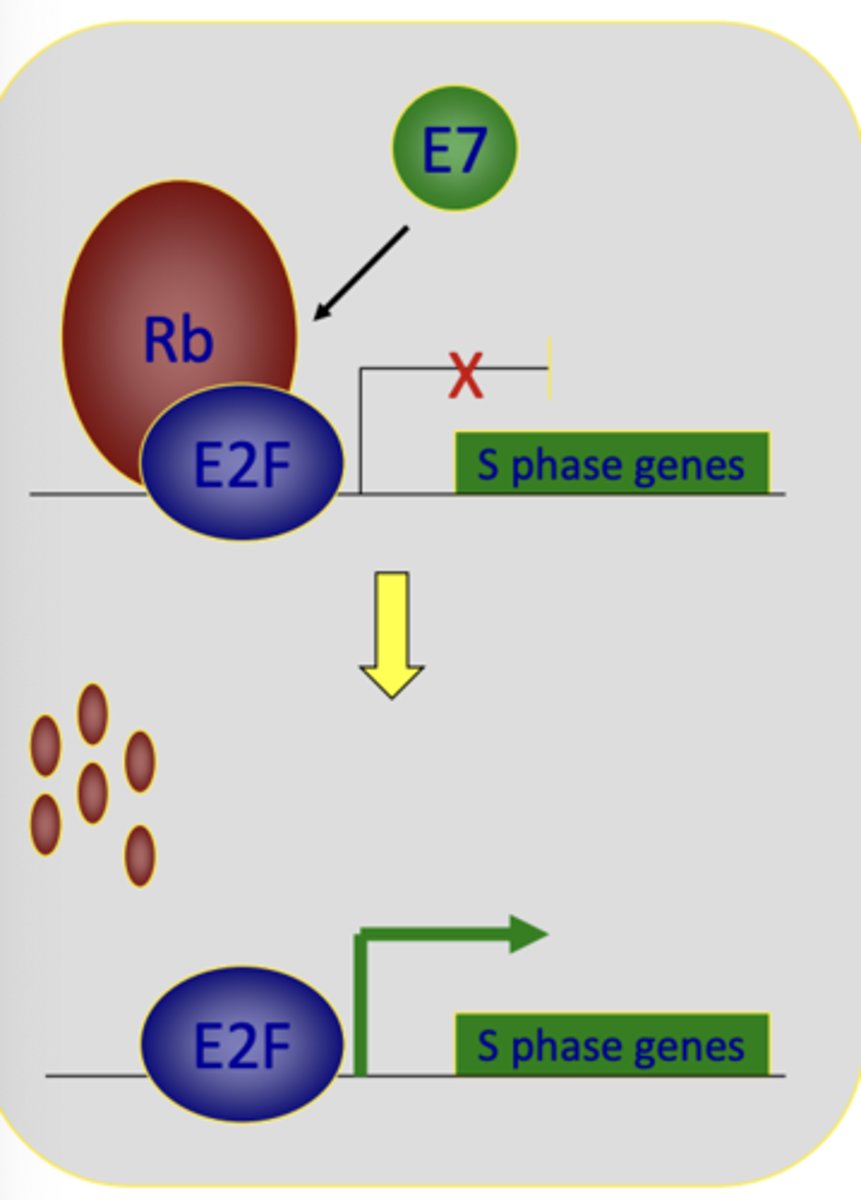
HPV proteins E6 and E7 drive cells to synthesize DNA and proliferate continuously
Virus uses cellular mechanisms to replicate DNA so wants cells in S phase
NOTE:
- E6 and E7 **** shit up in the cell cycle specifically in the S (synthesis phase)
- P53 is a baller (guardian of the genome)
- E6 ****s up P53 because they hate each other something
- E2F turns on S phase genes = allows for S phase
- Rb hangs onto the E2F transcription factor which prevents cells from moving to the S phase until its ready
- E7 ****ing destroys Rb and thus cell is forced forward to synthesis even when it just wants to hang out in G1
Overall result: Continuous cell cycle = aberrant proliferation
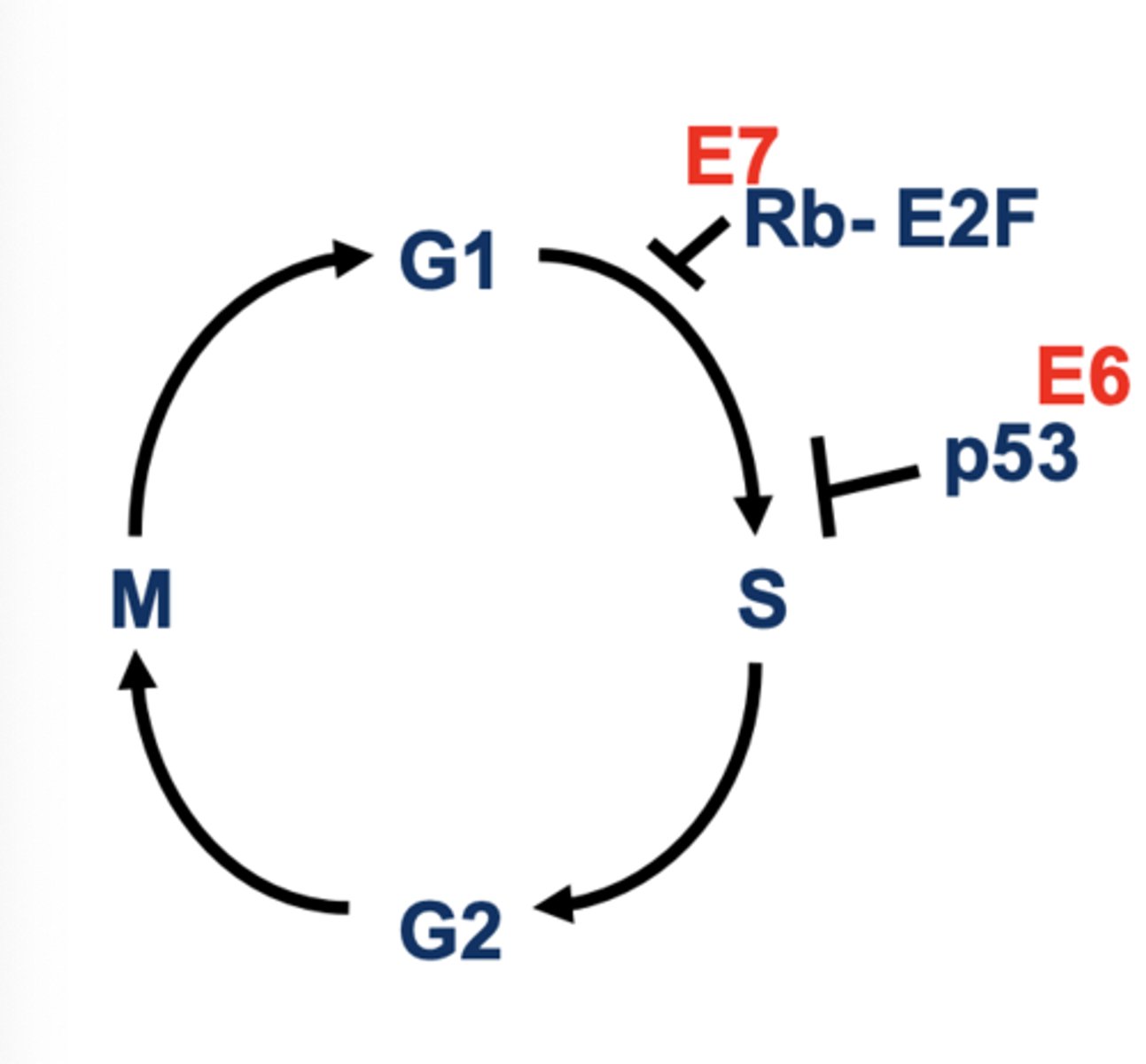
E7's degradation of __ causes release of E2F and stimulation of S phase genes
Rb
E6's degradation of ____ releases cell cycle control
p53
The E6 protein
Causes degradation of the cellular protein p53 through interaction with a ubiquitin ligase called E6-AP
HPVs that do not cause cancer are less able to degrade p53
Other E6 functions:
- Activates hTERT 9telomerase, an enzyme necessary for immortalization of cells) only types that cause cancer do this
- Degradation of other cell components important for controlling cell growth
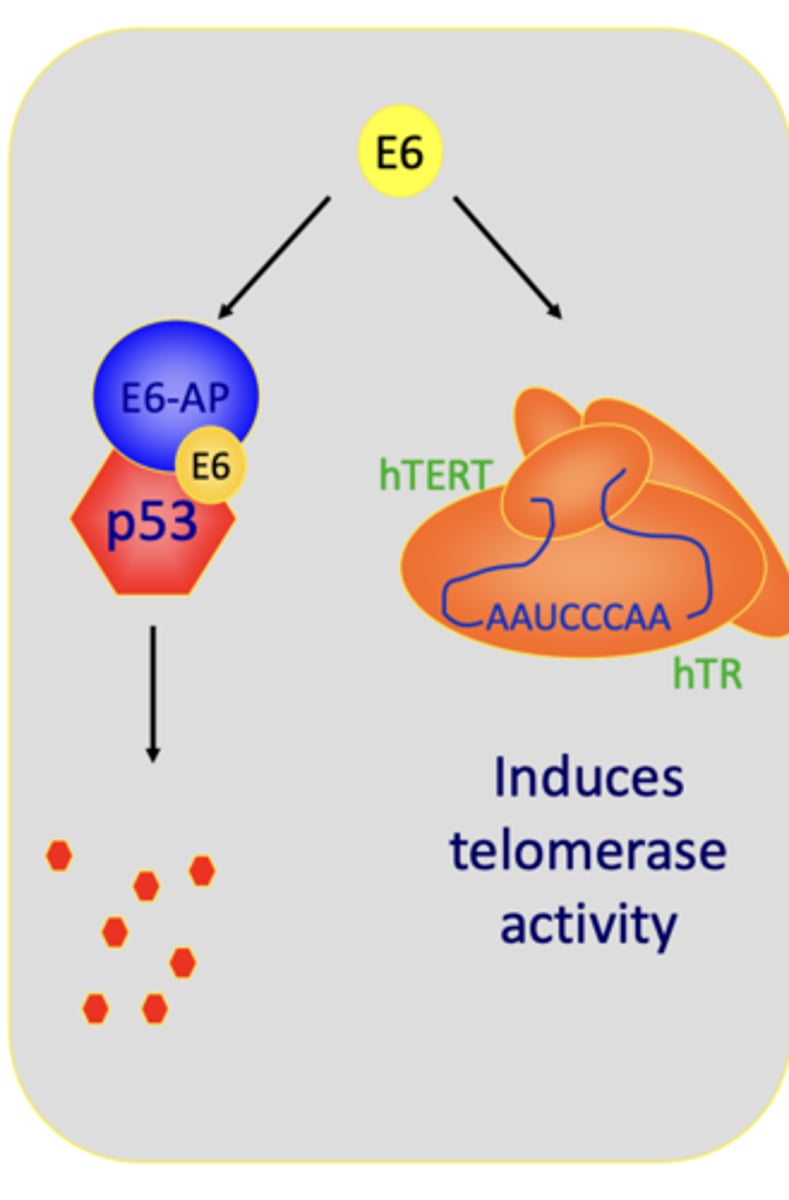
The E7 Protein
inactivates a cellular tumor suppressor protein called Rb
- Causes release of transcription factor E2F to stimulate DNA synthesis genes
- High risk HPV types are better at doing this than low risk types
Why does HPV do all this bad stuff to you cell
1. Needs to avoid recognition as damage
2. Needs to get those S phase genes going so it can use the resources from the S phase
HPVs infect stratified epithelium--> progression to malignant cancer often associated with viral genome integration
- Leads to unregulated high expression of E6 and E7
- Virus no longer produced after integration
- May stay this way for decades before cancer develops
NOTE:
- Cancer is not something that is on purpose of the virus
- Virus want to make more virus but once its integrated it not longer produces any infectious virus (dead end for replication)
- Dead end for replication of virion but it causes the cell to continue to proliferate
HPV-Associated cervical cancers: Detection and treatment
Caused mainly by:
- 16 18 31
PCR detection now regularly used in clinic
Prolonged or persistent HPV infection is comon
Pap smears can detect early lesion when they are treatable (surgery, cryotherapy)
Later stage lesion (surgery, radiation, chemotherapy)
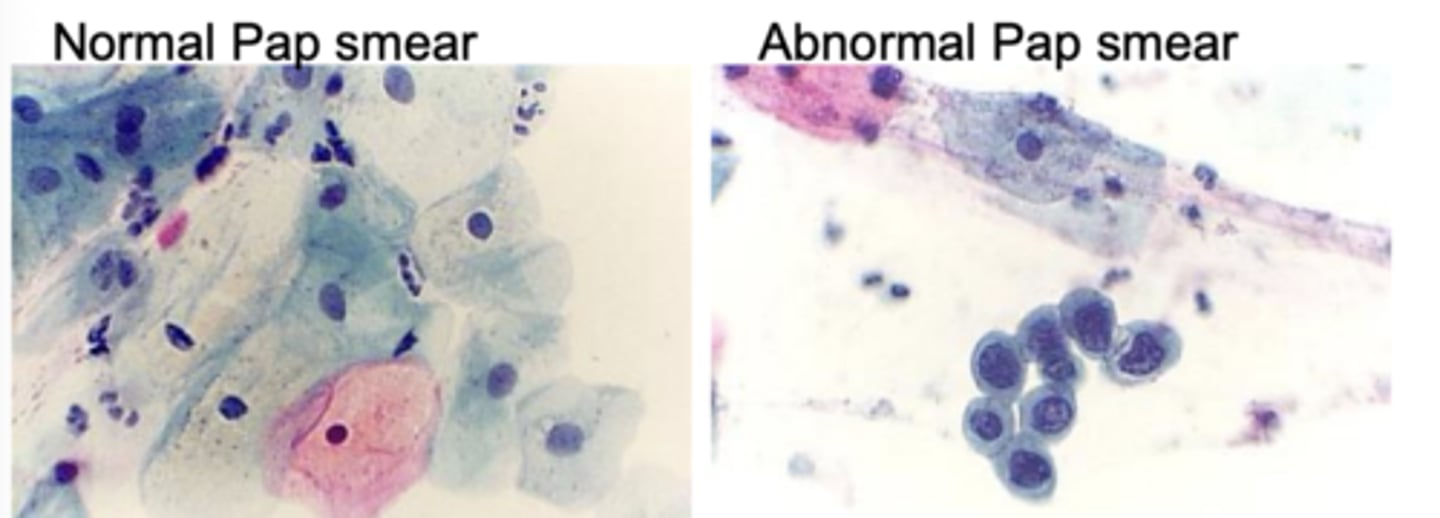
HPV-associated oral cancers: Detection and Treatment
Dentists are often the first to detect oral cancers
No pap smear type assay available for oral cancer
PCR can be done on biopsy to detect type of HPV
Approximately 50% of oropharyngeal cancers caused by HPV
Treatment of cancer usually through surgery and radiation (HPV oral cancers are more treatable than non-HPV oral cancers)
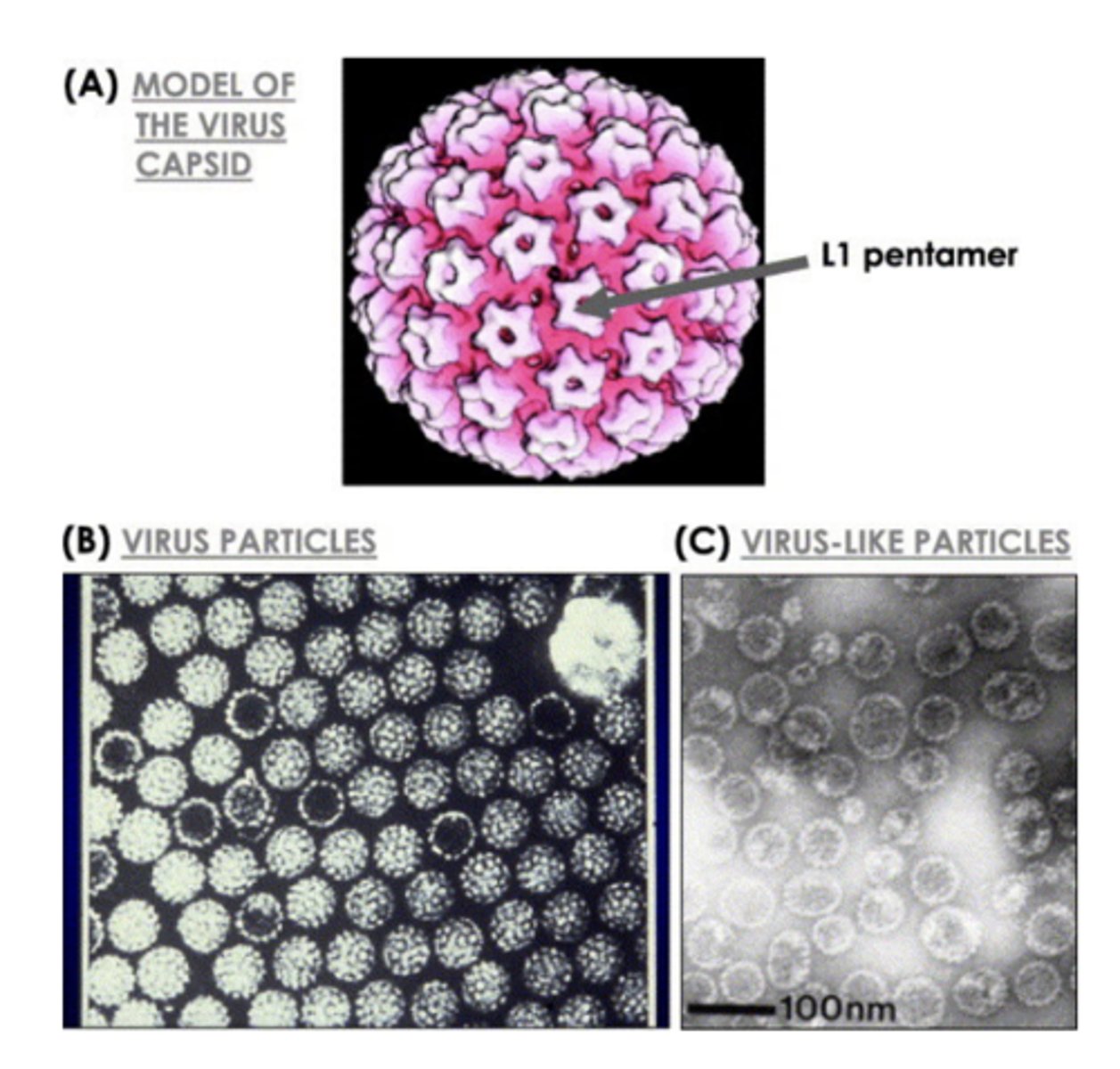
Development of Prophylactic HPV Vaccine
- HPV L1 protein expressed in yeast or by baculovirus
- Forms L1 pentamer
- Pentamers form virus-like particles that are non-infectious (no genome)
Commercially Available HPV Vaccines
Merck
- Gardasil: L1 like particles from
-- HPV 6 11 16 18
- Gardasil 9 (Nonavalent) recommended
-- HPV 6 11 16 18 31 33 45 52 58
GSK
- Cervarix (Divalent)
-- HPV 16 18
HPV vaccine studies demonstrate high _____ after vaccination
antibody titers
Large scale HPV vaccine studies demonstrate ___-__% efficacy in preventing HPV infections and subsequent HPV associated lesions
97-100%
Since the first HPV vaccine was recommended in 2006 there has been a ____% reduction in vaccine type HPV infections among teen girls in the US
64
HPV vaccine is reducing prevalence of ________ and
Cervical and HPV associated head and neck cancers
Adverse effects of HPV vaccines are typical:
headaches, aches, fevers
Fainting associated with vaccination very rare
Challenges of HPV Vaccination
Prophylactic not curative, millions infected already
Distribution and recommendation of vaccine by health care providers
Cost (insurance pays if you have it)
Multiple types (main types covered by nonavalent vaccine but others could emerge as a problem)
Acceptance of vaccine
- Religious and social concerns
- Misinformation
- Low compliance for boys
Michael Douglas
Had HPV 16 associated oropharyngeal cancer that was successfully treated
- Men are at higher risk of developing oral cancer caused by HPV than are women
- Vaccination recommended for boys
TOPHAT: What is the role of HPV E6 and E7 proteins in HPV infection
A. They act together in a DNA polymerase complex to preferentially synthesize viral DNA over cellular DNA
B. They inhibit the cell cycle checkpoint proteins p53 and Rb and drive DNA synthesis and cell proliferation
C. They enhance entry of the virus into cells
D. They act together as viral RNA polymerase to preferentially transcribe viral genes
B
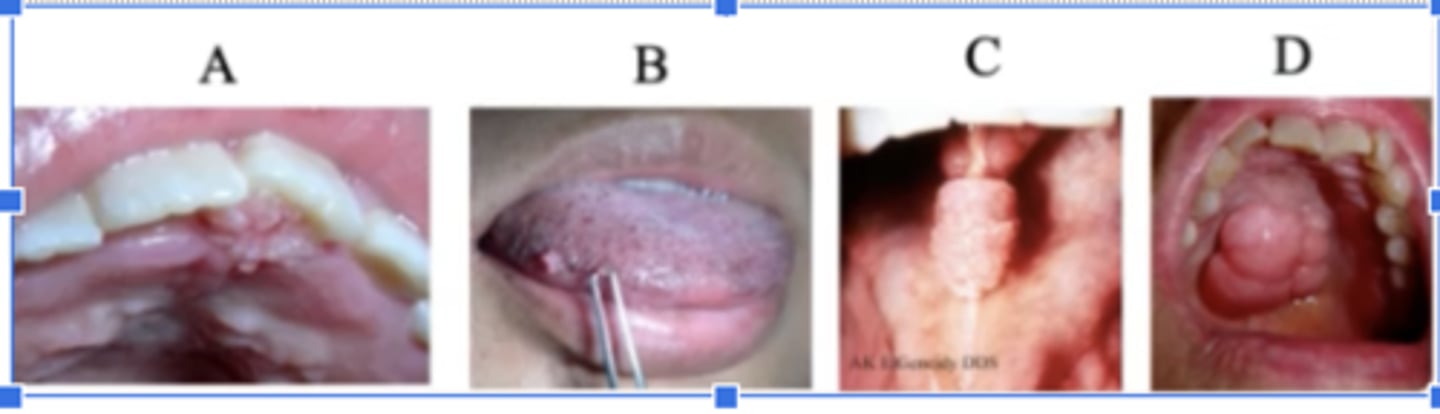
TOPHAT: Which photo most likely represents a squamous cell carcinoma
- Other side of card-
A
B
C
D
D
TOPHAT: What is untrue about HPV vaccines
A. They are made by using HPV L1 proteins expressed in baculoviruses or yeast
B. They can prevent certain HPV-associated oral lesions and cancers
C. They are effective at treating already-present HPV-associated lesions
D. They are non-infectious
C
TOPHAT: What is untrue about adenoviruses
A. The virion is icosahedral and non-enveloped
B. The target tissue and symptoms depends largely on the adenovirus type
C. The genome is double-stranded DNA
D. They are associated with the development of cancer
D
TOPHAT: Which of the following statements best describes the risk associated with HPV types 16 18 33
A. These types are associated with common skin warts
B. These types are primarily linked to benign oral lesions
C. These types are classified as high-risk associated with cervical cancer
D. These types are commonly known to cause benign oral lesions and anogenital warts
C