Flashcards to cram for AP HuG Exam
1/847
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
848 Terms
Acculturation
groups exchange ideas but keep distinct features
Assimilation
groups interact and one changes to resemble dominant culture
Built landscape
appearance of an area shaped by both human and natural influences
Cartography
science of making maps.
Census
official count or survey of a population
Climate
long term average weather condition in an area
Cluster
group of things positioned or occurring closely together
Concentration
extent of feature spread over space
Conservation
manage resources to meet needs while saving up for future
Contagious Diffusion
rapid diffusion of characteristic throughout a population
Culture
custom beliefs, social forms, and material traits that form a group’s distinct tradition.
Cultural landscape
Fashioning/modification of a natural landscape by cultural group
Density
frequency of something occurring in space
Environmental Determinism
how physical environment causes social development
Diffusion
process by which features spread across space
Distance decay
how interaction between groups lessens as distance increases
Disperse
distributing things equally over a wide area
Ecosystem
where living biotic organisms interact; biosphere
Erosion
when soil is washed away by wind and rain; abiotic factors like atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere.
Five Themes of Geography
Movement, Region, Human-Environment Interaction, Location, Place
Geographic information system (GIS)
computer that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data's surface, climate, continents, countries, peoples, industries, and products.
Global positioning system (GPS)
system that determines precise position of something on Earth using satellites, tracking stations, and receivers.
Globalization
Actions or processes involving entire world, Multinational/Transnational corporations
Hearth
region where an innovative idea originated.
Hierarchical Diffusion
Idea spreads from powerful people/authority
Human-Environment Interaction
Relationship between humans and surroundings; Adapt, Modify, Depend
International Date Line
imaginary line separating time zones from one day to another on the globe.
Latitude
horizontal numbering system indicating location of parallels on a globe; measure distance north and south of the equator (0°).
Location
Specific coordinates or relative associations pinpoint absolute position
Longitude
vertical numbering system indication location of meridians on a globe; measure distance east and west of the prime meridian (0°).
Map
flat 2d depiction of Earth's surface
Migration
The movement of individuals or groups from one location to another, often influencing cultural and economic exchange while spreading out ideas
Meridians
arc drawn on a map between North and South poles
Network
Chain of communication connecting places
Parallels
circle drawn around globe parallel to equator and angles to meridians at the right
Place
point on Earth distinguished by a particular physical landforms or human additions
Possibilism
Although environment is limited, people can adapt and adjust by modifying
Preservation
maintain condition of resources with little human interference
Projection
transfers Earth’s locations to flat map
Region
area distinguished by unique trends or features; Perceptual/vernacular is fueled by feelings, Nodal focuses on central function, uniform has formal economy, politics, or social structure
Regionalism
organization of earth's surface into distinct areas that are all different
Relocation
Idea spreads through migration/movement of people
Resource
substance in environment useful to people, helps economy and technology
Scale
Compare size of features on a map to real life
Site
physical character of a place
Situation
location of a place relative to other places
Space
gap or interval between two objects
Space-Time Compression
reduced amount of time for something to reach another place
Stimulus
underlying principle spreads although characteristic itself did not diffuse
Sustainability
ensure resources are available in future (renewable and nonrenewable)
Syncretism
both groups form new elements of culture
Toponym
Name of a place
Isoline
A line on a map connecting points of equal value, such as temperature or elevation.
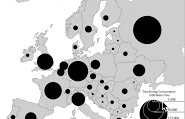
Dot distribution
Size of each dot shows numerical value
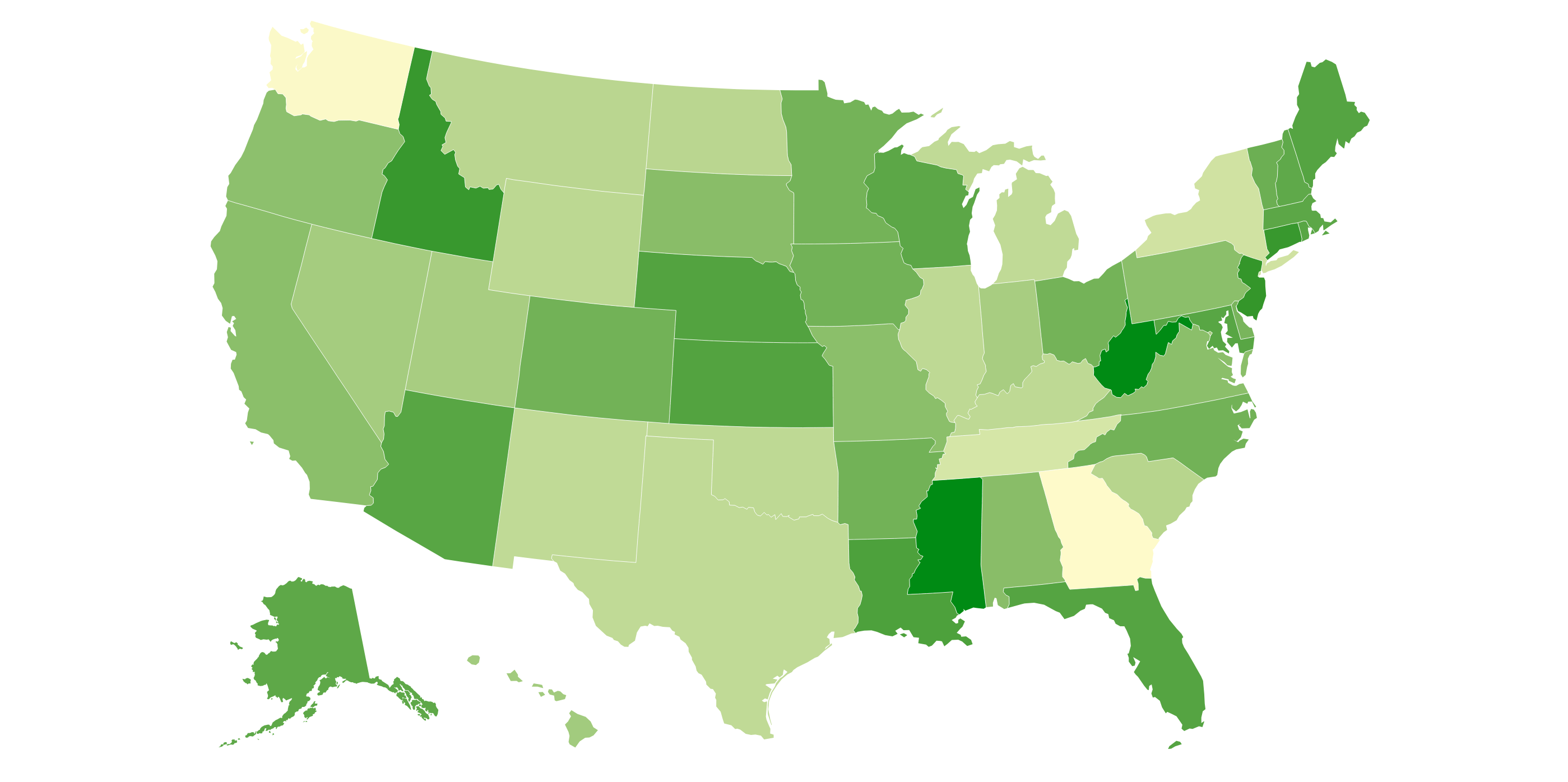
Choropleth
Darker color/shading represents greater numerical value
Graduated Symbol
Size of symbol changes according to numerical value
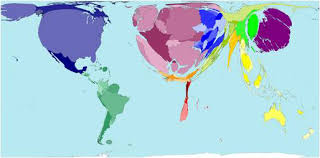
Cartogram
A map in which the sizes of geographic regions are scaled according to the value of a specific variable, distorting their actual shapes to emphasize data representation.
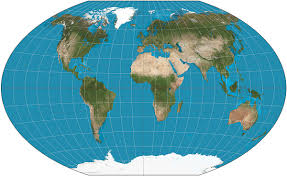
Winkel Tripel
Used in most textbooks/atlases, shows relative size of places near equator and distorts the North and South Poles
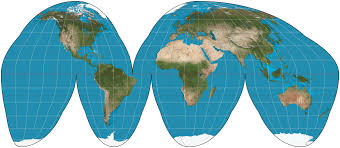
Interrupted Goode
Maintains the accurate size of landmasses while distorting shapes and distances. The disconnected sections makes it difficult to study spatial relationshipsand analyze patterns effectively.
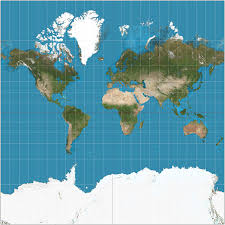
Mercator
Help navigate oceans, rectangular shape, keeps direction. Distorts sizes near the polar areas and doesn’t accurately represent some countries
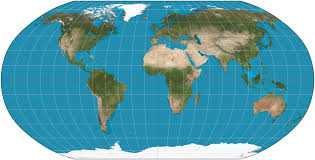
Robinson
Less distortion at equator; distorts everything by a bit, especially poles
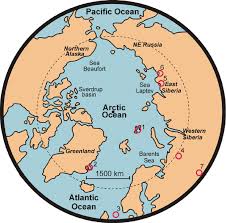
Polar
Focus on North/South Poles and places nearest and distorts places near the equator
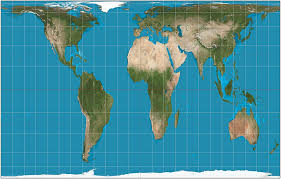
Gall-Peters
Shows correct size/shape of landmasses and oceans, distorts regions along edges
Asylum seeker
refugee who migrates permanently to another country for protection, not recognized by government as a refugee (an official recognition of a person fleeing a conflict)
Antinatalist
Support lower birth rates
Pronatalist
Government supports high birth rates
Brain drain
emigration of skilled workers in country
Brain gain
immigration of skilled workers to new countries
Carrying capacity
max number of people Earth’s resources can sustain, higher when near reliable source to accommodate population distribution
Census
Given by the U.S. government every decade; it collects demographic data, including age, race, and housing information, which helps in policy making and resource allocation.
Chain migration
migration that happens in a series of steps
Circulation
Short-term, repetitive movement that occurs regularly
Counterurbanization
net migration from urban to rural areas in more developed countries.
Crude birth rate (CBR)
number of births per 1,000 people each year
Crude death rate (CDR)
number of deaths per 1,000 people
Demography
scientific study of human populations
Distribution
pattern of where people live
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
model describing change in CBR, CDR, and population growth through stages of economic and scientific development
Dependency ratio
estimate of number of non working people supported by a society
Diaspora
communities of a given ethnic group living outside homeland
Disease diffusion
how diseases spread through population as mortality falls; include infectious and degenerative diseases
Doubling time
How long it will take for a population to double its size
Ecumene
portion of Earth's surface occupied by humans
Emigration
migration from a place
Immigration
migration to another place
Epidemic
widespread infection of disease in a community
Pandemic
epidemic occurring over wide geographic area, affects high populations at the same time
Epidemiology
incidence, distribution, control of disease in population
Epidemiological Transition Model (ETM)
stages of health threats and diffusion
Fertility
number of children that can be conceived
Forced Migration
people compelled to move by political or environmental factors
Voluntary Migration
migrant’s choice to move for economic reason
Gender roles
culturally determined behaviors and attitudes based on sex
Guest worker
someone who is paid to temporarily immigrate for work
Infant mortality rate (IMR)
number of deaths of infants under one year of age per 1000 live births
Internal migration
movement within a country
Interregional
movement between regions in country
Intraregional
movement within a region
Internally displaced persons (IDP)
someone displaced within their country due to war, politics, or persecution