General Chemistry
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
ion
an atom that has gained or lost one or more electrons, resulting in a net electric charge
cation
a positively charged ion that results from the loss of one or more electrons from an atom
anion
a negatively charged ion that results from the gain of one or more electrons from an atom
compounds
molecules comprised of two or more different elements bonded together
(ex: H2O, CO2)
ionic compound
metal + non-metal (contain ionic bonds)
(ex: NaCl, CuCl2)
molecular compounds
two or more non-metals (contain covalent bonds)
(ex: H2O, CO2)
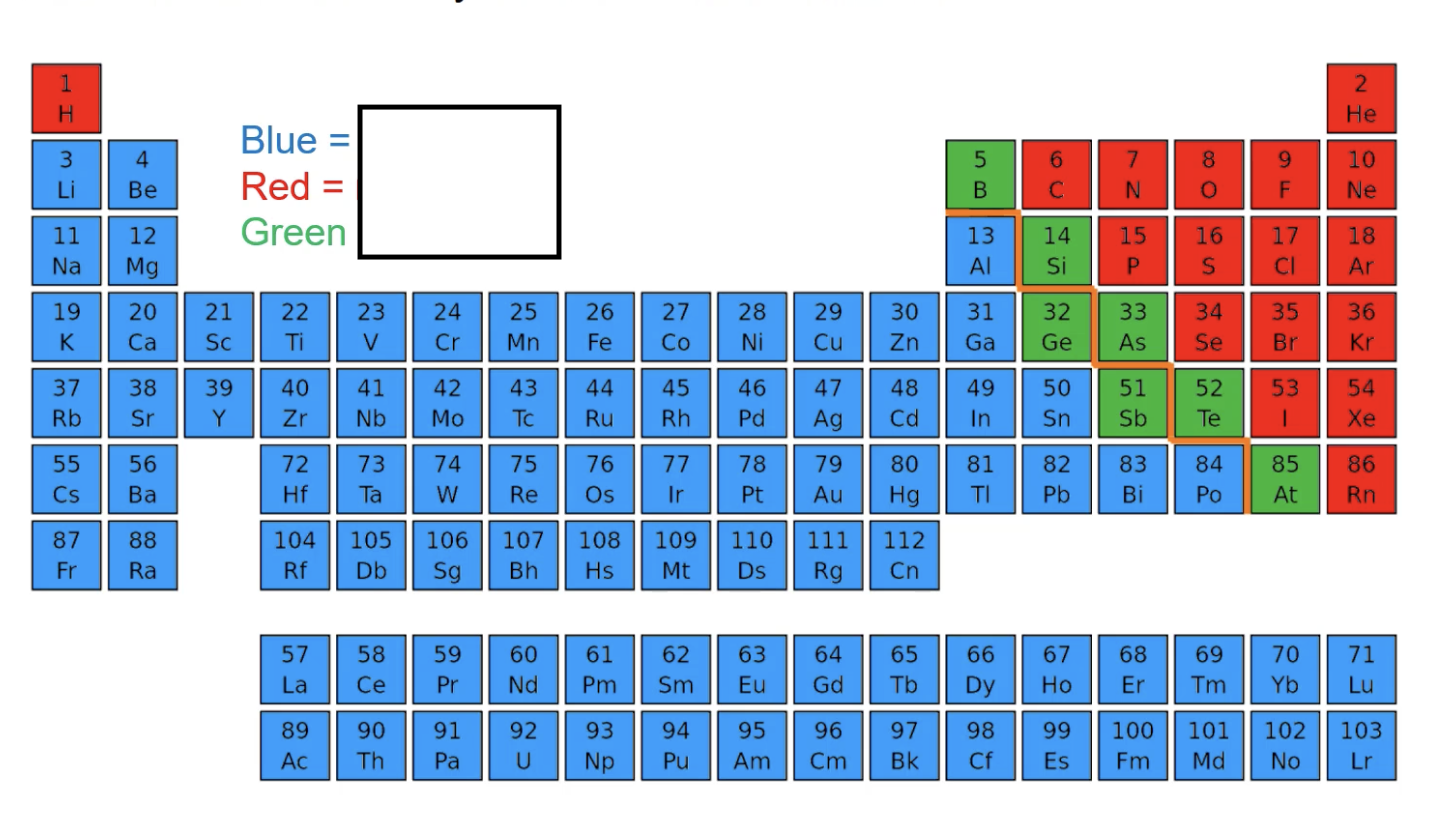
metal, non metal, metalloid
blue = ___
red = ___
green = ___
polyatomic ions
make ionic compounds even though they do NOT contain any metals
(ex: ammonium chloride NH4Cl. this is because NH4+ is a cation and Cl- is an anion)
NH4+
ammonium
(polyatomic ion)
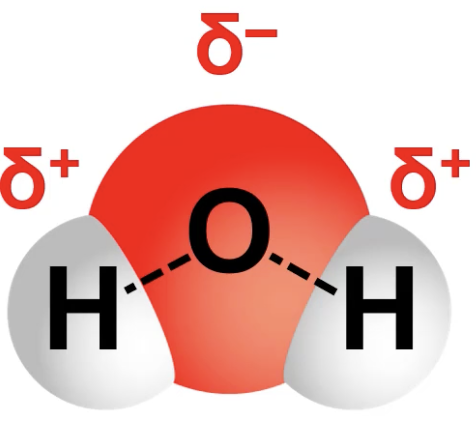
covalent bond
between non-metals
(atoms share their electrons, so they do NOT have true + or - charges. they can have partial + and - changes if they share their electrons unevenly)
(ex: oxygen hogs more e- so hydrogens are partially + and oxygen is partially -)
increases
electronegativity ___ as you go up and to the right on the periodic table
polar covalent bonds
bonds in molecular compounds that have an uneven sharing of electrons and partial positive or negative charges
(caused by a significant electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms)
nonpolar covalent bonds
occur when nonmetal bonded atoms do NOT have a significant electronegativity difference between them
ionic compounds
high melting points
high boiling points
brittle
hard
(ex: NaCl, MgO)
molecular compounds
low melting points
do not conduct electricity
intermolecular forces
(ex: H2O, Cl2)
metallic compounds
variable hardness and melting points
conduct electricity and heat
lustrous (shiny)
malleable
ductile
metallic bonding
(ex: Fe, Mg)
network covalent compounds
high melting points
high boiling points
hard
do not conduct electricity
network of covalent bonds
(ex: C - diamond, graphite, SiO2 - quartz)
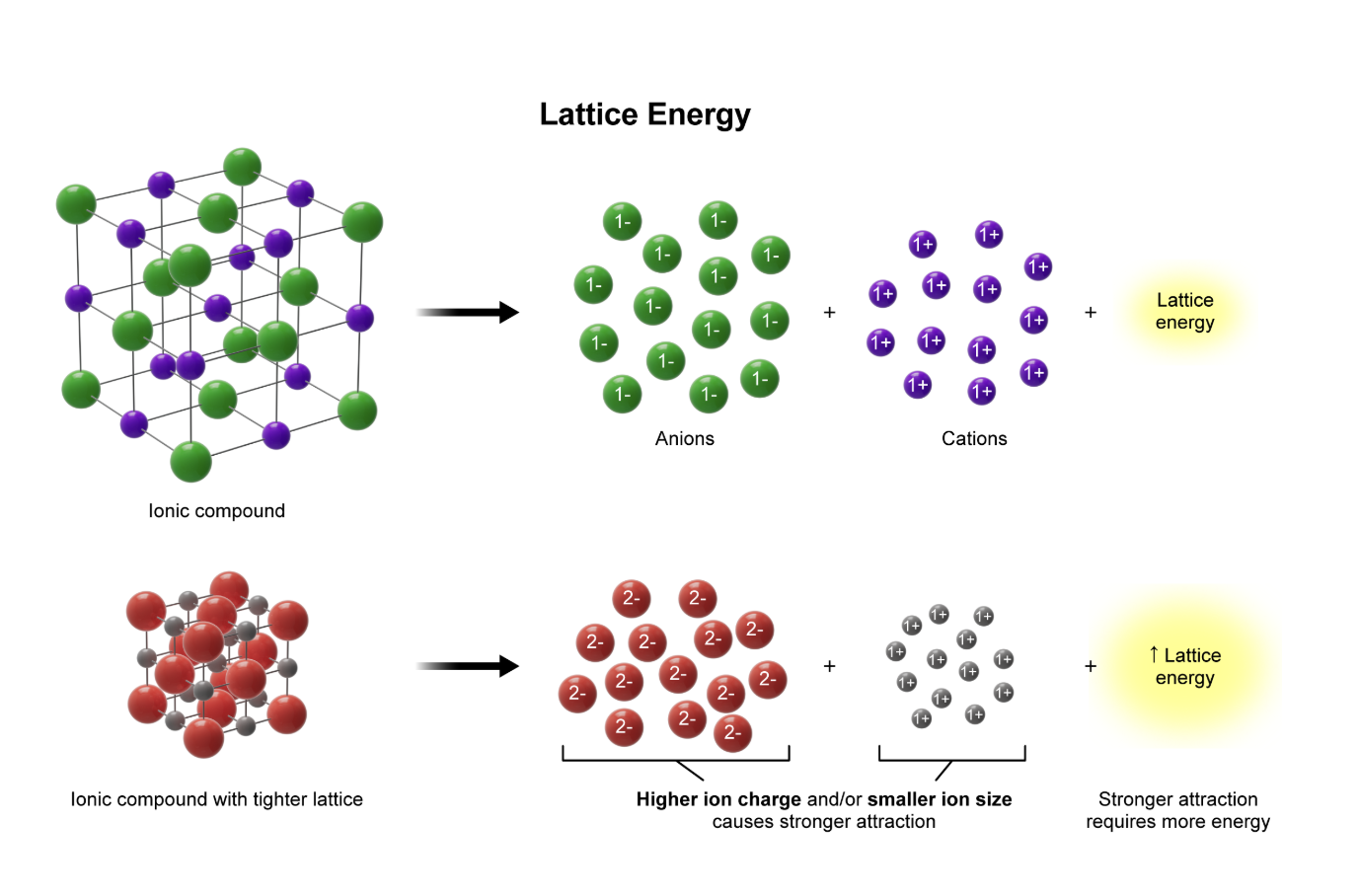
lattice energy
energy required to completely separate an ionic compounds cations from its anions
bigger charges = larger ___ energy
shorter bond distance = larger ___ energy

smaller
atom sizes get ___ as you go to the right across a row or up a column on the periodic table
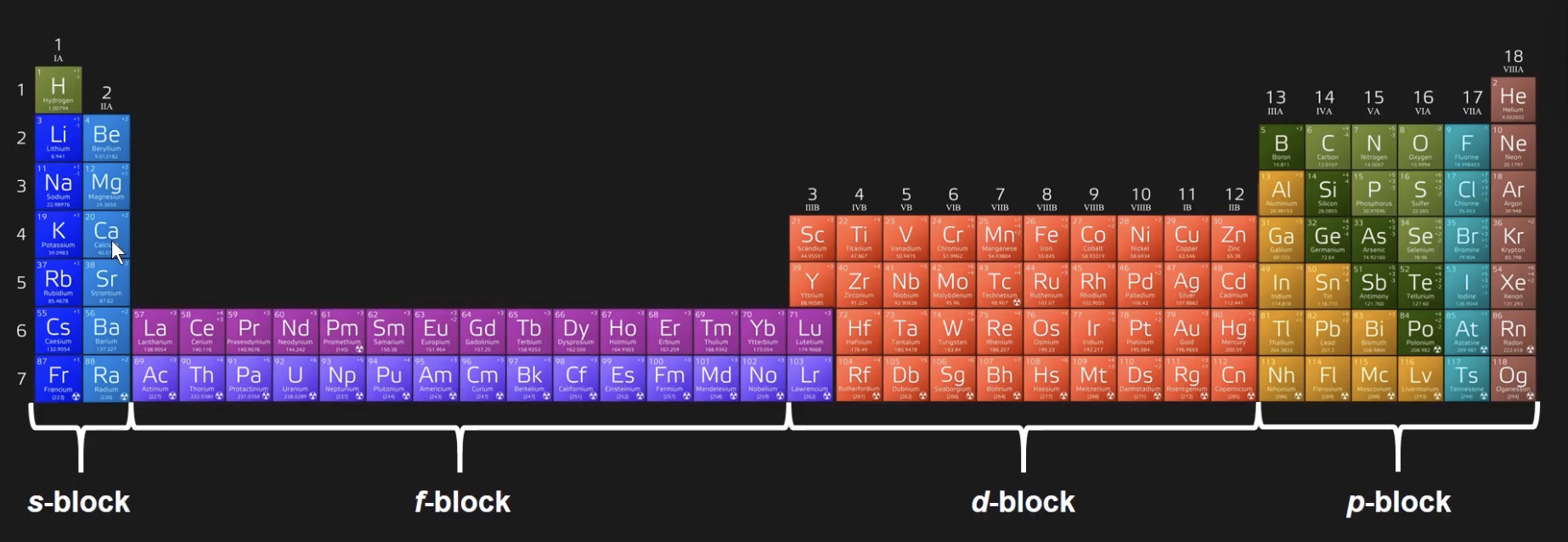
how many valence electrons?
usually the same as its column number on the periodic table
if d-block is completely filled, d-block electrons do NOT count
if d-block is NOT completely filled, d-block electrons DO count
(ex: Zn is in the last row of the d-block, also known as fully filled.) Only count the 2 s-block columns, skip all of the d-block electrons → Zn has 2 valence electrons)
valence electron exceptions to full octet rule
H: only needs 2 electrons, not 8
Be: only needs 4 electrons, not 8
B and Al: sometimes only have 6 electrons
electron configuration exceptions
Cr
Mo
Cu
Ag
Au
take away one electron from s orbital and add to d orbital
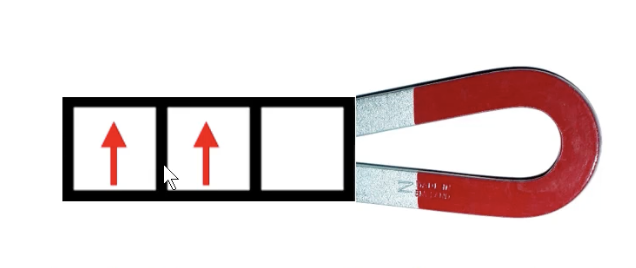
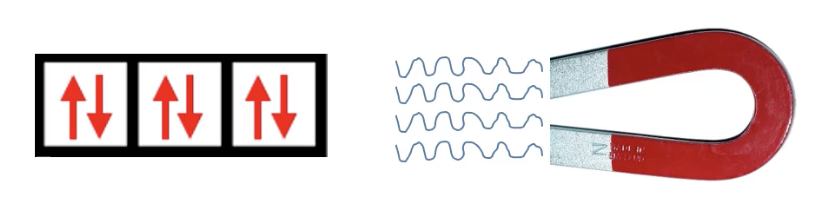
paramagnetic
has unpaired electrons
paramagnetic elements are attracted to magnets
if an element has an ODD number of electrons → paramagnetic
“unpaired”-a-magnetic
diamagnetic
all electrons are paired
diamagnetic elements are slightly repelled by magnetic fields
if an element has an EVEN number of electrons → paramagnetic OR diamagnetic (fill out electron configuration energy diagram to find out)
“DI = 2 → electrons are paired (2) → repel”
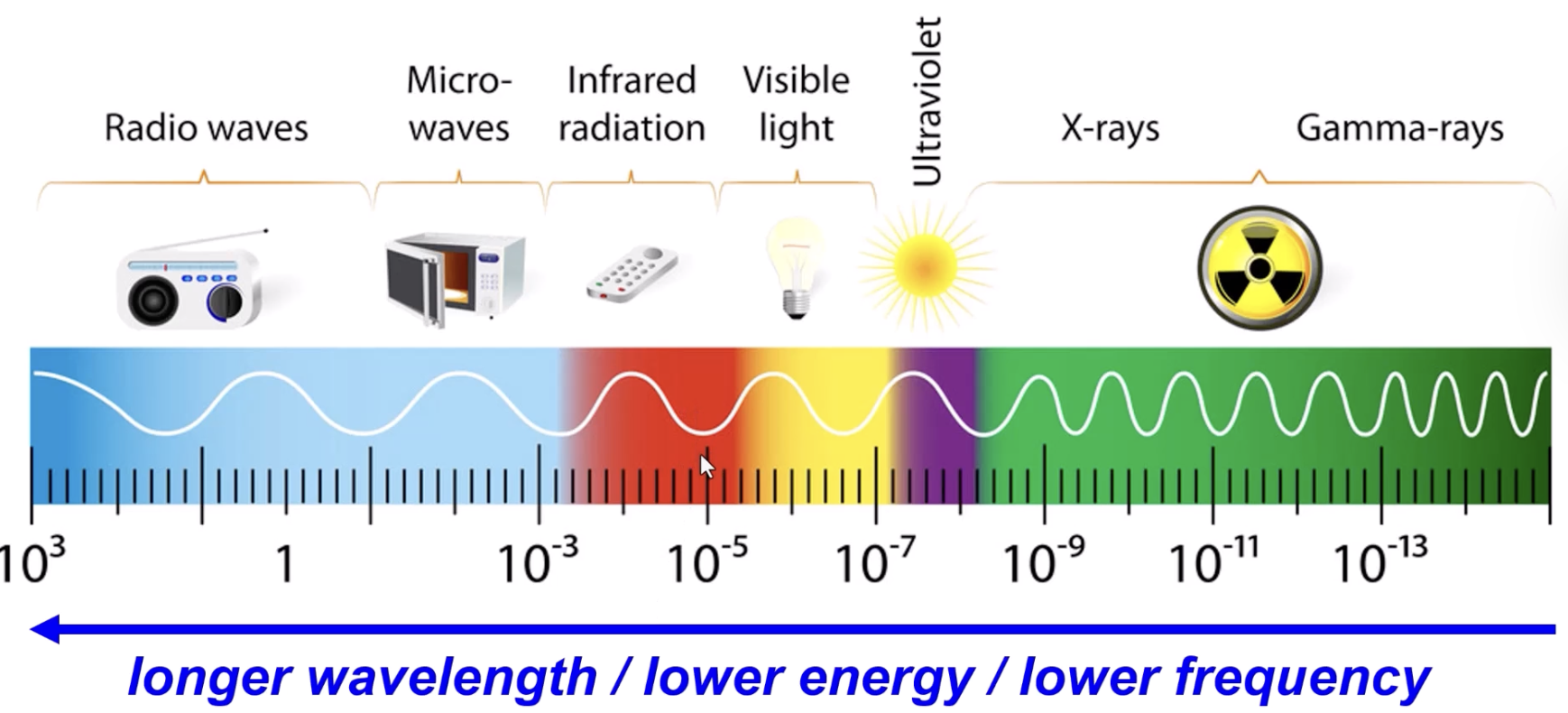
electromagnetic spectrum (lowest energy / frequency to highest)
Radio waves → Micro-waves → Infrared radiation → Visible light → Ultraviolet → X-rays → Gamma-rays
“Roman Men Invented Very Unusual X-ray G*ns”
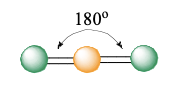
linear
2 electron groups (0 lone pairs)
bond angle: 180°
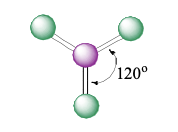
trigonal planar
3 electron groups (0 lone pairs)
bond angle: 120°
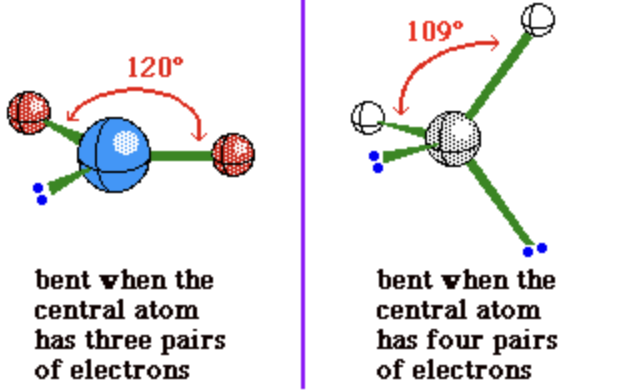
bent
3 electron groups (1 lone pair)
bond angle: <120°
OR
4 electron groups (2 lone pairs)
bond angle: <109.5°
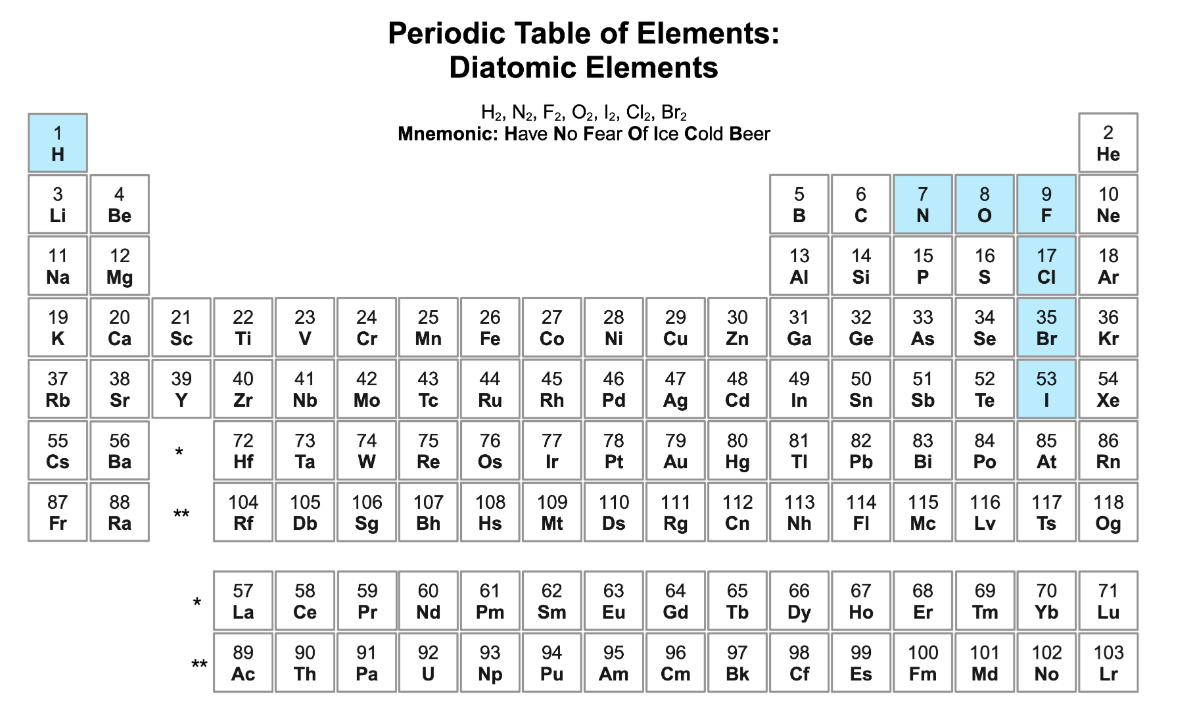
diatomic molecules
“Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beer”
H2, N2, F2, O2, I2, Cl2, Br2
7 molecules total, form a 7 on the periodic table
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Fluorine
Oxygen
Iodine
Chlorine
Bromine
atomic radius of an ion is affected by
Number of electron shells: More electron shells → larger atomic radius because the electrons are spread out over a larger physical space.
Nuclear charge: A higher effective nuclear charge (more protons in the nucleus) → smaller atomic radius because the electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus.
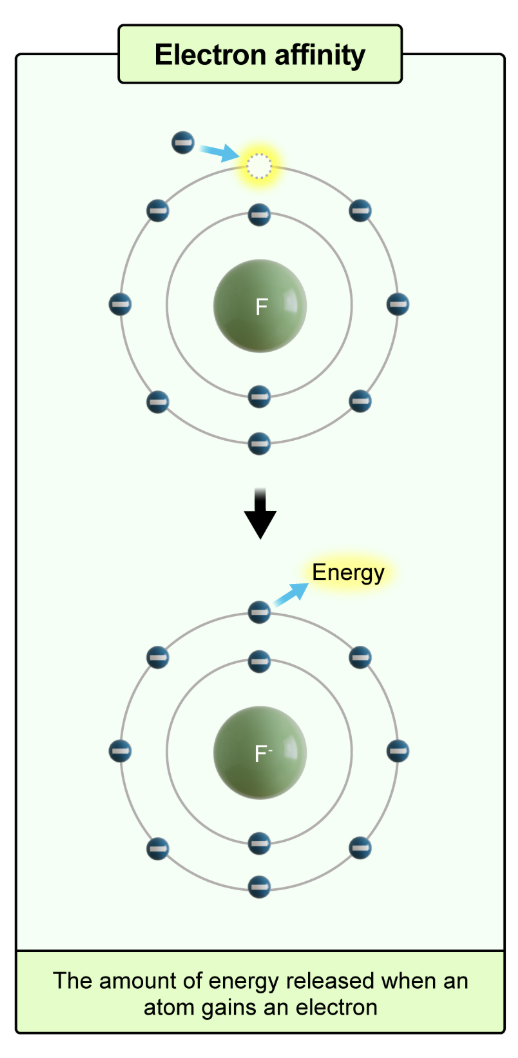
electron affinity
the amount of energy released when an atom gains an electron
increases moving up and to the right on the periodic table
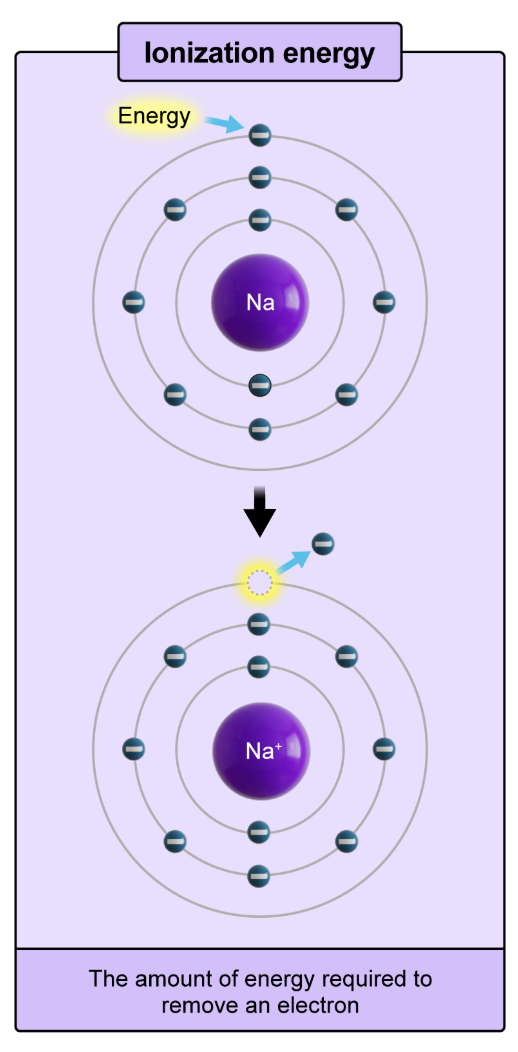
ionization energy
the amount of energy required to remove an electron
electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract shared electrons in a chemical bond
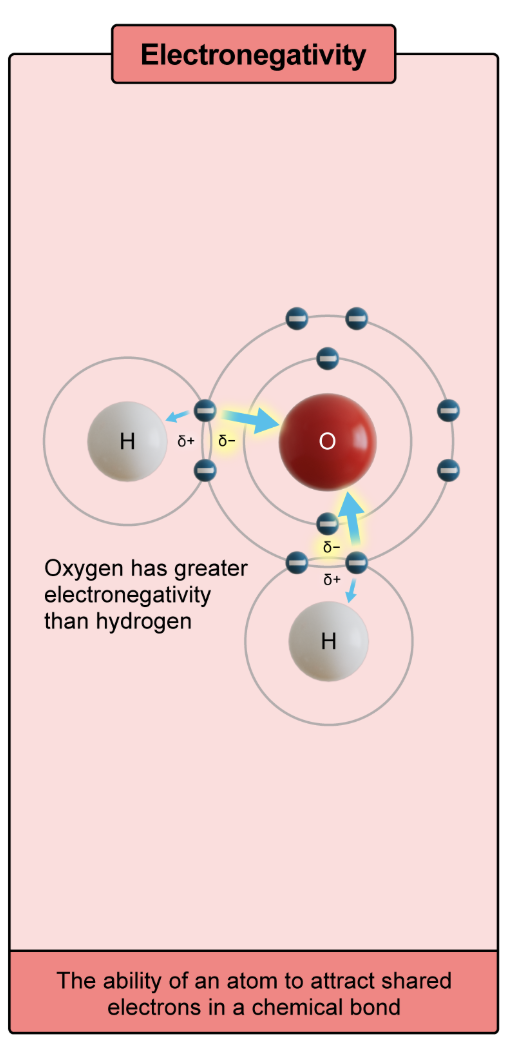
lattice energy
the energy required to separate an ionic compound’s cations and anions
effective nuclear charge
the force that attracts electrons toward the nucleus
first ionization energy
the energy required to remove the outermost electron from a neutral atom.
ionization energy increases moving up and to the right on the periodic table.
atomic radius
increases moving down and to the left on the periodic table
this is due to the addition of electron shells and a decrease in effective nuclear charge