Biol 102 Practice midterm
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Which of the following statements is false? Crossovers happen:
during synapsis
between non-sister chromatids
between sister chromatids
before sister chromatids separate
during the first meiotic division
between sister chromatids
Mendel’s laws state that
alleles segregate equally and pairs of alleles assort independently
alleles segregate independently and pairs of alleles assort equally
a monohybrid cross demonstrates a phenotypic 3:1 ratio
a dihybrid cross demonstrates a phenotypic 9:3:3:1 ratio
intrachromosomal recombination produces parental progeny at 50%
alleles segregate equally and pairs of alleles assort independently
According to Mendel’s laws of equal segregation and independent assortment, what ratio of progeny do you expect from a dihybrid testcross involving two unliked loci controlling independent traits?
9:3:3:1
3:1
1:1
1:1:1:1
none of the above
1:1:1:1
A parent that undergoes self-fertilization is heterozygous for a gene (A/a). What percent of the progeny will be expected to be heterozygous (A/a) for this gene?
¼
1/3
½
2/3
3/4
1/2
A gene can have more than two alleles (T/F)
True
A cell with 16 chromosomes after the first meiotic division is
diploid and contains 32 sister chromatids
diploid and is found in an organism with 2n = 16
haploid and contains no sister chromatids
haploid and is found in an organism with 2n = 32
none of the above
haploid and is found in an organism with 2n = 32
The final products of mitosis of a diploid cell are identical, diploid daughter cells. The final products of meiosis of a diploid cell are __ daughter cells
non-identical, haploid
identical, haploid
identical, diploid
non-identical, diploid
non-identical, haploid
You cross an A/a; B'/b; C/c; D/d individual to an A/A; B/b; c/c; D/d individual. If the four loci are unlinked, what proportion of the progeny are expected to be either A/a; b/b; c/c; D/D or A/a; B/b; c/c; d/d?
1/64
3/64
1/32
1/256
1/16
3/64
Are the following progeny numbers consistent with the results expected from selfing a plant presumed to be a dihybrid of two independently assorting genes, A/a; B/b? (A =round shape; a = wrinkled shape; B = yellow; b = green.) What is the chi-squared (X2) value and degrees of freedom?
Phenotype Number
Round, Yellow 315
Wrinkled, Yellow 101
Round, Green 108
Wrinkled, Green 32
X2 = 0.47, degrees of freedom = 3
X2 = 0.47, degrees of freedom = 2
X2 = 0.15, degrees of freedom = 3
X2 = 0.15, degrees of freedom = 2
X2 = 0.15, degrees of freedom = 1
X2 = 0.47, degrees of freedom = 3
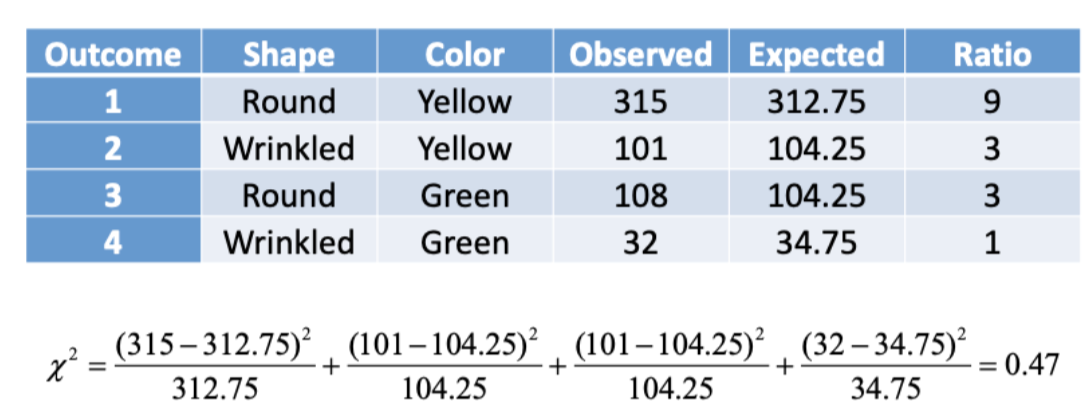
You obtain a chi-squared value of 4.7. The degrees of freedom are 2. Assuming a cutoff
of p=0.05 for statistical significance, how do you interpret this result?
p < 0.05; these data are not consistent with the NULL hypothesis
p > 0.05; there is no reason to reject the NULL hypothesis
p < 0.05; there is no reason to reject the NULL hypothesis
p > 0.05; these data are not consistent with the 1:2:1 hypothesis
None of the other choices
p > 0.05; there is no reason to reject the NULL hypothesis
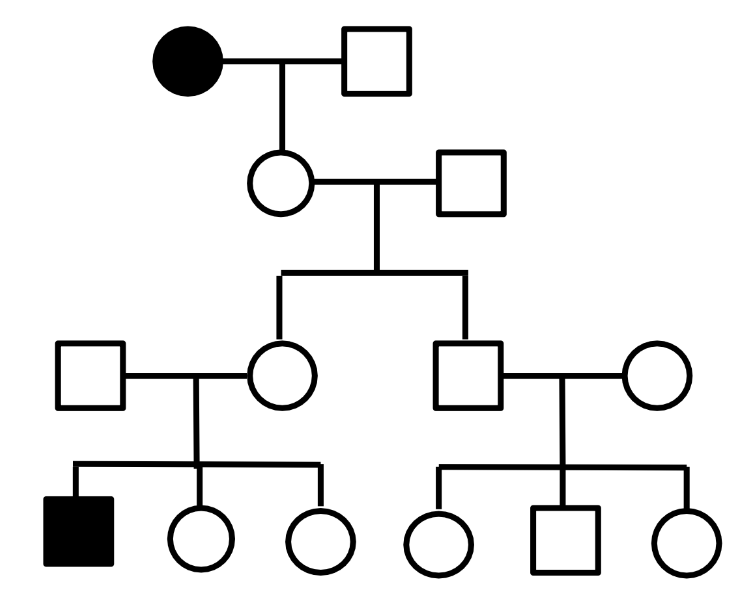
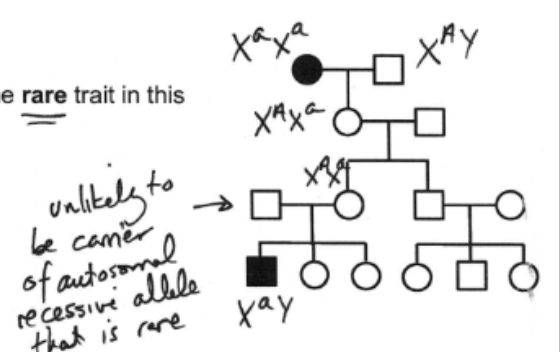
What is the most likely pattern of inheritance of the rare trait in this pedigree?
autosomal recessive
autosomal dominant
X-linked recessive
X-linked dominant
mitochondrial
X-linked recessive
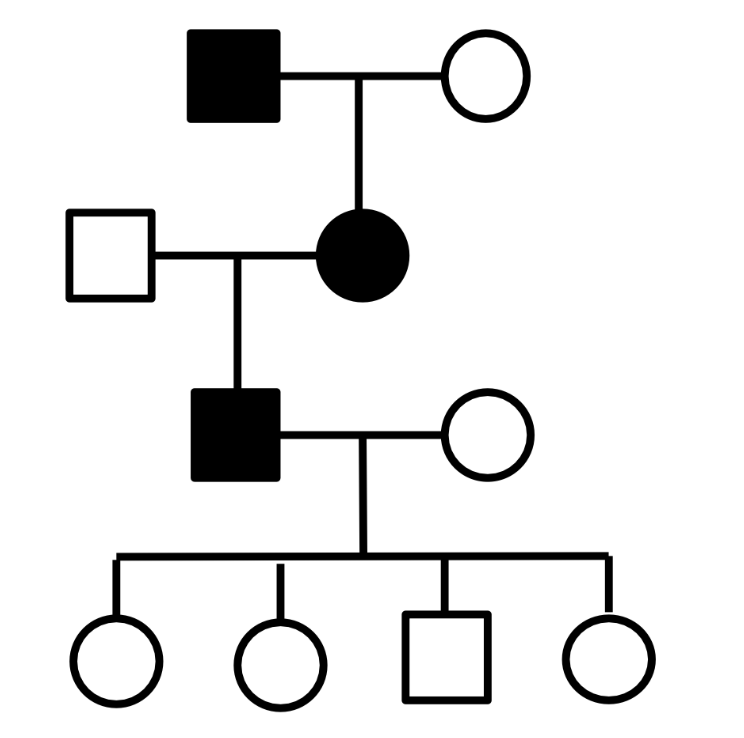
Among the following options, what is the best evidence that the trait in this pedigree is autosomal dominant and not X-linked dominant?
I-1 and III-1 are affected
II-2 is affected
III-1 is affected
IV-1 is unaffected
IV-3 is unaffected
IV-1 is unaffected

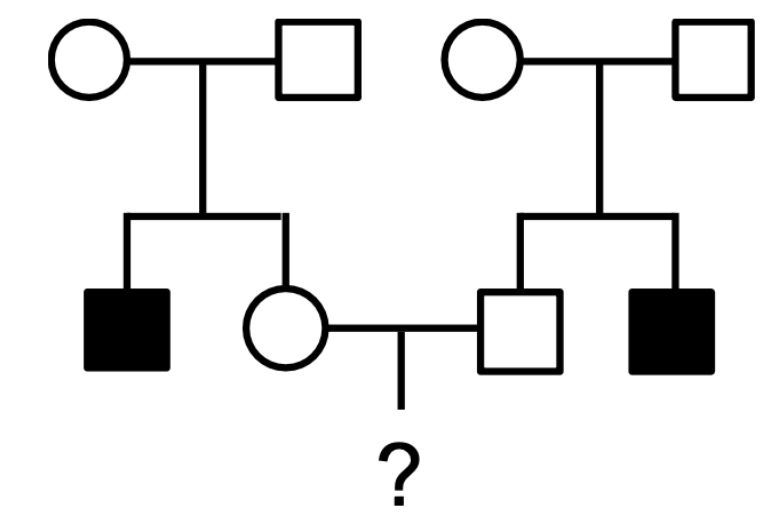
If the trait shown in the pedigree at right is X-linked recessive, what is the probability that a child of II-2 and II-3 will be affected?
0
1/8
1/4
1/64
1/16
1/8

The trait shown in the pedigree below is autosomal recessive. What is the probability that a child of II-2 and II-3 will be affected?
0
1/9
1/4
1/16
1/9

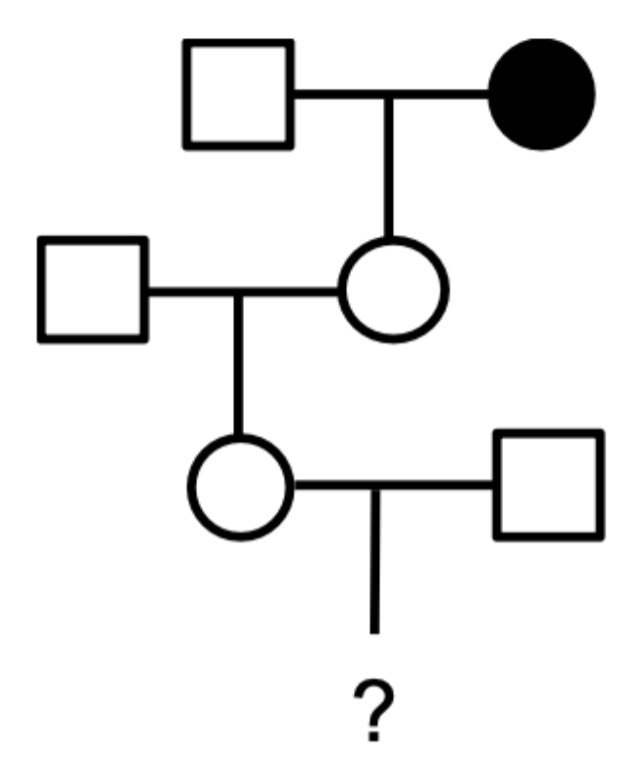
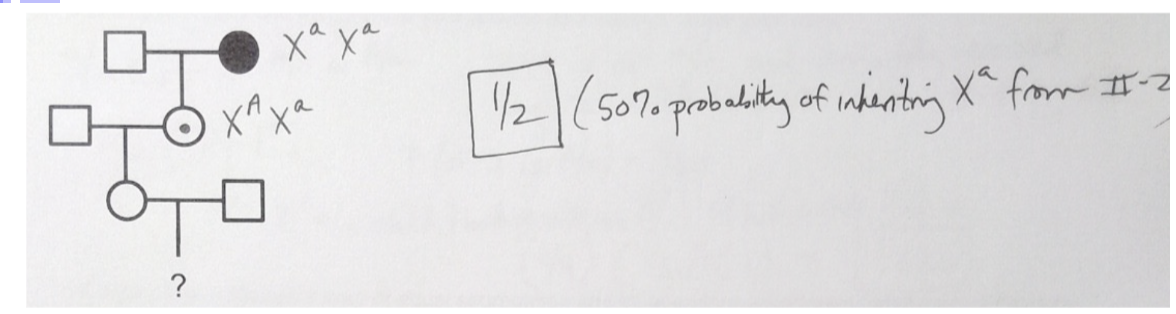
The grandmother of III-1 was affected with an X-linked recessive disorder. While serving in the Peace Corps after college, III-1 met and married the square of her dreams, III-2. What is the probability that III-1 is a carrier of the mutant allele?
1/4
1/3
1/2
2/3
3/4
1/2
A woman with Turner syndrome is found to be colorblind (an X-linked recessive phenotype). Both her mother and her father have normal vision. What is the woman’s genotype? X^A = normal vision, X^a = colorblind, 0 = no chromosome
X^A / X^A
X^a / X^a
X^A / 0
X^a / 0
X^A/X^a
X^a / 0
From question 16, what are the woman’s parents’ genotypes?
Mother X^A / X^a; Father X^A / Y
Mother X^A / X^a; Father X^a / Y
Mother X^a / X^a; Father X^A / Y
Mother X^A / X^A; Father X^A / Y
None of the other choices
mother X^A/ X^a; father X^A/Y
From question 16, nondisjunction occurred in the father. (T/F)
true
Explanation: The woman has only one X^a and it must be from the mother. So the null (empty) gamete was from father, which means the nondisjunction occurred in the father’s meiosis.
Which of the following karyotypes does NOT represent a male? X and Y denote a single copy of the X chromosome and a single copy of the Y chromosome, respectively, while A denotes a chromosome set.
XY AA in humans
XY AA in drosophila
XXY AA in cats
XXY AA in drosophila
All of the options above represent males
XXY AA in drosophila
Two inbred lines of beans are intercrossed. In the F1, the variance in bean weight is measured at 15 g^2. The F1 is selfed; in the F2, the variance in bean weight is 61 g^2. Estimate the broad heritability of bean weight in the F2 population of this experiment.
0.25
0.33
0.50
0.66
0.75
0.75
