MOLECULAR NUTRITION LIPID PRACTICAL
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
what are lipids
macromolecule soluble in non-polar solvents and insoluble in water
includes fatty acids, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins ADEK
functions of lipids
energy storage, cell structure, and cell signaling
how is acylglycerol formed
in condensation reactions between OH groups of glycerol and COOH groups of fatty acids
what are fatty acids
carboxylic acids with long chain hydrocarbon tails
where do the predominant fatty acid residues reside in higher animals and plants
16-18 carbons
are fatty acids hydrophobic or hydrophillic
hydrophobic
what does the non polar hydrocarbon chain confer to fatty acids
hydrophobicity
what are the three different classifications of fatty acids
saturated: all single carbon bonds
unsaturated: one or more double bonds in hydrocarbon tail
mono→one double bond
poly→more than one
how is mono palmitin formed
one of the three alcohol groups on glycerol and one molecules of palmitic acid
do plant lipids or animal lipids have lower melting points
plant lipids→tend to be unsaturated and therefore are liquid at room temperature
what are the main acids in olive oil versus sunflower oil
olive oil is mainly oleic acid and sunflower oil is mainly linoleic acid
what differentiates phospholipids from fatty acids
they have a phosphate group and are amphipathic
name the two types of phospholipids
glycerophospholipids: 2 fatty acid groups with 3 position on glycerol occupied by phosphate group attached to alcohol
Sphingolipids: glycerol is replaced with sphingosine
phosphate head versus fatty acid tail in phospholipids
phosphate head is negatively charged and contains polar groups therefore is hydrophilic
fatty acid tail is nonpolar and therefore hydrophobic
what is the most abundant phospholipid in animals and plants
phosphocholine→builds membrane bilayers
where is phosphatidylserine found
in myelin in brain tissue and egg yolk
what is the structure of cholesterol
tetracyclic ring system
purpose of cholesterol
in eukaryotic cells, it is a major component of the cell membrane and it has a roll in maintaining cell fluidity and it is a precursor for steroid hormones, bile salts, and vitamin D
what does chromatography do
separates individual components of a mixture based on characteristics differences in size charge or polarity
what are the three components of chromatography
stationary phase, chromatographic bed, and mobile phase
components of TLC
stationary phase=absorbant such as silica;
chromatographic bed=thin layer of the stationary phase spread onto glass or plastic plate;
mobile phase=liquid(organic solvent) moving up the plate via capillary action
what happens if the molecule is more polar in TLC
is it more strongly absorbed by the silica therefore will NOT move up the plate
what does iodine stain
unsaturated fatty acids→brown spots→almond and olive oil
fluorescein spary
stains all lipids giving a fluorescent light under UV→monopalmitin did not move up plate→most bind to silica
ninhydrin spray
binds to amino groups and gives purple spots when heated
molybdenum blue
binds to phospholipids and gives blue spots
what are fatty acids stored as
triglycerides
is there cholesterol in the mitochondrial inner membrane
NO, there is cardiolipin instead
is silica polar or nonpolar
polar so it acts as stationary phase
do more polar molecules move farther up or less far up the TLC plate
less far since they bind to silica
what can be used for most lipid detection
fluorescein and light
is mono or tri palmitin most polar and why
mono is most polar because it moved the least amount up the plate due to it having the least fatty acid tails
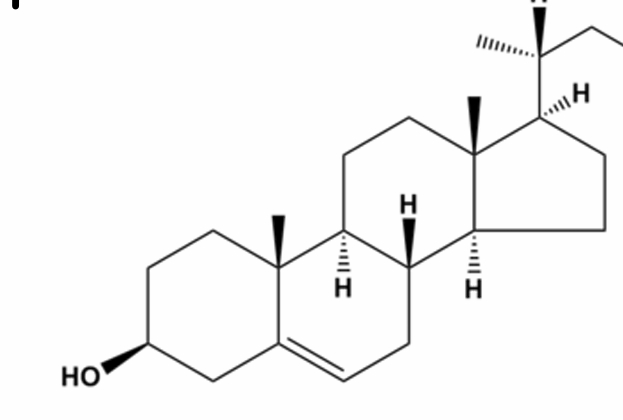
what is this lipid and what is its function
cholesterol→ major component of the cell membrane and it has a roll in maintaining cell fluidity and it is a precursor for steroid hormones, bile salts, and vitamin D
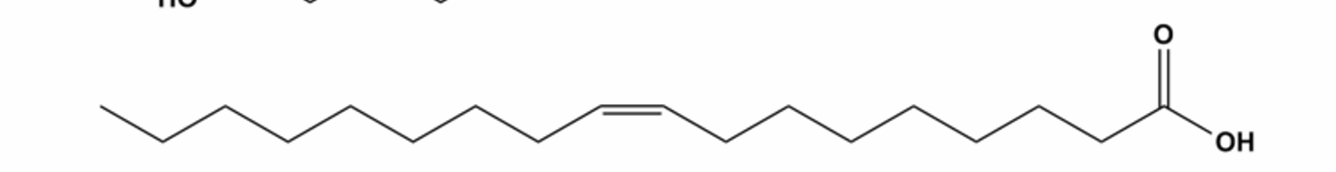
what is this lipid and what is its function
free fatty acid→energy source
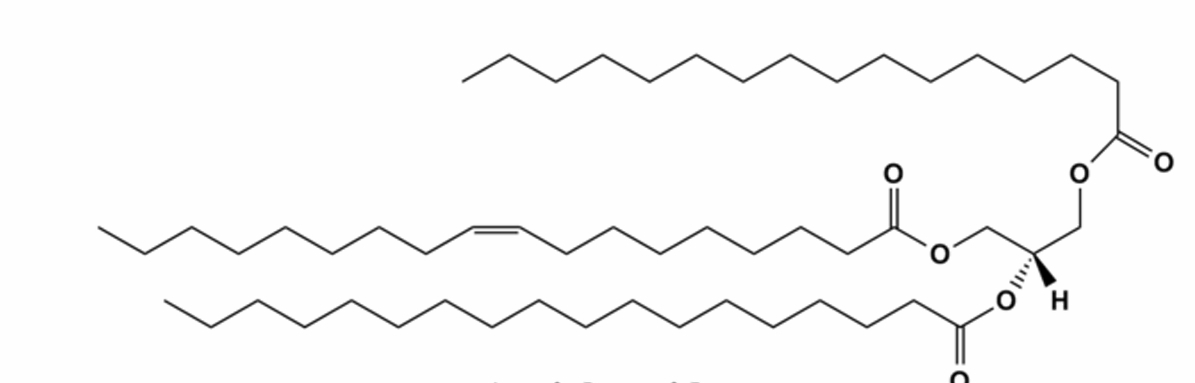
what is this lipid and what is its function
triglyceride→energy storage
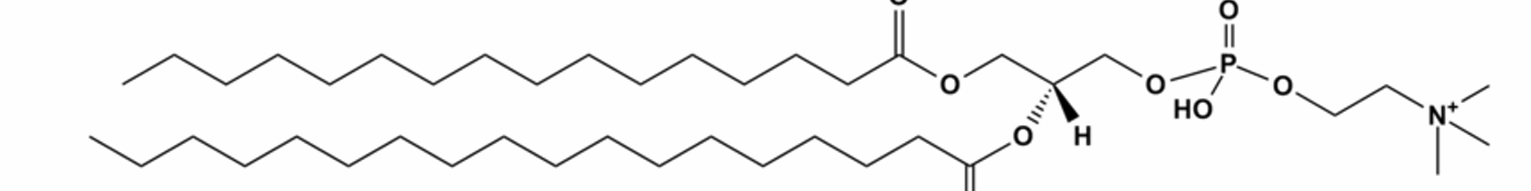
what is this lipid and what is its function
phospholipid→cell membrane phospholipid bilayer; hydrophilic phosphate head with hydrophobic fatty acid tail
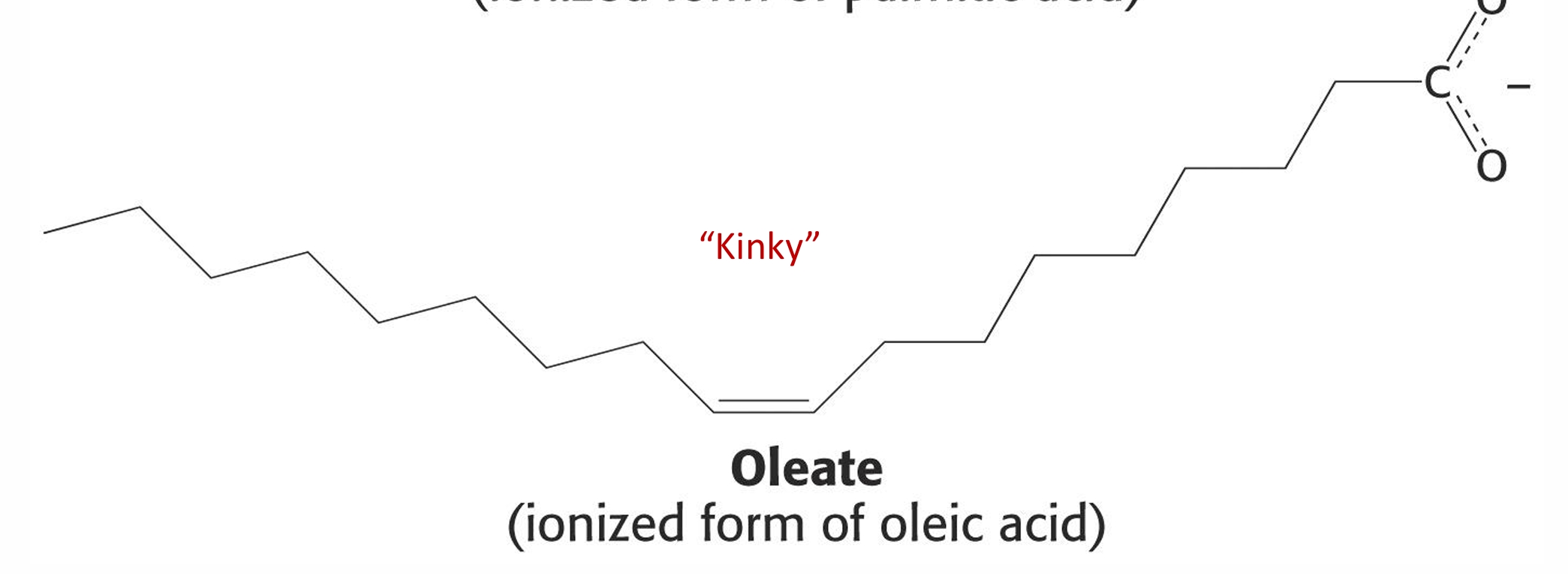
is this lipid saturated or unsaturated and why
unsaturated because it has a double bond
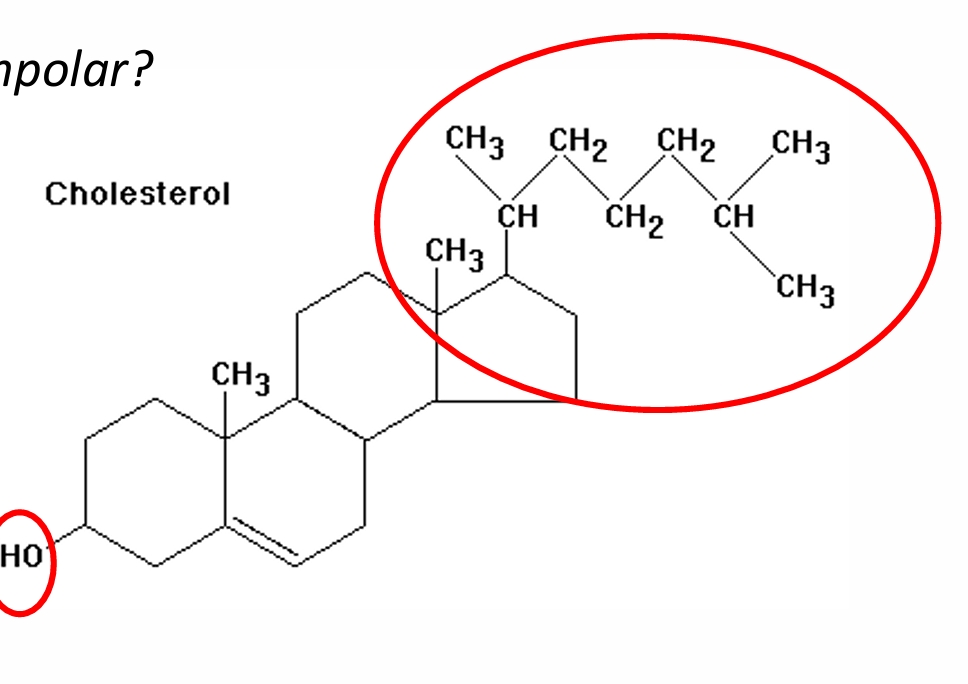
is cholesterol more polar or nonpolar
more nonpolar except for the hydroxyl group attached the first ring
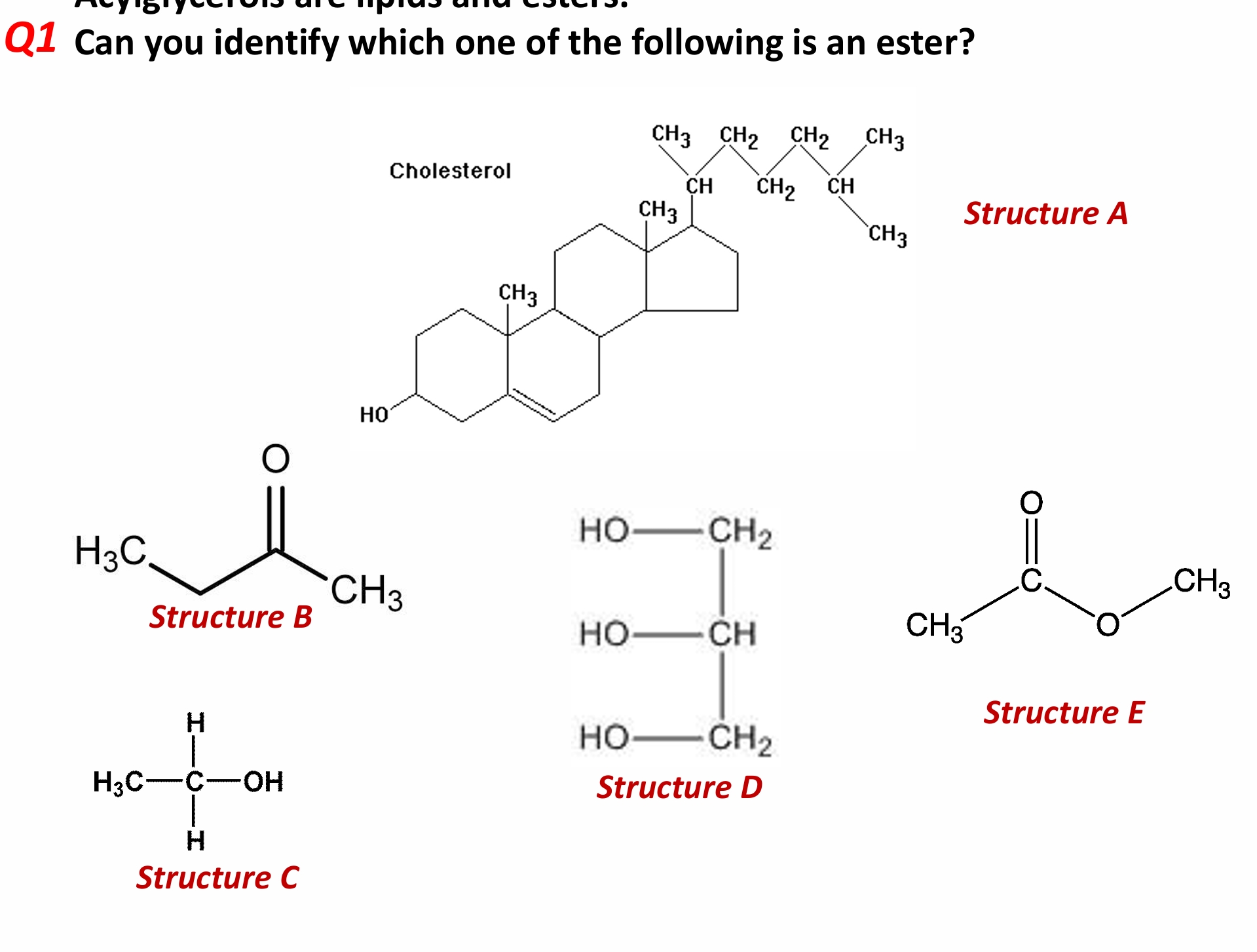
which of these is an ester
structure E→ C-O-C
is silica polar or non polar
polar
Why does ninhydrin not detect phosphatidylcholine
Ninhydrin does not detect phosphatidylcholine because ninhydrin specifically reacts with free amino groups (-NH₂), and phosphatidylcholine is a phospholipid