BioH S1 ALL UNITS
0.0(0)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/225
Last updated 6:54 AM on 12/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
226 Terms
1
New cards
phosopholipid bilayer
composition of plasma membrane, two layers of phosopholipids arranged tail-to-tail
2
New cards
Cholesterol
A lipid that forms an essential component of animal cell membranes and acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of other biologically important steroids. Acts as a buffer to maintain membrane fluidity
3
New cards
integral protein
A transmembrane protein with hydrophobic regions that extend into and often completely span the hydrophobic interior of the membrane and with hydrophilic regions in contact with the aqueous solution on one or both sides of the membrane (or lining the channel in the case of a channel protein).
4
New cards
peripheral protein
A protein loosely bound to the surface of a membrane or to part of an integral protein and not embedded in the lipid bilayer.
5
New cards
Semi-permeable
characteristic of a cell membrane which allows some molecules to pass through but not others
6
New cards
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
7
New cards
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
8
New cards
Hydrophilic
Attracted to water
9
New cards
Hydrophobic
Having an aversion to water; tending to coalesce and form droplets in water.
10
New cards
polar
Molecule with partial charges. Mixes with water.
11
New cards
nonpolar
No partial charges. Do not mix with water. A molecule in which all atoms have the same electronegativity and the electron distribution is equal
12
New cards
concentration gradient
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another
13
New cards
equilibrium
Equilibrium is reached when net movement stops
14
New cards
(1) Concentration is = on both sides of semipermeable membrane
15
New cards
net flow
the direction in which most particles are moving during diffusion or osmosis
16
New cards
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
17
New cards
Hypertonic
when comparing two solutions, the solution with the greater concentration of solutes
18
New cards
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
19
New cards
turgid cell
a plant cell that has absorbed water (due to osmosis) and has cytoplasm that is pressing outwards on the cell wall
20
New cards
nuclear envelope
layer of two membranes that surrounds the nucleus of a cell
21
New cards
surface area to volume ratio
A ratio that decreases as cells grow, so that it sets a limit to the size of cells.
22
New cards
cell cycle
series of events in which a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form two daughter cells
23
New cards
G0 phase
A nondividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle, sometimes reversibly.
24
New cards
G1 phase
* The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins.
25
New cards
G2 phase
stage of interphase in which cell duplicates its cytosol and organelles
26
New cards
S phase
The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated.
27
New cards
cell plate
In a plant cell, midline of dividing cells. Becomes the cell wall eventually.
28
New cards
cleavage furrow
The first sign of cleavage in an animal cell; a shallow groove in the cell surface near the old metaphase plate.
29
New cards
Equator of the cell
the central plane of the spindle in a dividing cell, to which chromosomes migrate during the metaphase of mitosis or meiosis.
30
New cards
mitosis
cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
31
New cards
prophase
1st (and longest) phase of mitosis, during which
* the nuclear envelope around the chromosomes disappears
* the centrioles separate and place the spindle fibers on opposite sides of the nucleus
* the nuclear envelope around the chromosomes disappears
* the centrioles separate and place the spindle fibers on opposite sides of the nucleus
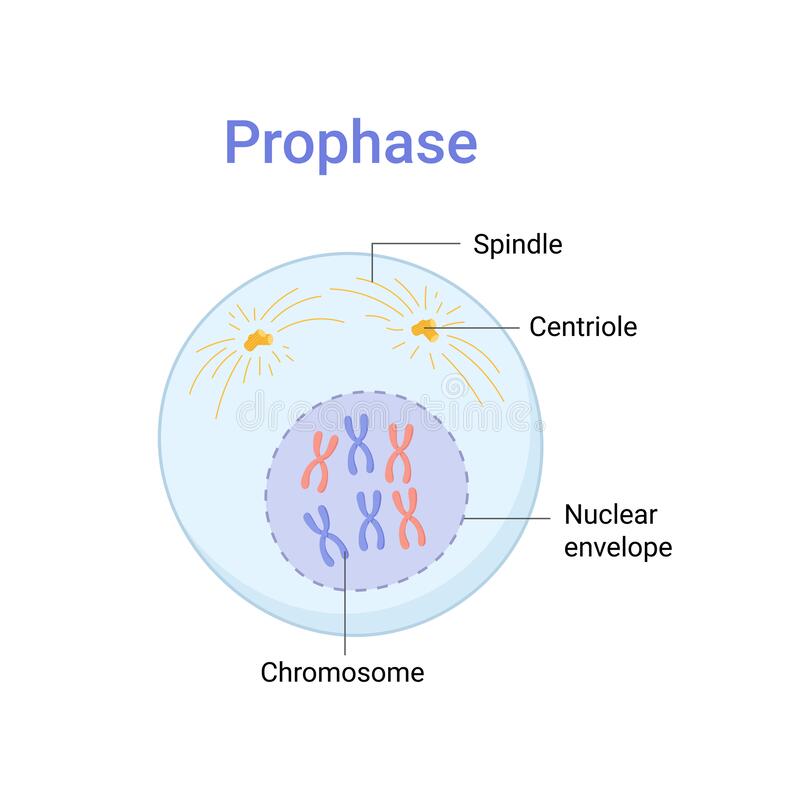
32
New cards
metaphase
2nd phase of mitosis, during which **the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell**
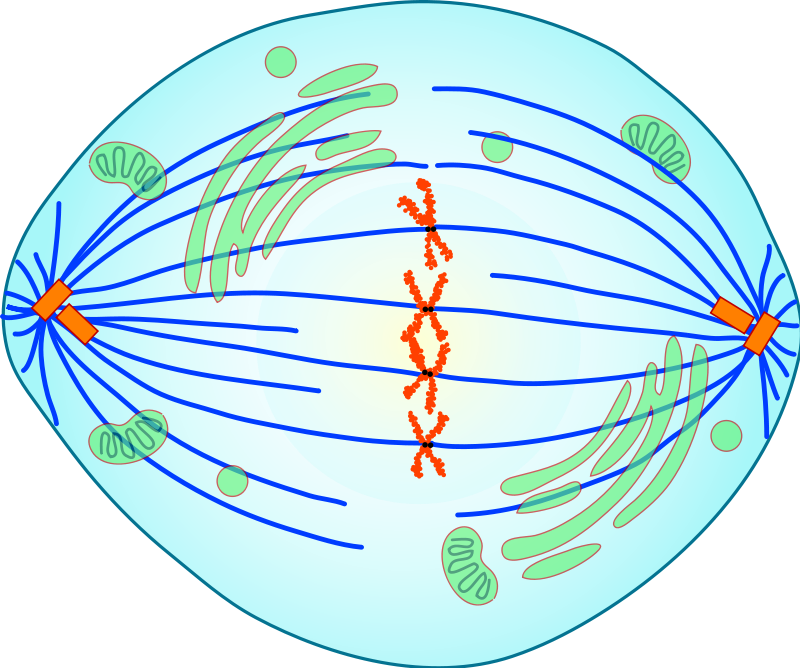
33
New cards
anaphase
3rd phase of mitosis in which **the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell**
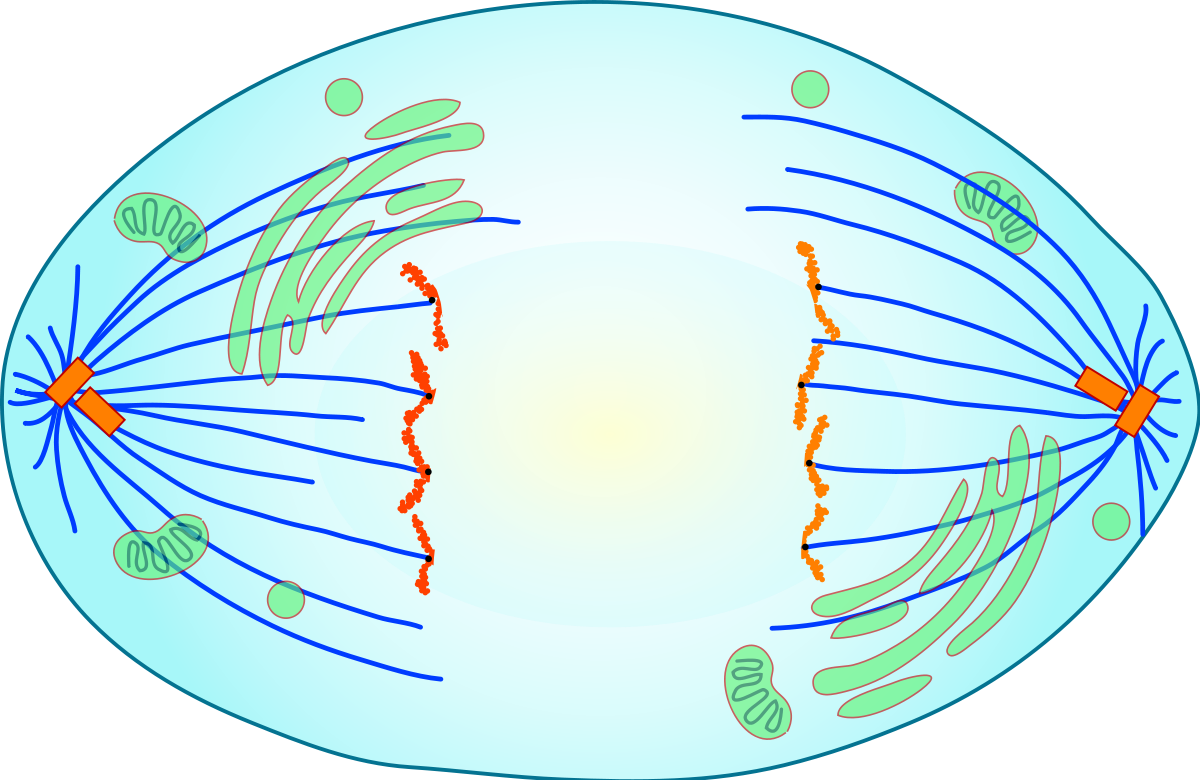
34
New cards
telophase
the final phase of mitosis, in which the chromatids (or chromosomes) reach opposite ends of the cell and **two nuclei are formed.**
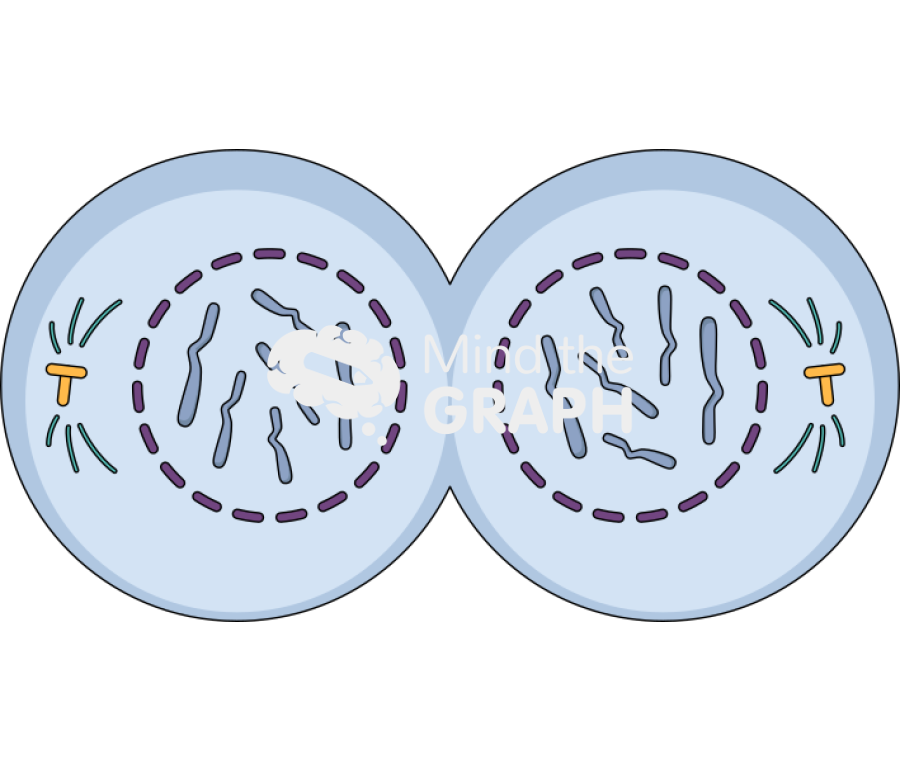
35
New cards
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
36
New cards
glycolipids
phospholipids with sugars attached (covalently bonded to lipids)
* both receptor AND recognition proteins
* increase membrane stability by forming H bonds with water molecules
* both receptor AND recognition proteins
* increase membrane stability by forming H bonds with water molecules
37
New cards
centromere
the region of the chromosome that holds the two sister chromatids together during mitosis
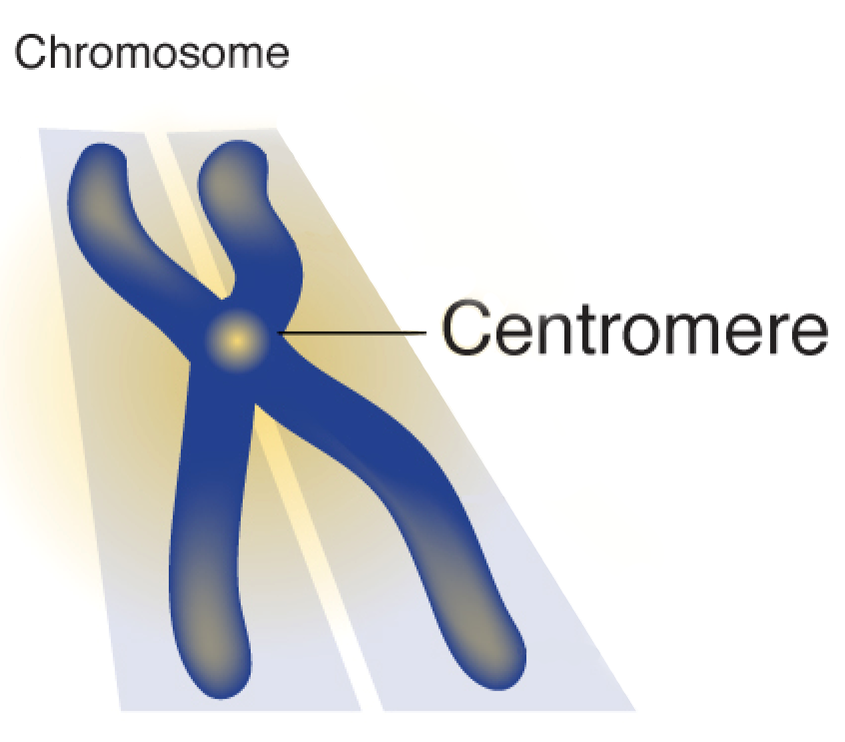
38
New cards
chromosome
* a gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus
* each chromosome consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins.
* each chromosome consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins.
39
New cards
sister chromatids
* **replicated forms of a chromosome** joined together by the centromere
* eventually separated during mitosis
* eventually separated during mitosis
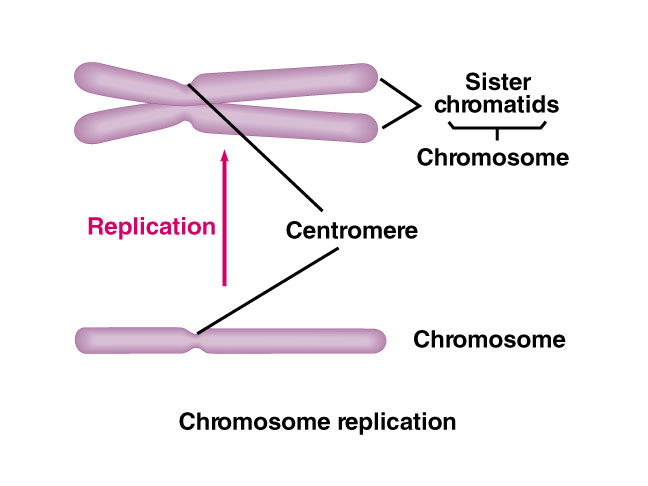
40
New cards
nucleus
* a part of the cell containing DNA and RNA
* responsible for growth and reproduction
* responsible for growth and reproduction
41
New cards
spindle fiber
emerge from centrioles, attach to chromosomes to pull them apart **during mitosis**
42
New cards
receptor protein
a protein that binds specific signal molecules, causing the cell to respond
43
New cards
recognition protein
plasma membrane protein that identifies a cell as belonging to **self** (one's own body or species)
44
New cards
adhesion protein
membrane protein that helps cells stick together **in animal tissues**
45
New cards
glycoprotein
* protein with 1+ carbohydrates covalently attached to it
* recognition protein
* cell adhesion (helps cells attach to other cells)
* recognition protein
* cell adhesion (helps cells attach to other cells)
46
New cards
transport protein
a protein that helps a certain substance to **cross the membrane**
47
New cards
centrioles
structures occurring in pairs and involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division.
48
New cards
endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
49
New cards
exocytosis
a process by which the contents of a vesicle are released to the exterior membrane of the cell membrane.
50
New cards
facilitated diffusion
* process of diffusion in which molecules pass across the membrane through cell membrane channels
* does NOT require energy
* does NOT require energy
51
New cards
active transport
* movement of substances across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient
* requires an input of energy
* requires an input of energy
52
New cards
pump protein
A molecule that actively transports molecules in and out of cells using energy
53
New cards
Enzyme
A type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living thing
54
New cards
what is the main difference between cytokinesis in animal & plant cells?
in plant cells, a cell wall is formed between the 2 daughter cells in animal cells, cleavage furrow is formed between the 2 daughter cells
55
New cards
what happens in interphase
(gap) G1: the cell prepares for DNA replication Synthesis: DNA replication G2: the cell makes proteins while waiting for cell division Mitosis: nuclear division
56
New cards
prophase
nuclear envelope disappears spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes
57
New cards
metaphase
spindle fibers align the chromosomes in the middle
58
New cards
anaphase
sister chromatids separate and move to the opposite sides of the pole
59
New cards
telophase
nuclear envelopes form around each (to-be) cell
60
New cards
cytokinesis
cell division
61
New cards
photon
a particle of light
62
New cards
Pigment
a compound that absorbs light energy & harvests it for photosynthesis found in photosystems
63
New cards
Chlorophyll
green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
64
New cards
electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge
65
New cards
accessory pigment
compound other than chlorophyll that absorbs light at different wavelengths than chlorophyll
66
New cards
photosystem
a cluster of pigments embedded into a thylakoid membrane proteins that carry out the absorptions of light & the transfer of electrons
67
New cards
primary electron acceptor
an acceptor of electrons lost from chlorophyll a found in the thylakoid membrane
68
New cards
photolysis
during the LDR, 2 water molecules are broken down into O, H+, and electrons
69
New cards
oxidation
the loss of electrons from a substance involved in a redox reaction.
70
New cards
reduction
gain of electrons
71
New cards
electron transport chain
A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to pump H+ ions and generate a concentration gradient.
72
New cards
H+ pump
A transporter that actively moves H+ across a cell membrane , thereby generating a gradient that can be used by the cell, for example, to import other solutes.
73
New cards
H+ gradient
movement of H+ ions through ATP Synthase powers the phosphorylation of ADP
74
New cards
ATP synthase
large protein in the cell membrane that uses energy from H+ ions to phosphorylate ADP to make ATP
75
New cards
NADPH
an electron carrier involved in photosynthesis light drives electrons from chlorophyll to NADP+, forming NADPH provides the high-energy electrons for the reduction of CO2 to sugar in the Calvin cycle.
76
New cards
Chloroplast
organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy
77
New cards
Thylakoid
a membrane system found within chloroplasts that contains the components for photosynthesis
78
New cards
grana
stacks of thylakoids
79
New cards
Thylakoid membrane
photosynthetic membrane within a chloroplast that contains light gathering pigment molecules and ETCs.
80
New cards
thylakoid space
space inside thylakoid.
81
New cards
stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast outside the thylakoids
82
New cards
light-dependent reactions
set of reactions in photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
83
New cards
Calvin Cycle
reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugars
84
New cards
ADP
(Adenosine Diphosphate) The compound that remains when a phosphate group is removed from ATP, releasing energy
85
New cards
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
86
New cards
Phosphorylation
transfer of a phosphate group , usually from ATP, to a molecule. nearly all cellular work depends on ATP energizing other molecules by phosphorylation.
87
New cards
oxidative phosphorylation
production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an ETC the third major stage of cellular respiration.
88
New cards
substrate-level phosphorylation
The enzyme-catalyzed formation of ATP by direct transfer of a phosphate group to ADP from an intermediate substrate in catabolism.
89
New cards
Carbon Fixation
The initial incorporation of carbon from CO2 into an organic compound by an autotrophic organism
90
New cards
rubisco
The most abundant protein on earth. Performs Carbon Fixation in the Calvin Cycle.
91
New cards
RuBP
ribulose biphosphate; a five-carbon carbohydrate that combines with CO2 to form two molecules of PGA in the first step of the Calvin Cylce
92
New cards
G3P
molecule that is made in the Calvin cycle; glucose is formed when two of these molecules combine
93
New cards
3PGA
first organic compound produced in the Calvin cycle. It is later reduced into G3P
94
New cards
Glucose
A simple sugar that is an important source of energy.
95
New cards
Reduction (Calvin Cycle)
PGA is converted to G3P with high energy electrons from NADPH and energy from ATP
96
New cards
Regeneration (Calvin Cycle)
The remaining G3P is used in reactions that use ATP to regenerate RuBP
97
New cards
Photosynthesis
process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and high-energy carbohydrates such as sugars and starches
98
New cards
respiration
The process by which cells break down simple food molecules to release the energy they contain.
99
New cards
anaerobic respiration
Respiration that does not require oxygen
100
New cards
Fermentation
A catabolic process that makes a limited amount of ATP from glucose without an electron transport chain and that produces a characteristic end product, such as ethyl alcohol or lactic acid.
Explore top notes
Chp 14 Materality: Constructing Social Relationships and Meanings with Things
Updated 1265d ago0.0(0)
Chp 14 Materality: Constructing Social Relationships and Meanings with Things
Updated 1265d ago0.0(0)