LCQ #2 BIO101A
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
storage polysaccharides are…
quick, mobilizable fuel
homopolysaccharide
polymer of only one type of monosaccharide residue
starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin polymer
heteropolysaccharide
polymer of two or more different monosaccharide residues
Where do amino acids (monomers) differ?
at R group
cellulose
stiff fiber → good for structure
polypeptide have directionality by their
N terminus
C terminus
cholesterol is soluble/insoluble in liquid
insoluble
the sequence of amino acids in a protein
primary structure
protein folding is stabilized by..
H-bonding between =O carbonyl of an AA and
-H on amino end of another AA
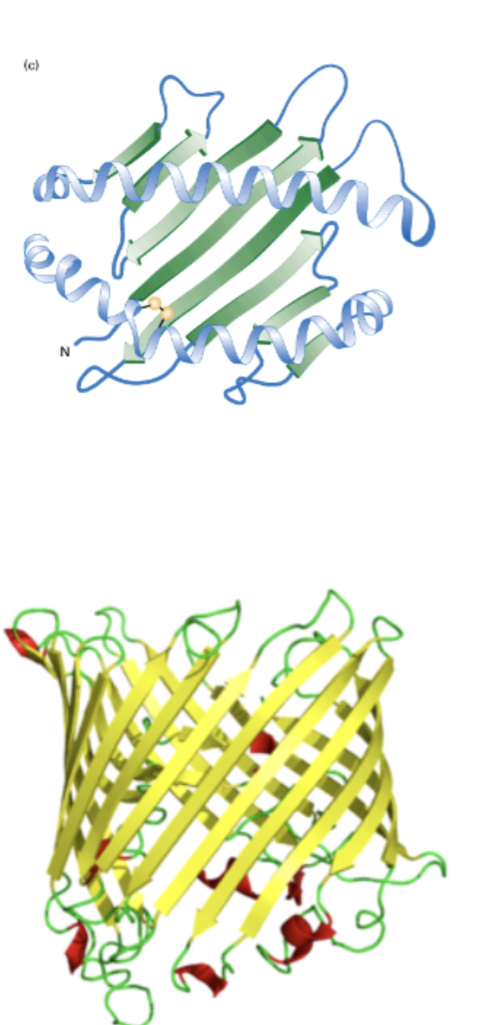
Name this structure
B barrel
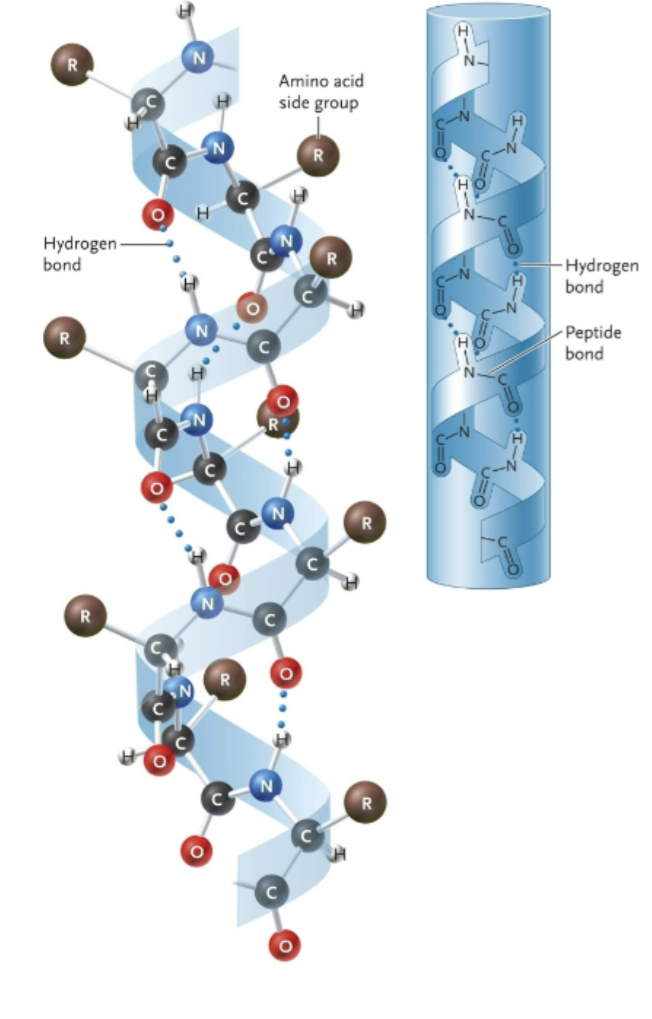
Name this structure
Alpha helix
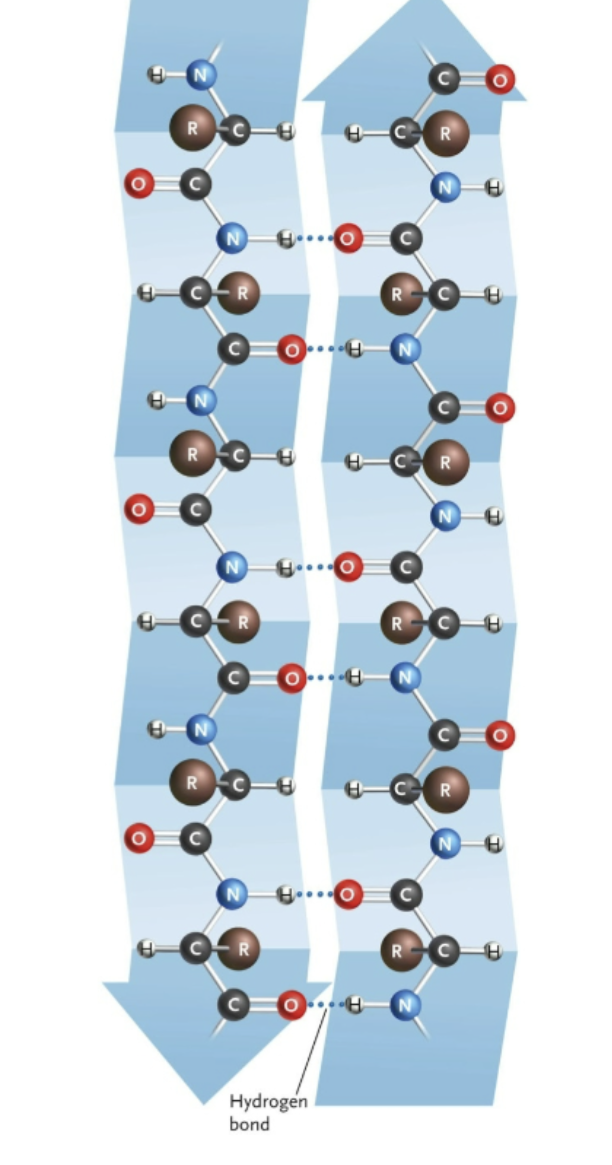
Name this structure.
Beta pleated sheet
In global bonding, there is..
H-bonds between _________
Ionic bonds
Covalent bonds— disulfide bridge between
R groups
groups of cysteine
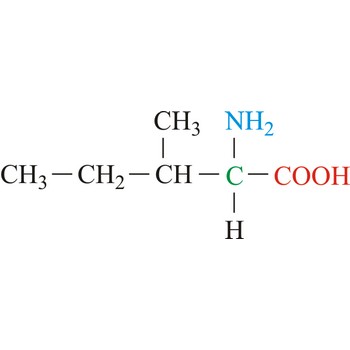
This is isoleucine, is it polar/nonpolar/charged.
Nonpolar.
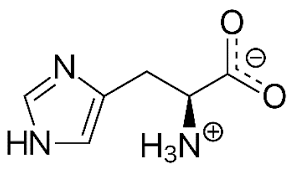
This is histidine, is it polar/nonpolar/charged.
Charged
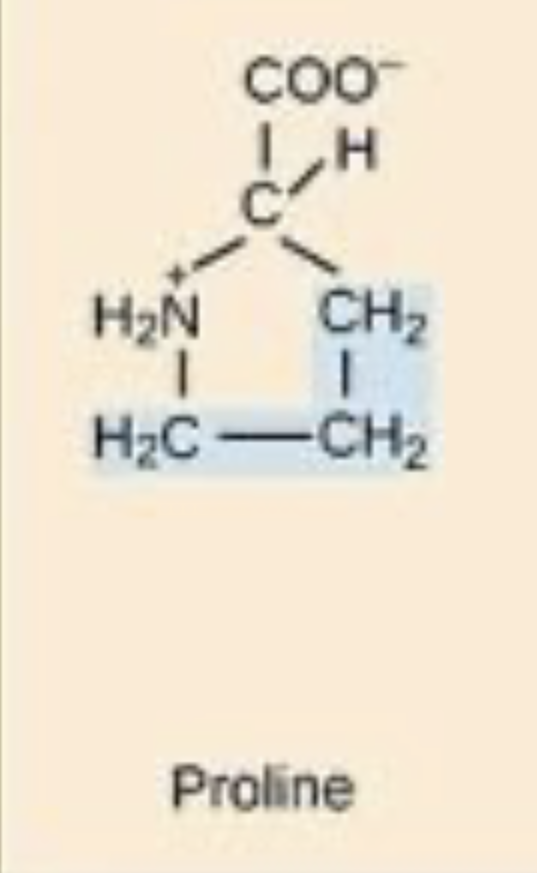
This is proline, is it polar/nonpolar/charged.
Nonpolar
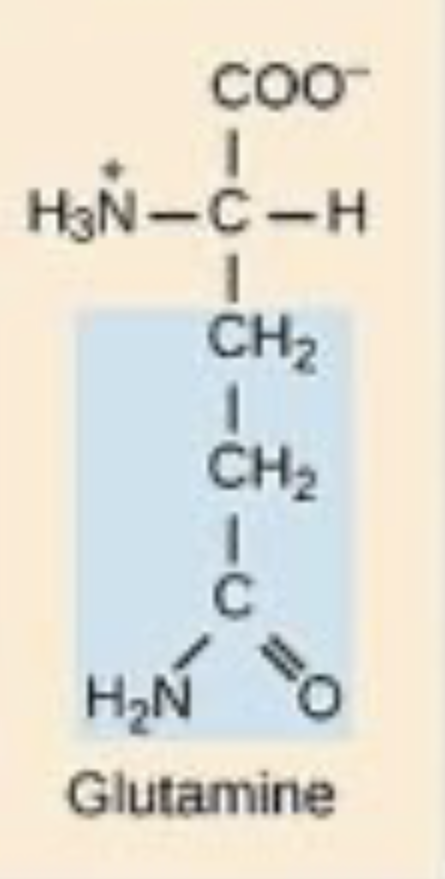
This is glutamine, is it polar/nonpolar/charged.
Polar
Quaternary structure
arrangement of polypeptide changes in a protein that has more than one chain
protein function will depend on
conformation
if you see an OH in the R group (amino acid) it is..
Polar
Carbohydrates usually have a
CHO , in a 1:2:1 ratio
Amino acid structure
-NH2 amino group
Carboxylic group
↑ temperature ↑ thermal vibration
overcomes weak H bonds
↓ pH adds hydronium H3O+
disturbs ionic interacitons
neutralizes charge on negatively charged R-group
Fats, oils, steroids, waxes are polymers
False
primary structure
linear sequence of AAs
one end (amino group)
other end (carboxyl group)
N Terminus represents
Amino group
C Terminus represents
Carboxyl Group
Secondary structure
localized area of folding (into a pattern)
alpha helix, beta pleated sheet
Tertiary structure
3-d shape of a protein from side chain interacitions
Nonpolar side groups like water
F
backbone peptide bonds
covalent, within chain
ionic interactions
between charged R groups
disulfide bridges
covalent between cysteine R groups
collagen
several identical polypettides
>2+ polypeptide subunits
native conformation
conformation normally assumed by functional protein
If you heat up a protein →
increases KE, vibration
cause denaturation (vice versa if lowered)