Unit 2
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
199 Terms
Mechanism: Electrophilic aromatic substitution
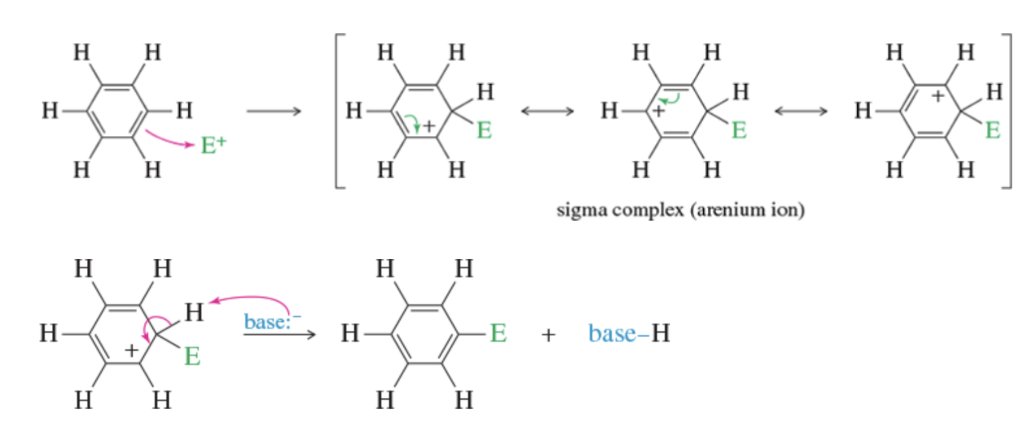
Mechanism: bromination of benzene
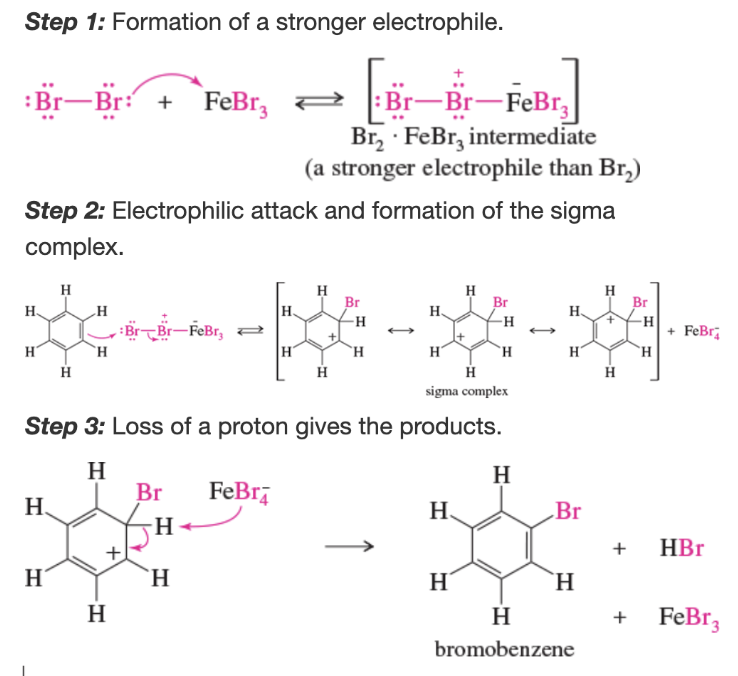
What is the rate-limiting step of the bromination of benzene?
formation of the sigma complex is strongly endothermic
Acid oxidizing agent examples
nitric acid, chromic acid, concentrated sulfuric acid
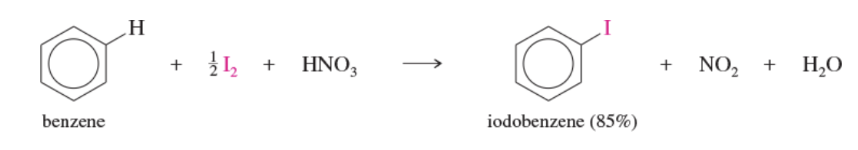
Reaction: iodination of benzene
Nitronium ion
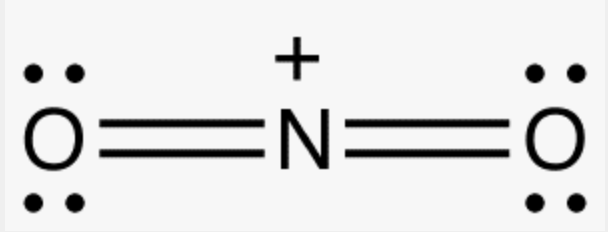
Mechanism: nitration of benzene
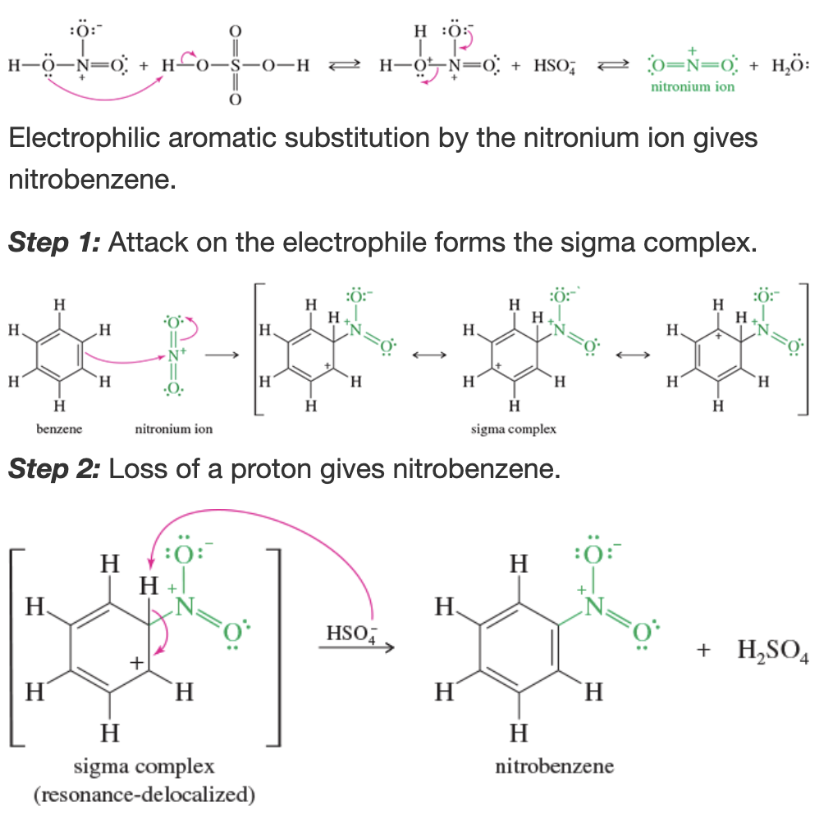
Product of sulfonation of benzene
arylsulfonic acids
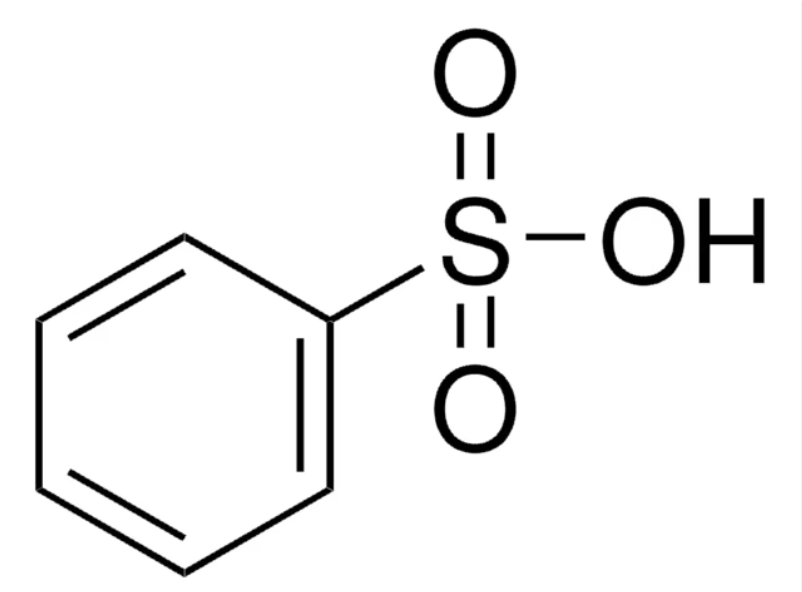
Why is sulfur trioxide a strong electrophile
S=O bonds draw electron density from the sulfur atom
Fuming sulfuric acid
7% SO3 in H2SO4
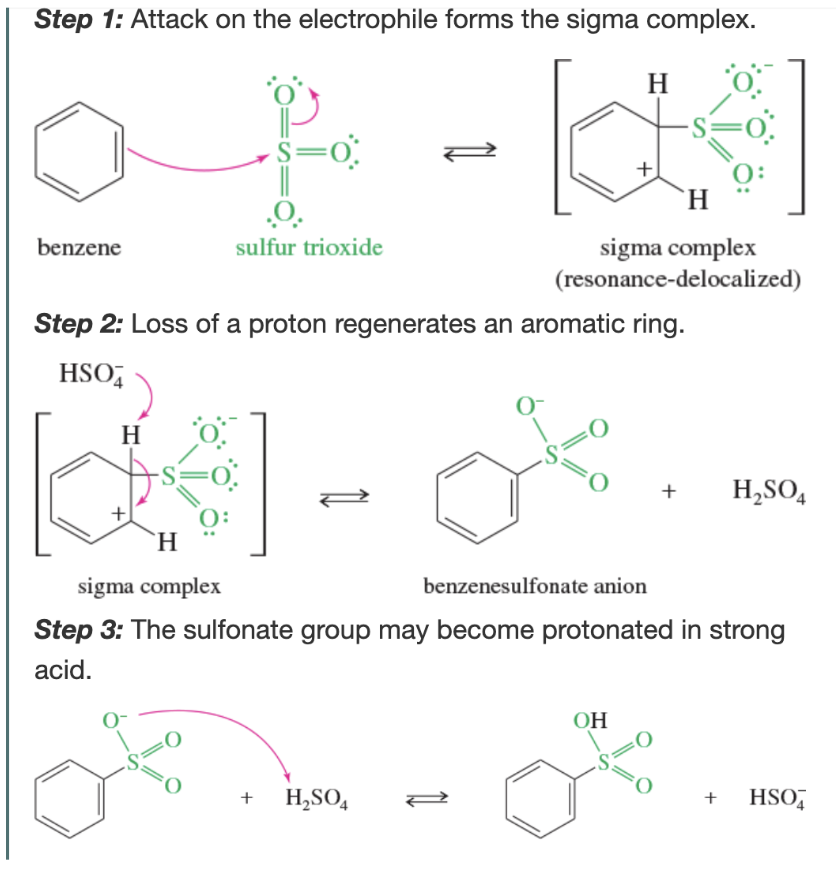
Mechanism: sulfonation of benzene
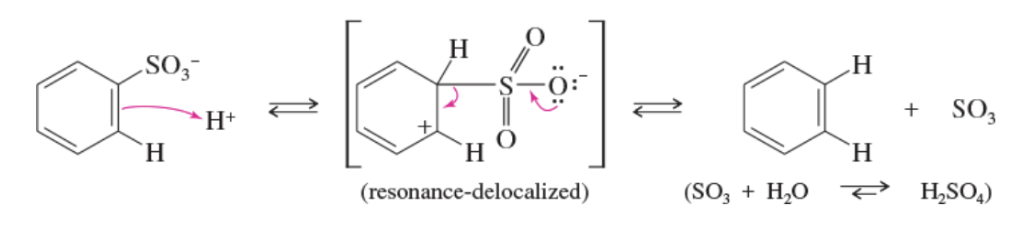
Mechanism: desulfonation
Why does tolune react 25x faster than benzene
methyl group is electron-donating which stabilizes the sigma complex
Activating group
a group that makes the aromatic ring more reactive, usually toward electrophilic aromatic substitution
Inductive effect
electron density is donated to the ring through the sigma bond making it more active
Understanding placement selectivity
draw resonance and consider the structures of the sigma complex
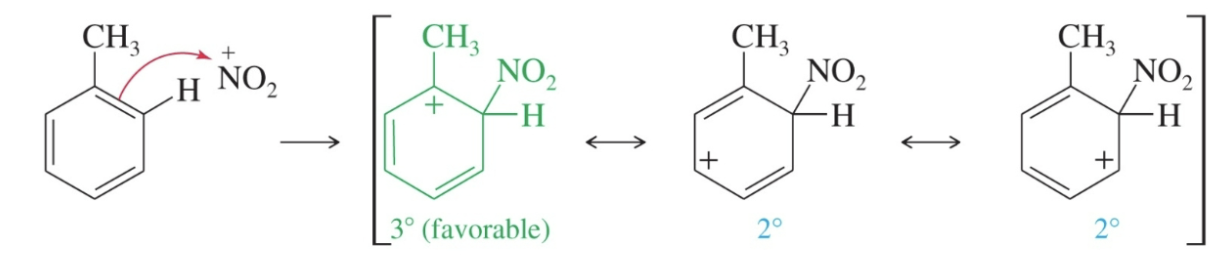
Ortho attack with an ortho, para director
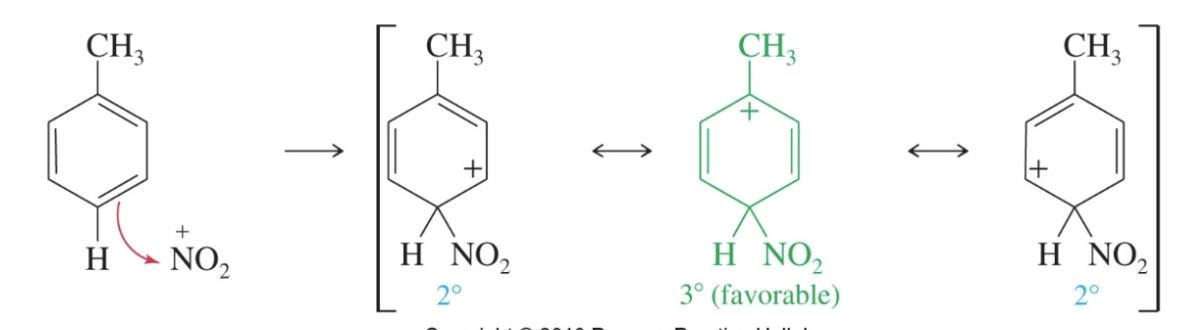
Para attack with an ortho, para director
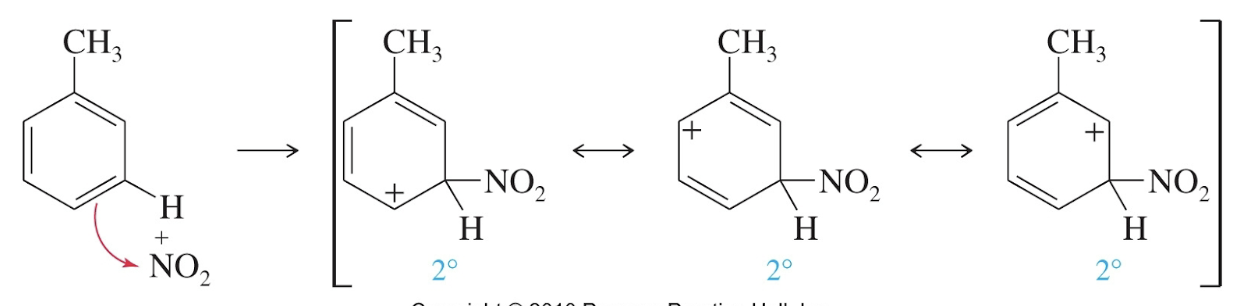
Meta attack with an ortho, para director
Why are alkoxy substituents activating
oxygen donates electron density to stabilize the transition state via the lone pair through resonance
resonance/pi donating
donates electron density through a pi bond in a resonance structure
What happens when an alkoxybenzene comes into contact with Br
quickly brominates. if Br is in excess, a tribromide is formed
Where does the extra resonance structure come from in alkoxy substituents on benzene?
the oxygen can be double bonded to the ring
How is benzene’s reactivity compared to nitrobenzene
nitrobenzene is 100,000 times less reactive
Why do meta directed reactions happen slower
the transition state requires more energy
What makes the nitro group deactivating
Nitrogen inductively withdraws electron density from the aromatic ring, making it less reactive to electrophiles
How are halogens deactivating but ortho, para directing
inductive withdrawal and resonance donation oppose each other, so when an electrophile reacts at the ortho or para position the positive charge of the sigma complex is shared by the carbon atom bearing the halogen
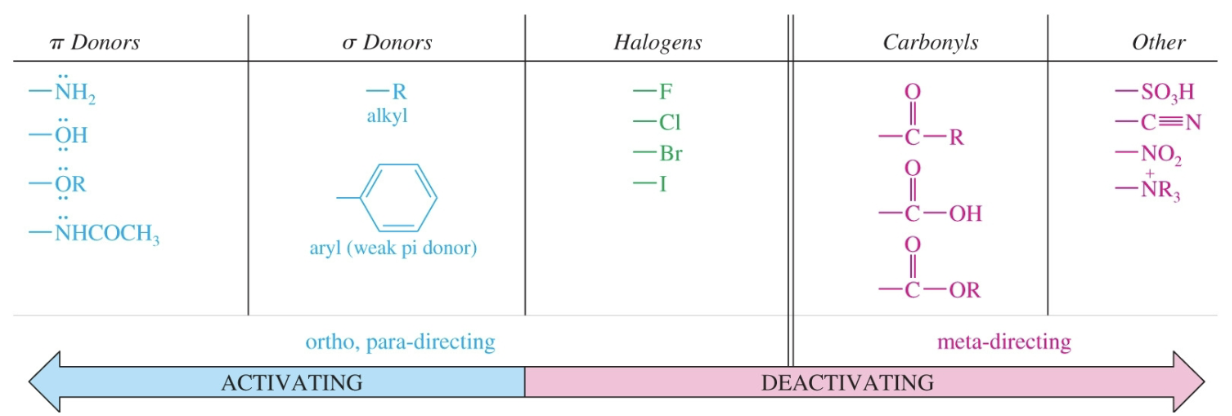
Summary of electrophilic aromatic substituent effects on reactivity and positioning
When there is a conflict between activating and deactivating groups, how will reactivity be affected
activating group will direct because they are usually stronger directors
How to predict substitution products for compounds with more than one ring
decide which ring is more activated or less deactivated, then find the most reactive positions on that ring
Mechanism: Friedel-Crafts alkylation
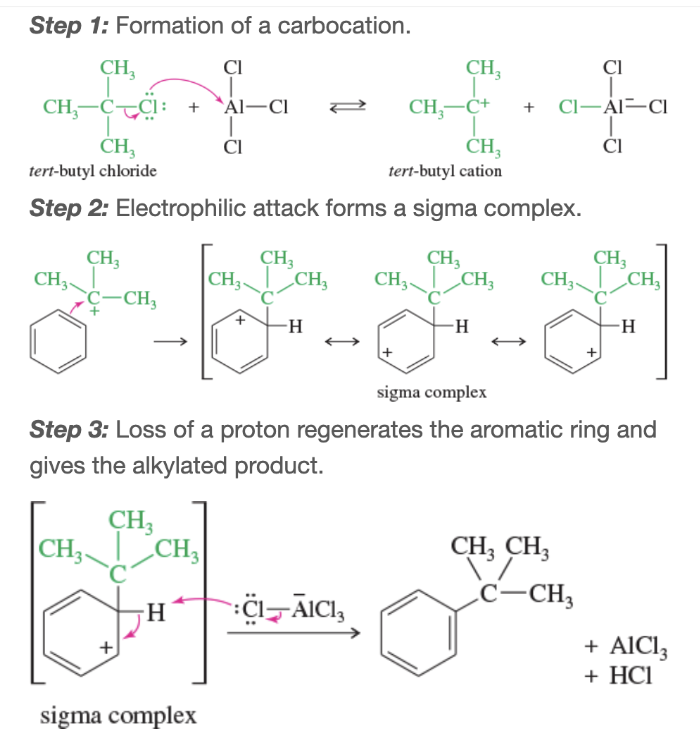
Sources of carbocations that can be used in Friedel-crafts alkylation
protonation of alkenes by H2SO4, treatment of alcohols with BF3,
Mechanism: carbocation formation from alcohols and BF3
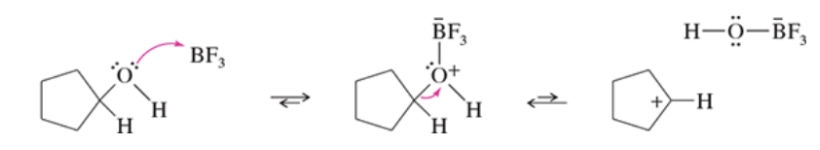
Limitations of Friedel-Crafts alkylation
does not work with deactivated systems, carbocation rearrangements can occur, multiple alkylations may occur
Minimum reactivity of Freidel-Crafts alkylation
halobenzene
How can multiple alkylations be avoided in Friedel-Crafts alkylation
excess of benzene
Acyl group
carbonyl with an alkyl group attached
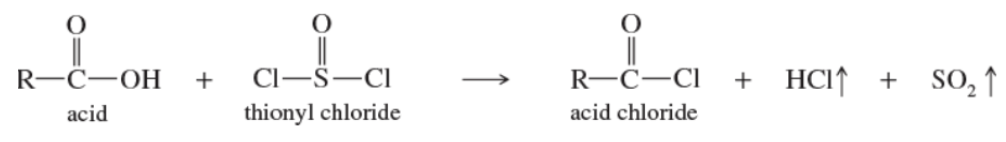
Acyl chloride formation
reacting carboxylic acids with thionyl chloride
Mechanism: Friedel-crafts acylation
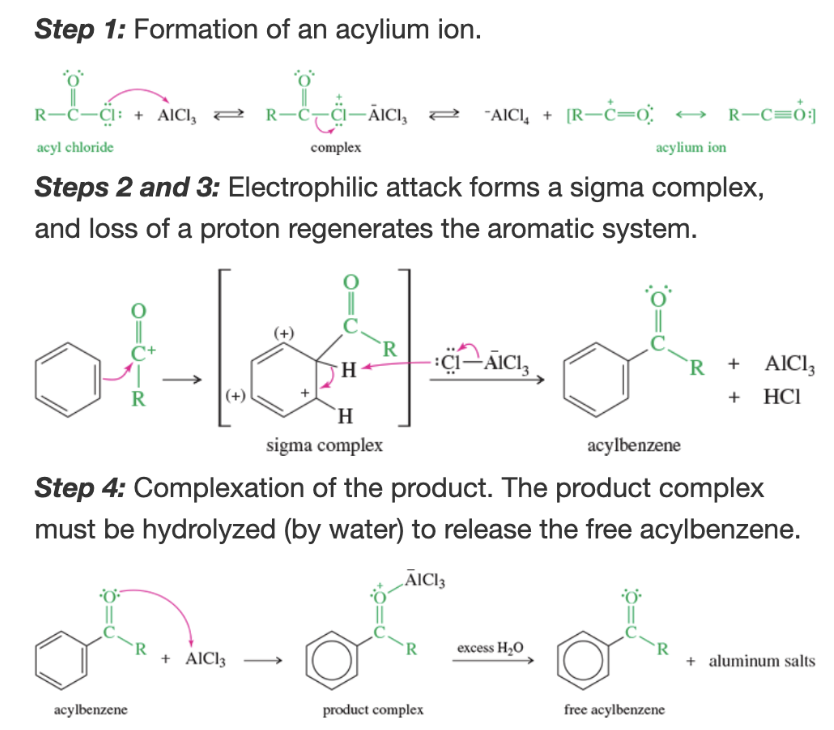
Why must water be added to Friedel-Crafts acylation
AlCl3 complexes with the ketone part of the acylbenzene, water hydrolyzes it to give the free acylbenzene
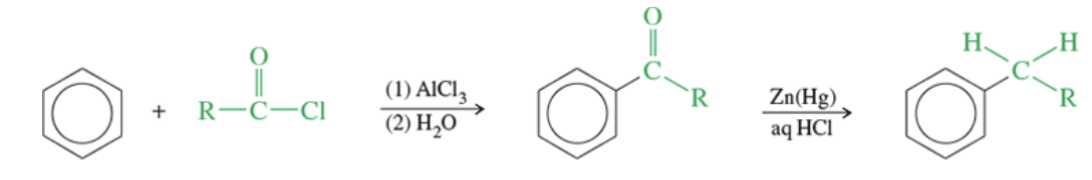
Reaction: Clemmensen reduction
Hydrazine
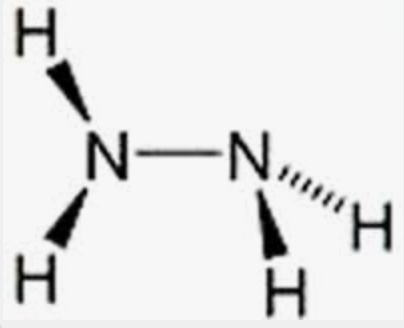
What kind of substituents activate a ring toward nucleophilic attack
withdrawing groups
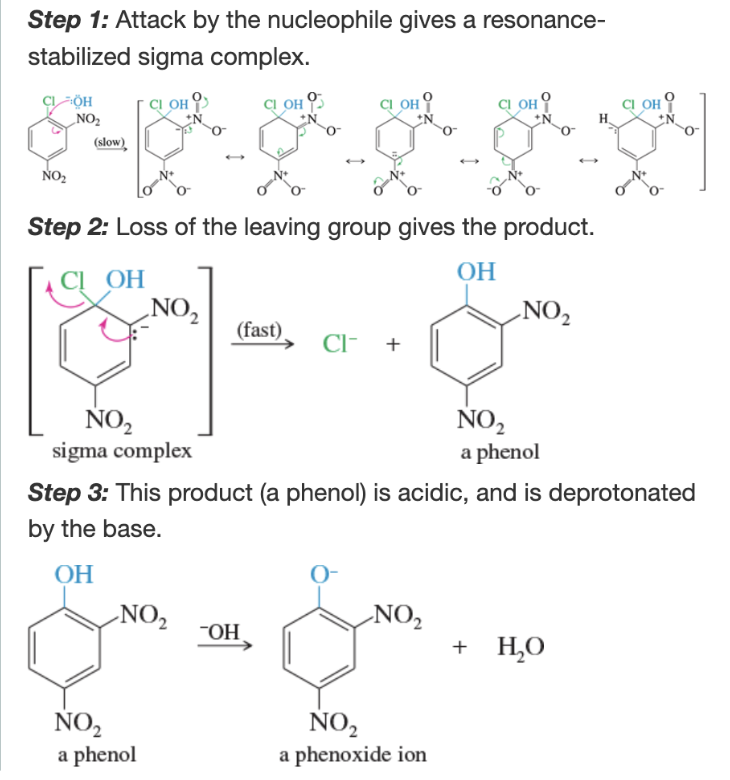
Mechanism: nucleophilic aromatic substitution
Benzylic position
alpha position of a side chain
Mechanism: side-chain halogenation
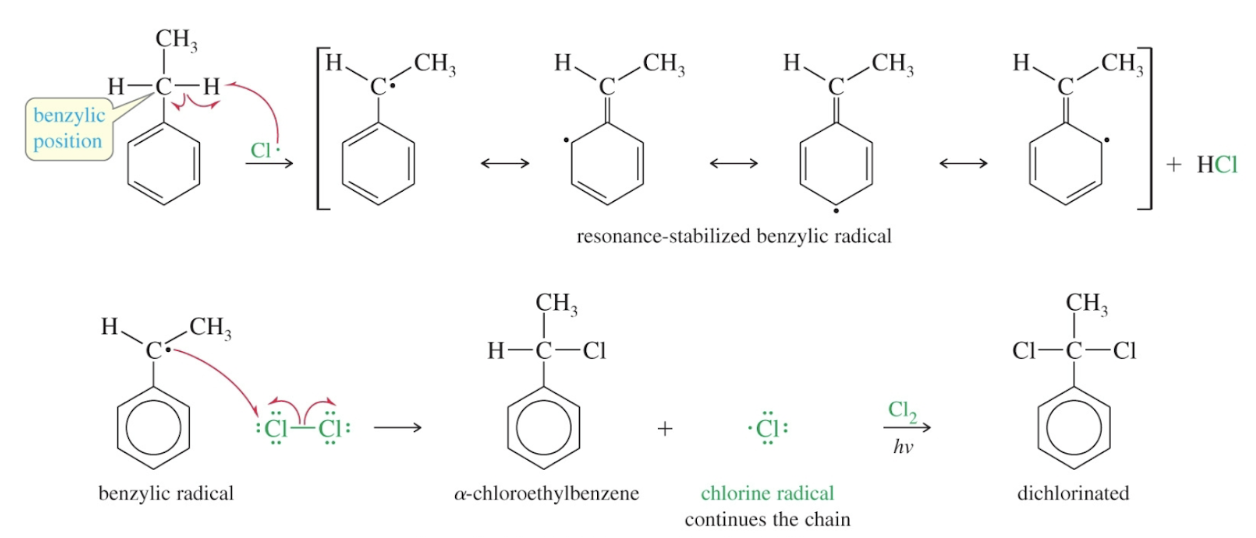
Selectivities of bromine and chlorine in side-chain halogenation
Br reacts exclusively at benzylic positions while Cl causes mixtures of isomers with a preference for the alpha position
Use of cross-coupling chemistry
substitute organic groups for halogens on aromatic rings or in alkenes
Reaction: making an organolithium reagent

Reaction: making a Gilman reagent

Reaction: cross-coupling with Gilman
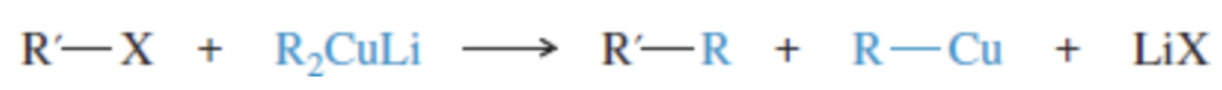
Mechanism: Suzuki reaction
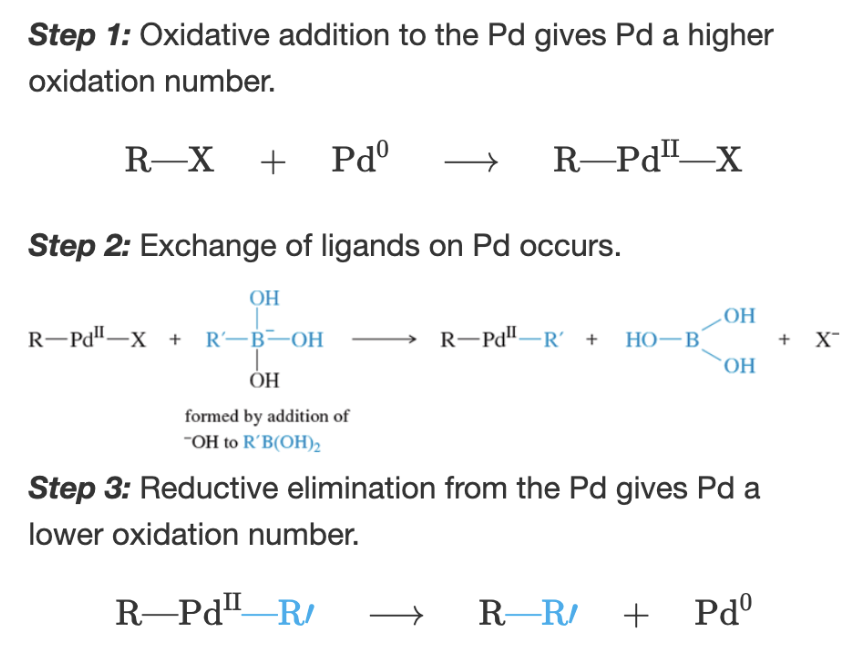
Stereochemistry of the Heck reaction
trans
Reaction: Heck reaction
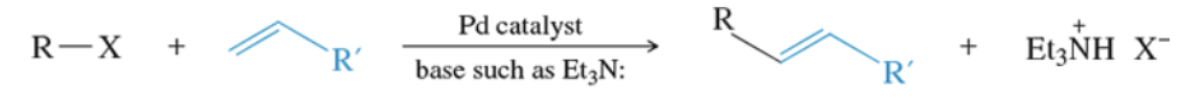
What bonds generally break during phenol reactions
O-H bond, not the C-O bond
Why are phenols highly reactive
lone pair on the hydroxyl group stabilizes the sigma complex
How are phenoxide ions generated
treating a phenol with NaOH
How does the order of substitution determine products
to produce the ortho or para product, attach that director first. to produce the meta product, add that director first
How to add COOH to benzene
adding an alkyl group and oxidizing it
How does SO3 work as a blocking group
blocks the para position so that substitution can occur on the ortho positions
structure of the carbonyl group
coplanar sigma bonds are about 120 degrees apart and the unhybridized p orbital overlaps with the p orbital of oxygen to form a pi bond
Energy of ketone double bond
745 kj/mol
Energy of aldehyde double bond
611 kJ/mol
Polarity of carbonyls
3 debeye
Acetone
simple ketone with two methyl groups
H bonding behavior of carbonyl compounds
can accept H bonds but cannot form them with each other
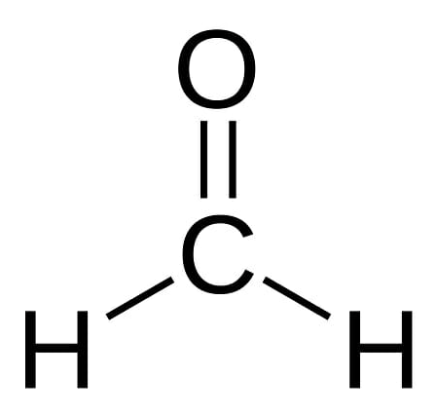
Formaldehyde
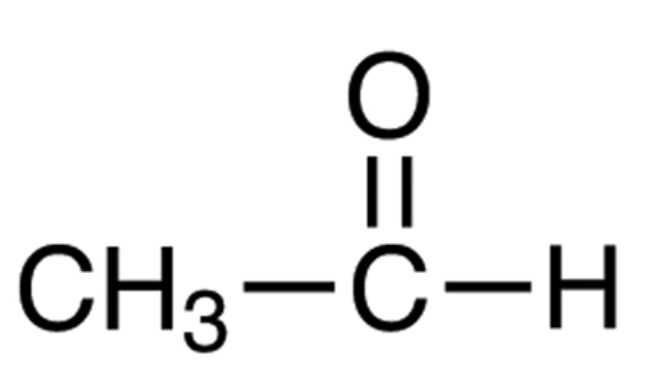
Acetaldehyde
IR spectroscopy of ketones
strong C=O at 1710
IR spectroscopy of aldehydes
C=O at 1725, C-H around 2710 and 2810
Formyl proton
proton attached to the carbonyl carbon on an aldehyde
How does conjugation affect IR spectroscopy of ketones and aldehydes
lowers it to around 1685 because partial pi bonding character on the single bonds reduces electron density on the carbonyl pi bond
1H NMR of ketones and aldehydes
characteristic formyl protons around 9-10, alpha carbon protons around 2.1-2.4
13C NMR of ketones and aldehydes
carbonyl carbon around 200, alpha carbon around 30-40
Common fragmentation patterns of ketones and aldehydes
loss of alkyl group to give an acylium ion, McLafferty rearrangement
McLafferty rearrangement
a cyclic intramolecular transfer of a hydrogen atom from the gamma carbon to the carbonyl oxygen that is equivalent to a cleavage between the carbon atoms alpha and beta to the carbonyl group plus the transfer of a beta hydrogen to the oxygen
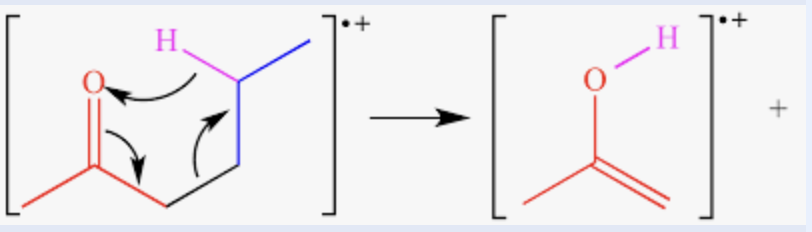
reagent for the oxidation of secondary alcohols to ketones and aldehydes
Jones reagent: chromium trioxide in sulfuric acid
How to use primary alcohols to make ketones and aldehydes
NaOCl + TEMPO or pyridinium chlorochromate
Pyridinium chlorochromate
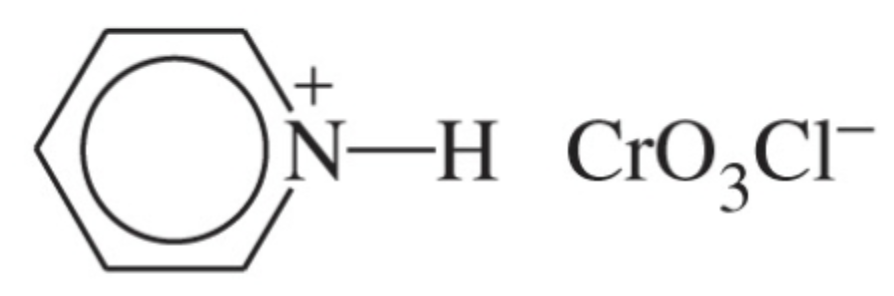
Ozonolysis of alkenes
creates ketones and aldehydes when the double bond is oxidatively cleaved by ozone followed by reduction
Use of DMS
protects the aldehyde in ozonolysis
Hydration of alkynes by acid and mercuric salts
initial product is an enol which tautomerizes to its keto form, catalyzed by sulfuric acid and a mercuric ion
Sia2BH
reagent used in hydroboration-oxidation of alkynes to form an anti-markovnikov aldehyde
Reaction: organolithium reagent with carboxylic acid
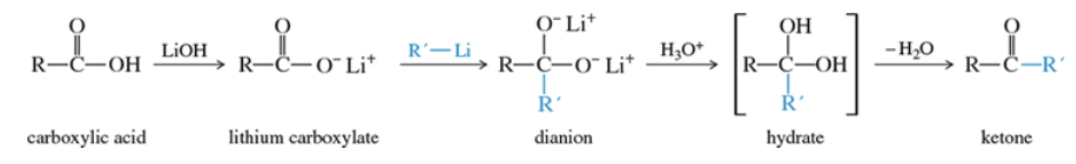
Mechanism: synthesis of ketones from nitriles
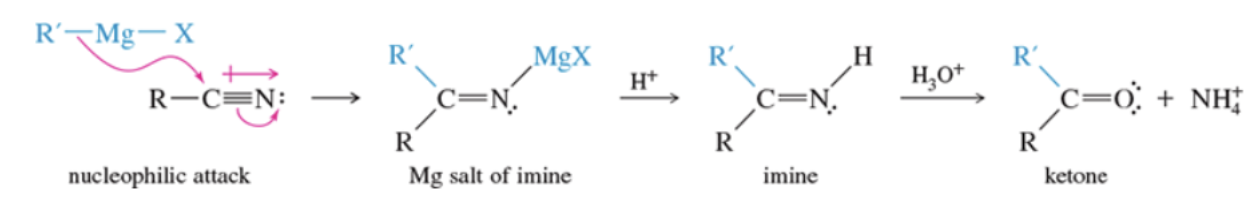
Reaction: reduction of nitriles to aldehydes
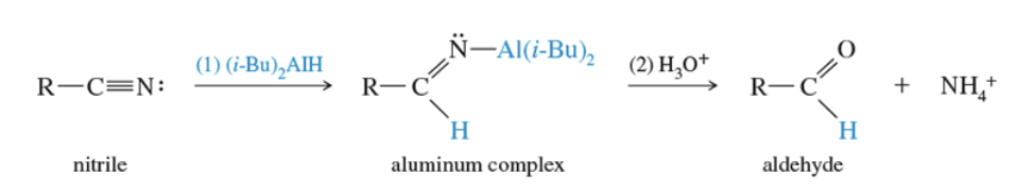
Acid chloride
reactive derivative of carboxylic acids in which the hydroxyl group is replaced by Cl
Reaction: synthesis of acid chlorides
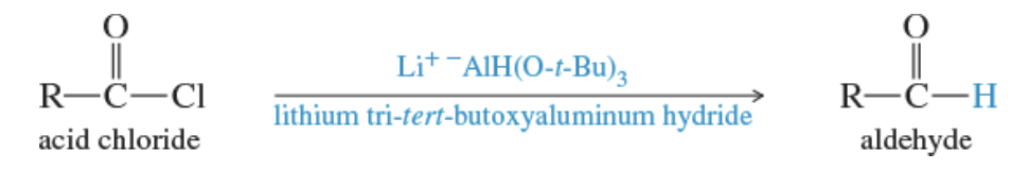
Reaction: reduction of acid chlorides
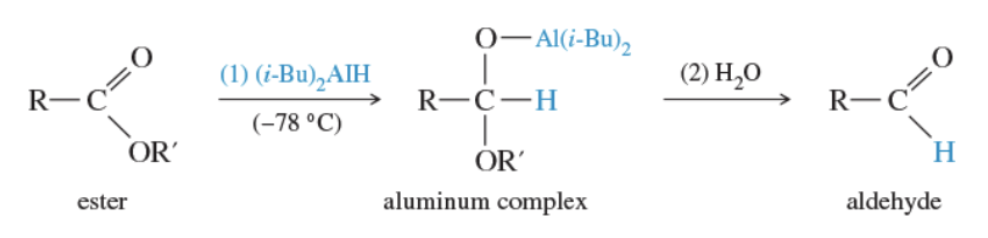
Reaction: reduction of esters
Grignard/organolithium reaction with acid chlorides
add an R group, gives a tertiary alcohol
Reaction: formation of Gilman reagents
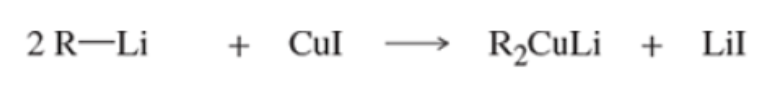
Reaction: Gilman and acid chloride
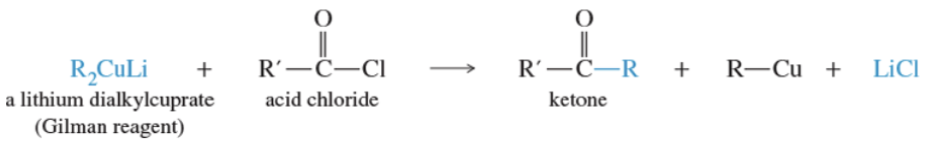
Why are aldehydes more reactive than ketones to nucleophilic addition
more electron poor, more exposed toward attack
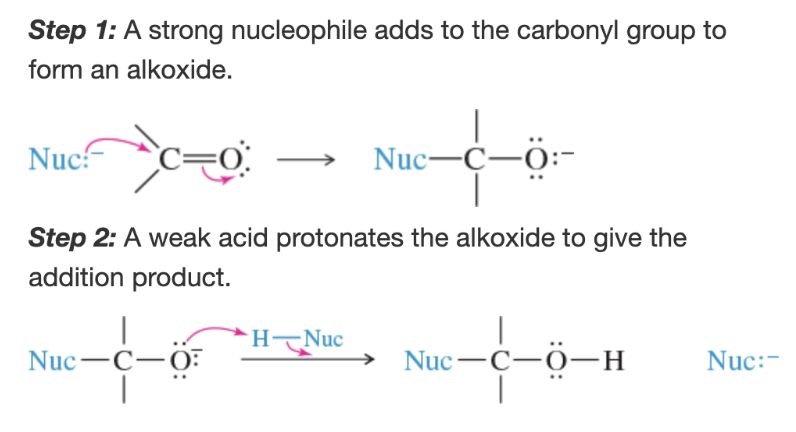
Mechanism: nucleophilic addition in basic conditions
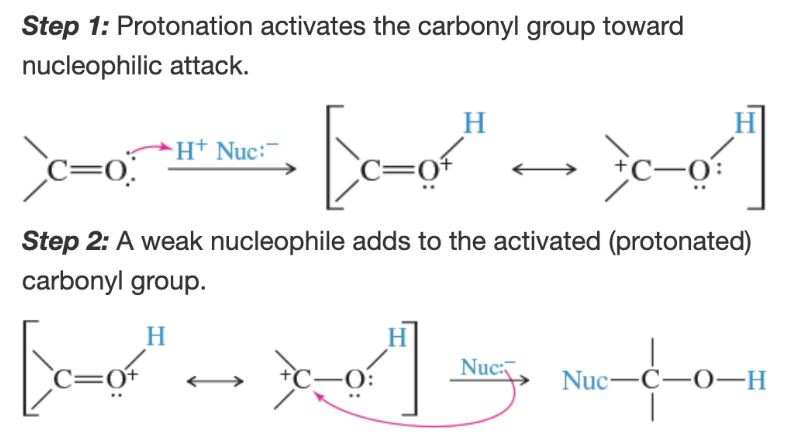
Mechanism: nucleophilic addition in acidic conditions
Why are aldehydes more likely to form stable hydrates than ketones
ketone carbonyl is stabilized by two alkyl groups
Keq of a ketone in aqueous solution
10-4 to 10-2
Keq of aldehyde in aqueous solution
~1