Research for Second Term Human Capital and Economics
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Chetty, Friedman, Rockoff (2014)

Statistical Model theorized that VA is constant
Measures teacher value-added for a large urban school district in the United States.
Data on student test scores, student demographics, and teacher assignments
2.5 million children, 1989-2009
They found a lot of variation in teacher quality, as measured by “value-added”
A 1 sd improvement in teacher VA by .14 sd in math and 0.10 sd in English
Larger variation in math teacher than English teachers
Second part: found that test score VA is a good proxy for other outcomes we care about
Talent Transfer Initiative
Paid high-VA teachers to transder to low-preforming schools
Implemented across 7 states, 2009-2011
Finds: The high-VA teachers had no effect on test scores in maths or reading in middle school. They had a small positive effect on test schools in elementary school.
Teachers who high VA didn’t have the same VA at the other schools because of other factors
Arteaga (2018)
Holds signal constant, but varies human capital
Classes did cause human capital, and the quality of the signal doesn’t change.
Evaluates a reform that reduced the required number of credits to obtain an economic degree by 20% at a university in Colombia
Potentially affects human capital, but does not affect signal
Finds that salary declines by 16% for economic majors
Reduced employment probability at high-paying firms
No actual salary reductions with the same firm (entry salaries are fixed)
Does not refute the signaling model, but shows that economics courses produce skills that are valued by the labor market.
Clark and Martorell
Varying the Signal and holding human capital constant (the range between passing and not passing would have relatively similar human capital)
Regression Discontinuity Design (RDD)
Evaluated the signaling value of a high school diploma in Texas in the mid-1990s
Found no effect of passing and obtaining a diploma on initial earnings.
No evidence that high school completion provides a useful signal of productivity
Maybe high school is too easy?
No asymmetric information? Employers may obtain the information they need in interviews
It does not address the signaling value of college or graduate degrees.
Does not address the signaling value of high school in a population with low completion rates.
Muralidharan and Sundararaman (2011)
Found Individual Incentives are efficient, because all methods cost the same
Teachers’ bonus pay increased linearly with the fraction of students whose test scores increased over the course of a year.
Average test score gain must exceed 5% for the teacher to receive a bonus
Value-added incentive scheme
Two treatment arms with teacher incentive pay:
Individualized incentive pay: teachers are paid based on the average test score gain of their own students
Group incentive pay: teacher paid based on the average test score gain of the entire school
Found: Individualized teacher incentive pay produced the highest test score gains
Spillover effects in subjects where teachers did not receive performance pay
Broad-based gains: weaker and stronger students benefited equally
Employer Learning Model
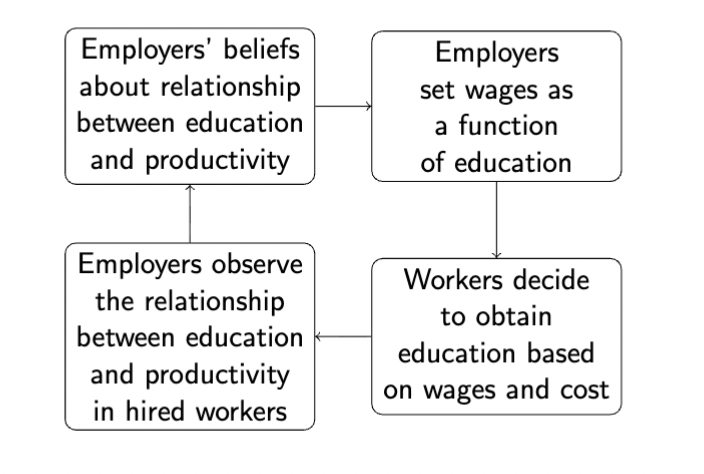
Productivity should be easier to observe for workers employed for many years
If education is a valuable signal in hiring, it should matter less for wage as the worker ages. wages
The correlation between wages and schooling should decrease with experience.
The correlation between wages and predetermined ability (scores on cognitive tests) increases with experience.
When employers can’t observe productivity they use education
Asymmetric information leads to employers having this belief system
The more experience at a company, the less critical education is, because employers can observe productivity